Displaying items by tag: Conwy
Inland & Coastal Marina Systems Provides Conwy Marina with Waiting Jetty Solution
County Offaly marina firm Inland and Coastal Marina Systems has successfully upgraded the ‘waiting’ jetty at Conwy Marina in North Wales. The new pontoon is now in constant use, providing users with a safe and secure place to wait for entrance into the marina.
Inland and Coastal installed a Continuous Concrete Pontoon (CCP), increasing berthing and load capacity for larger vessels. With greater wave reduction and stability properties, the system also requires less maintenance.
Due to varying water levels between the outer harbour and marina basin, access to the 500-berth marina is via a tidal sill.
“The large tidal range in the estuary here often causes the holding pontoon to ground at low water springs,” says Jon Roberts, Conwy Marina Manager. “Inland and Coastal’s continuous pontoon design works perfectly. The attention to detail also made the installation process extremely efficient. The work progressed during specific tidal gates without interfering with daily operations and I am delighted with the quality of the new structure.’’
Jon continues: “Our customers’ first impression of the marina comes from their experience on the waiting pontoon. The new pontoon, with its additional safety features and the reangled ramp to give less steep walk ashore access, make me confident that we are giving the best welcome possible.”
“Conwy is a stunning part of the coastline,” says Oliver Shortall, Inland and Coastal Managing Director. “We were delighted to provide a robust ‘waiting’ jetty. Our concrete pontoons have double the lifespan of wooden ones. The solid surfaces also offer much better grip properties - especially when wet.”
As well as continuously developing pontoon solutions for marina operators, yacht clubs and port authorities, Inland and Coastal is the official UK supplier of SeaBin, demonstrated at the recent Southampton International Boat Show.
Inland and Coastal will be exhibiting at METSTRADE on stand 05.514 in the Marina and Yard Pavilion.
New Race From Conwy Features in 2012 ISORA Calendar
It was agreed that virtual marks would be in fixed positions on a trial basis. ISORA Commodore Peter Ryan believes it will 'revolutionise' offshore racing in the Irish Sea and produce better and more exciting racing.
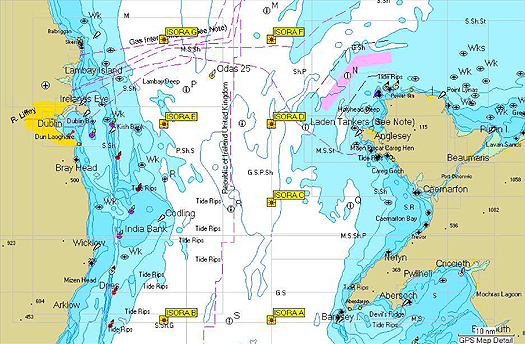
The new ISORA waypoint positions
It was also agreed at the weekend's agm at the National Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire that there would be two "Restricted / Silver Fleet" classes. The decision of what boats qualify for these classes will be made by the Sailing Committee prior to the first race. It is hoped that this will allow a fairer spread of prizes.
Virtual Waypoints Coordinates:ISORA A N52 45.000 W5 08.000
ISORA B N52 45.000 W5 40.000
ISORA C N53 06.000 W5 08.000
ISORA D N53 20.000 W5 08.000
ISORA E N53 20.000 W5 40.000
ISORA F N53 35.000 W5 08.000
ISORA G N53 35.000 W5 40.000
Preliminary Race Programme 2012
28th April - ISORA / RAYC / Lee Overlay Day Race - (50 miles)
Dun Laoghaire to Nt. Arklow Cardinal
5th May - ISORA Offshore - Dun Laoghaire to Holyhead (60 miles)
Qulaifying Race
19th May - ISORA Offshore - Conwy to Howth (100 miles)
Qulaifying Race
2nd June - ISORA Offshore - Pwllheli to Wicklow (100 miles)
Qulaifying Race
27th July - ISORA / RAYC / Lee Overlay Night Race - (35 miles)
Dun Laoghaire to Nt. India Qulaifying Race
18th August - ISORA Offshore - (75 miles) Qulaifying Race
Dun Laoghaire – Pwllheli (T.B.C)
1st September - ISORA / RAYC / Lee Overlay Day Race - (54 miles)
Dun Laoghaire to M2
8th September - ISORA Offshore - Pwllheli to Howth. (80 Miles)
James Eadie Race – Qulaifying Race
Overall Series: To win the overall ISORA series for the Wolf's Head Trophy boats must complete 2
of the 6 "Qualifying". Points for the overall series will then be taken from the best 5
results. Prizes will be awarded for a separate series to include all races in the
schedule.
All races will have a weighting applied.
There will be two Day Races starting and finishing in Pwllheli – dates TBC.


























































