Displaying items by tag: Fast 40
Henri Lloyd Sailing Gear Teams Up With Fast40+Class
Premium British marine and lifestyle clothing brand, Henri Lloyd has announced a three year partnership with the FAST40+ Class.
As the Official Technical Clothing Partner to the FAST40+ Class, Henri Lloyd will be working alongside the class organisers and owners to provide bespoke crew kit packages on Henri Lloyd’s latest inshore race apparel. In addition, all FAST40+Class crew will also benefit from the Henri Lloyd – FAST40+Class Privilege Club.
As part of the partnership, Henri Lloyd will be bestowing a perpetual trophy for the 2017 FAST40+ Race Circuit. Henri Lloyd will also be working with the FAST40+ Class on a number of other projects over the next two years.
“The FAST40+ Class is innovative and highly technical; the showcase racing at many top class regattas, this makes them the perfect fit for Henri Lloyd. Over the upcoming months, we will look forward to meeting the crews and watching some exciting racing.” Paul Strzelecki, Henri Lloyd Chairman.
“We are delighted to have Henri Lloyd on board for the next three seasons. Technical excellence, innovation, and best in class, are just some of the reasons why Henri Lloyd was chosen as our technical clothing partner. It will be an honour to present the Henri Lloyd FAST40+ Trophy, and we look forward to a rewarding and exciting partnership.” Robert Greenhalgh, FAST40+ Class President.
Henri Lloyd will be working with the FAST40+ Class during the 2017 FAST40+ Circuit, including Cowes Week and the One Ton Cup
Fast 40s Announce 2017 Solent Circuit
The FAST40+ Class have announced their plans for the 2017 Race Circuit with eight events starting in April and concluding in October 2017. The FAST40+ Class will once again contest the prestigious One Ton Cup an event in which Royal Cork's Ker 40 Antix (Anthony O'Leary) competed as the sole Irish entry.
Owned by the Cercle de la voile de Paris (CVP), the One Ton Cup was created in Paris in 1899, coinciding with the 1900 Paris Olympic Games, the first to include sailing as an Olympic Sport. The One Ton Cup will be the showcase event of the year, and one of the five events counting as points scoring rounds for the 2017 FAST40+ Race Circuit. In addition, the 2017 FAST40+ National Championship, will be held during the RORC IRC National Championship in June.
15 teams contested the inaugural season with teams from England, Germany, Ireland, Scotland and South Africa. The fleet is expected to increase in 2017 with at least two new FAST40+ yachts in build for English and Swedish teams, and a Dutch team has purchased the winning yacht from 2016.
Bastiaan De Voogd's Dutch team will compete with the FAST40+ Class during the 2016 Hamble Winter Series, having purchased the 2016 FAST40+ Series winner, Carkeek 40+ Mk3 Girls on Film. Bastiaan is best known for his Sydney GTS 43 Coin Coin, winning class in the 2015 Rolex Fastnet Race and winning numerous inshore regattas, including the 2015 Dutch IRC National Championship. The previous owner of Girls on Film, Peter Morton, has a new Carkeek 40+ Mk4 in build, and the team will be ready to defend their title for the 2017 Season. Stay tuned for future announcements by visiting the FAST40+ website for more details, including the full 2017 Events Schedule.
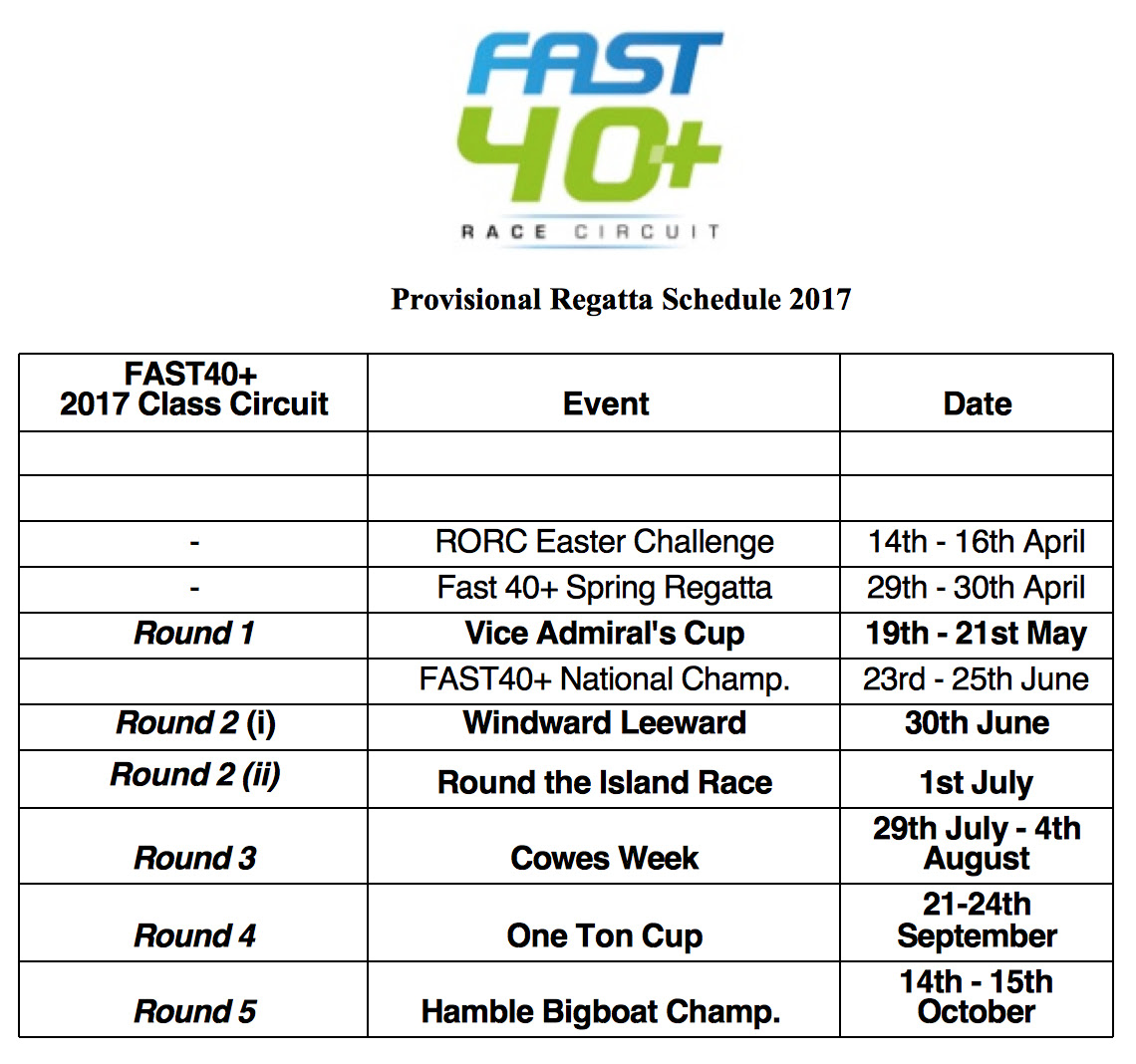 The FAST40+ Class have announced their plans for the 2017 Race Circuit with eight events starting in April and concluding next October
The FAST40+ Class have announced their plans for the 2017 Race Circuit with eight events starting in April and concluding next October
Irish Endorsement for Fast 40s 'One Ton Cup'
The FAST40+ Class announcement of a One Ton Cup (OTC) event in September has been given the thumbs up from Irish skipper Anthony O'Leary who competes in the new class in the Royal Cork Yacht Club entry, Antix.
The first Cup event will by hosted by the Royal Southern Yacht Club, Hamble between 16-18th September 2016. O'Leary hopes the Cup could even come to Ireland at some point in the future.
'It is a fantastic move by the Fast 40+ Class Assoc. It is most appropriate that the OTC be awarded to the leading team in this class', O'Leary told Afloat.ie 'It will make what is already a most competitive class all the more challenging', he added.
The ONE TON CUP is steeped in history and reputation in the world of yacht racing. Created by the Cercle de la Voile de Paris (CVP – Paris Yacht Club) back in 1899 and widely recognised as a masterpiece of art nouveau style, initially raced for in regattas between one tonner sailing yachts. The trophy itself was designed in 1897 by the jeweler Robert Linzeler and was made by Bratiau in 1898. It is made of solid silver and weighs 10 kgs standing at 57cm high and 58cm wide.
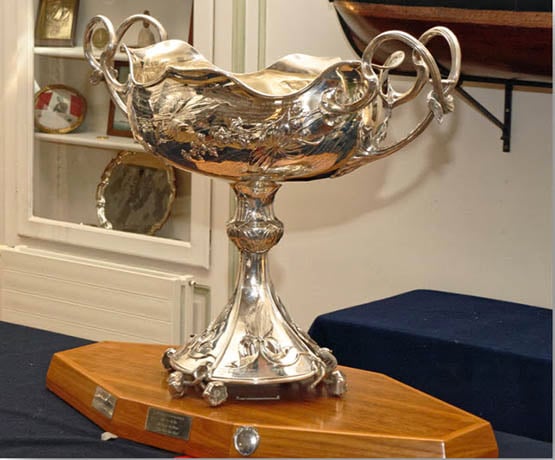

The One Ton Cup has been raced for in International 6 Metre yachts, and for a short time on 6.5m SIs. In 1965 this trophy moved into the world of ocean racing, and from there into the RORC and IOR ruled racing circuits. Most recently, in 1999, the Cup was presented to the Corel 45 Class. Winners of the Cup include many legends in our sport such as Syd Fischer, Royal Cork's Harold Cudmore, Henrik Soderlund, King Harald V of Norway, Paul Cayard and Russell Coutts.
The hosting of this event and the realisation of getting the magnificent One Ton Cup trophy to the UK has been made possible through the support of a number of organisations and individuals, especially Cercle de la Voile de Paris for recognizing the profile of this growing class and agreeing that this is an event worthy of such a trophy, and Hamble Yacht Services who will be the Presenting Partner for the event.
Francois Laborde (President of the Cercle de la Voile de Paris – Paris Yacht Club), commented:
"We are excited to announce this partnership with the Fast40+ Class for the 2016 edition of the One Ton Cup. The boats have amazing performance characteristics, are fun to race, and are attracting top sailing talents. Those characteristics are exactly in line with the tradition and objectives of our Cup."
The FAST40+ CLASS represents the modern day One Ton race yacht, light displacement race boats, with IRC TCCs of between 1.210 and 1.270. This narrow band of high performance race yachts is designed to deliver fast, close inshore racing.
Robert Greenhalgh, Class President, came up with the concept in 2014 and, after engaging the commitment of a number of interested owners and sailors, this year the class will host a fleet of 14 race boats competing at the highest level over a circuit of 5 UK based events. The boats hail from 7 countries – UK, Ireland, Scotland, USA, South Africa, New Zealand and Germany – and the fleet is growing quickly in competitor numbers and profile.
Robert commented, “The owners of this exciting class take their racing seriously – we are already experiencing incredibly close and exciting inshore racing and it seems to be ticking all the boxes. To secure such a significant trophy as the One Ton Cup to be our showcase trophy for 2016 is sure to add pressure and focus to the racing – this is THE trophy to win this year.”
Traditionally the One Ton Cup regattas consisted of inshore racing, a coastal race and a proper offshore race. Reflecting the changing times and demands of race circuits today, the Fast40+ One Ton Cup will be raced between 16th and 18th September hosted by the Royal Southern Yacht Club and will consist of 8 scheduled races over the 3 days with event rankings for each boat being multiplied by 2 for the overall 2016 Race circuit results. The courses will be a mixture of windward – leeward and coastal courses sailed in Solent Waters, each race lasting between 45-180 minutes.
Peter Morton , owner of Girls on Film, added his thoughts, “I have seen a new lease of life injected back into the Solent racing scene through the Fast40+ Class since 2015. Close racing, passionate owners and competitors who reveling in the competitive scene, a good onshore social scene and all run by a professional organisation – and now with the addition of this slice of history to win, what more could we want!”































































