#cargodublin – Dublin Port Company today published trade statistics for the first quarter of 2015. The figures show continued growth in import and export trade at Ireland's largest port with cargo volumes up 5.3% on the same period last year. This is the strongest first quarter Dublin Port has had in a decade and surpasses the previous record year of 2007 by 3.0%.
Total throughput (imports and exports) for Q1 2015 was 7.8 million gross tonnes, an increase of 5.3% on the 7.4 million tonnes handled in the first quarter last year. There were 1,642 ship arrivals in the first three months. Imports were particularly strong in Q1 at 4.7 million gross tonnes, while exports reached 3.1 million gross tonnes, up 6.9% and 3.0% respectively on Q1 2014 trade levels.
The overall strong growth was driven by a combination of increased movements of unitised goods (containers and trailers) and by imports of petroleum products. Whereas the recovery in Dublin Port's volumes has been export led in recent years, in more recent times there has also been strong growth on the import side as the domestic economy improves. The 8.5% increase in petroleum imports is particularly striking.
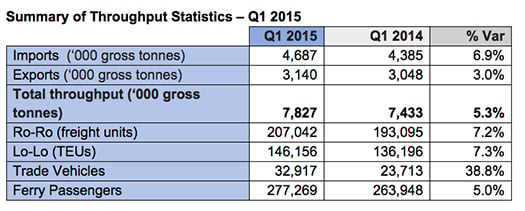
Imports of new cars and commercial vehicles continued to grow very strongly with almost 33,000 (32,917) new vehicles imported through Dublin Port in the first three months of the year, up 38.8% on the same period last year. With more people purchasing and registering new vehicles, Dublin Port is well placed to accommodate this increase having opened a new €3.4m 4.2 hectare trade car terminal last year as part of the port's Masterplan 2012 to 2040. Located on East Wall Road, the new trade car terminal can handle 2,500 vehicles at a time.
Unitised trade grew strongly in both the Ro-Ro and Lo-Lo modes. Compared to the same period last year, Ro-Ro trailers moved ahead by 7.2% to 207,042 and the port's Lo-Lo container business increased by 7.3% to 146,156 TEU.
The continued growth in unitised business reaffirms Dublin Port as the island's port of choice for both Ro-Ro and Lo-Lo services. Ro-Ro is Dublin Port's biggest mode and the large growth in Ro-Ro has been driven by increased sailings to both Britain and Continental Europe. There are now 12 daily sailings for passengers and 14 daily sailings for freight to Britain plus five weekly Ro-Ro sailings to Continental Europe.
On the tourism side, Dublin Port attracted 277,269 ferry passengers in the first three months of the year, a 5.0% increase on the first quarter of last year. Dublin Port expects continued growth following Stena Line's recent consolidation of its ferry services into Dublin Port and its introduction of a new ship (Stena Superfast X) on the Dublin to Holyhead route.
Eamonn O'Reilly, Chief Executive, Dublin Port Company, said: "Dublin Port's latest trade figures continue the positive trends of recent years. Our volume grew by 5.3% in the first quarter of 2015. This follows growth of 7.0% in 2014 and 3.0% in 2013, putting Dublin Port back on our Masterplan's growth trajectory which will see volumes double over the period from 2010 to 2040.
"Dublin is the chosen route for imports and exports because of our direct access to most of Ireland's population and frequent shipping services to Ireland's markets in Britain, Continental Europe and beyond. Ferry passengers benefit from a choice of operators and frequent services to and from Dublin Port, bringing them into the heart of the city and with immediate access to the M50 and the country's motorway network.
"We are expanding the capacity of Dublin Port to cater for future growth with a focus on working within the existing footprint of the port and maximising the use of existing port lands. Our plans include the lengthening and deepening of the port's berths and shipping channel and the redevelopment of existing lands for more intensive cargo handling.
"Our current plans are centred on the Alexandra Basin Redevelopment Project which we hope to commence during 2015. In addition to providing additional capacity for cargo, this project will allow us to bring the world's largest cruise ships right up to the East Link Bridge."
































































