Displaying items by tag: RYA
The Royal Yachting Association (RYA) and British Marine have welcomed HM Revenue and Customs (HMRC) announcement of a six-month extension to the one-year grace period for Returned Goods Relief (RGR) previously put in place by the British Government.
The news yesterday (Thursday 25 March) extends the grace period for RGR until 30 June 2022 for all goods including recreational craft, regardless of when they left the UK, and follows representations from the RYA and British Marine asking for a three-year transition period.
Both organisations have argued that the one-year grace period effective from the end of the Brexit transition period, in respect of the three-year condition for RGR, was not sufficient — highlighting such issues as pandemic travel restrictions, Schengen Area immigration rules, insurance and the length of the sailing season.
This issue was central to a letter that the RYA and British Marine sent to the chief executive of HMRC in February, calling for a holistic approach to addressing the post-Brexit issues impacting on recreational boat owners and the British leisure marine industry.
Howard Pridding, the RYA’s director of external affairs, said: “The HMRC announcement is timely, as we have seen additional concerns from members about the new restrictions on leaving the UK announced this week.
"We will continue our constructive dialogue with HMRC on all outstanding post-Brexit issues, including the repatriation of boats that have not been in the UK under their current ownership, and look forward to receiving a full response from the HMRC chief executive on the points that we have raised.”
Lesley Robinson, CEO of British Marine, added: “This collaborative work with the RYA shows that together we can better influence matters affecting the leisure marine sector and boaters.
“Whilst we requested and set out a strong case for a three-year RGR transition period, the six-month extension is welcomed.
“However, given the current restrictions on international travel, we hope HMRC will demonstrate flexibility to the extension to allow all UK boat owners to return their boats in a safe weather window. This flexibility would also be welcomed by UK boat retailers and brokers in order to keep fulfilling the rising demand for second-hand boats in the UK.”
British Marine & RYA Highlight New Costs of Trading Second-Hand Boats Between the UK & EU
Following the release of the UK - EU Trade and Cooperation Agreement British Marine and the Royal Yachting Association (RYA) have been working to understand the impact of various aspects of the agreement on both the marine industry and recreational boat owners.
British Marine and the RYA have now received further information from both the EU Commission and the UK Department for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy (BEIS) on the trade of pre-owned CE marked recreational craft between the UK and EU following the UK’s exit from the European Union.
Both the UK and EU have confirmed that any vessel being traded second-hand between the UK and EU will be required to meet the obligations set out in either the Recreational Craft Directive (RCD) in the EU or the Recreational Craft Regulations (RCR) in the UK when placed on either market after the 1 January 2021.
UK Conformity Assessed
Therefore, this means that a pre-owned vessel being imported from the EU to be placed on the UK market will, after 1 January 2022, be required to obtain a new UK Conformity Assessed (UKCA) mark in line with the requirements of the RCR. In order to obtain a UKCA mark, a boat will require a Post Construction Assessment and third-party verification.
Pre-owned CE marked vessels
Similar rules will apply when selling vessels into the EU. Pre-owned CE marked vessels that were in the UK at the time of departure, 11pm on the 31 December 2020, when exported to the EU will be required to undergo recertification of the CE mark when being placed on the EU market. This means a boat will require a Post Construction Assessment in line with the RCD and third-party verification.
As Afloat reported previously, boat brokerages, distributors, boat owners and buyers may well be heavily affected by this post-Brexit position, as the responsibility will fall upon them to ensure a vessel meets the applicable requirements before buying and selling second-hand boats between the UK and EU. Estimated costs of Post Construction Assessments and verification are between 500-5000 GBP dependent on the vessel.
British Marine and the RYA are currently liaising with the European Boating Industry association in order to raise concerns with this position in Europe whilst also directly engaging with BEIS in the UK.
Lesley Robinson, CEO of British Marine, commented; “As a consequence of Brexit, this is a complex and potentially difficult situation. Faced with the process of individual boat re-certification, boat builders, brokers and consumers will be impacted in terms of both time and cost when selling and buying second-hand boats cross borders. At this stage in time, British Marine is working hard to represent affected members and seek clarification of the exact ramifications of these regulations.”
Howard Pridding, RYA Director of External Affairs, said; “This is yet another unanticipated and unwelcome aspect of Brexit which could affect many owners financially through no fault of their own. We are working in partnership with industry to better understand and mitigate the situation and potential cost burden.”
Call for Holistic Approach to Issues Facing British Boaters & Marine Industry Post-Brexit
British Marine and the RYA have written a joint letter to the head of Britain’s HM Revenue & Customs to call for a holistic approach to the various issues facing private pleasure boaters, the second-hand market and the wider industry post-Brexit.
According to Marine Industry News, the letter covers such issues as the ‘VAT trap’ for British boaters, repatriation of vessels as pandemic restrictions continue, and the status of and reporting requirements for boats lying in Northern Ireland waters.
The two organisations are specifically calling for an extension of the one-year grace period for Returned Goods Relief to three years, on account of the various difficulties boaters currently face in regard to moving their vessels around Europe.
Howard Pridding of the RYA said: “Following months of dialogue with officials and exchanges with ministers at HMRC, we are now appealing directly to the chief executive of HMRC to bring coordination to urgently address the outstanding issues and deliver clear and unambiguous guidance that we can share with our members.”
The move comes in the same week that the Cruising Association launched its campaign for a 180-day cruising visa separate from the 90-day Schengen visa system, which would help preserve British cruisers’ traditional routes to the Netherlands, Greece, Spain and Portugal.
UK Boaters Sailing EU Waters In for Strange Year, RYA Warns
“All sorts of strange things” will emerge this year for UK sailors in EU waters as post-Brexit issues remain to be ironed out.
As Sailing Today reports, RYA cruising manager Stuart Carruthers has outlined some harsh truths for British boat owners who had been used to easy cruising excursions beyond home shores.
“As an example, the whole idea of taking a sabbatical in the Mediterranean, living on your boat, which you’ve bought with your pension, has just disappeared out of the window now that we are subject to Schengen Area visitor visa rules. That is just one post-Brexit reality,” he said.
Meanwhile, EU member states appear to be taking a less than harmonious approach to recognition of British boats’ VAT paid status, as the Cruising Association’s Brexit spokesperson Roger Bickerstaff has warned.
“We’re going to be seeing different countries taking different views,” he said.
Carruthers also noted: “The status of boats in Northern Ireland is also unclear — are they classed as UK goods, Union goods, will they be able to enter Great Britain VAT-free?”
Sailing Today has much more on the story HERE.
RYA Postpones April's 2021 Youth National Championships
The Royal Yachting Association has decided that in light of the current Covid-19 situation it is in the best interests of all parties to postpone its 2021 British Youth Sailing National Championships.
The regatta, the UK’s premier youth racing event, was due to take place from April 4 to 9 hosted by Plymouth Youth Sailing Club in Plymouth, Devon.
Typically, the annual event is attended by some Irish youth sailors, north and south of the border.
With the UK currently in lockdown and likely to revert to the tier system once restrictions ease, the decision has been made to delay the regatta until the summer.
This will give organisers the time to plan for the best possible event, as well as giving time for the nationwide vaccination programme to take effect.
We are also very mindful that the young sailors will have lost training time over the winter and this gives them time to be ready for such an event.
It is hoped the rescheduled event will take place at the same venue the week commencing August 9, 2021. It is intended that further details and any Notice of Race will be shared before the end of January. More here
RYA’s First Virtual Cruising Conference Set for March
Following last month’s news that its Northern Ireland branch’s cruising gathering is going online for 2021, the RYA has scheduled its first virtual cruising conference for the wider UK on Sunday 21 March.
The conference will cover the issues that matter most to cruisers, including post-Brexit guidance, training insights, real-life stories from fellow cruisers, as well as the latest developments in safety.
As always it will deliver informative and eye-opening talks from a range of speakers. And there will also be opportunities for the audience to get involved and a chance to ask your question to the experts.
The RYA says the event programme will be announced soon, and booking will go live shortly via rya.org.uk
RYA Round-Up of Brexit Issues for British Recreational Boaters Says Thousands Facing ‘Enormous Financial Disruption’
The RYA has published a new document outlining where British recreational boaters stand post-Brexit — with a deal still not struck eight days before the transition period ends.
In its end-of-year summary, which details what is currently understood about a raft of issues that will affect recreational boaters from 1 January, the RYA estimates that “up to 33,000 British people who go boating in Europe could be affected by Customs and VAT issues which would be applied to them retrospectively”.
It adds: “These are ordinary people who, as UK nationals and residents, have followed the rules and utilised freedoms that were available to them from the UK’s membership of the EU.
The document hits out at “inconsistent advice” from MH Revenue & Customs over the last two years — and says late-arriving clarity meant “insufficient time” for affected boat owners to qualify for Returned Goods Relief (RGR), leaving many liable to “double taxation”.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the latest advice from HMRC is for boat owners to carry proof of their vessel’s VAT-paid status at all times — a situation that could be particularly onerous for those who’ve built their own boat.
“At the moment many thousands of British boat owners are facing enormous personal and financial disruption to their lives despite adhering to the law of their country at that time. In many instances, it may even force them to sell their boat,” it states.
The summary also covers Schengen Area rules and new border control regimes both in the UK and the EU’s maritime countries, as well as the changing situation for recognised training centres and instructors working in the EU.
“We have all followed the latest drama of the trade deal negotiations on the daily news recently, but the reality is that sectoral issues have not featured in the high-level discussions involving politicians and negotiators on both sides,” RYA director of external affairs Howard Pridding says.
“That is why the RYA has endeavoured to seek answers from Government officials on the key issues for boaters. As 2020 draws to a close, we have put all that we know together in one document on our website.
“The early months of 2021 are going to deliver uncertainty and many challenges as we enter a post-Brexit era. The RYA Government Affairs Team will be continuing to represent members’ interests and strive to find the clarity that is currently lacking in many areas and we will keep members informed of developments through our website and RYA social media channels.”
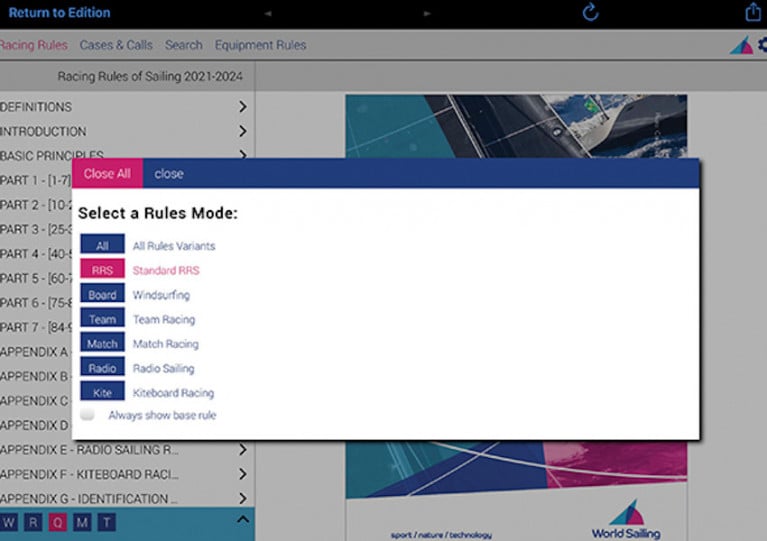
World Sailing Rules App Gets 2021-24 Update
Ahead of the 2021-2024 Racing Rules of Sailing which come into effect on 1 January, the RYA has released an update to the World Sailing Rules App — giving sailors access to a ‘one-stop shop’ for the 2021-2024 rules and associated documents.
Launched in 2016, the multilingual app was developed by the RYA in partnership with World Sailing and has proven popular with racing sailors and officials worldwide, ensuring they have all the relevant rules information at their fingertips.
Steen Ingerslev, RYA publications manager said: “We are delighted to be working with World Sailing once again. We’ve made huge advances with RYA eBooks and digital resources in recent years ensuring popular app features like the ‘Integrated eBook’ are more accessible than ever before.”
The ‘Integrated eBook’ links all the rules documents together, enabling the user to navigate seamlessly between the rules and cases, highlighting a number of cases for each rule in both overview and full case detail formats.
A rules mode in the settings allows the user to select Windsurfing, Team, Match, Radio or Kiteboard Racing amendments for their convenience. They can also select a country, enabling any translated rules and showing the local prescriptions from any participating National Authority.
The World Sailing Rules App can be downloaded for free through the Apple App Store and Google Play. If you’ve already downloaded the 2017-2020 version, it will be automatically updated. The ‘Integrated eBook’ will be available shortly as an in-app purchase.
Strangford Sailing Club Selected as Finalist for RYA/Yachts & Yachting Club of the Year 2021
Strangford Sailing Club has been named among the finalists for RYA and Yachts & Yachting Club of the Year 2021.
Ten clubs across the UK have been selected by the RYA Awards Panel, with online voting now open.
The Co Down club is the only Northern Ireland finalist this year for the annual gong, which saw Strangford Lough Yacht Club and East Antrim Boat Club in the running this time last year.
The RYA and Yachts & Yachting Club of the Year award, supported by Gallagher, recognises the outstanding achievement of sailing clubs across the UK and promotes the hard work and dedication that goes into running a successful club.
Voting closes on Monday 25 January, and the award presentations and overall winner announcement will be made at the RYA Virtual Dinghy Show on 27-28 February.
UK-Owned Vessels Currently Overseas Subject to New Rules Post-Brexit
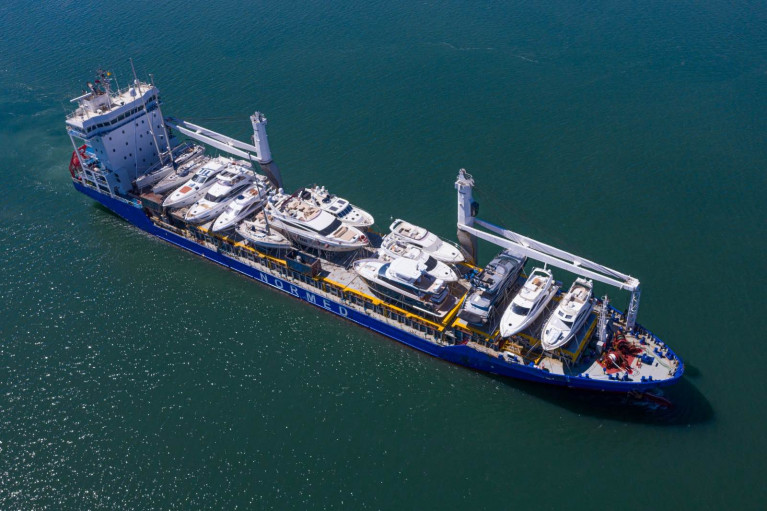
Rules determining UK owned boats’ VAT status will be subject to change after 31st December 2020 and Global marine transport and logistics provider Peters & May has is reminding UK boat owners with vessels outside the UK that as the Brexit transition period comes to an end at 11 pm 31st December 2020, the rules determining boats’ VAT status will be subject to change.
The latest information available from HMRC is that from 1st January 2021 the rule that yachts must return to the UK within 3 years of having last left the UK/EU in order to be entitled to Returned Goods Relief (RGR) on duty & VAT will be strictly enforced.
‘Whether RGR is applicable will be dependent on it not having undergone any repairs whilst outside the EU that increased its value when it last left the UK/EU and the amount of time it has been overseas, the date of its reimport into the UK and whether the place from where is it returning is inside the Customs Territory of the EU,’ says the company’s Sea Freight and Customs Manager Adam Towgood. He continues, ‘In order to claim the VAT relief element of RGR, it must also have not changed ownership since it last departed. Where a boat does not meet RGR criteria, duty and VAT will be payable to HMRC upon reimport’.
HMRC has recently announced the grant of a 12-month extension exclusively for boats that are currently within the EU, having departed the UK before 31st December 2017. These now have until 31st December 2021 to be reimported to the UK and claim RGR.
As Afloat reported previously, Ireland could see an influx after Christmas of visiting boaters from Northern Ireland seeking to secure the VAT and duty status of their vessels as the Brexit transition period ends.
Adam continues, ‘To ensure that there is no VAT payable to HMRC on the reimportation of their boats we are urging UK boat owners to take early action. Owners need to be aware of the dates of their boats’ movements and time away from the UK and act accordingly to claim Returned Goods Relief. A summary of whether HMRC will allow a claim to RGR according to the departure and arrival dates has been posted to our website and shared on social media channels.’
Peters & May has availability on sailing schedules from the Med which will arrive in the UK before the end of December 2020. Owners choosing Peters & May as their transport provide will benefit from the company’s experts managing the Customs clearance process on their behalf.
The Peters & May team has experience working with HMRC and understands the relevant VAT rulings. An integral part of the company’s yacht transportation service is the completion of complicated paperwork on behalf of the owner.
Adam Towgood says, ‘Navigating the import process and paperwork can be a minefield for owners not accustomed to the technicalities and governing rulings. We work closely with our customers to ensure their boat’s journey home goes smoothly and all relevant legal documentation is completed.’
Further information may be obtained by visiting the HMRC website or the website of the UK’s National Governing Body for sailing, the RYA.