Displaying items by tag: Beneteau 211
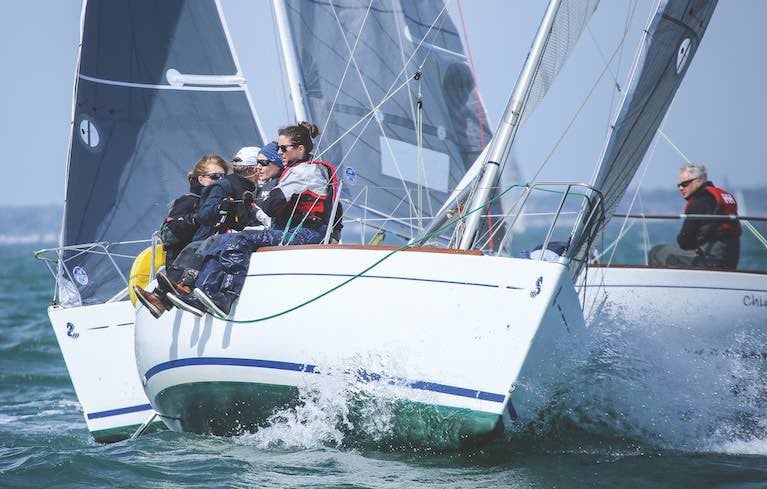
After five races sailed in the Beneteau 211 class, Royal Irish's Andrew Bradley in Chinook leads the 11-boat class by two points going into Sunday's final races of the 2023 Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta.
The Chinook crew have overtaken early leader Joe Smyth in Yikes, who sits in second place on seven points, and Pat Shannon in Beeswing is third on 13 points in a one-two-three-for the Royal Irish.
Racing was postponed for one hour on the penultimate day to allow strong winds to decrease, which proved correct as Dublin Bay yielded perfect summer sailing conditions in the afternoon.
The breeze was in a westerly quadrant at 15 knots, with strong gusts and significant wind shifts off the Dun Laoghaire shoreline to make for some exciting racing.
The 2023 regatta, the ninth edition of Ireland's largest sailing event, concludes on Sunday with two final races for most classes and a great festival of sailing across the waterfront and Dun Laoghaire town as four sailing clubs come together for the biennial event; Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club, Royal Irish Yacht Club, Royal St. George Yacht Club and National Yacht Club.
Joe Smyth's Yikes from the Royal Irish Yacht Club won the breezy first race of the Beneteau 211 class of the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta on Dublin Bay, but the race was not without drama as one yacht was dismasted.
According to provisional results, only two boats finished the race (despite five being on the course), with Smyth's clubmate Pat Shannon's Beewswing second.
 Joe Smyth's Yikes from the Royal Irish Yacht Club won the breezy first race of the Beneteau 211 class at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta Photo: Bob Bateman
Joe Smyth's Yikes from the Royal Irish Yacht Club won the breezy first race of the Beneteau 211 class at Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta Photo: Bob Bateman
Over a trapezoid course, ultimately shortened by international Race Officer Peter Van Muyden, the Championship-winning Billy Whizz skippered by Jimmy Fischer of the Royal St George Yacht Club was dismasted.
 Championship-winning Billy Whizz skippered by Jimmy Fischer of the Royal St George Yacht Club, going well in the comparatively flat sea state of the Salthill course in the first race of the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta 2033 when disaster strikes (below) as Billy Whizz is dismasted in the strong southerly winds Photo: Bob Bateman
Championship-winning Billy Whizz skippered by Jimmy Fischer of the Royal St George Yacht Club, going well in the comparatively flat sea state of the Salthill course in the first race of the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta 2033 when disaster strikes (below) as Billy Whizz is dismasted in the strong southerly winds Photo: Bob Bateman
Scroll down for provisional results
Consistent sailing with two race wins and five results in the top three gave the Beneteau 211 National Championships title to Peter Carroll's Yikes! at the Royal Irish Yacht Club this afternoon.
John Downey's B211 Capilano closed the gap by a point in today's final two races on Yikes to finish just one point adrift in second overall on seven points.
15-20 knot south easterly breezes proved to be testing championship conditions for the 12-boat fleet in a good chop, though the sheltered Seapoint racecourse protected the 20-foot keelboat class from the bigger waves on the Bay.
 John Downey's B211 Capilano
John Downey's B211 Capilano
Third in the 11-boat fleet was Andrew Bradley's Chinook on 13 points.
 Andrew Bradley's B211 Chinook
Andrew Bradley's B211 Chinook
Results are here
Beneteau 211 National Championships Photo Gallery
Peter Carroll's 'Yikes' Leads Beneteau 211 National Championships at the Royal Irish Yacht Club
The host club dominates the 2021 Beneteau 211 National Championships at the Royal Irish Yacht Club after the first three races sailed off Dun Laoghaire Harbour.
With a 2,1,1 scored so far RIYC's Peter Carroll helming Yikes has a three-point margin over clubmate John Downey's Capilano on seven points.
Royal Irish commodore Pat Shannon, sailing Beeswing, is lying third on 13 points in the 11-boat fleet.
 A start of a 2021 Beneteau 211 National Championships race at Dun Laoghaire
A start of a 2021 Beneteau 211 National Championships race at Dun Laoghaire
Dublin Bay presented 12 to 18-knot breezes from the southeast with a mist and fine drizzle.
Testing championship conditions for the 12-boat fleet were completed with a good chop, though the sheltered Seapoint racecourse protected the 20-foot keelboat class from the bigger waves on the Bay.
Racing continues on Sunday.
Results are here.
Beneteau 211s Win Premier Dublin Bay Sailing Club One Design Trophy for the First Time
Dun Laoghaire's Beneteau 211 class has won Dublin Bay Sailing Club's (DBSC) Premier George Arthur Newsom Cup for the first time.
The Cup is awarded to the boat which performs best compared to all One Design classes in Dublin Bay.
It was a clean sweep for Jimmy Fischer on his boat Billy Whizz, with two different crews taking the following trophy haul that, regrettably, the club did not get the chance to present as the annual prize-giving had to be deferred due to the Covid-19 restrictions.
- The George Arthur Newsom Cup - for the most successful boat in one-design racing
- The Facet Jewellers Cup - for Thursdays scratch overall
- The Beneteau 21 Tray - for Thursdays ECHO overall
- The Beneteau Cup - for Saturdays scratch overall
The feat was achieved by Jimmy with two different crews, one on Thursdays comprising Joe Smyth, Annette Ni Murchu and her brother Brian Murphy. Not only did they win Thursdays on scratch, but they managed the rare feat of winning Thursdays on ECHO also. Joe, Annette and Brian are all longterm members of Blessington Sailing Club.
Sailing with Jimmy on Saturdays, Peter Duggan and Les Richards won the series on scratch. Peter is another graduate of Blessington Sailing Club and has foredeck experience on J109 Jalapeño, with Paul Barrington et al. Les is a partner in a Trapper 501 in Bray Sailing club..
Jimmy says Afloat magazine's David O'Brien is the direct reason why he joined the B21s when he came back into sailing after a twenty-year absence while Catherine and Jimmy raised their two daughters. David and Jimmy know each other from way back in their IDRA 14 sailing days.
When Jimmy suggested he might take up sailing again, David recommended the B21s as he knows Jimmy's first love has always been one-design sailing. He also suggested there was good camaraderie and a helpful bunch in the class.
Jimmy crewed with current RIYC Commodore Pat Shannon in 2017 and bought Pat's boat, Billy Whizz, at the end of that season.
Seasons 2018 and 2019 were spent getting back in the groove, leading to success in 2020. Jimmy commented that the North Sails mainsail and jib that Prof O'Connell supplied proved to be both powerful and fast, adding to Billy Whizz's results on the water.
Watch this fleet, the B21s are growing fast and there's great fun and competition throughout the fleet.
Read more on the Beneteau 211 here
None other than Mark Mansfield predicted that the Scottish Series would prove an important warm-up for Irish raiders, and it certainly seems to be the case for Beneteau 31.7 owner John Minnis.
The Royal Ulster sailor struggled to make an impact at Tarbert in an IRC3 class dominated by the upgraded Half Tonners of Johnny Swan and the Wrights of Howth.
But in this week’s standalone Beneteau 31.7 class, his ‘Final Call’ crew finished Day 1 of the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta at the top of a 14-boat fleet.
‘Crazy Horse’ duo Frank Heath and Ivan Schuster, who finished third in the National Championships on the same waters 11 months ago, couldn’t take up the invitation that was staring them in the face at the Race 1 finish line.
Royal St George’s Michael Blaney finished ahead of them in second place at the helm of ‘After You Too’.
First 211s
Meanwhile the bijou Beneteaus - the First 211s - were engaged in the opening round of their Irish Championships.
Andrew Bradley’s ‘Chinook’ and Scottish duo Stu and Deb Spence were narrowly beaten to the title during VDLR17.
Two years on and rivalry between the Royal Irish and Clyde Cruising Club boats is just as keen.
But again they find themselves chasing first place, which this time is being held by Pete and Anne Evans on their Greystones entry, Anemos 2.
And Now, It's The New Dublin Bay 21...
#first21 – It's all so very 21st Century. The growth and development of this new Dublin Bay One Design has been healthily organic. And it hasn't been imposed from above – there's none of your old-fashioned de haut en bas here. Nor has it been dreamt up in some winter committee meeting by people with more notions than practical experience. On the contrary, it has developed at grass roots level, out of a genuine need, in an impeccably people-friendly way. And perhaps best of all, it involves a high level of re-cycling. For although this "new" boat perfectly fits the contemporary Irish sailing zeitgeist, the design has been around for 20 years. So making a new class out of it simply involves fulfilling the true potential of attractive little boats which have been just waiting to blossom since 1993.
Not that the First 211 was ignored when she made her debut back in the day. I can recall being utterly charmed aboard an early version in a Dublin Boat Show (remember them?) a long time ago. We old salts were particularly taken with the cute little porthole in the topsides, like a traditional little Edwardian cruising cutter, all made more charming by knowing the boat was designed by Groupe Finot and had drawn on the experience gained with Figaro Solo boats and Open 60s in order to produce a compact trailerable family cruiser with attitude.
But at the time the little boat made her debut, the Celtic Tiger was starting to flex his muscles. So the small-scale charms of the First 211 were overlooked in a mad rush for size and shine. Not that you couldn't get a deep shine on the boat's quality Beneteau hull, but you know what I mean. Yet for people with a particular set of sailing needs, the design has always neatly met their requirements, and today in its various forms, it is fulfilling many roles, including being the newest one design class in Dublin Bay.
It has come together in a diffident sort of way, and though they've had racing in the bay as a class for a year or so, next month's Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta will mark their debut as an official class on the national scene. There are 14 entries, made up mostly of local boats, but with a couple coming from the thriving class on Lake Windermere, plus another from Tralee Bay And there's one gallant boat from north of the Liffey, Brian Stewart's Mon Reve based at Malahide, where a summer evening's club race this week provided the opportunity to taste and test what is shaping up to be the new Dublin Bay 21.

Happy man. Brian Stewart on a perfect summer evening in Malahide with his First 21 Mon Reve, and some good club racing in prospect.
Photo: W M Nixon
The designs of Jean Marie Finot first came to prominence in the late 1960s when he won the Quarter Ton Worlds with a boat which went on to become the 26ft Ecume de Mer in the production version. The Ecumes defined the early Finot style, and they're a super little boat, well worth restoring if you happen to come across one needing TLC. Admittedly some minor flaws may have appeared over time, but they're all eminently fixable.
The 26ft Ecume de Mer of 1969 was hugely successful in launching Jean Marie Finot's international design career. And she really could sleep five adults in port.
Back in those days, the Sisk family of Dublin had a very successful Sparkman & Stephens 36ft sloop, Sarnia, an Italian-built version of the Swan 36 – she's still in Dun Laoghaire, and had a fine restoration job done a few years ago. But in 1969 Hal Sisk happened to see one of the earliest Ecumes de Mer at the Genoa Boat Show, and he also met up with Finot. Somehow he persuaded the rest of the family that they should have a very special 30ft aluminium offshore racer to the latest Finot designs to take every possible advantage of the new International Offshore Rule.

"Naked as a jaybird". The 30ft Finot-designed Alouette de Mer was totally unpainted when she arrived in Dun Laoghaire by road in July 1971 – and she stayed that way for her first season. Photo: Hal Sisk
Alouette de Mer was built in a factory near Le Bourget airport in Paris, and arrived in Ireland ready for sea in every way except that she was totally unpainted. The Sisks had been persuaded with irrefutable French logic that it wasn't necessary, so she went newly afloat in July 1971 naked as a jaybird, and won her first race, and many thereafter. I can remember racing against her that year, but it wasn't until a late July evening when were sailing gently through the moorings in Dun Laoghaire, and saw Alouette de Mer on her moorings among more traditional boats, that the utter starkness of her appearance really registered.

Spooky prescience - section of a page of the Seascape column in Irish Yachting & Motorboating, August 1971.
Nearby, Dun Laoghaire's most senior skipper James McAsey was quietly gliding along in his 1894-built gaff cutter Peggy Bawn, which he'd owned since 1919. It may well have been his last season sailing her. But many years were to elapse before Hal Sisk rescued Peggy Bawn from mummification to become a star of the international classic yacht circuit. At the time, Afloat magazine was known as Irish Yachting & Motorboating, and in the August 1971 issue, in a general column called Seascape, we published photos of the two boats and contrasted them. It certainly was some sort of weird prescience, even a bit spooky.
Subsequently, Alouette was painted red, but it didn't stop her winning. Though she wasn't the prettiest girl on the block, she was remarkably comfortable to be aboard, particularly in the cockpit - a Finot characteristic also found in the Ecume de Mer. Alouette personified racing enthusiasm, so when the Sisks decided that they had done enough for the cutting edge, and moved to the more traditional elegance of the 43ft Standfast designed by Frans Maas, Alouette went to Cork and the ownership of Hugh Coveney, who'd a great time sailing her with Harry Cudmore, before they in turn moved on to the new Ron Holland One Tonner Golden Apple.

In those days, genoas were ENORMOUS – Alouette de Mer going well in her second season in Sisk ownership. The cockpit was notably comfortable. Photo courtesy Hal Sisk
The next Finot design to make any significant impact in Ireland was the Fastnet 34 built in Limerick, probably the roomiest performance 34-footer ever built. You'll still see them around – Derek and Viv White's 1976-built Ballyclaire in Strangford Creek is a well-loved example. But with French sailing becoming turbo-powered by the 1980s, the Finot design office moved on from being a one man band to become a substantial organization, Groupe Finot, and their work expanded into some very big racing machines. Yet they still could produce very sensible smaller boats when asked, and the First 25 of the mid-1980s is an excellent example.
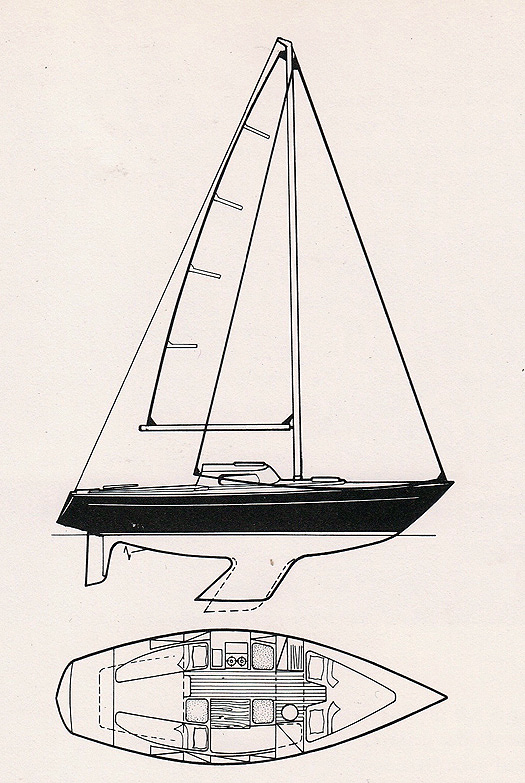
So when the Beneteau organization focussed its attention on a new trailer sailer for the early 1990s, it was to Groupe Finot that they turned for innovation and fresh thinking generally. You get an impressive package with the First 21. She has twin rudders, which makes a lot of sense for ease of steering in any beamy boat with the beam carried well aft. But in this case there's a bonus, for when the lifting keel is raised the depth of the rudders is such that the boat stands upright, supported by the rudders.
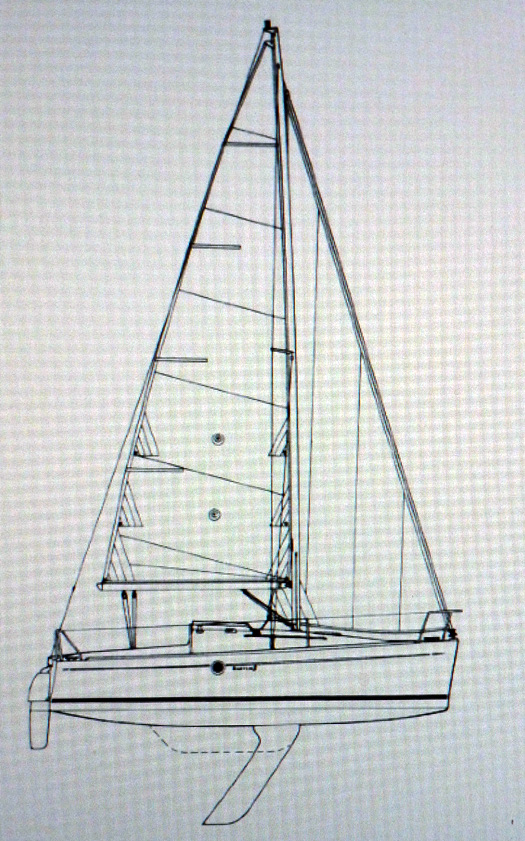
The plans of the First 21 show an effective rig, while the twin rudders keep the boat upright when dried out on the raised keel.
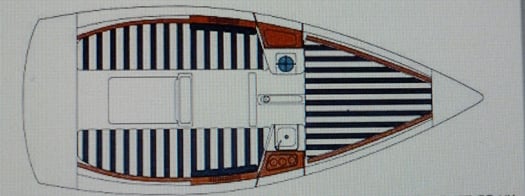
The accommodation packs in as much as possible in a performance 21-footer.
For most sailors, twin rudders and a lifting keel provide enough innovation to be going along with, so when I joined Brian and his crew of Kieran the tactician and Zenda the trimmer and Derek the bowman on an evening when Malahide was like San Diego only better, the workings of these features was of prime interest.
The keel stays down permanently. It's held down by a strut which will give way if you biff a rock, but is vastly superior to having a weighted centreboard which solely relies on gravity to stay down. Replacing the strut mechanism is not cheap if you indulge in impactive pilotage, but it's much less costly than major hull repairs at the upper aft end of the keel.

The keel is raised by 57 turns of a winch handle inserted in the socket at the top of the keel housing. Photo: W M Nixon
The keel is raised by 57 turns of a winch handle, so if the significant other in your life happens to acquire a First 21, you can get him or her one of those battery powered winch handles as a Christmas present. It will only need to be re-charged once in the season, as the boat is effectively a keelboat when in commission. But particularly in the Dublin context of limited and expensive waterfront boat storage space, the First 21 has the very attractive option of end-of-season trailerability and ease of getting her home if you happen to have space there. Brian Stewart lives in Castleknock, and it's only a morning's work to get Mon Reve onto the trailer and back to the house for free winter storage.
As for broadening the scope of sailing, Ireland's improved roads have brought West Cork comfortably into his summer sailing plans. That said, the boat is only just over 21ft long, and while she has very comfortable sitting headroom and is well thought out within her size limitations, and can at a pinch sleep four, this really is a boat only for enthusiasts to cruise in liveaboard style, but if you limit yourself to day sailing in your chosen area, she does very well indeed for general use by varied levels of sailing interest.
Auxiliary power is provided by an outboard, and much as we all may dislike the look of an outboard hanging out of the stern of an otherwise attractive boat, you get used to it and it's very convenient. Plus when you're racing you only look astern if you're leading the fleet, which greatly offsets the outboard's jarring visual intrusion.
While the functional appeal of twin rudders is obvious, the fact that inter-connecting them to a single tiller involves several links inevitably causes a certain amount of play in the steering. That said, I'm told some of the Dun Laoghaire hotshots have already worked out ways of reducing this play to virtually nothing, but it requires perfect setting of the tracking.

The development of the First 21 class in Dublin Bay has greatly increased the knowledge and skills to make these attractive little boats perform even better Photo: David O'Brien
Mon Reve sets a very nice set of threads made in Malahide by Philip Watson, and they did sterling service in a cruiser race in which the smallness of the fleet was more than offset by its variety. In a pleasant southeast breeze racing a windward-leeward, we were the smallest boat in conditions which were bound to suit the fastest, as the upwind leg was against the last of the flood, while the ebb was building as we ran back to the finish.

Brian and Kieran limbering up for the start Photo: W M Nixon
The enemy consisted of J/24, a Bolero 25, a Corby 25 and a Kelt 850. It makes you realize just how much of a compact cruiser a First 21 is when you realise these all seemed like big bullies. But Mon Reve punched above her weight. With Brian on the helm and Kieran calling the shots and keeping up a constant commentary on speed fluctuations, we gave it a good shot. As visiting ballast, I moved about the cabin sole, as it's crucial to trim to heel her such that you keep the lee rudder vertical at the very least, and ideally heeled a little. It was no hardship down below – you really can keep an eye on things through those ditzy little portholes in the hull topsides.

The enemy through the porthole – the J/24 eventually won. Photo: W M Nixon

This was as near as the much larger Kelt 850 got to Mon Reve Photo: W M Nixon

The skipper concentrates with the Kelt 850 nicely tucked away Photo: W M Nixon
We were fourth round the weather mark, having seen off the Kelt 850, and then things got exciting. Far from collapsing, the evening breeze kept up strength, sweet and warm. Up ahead, the Bolero 25, having sailed a blinder of a beat to lead at the weather mark, blew it all with eccentric spinnaker work and let the J/24 through. With the tide building against us, first to finish was going to win on handicap, and both the J/24 and the Bolero were to have us on handicap by a minute or two.
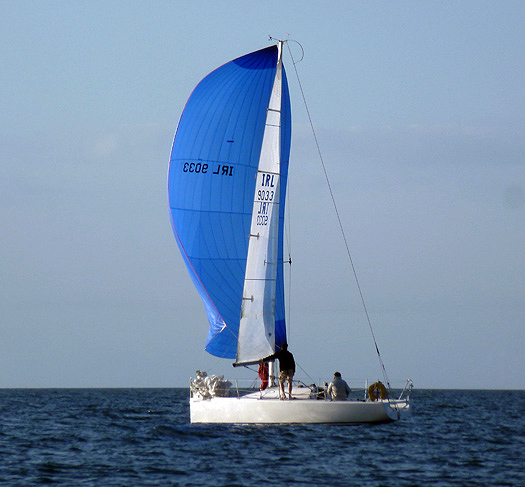

The Corby 25 had an idea about going off to starboard on the run, but it wasn't a winner and it brought Mon Reve into the hunt for a close finish. Photo: W M Nixon
But we'd a real tussle with the Corby 25. They went off on starboard gybe presumably to position themselves better across the increasing foul tide towards the finish line. But we found the groove on port, and made hay with a private air. If you look at the plans, you'll see the First 21 has quite a decently tall rig, and it worked a treat on Wednesday evening, with spinnaker and mainsail in harmony. The Corby finally got it together to scrape across ten seconds ahead, but Mon Reve was a very solid third on corrected time, and we'd had a lovely sail on an evening when no-one had expected the breeze to hold up.

Happy boat, happy crew – Mon Reve back in her berth in Malahide Marina Photo: W M Nixon
So the First 21 is much more than just a clever trailer-sailer. She's a super little club racer, and she'll provide a fine one design class in Dublin Bay. And not just there, either. While Mon Reve and her friendly crew may have to go to Dun Laoghaire for a bit of level racing in a fortnight's time, it seems to me that Malahide would make the perfect centre for another nucleus of First 21s racing regularly as a class. They're one very likeable little boat, and Malahide needs a class like this.

They're gearing up for the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta's first series for the First 21 class – Mon Reve's keen crew are (left to right) Derek the bowman, Brian the VRO, Kieran the tactician, and Zenda the trimmer. Photo: W M Nixon
Beneteau is distributed in Ireland by BJ Marine Ltd
Comment on this story?
We'd really like to hear from you! Leave a message in the box below or email William Nixon directly on [email protected]
WM Nixon's Saturday Sailing blog appears every Saturday on Afloat.ie
Follow us on twitter @afloatmagazine and on our Afloat facebook page






























































