Displaying items by tag: UK Sailmakers
With the racing season underway, UK Sailmakers Ireland looks forward to this season's big events, such as the Round Ireland Race, Cork Week and the IRC European Championships.
We have had a super busy start to 2024, and we're keen to see all the sails we fixed/serviced/washed and new sails out on the water.
For those of you who cut the grass and found your sails behind the lawnmower or in the attic, don’t worry; you're in good hands! We are only 50 years doing this! We will get you sorted and back out sailing...
 The UK Sailmakers Ireland plotter cutting sails in Cork
The UK Sailmakers Ireland plotter cutting sails in Cork
We have completed all our winter service work, washing sails and repairing sails, and UK Sailmakers Ireland are now super busy with racing repairs/recuts currently for new furlers and getting sails optimised for the racing season ahead.
 A UK Sailmakers Ireland XD carbon mainsail
A UK Sailmakers Ireland XD carbon mainsail
This new J109 XD Carbon mainsail with taffeta for offshore racing is one example, with Rutgerson slides on the luff for ease of handling while racing and with low friction rings in the clews to make reefing easier.
 Low friction rings with tie in battens on a J109 XD Carbon mainsail with taffeta
Low friction rings with tie in battens on a J109 XD Carbon mainsail with taffeta
We are delighted to finally have all the Shannon One Design main sails delivered and out on the water at a mid-May training weekend. Mermaid sails are also in production and are about to be finished for the season. Howth 17 sails are also in production.
 UK Sailmakers Ireland Shannon One Design mainsail
UK Sailmakers Ireland Shannon One Design mainsail
Remember if you need any repairs or recuts. You can put your sails in any of our sail repair boxes in Howth, Dun Laoghaire marina, RCYC, or Kinsale, or call Hammy Baker in the North, and we will get you back on the water in no time.
 The UK Sailmakers Ireland Sail Box at Howth Yacht Club (above) and Dun Laoghaire Marina below
The UK Sailmakers Ireland Sail Box at Howth Yacht Club (above) and Dun Laoghaire Marina below
 The UK Sailmakers Ireland Sail Box at Howth Yacht Club (above) and Dun Laoghaire Marina below
The UK Sailmakers Ireland Sail Box at Howth Yacht Club (above) and Dun Laoghaire Marina below
Sailmaking Changes After 50 Years in Crosshaven
After 50 years, there is a major change in sailmaking at Crosshaven, Cork Harbour’s dominant sailing centre.
.
Outside the village, the loft associated with the legendary Des McWilliams and family is no longer a sailmaking centre.
Barry Hayes and his wife, Claire Morgan, who took over the business seven years ago, have moved sailmaking to a new loft at Carrigaline, a few kilometres away. In addition, they have opened the first sailing shop in the village of Crosshaven itself, an impressive premises looking out onto Cork Harbour, the marinas and the RCYC sailing grounds.
 The new McWilliam Sailing Shop in Crosshaven was opened on Friday, November 17, 2023. The impressive premises looks out onto Cork Harbour
The new McWilliam Sailing Shop in Crosshaven was opened on Friday, November 17, 2023. The impressive premises looks out onto Cork Harbour
For this week’s Podcast, I discussed these changes at Sailmakers at The Square, Crosshaven, with Barry Hayes, who did not start his working life as a sailmaker - he was making chocolate when Des McWilliam convinced him to switch careers.

We discuss the modern changes in designing and manufacturing sails. He describes making canvas sails in Hong Kong, the long-lasting effect that had on his hands and how today, sails made from many different fabrics are also made to last longer.

Listen to the podcast and check out the photo gallery of the Sailmakers at The Square launch in Crosshaven below.
Photo Gallery: Sailmakers at The Square Launch in Crosshaven
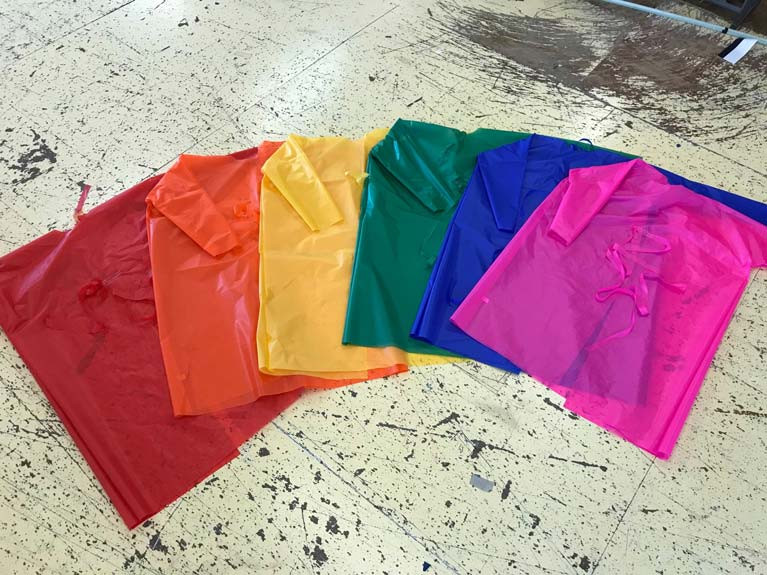
UK Sailmakers in Cork Harbour have busy fulfilling the many orders for gowns for healthcare workers in the frontline against COVID-19.
As Afloat reported previously, sailmaker Barry Hayes and his team at Crosshaven have been deploying their resources to help make Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) for local healthcare workers at the front line in the fight against this disease.
"We hope the rainbow colours bring a touch of joy to those working tirelessly on the frontline", Hayes said on social media.
First conceived by UK Sailmakers Norway, the UK lofts in New York, Canada and the Irish loft have made refinements on the design and material selection.
UK Sailmakers’ Barry Hayes In Howth Next Thursday For First In New Series On Top Tips For Sailors
Barry Hayes from UK Sailmakers Ireland begins a new series of talks with Top Tips For Sailors next Thursday 16 January at Howth Yacht Club from 7.30pm.
Members and guests alike are welcome to attend the two-part session which will cover both optimisation for racing or cruising vessels, and learning how to service your deck hardware — overalls recommended.
Barry will also visit the Royal St George on Thursday 30 January (time TBC) and Kinsale Yacht Club on Thursday 13 February at 7.30pm.

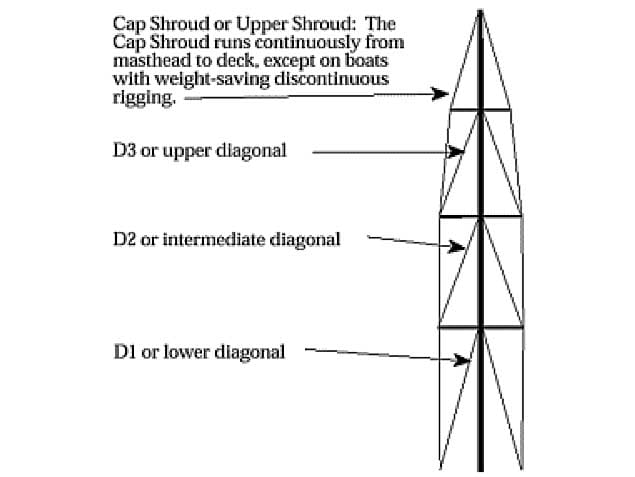
Tuning a Fractional Mast & Rig
People seem to think that tuning a fractional rig is very difficult. In reality, it is not that hard as Mark Mansfield, Professional sailor and racing consultant/agent for UK sails Ireland, describes below in the first part of a series of 'How To' articles.
There are four fairly straightforward areas to do and once you go through these is a systematic manner it normally works out fairly well first time. These four areas are:
- Make sure the rig is in the centre of the boat
- Make sure the rake is correct
- Get the prebend right
- Tighten the shrouds to the correct level
 Article author Mark Mansfield, Professional sailor and racing consultant/agent for UK sailmakers Ireland Photo: Afloat.ie
Article author Mark Mansfield, Professional sailor and racing consultant/agent for UK sailmakers Ireland Photo: Afloat.ie
I will go through these four in detail in a moment, but whether it is a single spreader, double spreader or triple spreader mast, the system to get it right is the same, just a bit more work with the extra spreaders and shrouds. Also, it is the same whether it is a one design mast like a 1720, Etchells etc. or whether it is a one off custom boat. Most one design classes will have a tuning guide prepared often by a sailmaker and these are certainly a good base point. However, even if you have one of these tuning guides, much of what I will be going through still it very relevant. Over the years I have tuned everything from Admirals cup 45 footers, to Olympic Stars, to Figaro offshore boats to 1720’s, Etchells, Commodores Cup Boats, J109’s and a host of others and though there are small differences between them, the basics remain the same. So let’s go through the four headings above.
CENTRALISE THE RIG
It sounds a very basic and simple thing but it is amazing how many masts are over to one side more than the other. I am taking it that the mast step and the mast gate are in the center (as most are) but if you find having done all the items I mention, that the mast is still not setting up straight, then these should be measured and checked. OK, first thing is to loosen off all the shrouds a good bit until they are relatively loose. Then get a heavyish weight, like a large bucket of water, or a full diesel can and attach it to the Jib halyard. We will be using this to measure from side to side. It is important that you do not use the main halyard as if there is a bit of a bend in the tip, the main halyard will end up over to one side. The jib halyard is where the hounds are and if you can get that point in the center, all the remaining parts of the mast will line up.
Hang the heavy can (attached to the jib halyard) over the side of the boat ensuring that it is not being deflected by the stanchions or guard wires. Mark on this halyard with tape near the shrouds where the rope disappears over the deck. Then bring the halyard around to the other side and see if this tape mark is in the same place, when measured at a similar point. If it is not then you need to loosen the outer shroud on one side and tighten the outer shroud on the other until they are equal. You may need to do this a few times but it is worth the effort.
Now temporarily tighten the outer shrouds nearly back to where they were before you started. Looking up the mast track from behind the mast, tighten up the diagonal shrouds on both sides to ensure the sideways bend in eliminated. Start at the upper diagonal shrouds first, if you have more that one set of spreaders, them move downwards to the lower diagonal shrouds. Once you have the mast looking fairly straight, now we turn our attention to getting the correct mast rake.
 Looking up the mast track from behind the mast, tighten up the diagonal shrouds on both sides to ensure the sideways bend in eliminated
Looking up the mast track from behind the mast, tighten up the diagonal shrouds on both sides to ensure the sideways bend in eliminated
MAST RAKE
Most modern boats are best set up to about 2.5 to 3 degrees of rake. There are exceptions with some boats only needing one degree and others wanting as much as five degrees. However, the vast majority of boats favor around 2.5 degrees and their keel positions and rig plans are designed around this figure. To measure and adjust your rake, again you will need the bucket of water or other heavy weight. This time hang it from the main halyard until it hangs just below the boom. Ensure the weight aboard the boat is in its normal racing position and get all the crew off the boat. Tighten the backstay to a just taut position. Wait for the bucket to settle and mark where the halyard hits the side of the boom. If the rig is at 2.5 degrees of rake the distance from the back of the mast, measured just above the gooseneck should be circa 4.5% of your P measurement which you will get from your IRC cert. So take a J 109 with an approx. P measurement of 13 metres, 4.5% of this would be 585mm. If your bucket is hanging back further than this, then you need to bring the mast forward by tightening your forestay bottlescrew. If your bucket is hanging closer to the mast than that, then the forestay bottlescrew will need to be loosened. Always ensure you adjust the figures if the main halyard exits to the top of the mast further aft than the main track.
MAST PREBEND & TENSION
OK, So we have the mast now in the middle with the correct rake. Next step is to tighten the shrouds to the correct levels, which should in turn put prebend into the mast. Most sails are cut for a slightly prebent mast with about 1% of P as a decent guide. So, with a J109 with an approx. 13-metre P measurement that means about 130mm of prebend. To measure this, again take your main halyard, attach it to your gooseneck and tighten it hard. Push the halyard against the mast track and look up to see what is the max this halyard is positioned behind the middle of the mast. In the above J109 mast, that should be circa 130mm. If it is more then the diagonal shrouds need to be tightened more to straighten the mast. If it is less then the diagonal shrouds need to be eased. Always remember this is based on your outer (cap) shroud being up to full tension. As you tighten the outer shroud, the mast will likely compress and this will cause bend.
 Most modern boats are best set up to about 2.5 to 3 degrees of rake Photo: Afloat.ie
Most modern boats are best set up to about 2.5 to 3 degrees of rake Photo: Afloat.ie
Final tuning of a mast always needs to be done out on the water, preferably with about 12 to 15 knots of wind, with a few bodies on the side. As a general rule the correct tension of the shrouds would be when they just come slack to leeward. If when you go out the leeward shrouds are still bar tight, then you need to ease them a little on both sides. If, as is more likely, the shrouds are too loose, then they need to be tightened, a little on both sides. As the breeze gets stronger it will be difficult to get the shrouds so tight that the leeward shrouds are always hard, especially with an aluminum mast. What happens is as you increase the tension in stronger winds, the mast compresses accordingly and the leeward shrouds stay a bit slack. With a carbon mast, it may be possible however to get the leeward shrouds snug as carbon masts generally bend less from side to side. Getting each individual shroud at the correct tightness level will require quite a few runs side to side, looking up the mast track, trying to see which area is not straight and then adjusting an individual shroud and trying again. Even when the mast is straight, you my find then that there is too much prebend which might necessitate further adjustments to the mast, or may even signal that a small luffround adjustment is needed.
I will be doing a follow-on article on this in a few weeks, which will deal with changing gears on the race course from light winds, right up to very strong winds. For many, finding one decent setting may be what they are looking for, say a medium setting, and then prefer to lock everything off at that stage. Others will want to adjust the rig every couple of knots to try and get that last fraction of speed out of it.
Mark Mansfield—Professional Sailor and racing Consultant/Agent for UK sails Ireland.
e mail—[email protected]
UK Sailmakers, in conjunction with the Irish Cruiser Racing Association and Afloat.ie, will be publishing a series of knowledge sharing and how-to articles for the 2018 season.
Tralee Bay Hosts UK Sailmakers For Coaching Weekend
#TBSC - Tralee Bay Sailing Club hosted the UK Sailmakers Ireland team of Des McWilliam and Graham Curran on the water for two days of coaching this past weekend (13-14 June).
A series of 16 races was run over the two-day event in Fenit, where a lot was learned and plenty of fun was had by all, as the video above can attest! A photo gallery of the weekend is also available HERE.



























































