Displaying items by tag: RV Celtic Explorer
The first and second legs of this year’s Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey (IAMS 2022) will be carried out from next Saturday 5 February to Tuesday 1 March.
Surveys will be conducted to the West, Southwest and South Coasts of Ireland by the Marine Institute in fulfilment of Ireland’s obligations under the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP).
IAMS is a demersal trawl survey consisting of approximately 110 otter trawls, each of 60 minutes duration, in ICES areas 7b, 7c, 7g, 7h, 7j and 7k.
Fishing in 2022 will take place within a three-nautical-mile radius of the positions indicated in Appendices 1 and 2 of Marine Notice No 04 of 2022, a PDF of which is attached below.
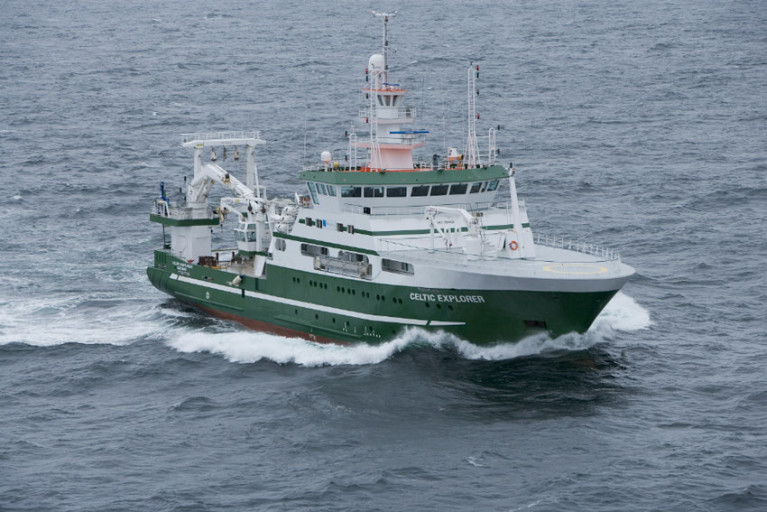
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will display appropriate lights and signals. The vessel will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl during fishing operations.
The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators keep a 3nm radius area around the tow points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period.
Further details are included in the Marine Notice below.
I-MORE Mapping Survey of North Irish Sea in New Year
The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport advises that the Informing and Mapping the Offshore Renewable Environment (I-MORE) Survey will be carried out in the North Irish Sea from early in the New Year.
From 4-13 January 2022, the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) will carry out the survey on a 24-hour schedule using the Manta–200 Seabed Cone Penetration Testing (CPT) system.
The aim of this survey is to gather critical seabed data to feed into existing postdoc and group research across a range of disciplines, including marine geotechnics and physical geology, to better understand the geology and engineering properties of the sediment in this area and to identify potential geohazards to infrastructure development.
 Map of the proposed iMORE survey area
Map of the proposed iMORE survey area
Coodinates of the survey area and other details can be found in Marine Notice No 66 of 2021, available to download below.
2021 Irish Groundfish Survey Set for Later This Month
The annual Irish Groundfish Survey (IGFS) for 2021 will be carried out by the Marine Institute off the North West, West and South Coasts of Ireland from Saturday 30 October to Tuesday 14 December.
The IGFS is a demersal trawl survey consisting of approximately 170 fishing hauls of 30-minute duration each in ICES areas VIa, VIIb, VIIg and VIIj.
As part of the requirements for the 2021 survey, fishing will take place within a two-nautical-mile radius of the positions indicated in the appendices to Marine Notice No 57 of 2021, which can be downloaded below.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will display appropriate lights and signals. The vessel will be towing a high headline GOV 36/47 demersal trawl during fishing operations.
The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators keep a two-nautical-mile area around the tow mid-points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period outlined above.
Further details can be found in the Marine Notice attached below.
The ability to track free-swimming salmon juveniles has been extended hundreds of kilometres into the open ocean using advanced robotic technology.
As part of the EU INTERREG VA-funded SeaMonitor project, Dr Ross O'Neill of the Marine Institute and Kieran Adlum, P&O Maritime, tested a remotely operated ocean glider along the steeply sloping area of the shelf edge some 130km north-west of the Scottish Hebrides.
The torpedo-shaped device, equipped with an acoustic tag detector, was deployed from the RV Celtic Explorer on 16 April during the 2021 Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey.
This is the first time such active tracking technology has been applied to Atlantic salmon in Europe.
During its two-month mission, the glider successfully detected four individual juvenile salmon smolts measuring only 15-19cm, nearly 600km from their home rivers in Ireland, Northern Ireland and Scotland.
These fish had been tagged between four and six weeks previously with electronic acoustic transmitting tags along with hundreds of other juvenile salmon as part of the SeaMonitor project as well as the West Coast Tracking Project, a partnership between the Atlantic Salmon Trust, Fisheries Management Scotland and Marine Scotland, EU INTERREG VA-funded COMPASS project and Agri-Food Biosciences Institute (AFBI) research initiatives.
One of the main aims of these projects is to investigate the persistent low marine survival of Atlantic salmon in the early stages of their oceanic migration to feeding grounds in the North Atlantic.
The four fish originated from the River Burrishoole in Co Mayo, the River Bann in Northern Ireland and the rivers Clyde and Awe in Scotland.
Up to now, most tracking studies had been limited to estuarine or coastal areas due to technology limitations and the need for stationary receivers.

According to Dr Niall Ó Maoiléidigh of the Marine Institute and principal investigator for the SeaMonitor project: “The detection of these fish confirms the importance of the shelf edge in this amazing journey, as the faster currents associated with the steep slopes most likely act as an aquatic transport system facilitating the northward migration of these tiny fish through a very harsh environment.”
Prof Colin Adams of the University of Glasgow and principal investigator for the SeaMonitor Project added: “This study shows that tracking salmon over considerable distances at sea can be achieved which is crucial for research into highly migratory marine species especially where mortality may be occurring far from the shore.”
Dr Ciaran Kelly, director of fisheries ecosystems and advisory services at the Marine Institute, said: “The use of the glider to track the movements of even very small fish has been clearly demonstrated and this will encourage the use of autonomous underwater vehicles to improve information on many marine species of animals which may be endangered or threatened without interfering with their natural migrations.”
The SeaMonitor project is “breaking the boundaries of research into the marine migration journey of the iconic Atlantic salmon”, said Loughs Agency chief executive Sharon McMahon.
“This innovative research will help to identify migratory routes and factors influencing salmon survival at sea, providing data to inform future research and decision making.”
The glider is part of the SeaMonitor integrated cross-jurisdiction major network of acoustic receivers, robotic underwater vehicles, satellite tracking and passive acoustic receivers in European waters and its use will be extended to track cetaceans, basking shark and skates as well as to collect physical oceanographic data.
When combined, the data will enable a holistic view of the regions mobile marine species and will prove invaluable to the regions managers, as well as establishing an integrated network of marine receivers for future applications and extended monitoring.
Match-funding for the project has been provided by Northern Ireland’s Department of Agriculture, Environment & Rural Affairs (DAERA) and the Department of Housing, Local Government and Heritage in Ireland.
For more information about the project visit the Lough Agency’s SeaMonitor portal or follow the project on Twitter at @SeaMonitor1.
Call for 2022 & 2023 Applications for Ship Time on Ireland’s Research Vessels Now Open
Applications are currently being accepted for ship time in on Ireland’s national marine science research vessels in 2022 and 2023.
In addition to the RV Celtic Explorer and RV Celtic Voyager, placements will also be available on the new RV Tom Crean which is expected to be operational in mid 2022 and will replace the RV Celtic Voyager.
The ROV Holland I as well as the Marine Institute’s Slocum Glider submersibles Laochra na Mara and Aisling na Mara are also offered.
Applications must be submitted using Research Vessel Operations’ online Survey Planning System by Thursday 16 September. Contact Research Vessel Operations at [email protected] to obtain a username and password.
Each application will be reviewed and the applicant will be informed as soon as possible whether the ship time they requested is available. If the requested timing is not available, alternative dates may be offered.
The Vessel Charter Guidelines should be read carefully before submitting the ship-time application form.
Further information, technical specification and contact details for the Slocum Gliders are available on the Glider webpage.
Applicants may seek grant-aid to cover all or part of the vessel charter costs for Research Surveys or Ship-Based Training Programmes in 2022. The closing date for receipt of grant-aid applications is 5pm on Thursday 16 September.
Applicants for ship-based training are advised to consult with the Strategic Marine Alliance for Research and Training (SMART) at [email protected]. SMART aims to standardise and optimise ship-based training for undergraduate and post-graduate students and develop nationally accredited ship-based training activities for national higher education.
Applicants are advised that survey schedules can change during the year; contact Research Vessel Operations at [email protected] to check whether any survey slots remain for 2021 and/or request to be notified if any dates become available.
Unmanned Irish Miniature Sailboat ‘Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor’ to be Deployed from the RV Celtic Explorer
Yesterday, a group of students from 5th and 6th class from Kilglass National School in Co Galway delivered their 1.5 metre unmanned mini sailboat called ‘Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor’ to the Marine Institute’s research vessel, RV Celtic Explorer, in Galway Harbour. Marine Institute scientists will deploy the mini-boat from the RV Celtic Explorer into the Atlantic Ocean, near the M6 Weather Buoy, during the AIMSIR (Atlantic In-situ Marine Scientific Infrastructure Replacement) survey.
The mini-boat is equipped with a sail and a satellite tracker, or transmitter, which allows the students to track it as it sails across the ocean and gain a better understanding of ocean currents. This initiative is part of the international Educational Passages programme which connects schools from across the globe through the mini-boat activity.
Congratulating the collaborative effort of the Explorers Education Programme team, Kilglass National school, the infrastructures team at the Marine Institute, as well as Educational Passages in the USA, Patricia Orme, Joint Acting CEO said, “The Explorers mini-boat project is a wonderful example of marine science literacy and citizen engagement with the oceans. It supports the Marine Institute’s Oceans of Learning campaign which highlights the value of partnerships essential for sharing marine science with the wider community. For children, this project provides an exciting way of seeing real life examples of how the ocean has an influence on all our lives, learning how the ocean influences our weather and climate, and the types of technology used.”
 ‘Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor’ about to be Deployed from the RV Celtic Explorer
‘Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor’ about to be Deployed from the RV Celtic Explorer
Peter Kane, teacher at Kilglass National School, Galway highlighted that working with the Explorers Education team and Educational Passages has helped to provide children with a better understanding of the ocean through real life hands-on activities. “The project involved more than 100 children in our school. Students have painted and decorated the boat, created artwork and good luck messages, and named the boat ‘Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor’. Alisha McHugh from 4th class explained that the Irish term recognises the tradition of fishing in Galway and Ireland.”
Thanking the Marine Institute and the Explorers team for coordinating the delivery of the boat and teaching resources, Peter Kane said, “It has been a comprehensive STEM project and cross-curricular in nature. Using the boat as a focal point provides a great example of how teachers can integrate marine themes through a range of cross-curricular activities. This included learning how the boat was built, to covering a range of science and technology concepts using GPS and satellites.”
Padraic Creedon, Explorers Education Officer, Galway Atlantaquaria said, “It was great to see the children increasing their understanding of the ocean, completing science experiments and producing amazing class presentations about our ocean. The children also learned about marine biodiversity in the ocean from the smallest microscopic plankton to the largest animals in the world – the blue whales migrating across the Atlantic.”
The provision of the boat has been funded as part of the EU Interreg iFADO project, in which the Marine Institute are partners. Engaging in the mini-boat project, the iFADO consortium of researchers are launching five mini-boats this year around the Atlantic from Ireland, Portugal, Spain, France, and the UK.
“People all over the world can monitor and track the mini-boats in the ocean, including Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor. The project webpage is available to children, teachers and their classes. This is a really fun way of connecting people, and predicting where the boat may land is part of that experience. At least 11 mini-boats have landed in Ireland since 2009, and some have been recovered, fixed, and relaunched. Currently, there are six actively reporting boats in the Atlantic, and some in the Pacific as well. Both the Explorers Education Programme and Educational Passages are absolutely delighted to see another boat leaving Galway, and look forward to seeing how it can connect more people around our world ocean,” said Cushla Dromgool-Regan, Explorers Strategic Education Manager, Camden Education Trust.
To follow the mini-boat Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor, visit here
The Marine Institute and partners are celebrating our seas and Ireland’s marine resource through the Oceans of Learning series. Over four weeks, Oceans of Learning enables everyone to engage with our ocean through a podcast series, short films, news and online resources all about our ocean.
Teachers, children and parents can also follow the Explorers Education activities on Facebook: @ExplorersMarineEducation and Twitter @explorersedu for great ideas and fun facts about the ocean. The team in Galway will also be tracking the Seoltóir Na Gaillimhe – the Galway Sailor.
The Explorers Education Programme is funded by the Marine Institute, Ireland's state agency for marine research and development.
The Department of Transport advises that a survey will take place at several offshore reefs and sandbanks off the North West Coast from next Friday 23 April to Tuesday 4 May.
Survey works with marine robots in support of the EU Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme will take place within a three-nautical-mile radius of six shipwrecks, the coordinates of which are included in Marine Notice No 24 of 2021 which can be downloaded below.
The survey will be conducted from the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will conduct acoustic surveying during the night using its hull mounted multibeam, with remotely operated vehicle (ROV) sampling during daylight hours.
In addition, the vessel will be used as a platform to deploy a range of unmanned underwater vehicles (UUVs) and a series of six small (1.2m3) pyramidal landers, referred to as baited remote underwater video (BRUV).
At all times, the RV Celtic Explorer will display appropriate lights and signals.
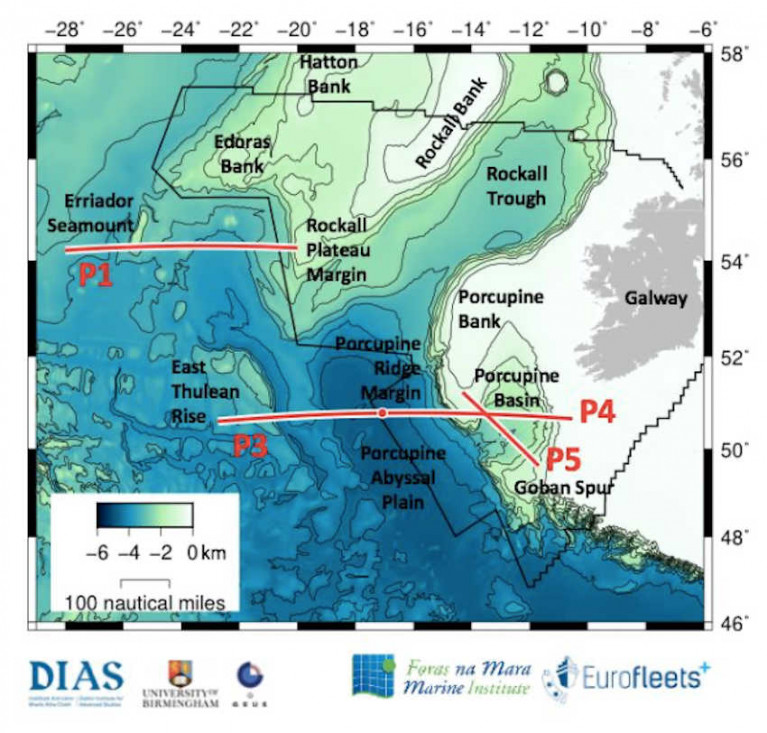
Notice of Upcoming Geophysical Survey at Rockall Plateau, Porcupine Abyssal Plain & Porcupine Seabight
The Department of Transport has been advised that a marine geophysical survey will be carried out from 5-30 May southwest of Rockall Plateau and across the Porcupine Abyssal Plain and Porcupine Seabight.
This survey is part of the Irish marine research programme project PORO-CLIM and is being carried out with the support of the EU Eurofleets+ programme (Project PORO-CLIM, Survey Code CE21008).
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB). The vessel will display appropriate lights and signals. All survey operations are 24 hours, continuous over day and night.
The vessel will on occasion be towing a hydrophone cable and other equipment up to a maximum of 1,000 metres behind the vessel. The vessel will be restricted in its movements when towing a cable astern.
Full details of coordinates for these survey works are included in Marine Notice No 17 of 2021, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport advises that INFOMAR will undertake a hydrographic and geographic survey operation in the Celtic Sea and Atlantic Ocean for six months from this April.
The massive operation will involve research vessels from Geological Survey Ireland (Keary, Geo, Lir, Gale and Mallet) and the Marine Institute (Celtic Voyager and Celtic Explorer) in a variety of surveys — along the South-West Coast from Roaringwater Bay to Kilkee, and offshore south of Mizen Head and between Kerry Head and the Aran Islands.
All vessels will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the survey, and will display appropriate lights and markers. The RVs Celtic Voyager and Celtic Explorer will also be towing a magnetometer sensor with a single cable up to 200m in length, and a moving vessel profiler cable of variable length up to 200m.
Full details of the surveys, including dates, maps and coordinates, can be found in Marine Notice No 10 of 2021, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
2020’s Irish Groundfish Survey Gets Under Way
This year’s Irish Groundfish Survey (IGFS 2020) of the North, West and South Coasts of Ireland is set to commence today, Sunday 25 October.
Carried out by the Marine Institute, the IGFS is a demersal trawl survey consisting of around 170 fishing hauls, each of of 30 minutes’ duration, in ICES areas VIa, VIIb, VIIg and VIIj.
As part of the requirements for the 2020 survey, fishing will take place within a two-nautical-mile radius of indicated positions.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (callsign EIGB) which will display appropriate lights and signals.
The vessel will be towing a high headline GOV 36/47 demersal trawl during fishing operations.
Co-ordinates and approximate locations of these hauls are included in Marine Notice No 48 of 2020, a PDF of which is available to download below.
The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators keep a 2nm area around the tow mid-points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period between now and October and Thursday 10 December.
This survey follows the annual Irish Anglerfish and Megrim Survey which was conducted off the West, South West and South Coasts this past February and March.