Displaying items by tag: RStGYC
Book Now For Powerboat Training At The RSGYC
Places are still available for the latest powerboat training course at the Royal St George Yacht Club later this month.
The two-day course, on Saturday 29 February and Sunday 1 March from 8.45am to 5pm, provides the ideal way to get afloat for the first time, or to build on skills you already have.
The Irish Sailing syllabus Powerboat II course (National Powerboat Certificate) will formally teach you the fundamentals in the safe operation of a powerboat, its preparation and allied aspects, while helping you to build your confidence on the water and get the most from your RIB or powerboat in a safe and comfortable manner.
This weekend course (which will also run in May) is priced at €260 which includes all course materials, instruction and certifications. Book online via the RSGYC website HERE.
Royal St George To Host Table Quiz In Aid Of Rehab Care Dun Laoghaire
The Royal St George Yacht Club will host a table quiz on Friday 6 March to raise funds for Rehab Care Dun Laoghaire.
Join quizmaster Sarah Mullen-Rackow as she challenges with questions on an evening of fun and prizes that’s not to be missed.
Tables are €50 and the quizzing begins at 8pm in the dining room, with platters of sandwiches served at half time. Places are limited so be sure to book early to avoid disappointment.
For any queries contact Danielle Gagg at reception and marketing on 01 280 1811.
Royal St George To Host Sailing Results Workshop
A special workshop that aims to demystify the area of sailing results for events will take place at the Royal St George Yacht Club on Saturday 29 February.
The workshop day will also provide attendees with the skills and confidence to expertly run results for a sailing race or event of their own.
Attendees should bring their own laptop (which runs Windows) to the workshop, which starts at 10 am on the day in the Club Room and continues to the afternoon with a break for lunch.
This workshop is open to all RSGYC members, with spaces limited to 15 attendees. The fee is just €5 and online registration is required.
Any questions should be directed to Karin in the Sailing Office on 01 280 1811.
UK Sailmakers’ Barry Hayes In Howth Next Thursday For First In New Series On Top Tips For Sailors
Barry Hayes from UK Sailmakers Ireland begins a new series of talks with Top Tips For Sailors next Thursday 16 January at Howth Yacht Club from 7.30pm.
Members and guests alike are welcome to attend the two-part session which will cover both optimisation for racing or cruising vessels, and learning how to service your deck hardware — overalls recommended.
Barry will also visit the Royal St George on Thursday 30 January (time TBC) and Kinsale Yacht Club on Thursday 13 February at 7.30pm.

Dublin Dinghies Prepare for Royal St. George Final Fling Regatta
The CH Marine sponsored 'Final Fling' Dinghy Regatta takes place for the 3rd consecutive year, this Sept 28th in Dun Laoghaire writes Gavan Murphy, Dublin Bay Laser Class Captain
This year, the regatta will offer a very innovative format in that there will be two fleets, a Regatta Fleet and a Main Fleet.
The Regatta Fleet, facilitated by the Royal St George Yacht Club, is designed to accommodate less confident Laser (only) sailors. This fleet with race 5 short races inside the Harbour, with plenty of RIB support and on the water coaching. It will comprise of sailors that have perhaps done some of the Laser 'Kindergarten' workshops that have been running throughout the season in locations including Dun Laoghaire, Malahide & Wexford. Other participants in this group may include parents whose child has a Laser but their own sailing has lapsed and they're a little rusty. Regatta Fleet sailors are expected to be able to sail around a simple triangular course. There will be a briefing and debriefing session in the Royal St George to help the learning experience and a 15-minute workshop looking at rigging and sail control lines, all given by Sean Craig, local Laser sailor and Regatta Fleet Race Officer for the day.
The Main Fleet will be facilitated by the DBSC and will comprise of PY's (IDRA, Fireball, Vago etc.), Laser Standards, Laser Radials and Laser 4.7's who will complete 4 quick-fire races for the coveted 'Final Fling' prizes!
Prizegiving for both fleets will take place in the Royal St George from 6 pm. This will be followed by the 'now infamous' end of season Laser fleet dinner and social in the George that evening.
Follow this link to enter both the Regatta & Main Fleet here
Quick Nap for Henry in the International 12-foot Dinghy Championships
In any sailing event, the helmsman must concentrate on his sails, and on the motion of the vessel through the water. Most crews really don’t have much to do except when the boat arrives at the corners on the course writes Vincent Delany
At the International 12-foot Dinghy Championship at the Royal St George Yacht Club, Dun Laoghaire on 15th September, young Henry Shackleton knowing that he had nothing to do until he heard the words ‘Ready about’ from his dad, David, took the opportunity of a quick nap after a hard night on the town. Despite, Henry napping, he finished in second place in the competition for the historic Altair Cup originally won by Billy Mooney.
We look forward to Henry competing as a helmsman in the Irish 12 Foot Dinghy Championship in ten year’s time in his grandfather’s 12-foot dinghy which is due for restoration in the near future.
 Aus 1 and others
Aus 1 and others
Big Results For Royal St George’s U25s In Women At The Helm Regatta
The Royal St George Yacht Club had reason to celebrate when members of the U25 squad took Class 1 and won the overall team prize in the Irish Sailing Pathfinder Women at the Helm Regatta this past weekend.
With Niamh Henry at the helm, Alanna Lyttle on main trim, Ellen Murray on pit, Roberta Bell King on bow and Gillian Ballesty on kite trim, the Class 1 team won both of their Saturday races on Dublin Bay in the event hosted by the neighbouring National Yacht Club.
“It was tough going but we worked well as a team and had some fun with the spinnaker in the big wind,” the crew said later.
The RSGYC also won the overall team prize with Helen O’Beirne in the Laser Radial and Grace O’Beirne in the 420.
Sligo Yacht Club’s sailors were the big winners on the day, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Royal St George Oscars Nominees Revealed For 2019
The Royal St George Yacht Club has revealed the nominees for its Annual Sailing Awards, otherwise known as the RStGYC Oscars.
Chris Power Smith’s J/122 Aurelia is guaranteed a share in the Commodore’s Cup for best offshore performance as the nominees comprise Team Joshua Trio (Aurelia, Platinum Blonde and Windjammer) and his own campaign.
Keelboats and crew in the running for the Enriquetta Cup this year are Brendan and Sarah Foley and their Impala Running Wild (pictured top), Michael O’Connor’s SB20 Sin Bin, and Richard and Philip Lovegrove with their Sigma 33 Rupert.
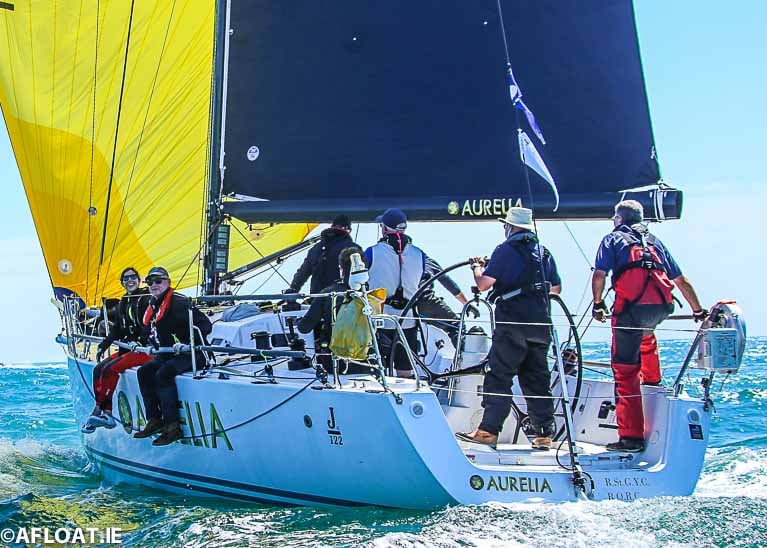 Chris Power Smith’s J/122 Aurelia
Chris Power Smith’s J/122 Aurelia
Significant dinghy performance is rewarded with the Vice-Commodore’s Cup, whose nominees include promising Optimist talent Charlie Cullen and Laser sailors Jack Fahy, Tom Higgins and Shirley Gilmore.
Gilmore is also nominated for the Causeway Trophy for sportsmanship alongside Harriet Walker, Ross O’Leary and Emily Riordan.
 Ross O'Leary
Ross O'Leary
Optimist sailor Riordan shows up again in the shortlist for the Youth Award, with Laser 4.7/Waszp sailor Alana Coakley, 420 pair Grace O’Beirne and Kathy Kelly, RS Feva duo Elysia O’Leary and Lily Dwyer, and former Oppy and now Laser competitor Moss Simington.
Ross O’Leary, meanwhile, is also in the running for the Waterfront Award for significant contribution to the sport of sailing.
His excellent work as Laser class captain is recognised along with Laser Masters Worlds committee chair David Kelly, rowing fitness instructor John Sheehy, and Irish Sailing Pathway Nationals chair Ian Simington.
And rounding out the awards, Paul Conway’s Cervantes and Birmayne (Justin McKenna, Paul Dobbyn and Crew) are up for the O’Hanlon Cup for best cruise of 2018.
The RStGYC Oscars will be awarded on Friday night 6 April at a black tie gala dinner in the clubhouse from 6.30pm. Members can book their places HERE.
Tom Dolan Set For Brunch Talk At The Royal St George This Saturday
‘Flying Irishman’ Tom Dolan will join Royal St George Yacht Club members for brunch at the Dun Laoghaire waterfront clubhouse from noon this Saturday 19 January.
Tom was nominated for Irish Sailor of the Year 2017 and again in 2018, and his adventures feature prominently in the 2019 Afloat Irish Sailing Annual.
The France-based Irish sailing professional has been nicknamed ‘l’irlandais volant — or ‘the Flying Irishman’ — for his accomplishments in the challenging solo offshore Figaro race.
Tom will tell RStGYC members about his intense 2018 season which culminated in the Solitaire du Figaro, a story illustrated with slides and videos that he’s already brought around Ireland.
He will also elaborate on his plans for this year’s race with his new boat, the revolutionary foiling Beneteau Figaro 3, which he previously revealed in a talk at Poolbeg Yacht & Boat Cub earlier this month.
The offshore sailor’s visit comes after a welcome talk by Annalise Murphy last week, and should be of interest to sailors young and old alike.
The talk starts at noon sharp, with the usual George Brunch available from 11am to 2.30pm. There is no extra cost for the talk. To book call Laura in Reception at 01 280 1811.
Get In New Year Shape With ‘RowFit’ Classes At The Royal St George
#RowFit - The Royal St George Yacht Club has teamed up with former Olympic rower and world record holder Niall O’Toole to offer members and friends a unique fitness experience for the New Year.
Participants in the Crew Class Indoors programme will get ‘RowFit’ as they work 85% of their muscles with every stroke of the rowing machine.
The programme is described as “a fantastic unparalleled exercise to get stronger, leaner, and work your core and learn to row in a fun team environment.”
Classes began this week, with two sessions on Tuesday and Thursday evenings. For more details and how to book a session see the RStGYC website HERE.







































































