Displaying items by tag: sharks
Marine Institute Launches New Resources to Promote Ireland's Marine Biodiversity in Primary Schools
The Marine Institute Explorers Education Programme team has launched a new set of resources for primary schools, aimed at promoting Ireland’s rich marine biodiversity in the classroom. The new class projects, called Fin-tastic Sharks+, will focus on the 71 species of sharks, skates, and rays that can be found in Irish waters.
Cushla Dromgool Regan, Explorers Education Manager and lead author of the resources, said that the team was "delighted to be celebrating the launch of the Explorers Fin-Tastic Sharks+ new online shark resources over Valentines."
The resources, which are available for free download from explorers.ie, include a range of cross-curricular activities that teachers and children can use to explore different shark themes in class or on the seashore. The content covers everything from STEM activities to design and communication projects, and is suitable for children of all ages.
Patricia Orme, Corporate Services Director at the Marine Institute, congratulated the Explorers team on creating new materials to promote Ireland's marine biodiversity in primary schools. "Primary school teachers and children around the coast love learning about sharks and their relatives," she said. "It is always a favourite topic to cover with children, teachers and our outreach teams, who visit the classes of over 13,000 children annually."
The resources include a new Explorers mermaid’s purse key that is suitable for children to use in the classroom and on the shore. The key covers the top ten shark and skate cases typically found on the shores around Ireland, and provides lots of extra shark and skate information to encourage children to become citizen scientists, recording their egg case finds online.
The launch of the new resources comes at a time when the Marine Institute's fisheries scientific team has recorded two baby white skates during the annual groundfish survey while on the RV Celtic Explorer. This was an extremely rare find, as the white skate is listed as Critically Endangered. Of the 58 cartilaginous shark, skate and ray species researched in Irish waters, over 60 percent of them are listed as a Near Threatened, Vulnerable, Endangered or Critically Endangered.
Ms Dromgool-Regan explained that sharing positive stories about sharks, skates and rays can help people understand the importance of having these species in Irish waters. "This helps us all get involved in better managing and protecting our marine resource now and for the future," she said.
Reef Sharks Do Take Naps and Not In Perpetual Motion - New Study
Reef sharks were always thought to be in perpetual motion, but a new study suggests sharks can nap or sleep.
The study is based on grey reef sharks in the Seychelles, and has been published in the Journal of Fish Biology.
As it explains, sharks use gills to breathe, applying two methods. Some sharks, called obligate ram ventilators, ‘ram’ oxygen-rich sea water over their gills and need to keep moving to do so, the paper says.
Other species, called buccal pumpers, actively pump sea water over their gills while stationary, it says.
The study entitled ‘Just keep swimming? Observations of resting behaviour in grey reef sharks Carcharhinus amblyrhynchos’ overturns existing knowledge, the authors state.
“The grey reef shark is an endangered reef dweller in the family Carcharhinidae and was the quintessential representative of a shark that moves to breathe,” according to the Save Our Seas D’Arros Research Centre (SOSF-DRC) in Seychelles.
“On routine survey dives around D’Arros we found grey reef sharks resting under coral reef ledges,’ the centre’s director of research, Dr Robert Bullock, says.
‘This is not something we believed they could do. The grey reef shark has been considered a ram-ventilating species, unable to rest, so to find these ones resting, turns our fundamental understanding of them on its head,” he said.
The researchers say they encountered grey reef sharks resting alone and in groups at different sites around Seychelles.
“And through it all, the sharks seemed blissfully unaware of their observers,”they say, remaining still, except for lower jaw movements that suggest the ram-ventilating sharks can switch to buccal pumping behaviour.
Craig Foster, founder of the SeaChange Project, was one of the divers and authors of the paper.
“There is something very special about “tiptoeing” around underwater at a depth of 25 metres and looking into the open eyes of sleeping sharks, moving carefully so as not to wake the peaceful beauties,”Foster says.
Save Our Seas Foundation chief executive Dr James Lea said that the findings were “key to understanding how they use their environment and also how this may change in response to shifts in environmental conditions”
Founded in Geneva, Switzerland, in 2003, the Save Our Seas Foundation (SOSF) is a philanthropic organisation which states that its ultimate goal is “to create a legacy of securing the health and sustainability of our oceans, and the communities that depend on them, for generations to come”.
Its support for research, conservation and education projects worldwide focuses on endangered sharks, rays and skates. Three permanent SOSF research and education centres are based in Seychelles, South Africa and the USA.
Fin-Tastic Shark Display Set to Make a Splash at Galway Science and Technology Festival This Sunday
The Marine Institute, alongside the Explorers Education Programme for primary schools, will be showcasing marine science at the 2023 Galway Science and Technology Festival this weekend.
Families are invited to the Bailey Allen Hall on the University of Galway campus on Sunday 12 November to learn more about Ireland’s shark species.
“We greatly enjoy the opportunity provided every year by the Galway Science and Technology Festival to highlight the work we do here at the Marine Institute, and to showcase in particular the Explorers Education Programme,” said Patricia Orme, director of corporate services at the Marine Institute.
“The event is perfect for fostering an interest in marine science in children and adults alike. With this year’s focus on sharks, we hope families will enjoy learning more about these fascinating creatures.”
Celebrating the launch of Explorers’ new children’s information book Fin-tastic Sharks: An Introduction to Elasmobranchs, the team will be sharing stories of the wonders of sharks from around the world to those found in Irish waters.
“We all know that children love sharks, skates and rays,” said Cushla Dromgool-Regan, strategic education and communications manager of the Explorers Education Programme. “The Explorers team is very excited about examining the jaws of the great white shark, to the giant teeth of the megalodon and to also learn about the super powers of many different shark species closer to home.”
 A still from video captured of the shark nursery in deep waters off the West of Ireland during the SeaRover ROV survey in 2018 | Credit: Marine Institute
A still from video captured of the shark nursery in deep waters off the West of Ireland during the SeaRover ROV survey in 2018 | Credit: Marine Institute
Ireland’s ocean resource is the perfect refuge for endangered species, such as the world’s second largest shark, the basking shark, the common stingray and the white skate which is critically endangered.
Dromgool-Regan added: “Seventy-one species of sharks, skates, rays and chimaeras are found in Irish waters. This is over half the number of all of these species in Europe. This highlights the importance of the collaborative work of the scientists at the Marine Institute who work with other scientists, fishers and local communities to help establish [the status of] sharks, skates and rays in Irish waters.”
The Explorers team will also be displaying lots of shark biofacts and some of their favourite sharks, including baby lesser spotted dogfish and shark egg cases, also known as mermaid purses.
Families will have the opportunity to learn more about the 2018 discovery of an extremely rare shark nursery. Very large numbers of mermaid’s purses were observed on the sea floor at depths of 750 metres. Such large concentrations are very uncommon, indicating that females may gather in this area on the seafloor to lay their eggs.
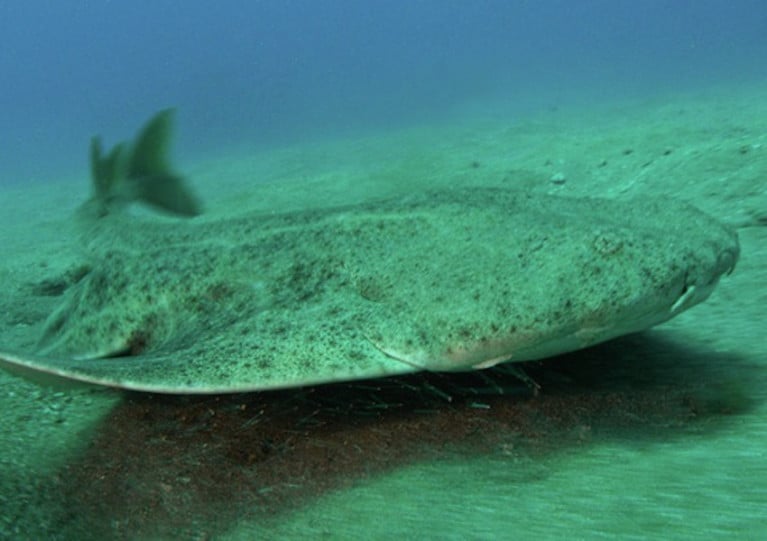
Video footage of an extremely rare angelshark sighting in Rinville during the summer by some student kayaking enthusiasts will also be on display.
The Marine Institute’s exhibition ‘The Wild Atlantic – Sea Science' is also open at the Galway City Museum. Free to visitors, the gallery features seabed mapping, amazing scientific discoveries and creatures of the deep. In the ROV (remotely operated vehicle) simulator, explore ocean depths like a marine scientist and discover cold-water corals, shipwrecks and a rare shark nursery.
For more information on the 2023 Galway Science and Technology Festival programme and to register for free event tickets, visit www.galwayscience.ie. It’s sure to be a fin-tastic day out for the whole family!
Discovery That Basking Sharks are Warm Bodied Like "Finding Cows Have Wings" - TCD Scientists
Researchers have discovered that basking sharks are as warm-bodied as great white sharks, in spite of having a more sedentary lifestyle.
An international team led by scientists from Trinity College, Dublin, says the “surprising” discovery has implications for the conservation of this species, which gained legal protection in Irish waters last year.
Their findings are published in the international journal, Endangered Species Research.
The scientists explain that approximately 99.9% of fish and shark species are “cold-blooded”, meaning their body tissues generally match the temperature of the water they swim in.
However, “the mighty basking shark is a one-in-a-thousand exception”, they say.
Basking sharks keep the core regions of their bodies warmer than the water – just like the most athletic swimmers in the sea such as great white sharks, mako sharks and tuna ,”they state.
Great whites, mako sharks and tuna are all fast-swimming “apex predators” at the top of their food chain, known as “regional endotherms”.
It has long been believed that their “athletic predatory lifestyle” was helped by this ability to keep warm – and that evolution had shaped their physiology to match their requirements.
The research team, including scientists from University of Pretoria, Marine Biological Association, Queen’s University Belfast, Zoological Society of London, University of Southampton, and Manx Basking Shark Watch, first undertook dissections of dead basking sharks that washed up in Ireland and Britain.
They found that the sharks have cruise-swimming muscles located deep inside their bodies as seen in white sharks and tunas; in most fish this “red” muscle is instead found toward the outside of the animals.
They also discovered basking sharks have strong muscular hearts that probably help generate high blood pressures and flows. Most fish species have relatively “spongy” hearts, whereas basking shark hearts are more typical of the regional endotherm species.
The team says it then designed a new low-impact tagging method to record body temperature of free-swimming basking sharks off the coast of Co Cork.
The researchers says were able get close enough to 8 m basking sharks to safely deploy the tags, which recorded muscle temperature just under the skin for up to 12 hours before they automatically detached from the animals and were collected.
“These tags revealed that basking shark muscles are consistently elevated above water temperatures, and to almost exactly the same extent as their regionally-endothermic predatory cousins,”they state.
Lead author of the study Haley Dolton, who is a PhD candidate in TCD’s School of Natural Sciences, said the basking shark is “a shining example of how little we know about shark species in general”.
“That we still have lots to uncover about the second biggest fish in the world – such a huge, charismatic animal that most people would recognise it – just highlights the challenge facing researchers to gather what they can about species to aid in effective conservation strategies,”Dolton said.
“Regional endotherms are thought to use more energy, and possibly respond differently to ocean warming than other fish species,”Dolton continued.
“So lots more work will need to be done to work out how these new findings regarding an endangered species might change previous assumptions about their metabolism or potential distribution shifts during our climate crisis, which is something marine biologists are focusing on as our planet and its seas continue to warm.”
The study’s senior author, Nicholas Payne, who is an assistant professor in TCD’s School of Natural Sciences, said the results “cast an interesting new light on our perception of form versus function in fishes because until now we thought regional endothermy was only found in apex predatory species living at high positions in the marine food web”.
“Now we have found a species that grazes on tiny plankton but also shares those rather uncommon regional endotherm features, so we might have to adjust our assumptions about the advantages of such physiological innovations for these animals,”Payne said.
“It’s a bit like suddenly finding that cows have wings,” he said.
Haley Dolton is funded by the Irish Research Council, with support from the Fisheries Society of the British Isles and Dr Nicholas Payne was funded by Science Foundation Ireland.
The journal article can be read at: https://www.int-res.com/abstracts/esr/v51/p227-232/. A PDF copy is available on request.
Time Running Out to Support Campaign Against Shark Fin Trade in Europe
An EU-wide campaign against the shark fin trade in Europe is seeking votes from the public to take the matter to the European Parliament.
The removal of fins on board EU fishing vessels and in EU waters is prohibited by EU law and sharks must be landed with their fins naturally attached.
However, the European citizens’ initiative Stop Finning - Stop the Trade claims that the union is actually among the biggest exporters of fins and a major transit hub for the global fin trade.
“[The EU] is a major player in the exploitation of sharks and as inspections at sea are scarce. fins are still illegally retained, trans-shipped or landed [in the union],” campaigners say.
The initiative aims to end the trade of fins in the EU including the import, export and transit of fins other than if naturally attached to the animal’s body.
As finning prevents effective shark conservation measures, campaigners are requesting to extend REGULATION (EU) No 605/2013 to the trade of fins and therefore ask the commission to develop a new regulation, extending “fins naturally attached” to all trading of sharks and rays in the EU.
The initiative has collected more than 370,000 signatories out of the million required — but many member states have not met their individual threshold, including Ireland which needs another 5,000 supporters before the collection period closes on 31 January 2022.
Individuals can find out more about the campaign at www.stop-finning-eu.org and register their support for the initiative via the EU government portal HERE.
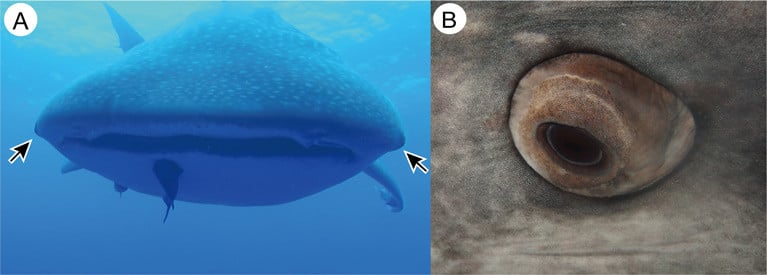
Japanese researchers have found that whale sharks have protective “armour” around their eyeballs in the form of tiny teeth.
Japan's Okinawa Churashima Research Centre scientists studied the eyes of both living and dead whale sharks, which can grow to 18-metres and have eyes on the sides of their head.
The sharks, which eat mainly plankton, can retract their eyes to protect them from other creatures in the sea, and don’t have eyelids.
Their eyes are protected in a casing, which bulges out into the water, and the researchers found that these casings are covered in dermal denticles or tiny teeth. The denticles have an “oak-like shape” similar to human molars, they say.
Dermal denticles have been found in previous research on other parts of the whale shark’s body. The researchers found each whale shark eye covering has approximately 3,000 denticles, and most densely packed near the irises.
They suggest these may serve to protect the whale shark eyes from attacks by other sea creatures.
More details of the research are on the open-access website, Plos One here
Tralee Bay is a “major nursery” for sharks and rays in Irish waters, says a local marine wildlife expert.
And Kevin Flannery insists the important breeding ground for the likes of angel sharks and porbeagle sharks needs protection.
Marine biologist Flannery, of Dingle OceanWorld, described the little-known nursery off the Kerry coast as “a Serengeti of the Atlantic for rays and sharks”.
And as National Biodiversity Week begins, he’s calling for Tralee Bay to be designated as a marine protected area to provide a safe haven for the many species that lay their eggs there in summer months.
The Irish Mirror has more on the story HERE.
Workshop Aims To Map Deepwater Sharks In North-East Atlantic
Experts in shark biology, data and mapping recently met at the Marine Institute’s headquarters in Oranmore, Co Galway to map the distribution of deepwater sharks, skates and chimaeras in the North-East Atlantic Ocean.
Scientists and marine experts at the International Council Exploration of the Seas’ (ICES) WKSHARKS Workshop analysed decades of data from research surveys in the North Atlantic Ocean.
This included nearly 30 years of data collected by Irish scientists on board the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer and commercial vessels.
The WKSHARKS Workshop included experts from Ireland, the United Kingdom, Portugal, France and Denmark, with other experts contributing remotely from Norway, Iceland and the Netherlands.
And their aim was to produce maps that indicate the area and depth of 25 species of deepwater sharks, skates and chimaeras — information that will assist in understanding the range and habitat of these marine wildlife species, underpinning future management decisions.
It will also be considered by the Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic (OSPAR) and the North-East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC) to determine future action to sustainably manage these populations.
These two organisations have a joint interest in the open North Atlantic, while ICES scientists have unique knowledge of the deepwater fisheries and species in this area, which focuses on waters off Ireland, Portugal and Iceland.
Maurice Clarke, fisheries scientist at the Marine Institute and WKSHARKS Workshop chair, said: “Sharks and rays have an important function in maintaining balanced and healthy marine ecosystems. Providing scientific advice is essential to protecting these marine species in the North-East Atlantic.
“For many of these species, this is the first time that data from European surveys is being collated and analysed for this purpose.”
Irish waters are home to 71 species of sharks, skates, rays and chimaeras. These species include some of the latest maturing and slowest reproducing of all vertebrates, resulting in very low population growth rates with little capacity to recover from overfishing and other threats such as pollution or habitat destruction.
ICES received a joint request from the Convention for the Protection of the Marine Environment of the North-East Atlantic (OSPAR) and the North-East Atlantic Fisheries Commission (NEAFC) to develop distribution maps of deep-sea sharks, rays and skates, and also to advise on methods of mitigating bycatch of these species.
New Shark Species Spotted In Irish Waters
A shark species previously unrecorded in Irish waters has been sighted in the Celtic Sea.
A smooth hammerhead shark was reported on the edge of the continental shelf, south-west of Ireland, during a recent fisheries survey on the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer.
The sighting was made by experienced marine mammal observer John Power and bird observer Paul Connaughton during the Marine Institute’s Western European Shelf Pelagic Acoustic Survey (WESPAS).
“While scanning the ocean surface, we sighted a dorsal fin unlike anything we had encountered before,” said Power.
“It was quite different to the fins seen on basking sharks and blue sharks. After consulting available ID keys, we agreed that the shark must be a smooth hammerhead.”
The large, tall and slender dorsal fin of the smooth hammerhead shark distinguishes it from other shark species. The smooth hammerhead also has a single-notch in the centre of its rounded head and is up to four metres in length.
The species gives birth to live young and the pups are usually found in the shallow sandy waters near Florida, the Caribbean and West Africa. However, the species has been recorded as far north as England and Wales.
The smooth hammerhead was sighted during the WESPAS survey, which surveys the waters from France to Scotland and the West of Ireland each year.
Marine scientists collect acoustic and biological data on herring, boarfish and horse mackerel, which is used to provide an independent measure of these fish stocks in Irish waters. Scientists also monitor plankton, sea birds and marine mammals during this survey.
This is an exciting encounter, especially since a rare deep-water shark nursery was discovered by Irish scientists last year
Dr Paul Connolly, director of fisheries and ecosystems services at the Marine Institute, said: “Our Irish waters support a range of marine life and diverse ecosystems, including 35 known species of sharks.
“This is an exciting encounter, especially since a rare deep-water shark nursery, 200 miles west of Ireland, was discovered by Irish scientists last year using the Marine Institute's Remotely Operated Vehicle [ROV Holland 1].”
He added: “This sighting of a new shark species shows the importance of our fishery surveys to monitor our marine environment, and to observe changes in our oceans and marine ecosystems.
“Observing and understanding a changing ocean, is essential for protecting and managing our marine ecosystems for the future.”
The hammerhead shark poses little risk to humans, and there have been no known fatalities from hammerhead sharks anywhere in the world to date.
The species is listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, and is being increasingly targeted for the shark fin trade as its large fins are highly valued.
Thirty-five species of sharks have been recorded in Irish waters, including the blue shark, porbeagle shark, lesser spotted dogfish and the second-largest shark in the world, the basking shark — a regular visitor inshore during the summer months.
Children from Rang 2 at Scoil Shéamais Naofa in Bearna got up close and personal with sharks on the RV Celtic Explorer as part of the Marine Institute’s outreach and engagement programme.
The pupils completed a project module on sharks in Irish waters as part of the Marine Institute’s Explorers Education Programme, and also had the opportunity to visit the State research vessel.
Outreach officer Padraic Creedon of the Explorers Education Programme said one if the programme’s unique elements “is the content and support provided to teachers in the classroom in an easy and fun way.
“The students were inspired by the discovery of a rare shark nursery 200 miles off the west coast of Ireland in 2018, and we were delighted to create lessons, interactive experiments and discussion about the ocean, sharks and their environment for the class.”
While on board the RV Celtic Explorer, pupils met with the captain and scientists and saw what it might be like to work on a research vessel.
Students spoke with Captain Denis Ronan about the Celtic Explorer, and learn more about the acoustically silent ship that can stay out at sea for up to 35 days.
The pupils were excited to tour the vessel and speak with marine scientists to discover more about shark species, seabed mapping, shipwrecks and the marine environment.
Visiting the dry and wet labs, the pupils saw various fish species from recent surveys and shark species, such as dogfish and the tope shark.
Clár Ní Bhraonáin, teacher at Scoil Shéamais Naofa, said: “It has been an amazing experience … Students don’t forget days like this.”
The Explorers programme offers a range of materials including lesson plans to conduct experiments in class, watching films that helps generate discussion, and peer learning among pupils.
“Because of the students’ enthusiasm to learn more about sharks, we have been able to incorporate marine themes across the curriculum, where they have excelled and produced some incredible work, from writing books about sharks to a series of posters and artwork,” Ní Bhraonáin added.
“This project has really helped myself and the students learn more about the ocean.”
For more information on the Explorers Education outreach centres, visit the Explorers Contacts page at Explorers.ie. The programme is supported by the Marine Institute and is funded under the Marine Research Programme by the Government.