Displaying items by tag: RIYC
Keynote Speaker and More Announced for ICRA National Conference and AGM This Month
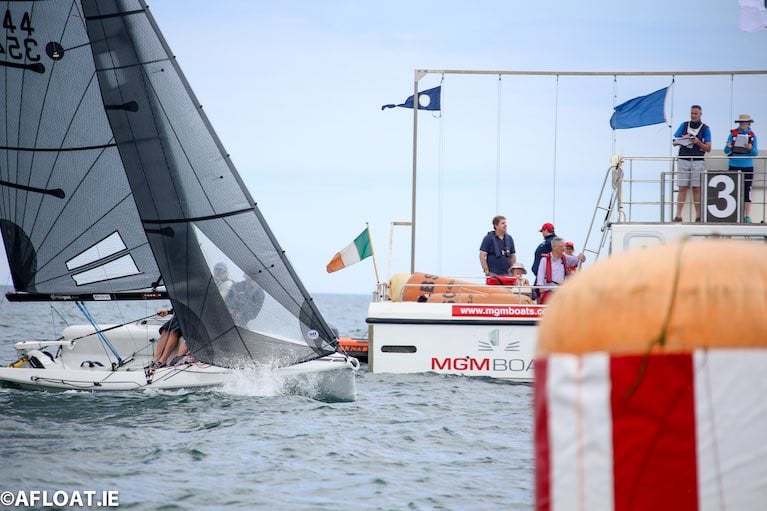
The Irish Cruiser Racing Association (ICRA) has provided more details of its 2024 conference, which will be hosted by the Royal Irish Yacht Club on Saturday 10 February.
This year’s keynote speaker will be Jason Smithwick, director of the RORC rating office who will discuss the ongoing works being undertaken by RORC to enhance the IRC handicap rating system.
Also speaking will be Cian McCarthy and Sam Hunt of Kinsale, on the highs and lows of travelling to the other side of the world to compete in the double-handed class in the recent Sydney-Hobart Race.
These special guests are in addition to updates from the hosts of the major events planned for the 2024 season, not to mention the Sailors Forum — where you will have your chance to discuss and debate the big issues in our sport.
The conference starts 10:30am and will close at lunchtime. Register via the ICRA website to attend in person or remotely via Zoom.
All members are also invited to attend the ICRA AGM which immediately follows the conference.
The AGM will include a vote for a new Executive Committee, and any cruiser racer boat owner, or boat owners’ representative, can apply to become a member. Please note that two other cruiser racer boat owners are required to nominate you; get in touch with [email protected] with any queries about the process.
Entries Open for Drumshanbo Gunpowder Irish Gin Royal Irish Regatta 2022 This Weekend
Entry is now open for the Drumshanbo Gunpowder Irish Gin Royal Irish Regatta 2022, hosted this Saturday 25 June by the Royal Irish Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire.
Race tickets run from €70 for cruisers to just €10 for a Water Wag, which represents excellent value for money.
And the club promises a jam-packed day ashore as well as on the water in Dublin Bay with music, food and of course cocktails. Details of the day’s entertainment options can be found below and on the RIYC website HERE.

The Royal Irish Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire Harbour hosted 'An Evening with Tracy Edwards MBE' on Wednesday, May 18th.
The legendary Whitbread Round the World Yacht Race skipper was welcomed by RIYC Commodore Jerry Dowling and Flag Officers.
Edwards gave a talk to members and guests from the original Maiden Project through to the Maiden Factor, a global foundation that inspires women and girls all over the world.
In 1989 Edwards skippered Maiden, the first all-female crew, in the Whitbread Round the World Yacht Race, achieving second overall in Class and becoming the first woman to receive the Yachtsman of the Year Trophy.
 Tracy Edwards is presented with a Royal Irish burgee by Commodore Jerry Dowling during her Dun Laoghaire visit. Photo: Rachel Fallon Langdon/Ocean Images
Tracy Edwards is presented with a Royal Irish burgee by Commodore Jerry Dowling during her Dun Laoghaire visit. Photo: Rachel Fallon Langdon/Ocean Images
Royal Irish Yacht Club's Home Together Series “Winning Races in Dublin Bay" - Top Tips from North Sails Ireland's Prof O'Connell
The Royal Irish Yacht Club's successful 'Home Together' series of virtual talks returns this Wednesday 27th January at 19:30hrs with Maurice “Prof” O’Connell.
O'Connell from North Sails Ireland never misses a Dublin Bay Sailing Club (DBSC) race with his customers unless he is out of the country.
Over the years, he has raced in 100's of DBSC races in everything from the biggest IRC Cruiser 0 yachts to the smaller one-designs. He has put together his "10 Top Tips for racing in Dublin Bay" which he will share with RIYC members and guests.
Commences 19:30hrs contact [email protected] to register.
Across the Atlantic by Inflatable & Other Ways to Get Wet with Enda O’Coineen
On Thursday, 4th February Enda O’Coineen reprises memories of his epic transatlantic solo voyage onboard his 16-foot inflatable, the Kilcullen just over 35 years ago.
Having first made landfall in Dunmore East, upon arriving finally in Dun Laoghaire, Enda promptly sold the Kilcullen. It subsequently changed hands several times before Enda finally bought her back and restored her, reviving memories of some extraordinary adventures, long submerged and almost deliberately forgotten.
Commences 19:30hrs contact [email protected] to register.
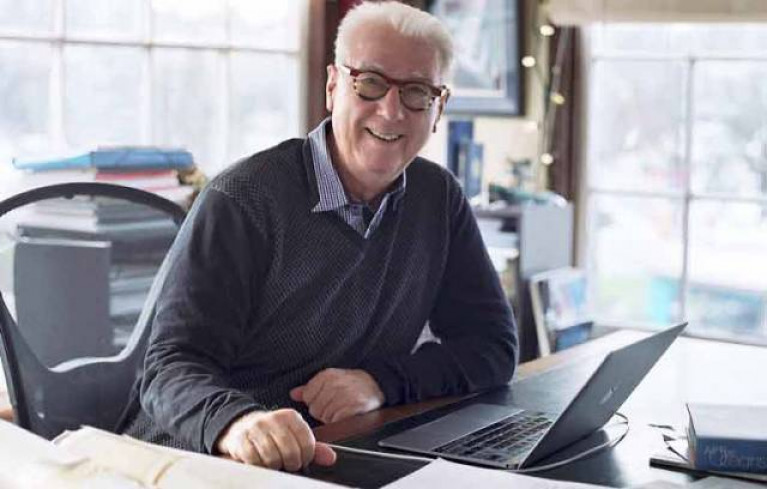
Yacht designer Mark Mills is the latest speaker in the Royal Irish Yacht Club’s special series of online talks tonight, Wednesday 10 June.
Mark Mills started Mills Design in 1995 with an order from Peter Beamish for the 31ft Aztec, built in Malahide by Mizzen Marine.
Building on her success, his custom designs have won numerous titles including the 100ft Wallycento Tango, the Maxi72 World Champion Alegre 3, multiple IRC Championship winners Mariners Cove and Tiamat, and the 69ft IMA Mini-Maxi Champion Alegre.
Equally his production designs such as the IC 37 for the NYYC, double ORC World Champion Landmark 43, C&C30, Cape 31, King 40 and DK 46 are well known worldwide.
Originally from California, Mills studied yacht design at the Southampton Institute while racing with some of the best teams in the UK.
He won with the Seahorse Sailor of the Month in December 2014, the 2009 Irish Sailor of the Year award, was named the Asian Marine & Boating Best Designer of 2010 and 2015, and recognised closer to home with Wicklow Sailing Club’s Irish Holly trophy.
Most recently, he won first prize at the premiere edition of the MDO Montecarlo prize for the Wallycento Tango.
A member of the RORC Technical Committee and an advisor to both the US and Irish IRC owners groups, Mills has spoken around the world on yacht design and rating rules for events such as IBEX both in the US and Europe, the International Yacht Forum, and regularly at ICRA meetings.
He was one of the initial HPR Committee members who helped draft the High Performance Rule for the NYYC, and subsequently joined the Sailing Yacht Research Foundation (SYRF) Advisory Board.
This evening, he follows the likes of Julian Everitt in the RIYC’s special series of talks with some of the world most renowned yacht designers. RIYC members should contact [email protected] to attend this talk, which starts at 7.30pm this evening, Wednesday 10 June, via the Zoom platform.
Yacht Designer Julian Everitt Is Latest Speaker In RIYC’s Members-Only Online Talks Series
The Royal Irish Yacht Club welcomes acclaimed yacht designer Julian Everitt as the latest speaker in its members-only series of online talks tomorrow evening, Wednesday 27 May.
First inspired to become a yacht designer when he saw Sceptre leaving Poole Harbour in 1958 in training for the America’s Cup, Julian Everitt produced his first full design with an RORC Rule half-tonner in 1968.
His first IOR design, for Bantam Yachts, provided the basis for a string of successful half-tonnes, then quarter-, three-quarter- and one-tonners.
Then came the E-Boat, designed in 1974 to the IOR, of which over 250 were built; the Mirador, a 20ft lifting keel yacht in collaboration with the Daily Mirror newspaper; and the radical Wavetrain, which currently sails out of Greystones.
Julian also edited Seahorse Magazine between 1970 and 1975, and has contributed to many sailing magazines and journals over the years — so expect strong views, such as his position on how ratings systems shape yacht design, and not always for the best.
Julian Everitt’s talk is part of the mini-series on yacht design that kicked off two weeks ago with Ron Holland. Only RIYC members can attend via the Zoom platform from 7.30pm on Wednesday 27 May. Contact [email protected] for details on how to attend.
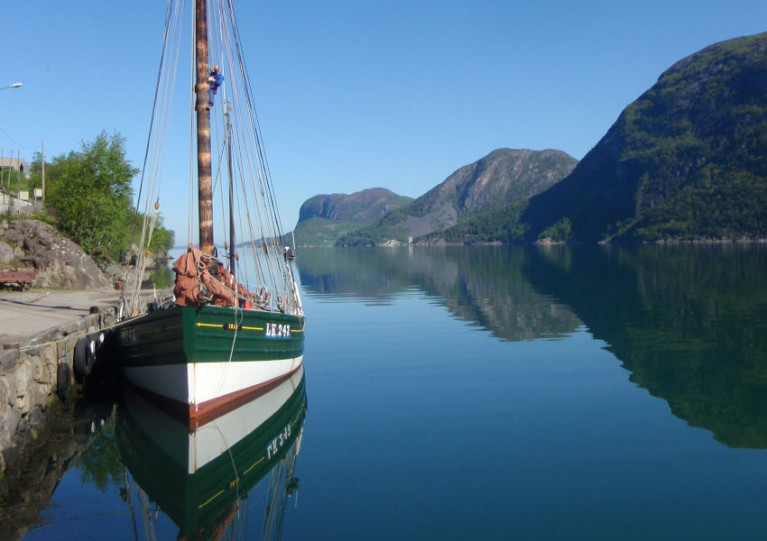
‘Cruising Scandinavia’ is the subject of this evening’s (Wednesday 20 May) online talk presented by Prof Andrew Curtain and hosted by the Royal Irish Yacht Club.
The Nordic region provides a huge variety of sailing opportunities and a single presentation could be devoted to just a small region.
This talk by Prof Curtain, RIYC member and Roving Rear Commodore for the Ocean Cruising Club, will offer a pictorial view — a virtual cruise, if you will — of three of the most popular areas and two never before visited by an Irish yacht.
These include the Norwegian fjords, Sweden’s west coast archipelago, the Gota Canal system, travel through a Russian canal to the Finnish lakes, and a cruise up the Bay of Bothnia to near the Arctic Circle in Lapland, with a surprise ending.
The Zoom talk begins at 7.30pm this evening. Get in touch with the RIYC for details.
This week’s slot in the Royal Irish Yacht Club’s ‘Home Together’ series of online talks sees yacht designer Ron Holland headline a new mini-series featuring some of the best known names in international yacht design.
Julian Everitt, Mark Mills and John Corby are some of the other legendary figures who will give their own virtual talks over the coming weeks, following Holland’s introductory talk tomorrow evening (Wednesday 13 May)
And what’s more, Holland will be joined on this panel by Ireland’s own veteran sailing superstar Harold Cudmore.
For over 50 years, Ron Holland’s innovative designs have repeatedly shaken up the world of sailing.
Renowned as one of the most successful and sought-after designers in the highly competitive world of international ocean racing, he later brought his influence to — and continues his success in — the superyacht industry.
Holland’s online talk is set for 6.30pm on Wednesday 13 May. Contact [email protected] to register to attend.
The latest in the Royal Irish Yacht Club’s ‘Home Together’ series of online talks will see Hal Sisk recount a brilliant season with Peggy Bawn in classic events across the Atlantic from Maine to New York.
Many members are familiar with images and tales of classic regattas in the Med, but New England is a different prospect.
Hal will describe a very special campaign in the classic regattas of New England in his historic cutter Peggy Bawn and the cruising in between such venues as Newport, Camden, Castine and Stonington.
The illustrated adventure will also include a professionally made short film of Clare Francis racing Peggy Bawn in Cowes in 2018. Clare was the first woman to race singlehanded across the Atlantic in 1973 and skippered a Swan 65 in the Round the World race in 1977.
Be sure to tune in from 7.30pm tomorrow evening, Wednesday 6 May. RIYC members should have their invite emails but contact the Club Secretary if there are any issues.
Upcoming talks include acclaimed yacht designer Ron Holland (13 May), Bobby Kerr on climbing Point Burnaby in the Alps (15 May) and Prof Andrew Curtain on cruising Scandivanva (20 May).
The Royal Irish Yacht Club begins a new series of online talks this evening, Wednesday 15 April.
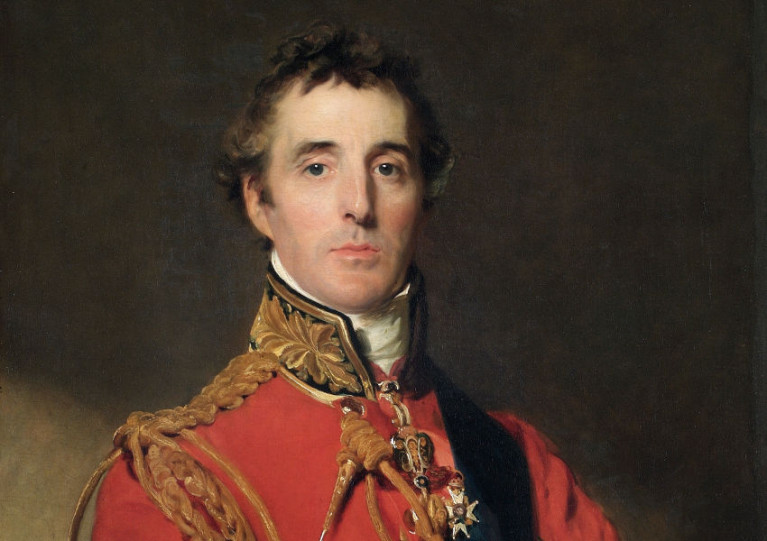
Each talk will be presented by an RIYC member or invited speaker using the video conferencing platform Zoom, with the first event this evening from 7.30pm being a presentation by Des Cummins on The Peninsular War.
The Peninsular War was the only time that British troops fought Napoleon on land in Europe. The campaign from 1807 to 1814 was dubbed the ‘Spanish Ulcer’ by Napoleon for tying down as many as 350,000 troops and was a major contributor to his disastrous defeat in Russia.
Cummins will examine the strategy of the Duke of Wellington, Arthur Wellesley (born in Dublin in April 1769), who rose to prominence during this campaign, and the building of the Lines of Torres Vedras.
Talk attendees can join in via computer, laptop, tablet or smartphone — and questions and comments during the live talk are welcome.
Attendees are requested to follow the instructions on how to install and use Zoom, and to log on a few minutes before the scheduled start.