Displaying items by tag: Safehaven Marine
Bord Iascaigh Mhara has acquired a new inshore survey vessel for monitoring the state of mussel bed stocks on the south-west and east Irish coastlines.
The 12m-long survey vessel, named T Burke II, was built by Cork company Safehaven Marine.
The Wildcat 40 vessel is one of 19 built by Safehaven and in service worldwide, and has a maximum speed of 26 knots and 18 knots operational speed. It is fitted with crane gear to deploy sonar equipment and a bottom sampling dredge.
Safehaven Marine says its seakeeping abilities were demonstrated during rough weather trials off the south coast in 50-knot winds and five-metre seas during Storm Gareth.
It will be deployed by BIM in Dingle Bay, Co Kerry, and on the east coast from Wexford’s Carnsore Point to Carlingford, Co Louth.
The Irish mussel industry was valued at 11.7 million euro to the economy in 2018, and almost 14,000 tonnes of mussels were produced in Ireland last year.
Bottom grown mussels made up 4,800 tonnes of that total.
The sector has had Marine Stewardship Council accreditation – the “gold standard” for sustainable fisheries – since 2013. The bottom grown mussel industry is almost “entirely export-led”, according to BIM, and employs almost 200 people, directly and indirectly.
Its potential was highlighted during the recent Supreme Court action by four mussel fishermen over the “voisinage” agreement north and south of the border.
The T Burke II was launched by Minister for Agriculture, Food and Marine Michael Creed in Kinsale, Co Cork on Monday morning with Olivia Moylan Burke.
Ms Burke is the wife of the late Dr Tomás Burke, formerly technical officer with BIM, after whom the boat is named.
Speaking at the launch, Mr Creed said that the surveys conducted by the vessel would form “an integral part of the management of the seed mussel fishery, which has been awarded the prestigious MSC sustainability certification”.
This accreditation “opens up access for our Irish mussels into the very best markets in the EU and further afield”, Mr Creed said.
BIM chief executive Jim O’Toole said the surveys conducted by BIM’s technical officers would “provide invaluable data to help drive the growth of this important sector”, while also minimising its carbon footprint.
Safehaven Marine Makes Deal With Two Spanish Ports After Latest Pilot Boat Delivery to Portugal
Following delivery of their latest pilot boat for the Port of Leixoes in Portugal, the Cork Harbour performance boat specialsts at Safehaven Marine announced the signing of contracts with two Spanish ports.
The port of San Ciprian has contracted for an Interceptor 42 pilot vessel while the larger Port of Coruna to the south-west has commissioned an Interceptor 48 pilot. Both are to be delivered in mid 2020.
Safehaven Marine says its pilot craft have proven very popular in the Iberian Peninsula.
Once these latest commissions are delivered — and the ports of Gijon and Algeciras begin undertaking pilot transfers with their own Interceptors — Safehaven will have 14 pilot boats working in the peninsula.
Both new contracts were signed simultaneously after pilots from Coruna and San Ciprian were impressed by sea trials of the new Leixoes pilot, named Lada, on delivery last month.
Safehaven Marine Unveils Latest Pilot Boat Commission For Portugal
Safehaven Marine in Cork has unveiled its latest pilot boat for the Port of Leixoes in Portugal.
The Interceptor 48 will be put through sea trials over the next few weeks before delivery to the port north-west of Porto.
In the meantime, work continues on the new XSV20 powerboat design Thunder Child II for Safehaven managing director Frank Kowalski’s Atlantic speed record bid.
New Interceptor 48 pilot boat built for the Port of Leixoes in Portugal @PLeixoes She's looking nice and performing well. We will begin sea trials over the next few weeks. @AfloatMagazine @Coast_Monkey @whatrobdidnext @KENNYTCORK @EoinBearla #madeincork pic.twitter.com/XxG9APrwvb
— Safehaven Marine (@SafehavenMarine) January 25, 2019
Thunder Child II Taking Shape At Safehaven Marine
Thunder Child II is finally taking shape at Cork-based performance boatbuilders Safehaven Marine, with “another couple of more months” go before launch for sea trials in the New Year.
As previously noted on Afoat.ie, the XSV20 design developed over the past year crosses a wave-piercing monohull with a catamaran and is optimised for cutting through 4,000km of Atlantic sea with the aim of setting a new powerboat world record.
Safehaven Marine — with its design HQ in Cork Harbour and boatbuilding yard in Youghal — is also busy with its pilot boat commissions, the latest coming from Puerto Rico.
So finally after a year in development 'Thunder Child II' takes her shape. She looks pretty cool. Just another couple of more months work till her launch. pic.twitter.com/vXGnqKioKj
— Safehaven Marine (@SafehavenMarine) November 23, 2018
Safehaven Takes Order For Interceptor Pilot Boat From Puerto Rico
Safehaven Marine’s latest commission comes from Puerto Rico, as its capital San Juan has ordered an Interceptor 48 pilot boat.
This will be the 41st pilot vessel and the 17th in the Interceptor 48 class produced by the Cork Harbour boatyard, which builds its vessels in Youghal.
It’s been a busy few months for Safehaven, which recently took an order for a second vessel from Norwegian crew and pilot transfer company Fonnes Batservice AS.
San Juan Pilots & Port have ordered an Interceptor 48 pilot boat from Safehaven. San Juan, Puerto Rico's capital city is situated to the east of the Dominican Republic & west of the Virgin Islands in the Caribbean. This is our 41st pilot vessel and the 17th Interceptor 48 pilot pic.twitter.com/R6z7L2gjx0
— Safehaven Marine (@SafehavenMarine) October 25, 2018
Meanwhile, managing director Frank Kowalski is working towards next summer’s transatlantic record attempt with the new powerboat Thunder Child 2.
Safehaven Marine's New Norwegian 'Masculin' Order
The Norwegian crew and pilot transfer company Fonnes Batservice AS have ordered a second vessel from Safehaven in County Cork. Four years after taking delivery of his Wildcat 53 ‘Feminin’ Tommy Fonnes signed contracts for an Interceptor 48, pilot & crew transfer design capable of transporting 12 personnel. To comply with the Norwegian Maritime Authorities the superstructure design is modified to incorporate forward angled windows. ‘Masculin’ will be powered by a pair of Scania DI13 500hp engines delivering a 26kts operational speed. The specification also incorporates a powerful hydraulic bow thruster integrated to a Twin Disc dynamic propulsion control system.
 Tommy Fonnes (left) with Safehaven's Frank Kowalski
Tommy Fonnes (left) with Safehaven's Frank Kowalski
Safehaven's Frank Kowalski relates the story of when the Norwegian customer first visited the Irish boatyard. "Tommy first visited us in 2013 with just an initial interest in our vessels. The day he arrived we were due to undertake sea trials in a couple of our vessels, I suggested he might like to come along, but warned him it might be a bit rough and that I hope he doesn’t get seasick. Tommy was up for it and for sure it was rough, with winds gusting over Force 10 and 5m seas. Later that night, suitably impressed with our vessels we signed contracts for his Wildcat 53. Always interested in what we do, during one of his build visits Tommy insisted in joining me strapped inside the cabin when we first rolled over the first 48 in a self-righting, capsize recovery test. Look forward to working with him on his new boat and seeing her operating in the amazing Norwegian fjords".
Safehaven Announces ‘Thunder Child 2’ Atlantic Record Attempt
#WorldRecord - Safehaven Marine has announced a new powerboat world record attempt — this time across the Atlantic.
Frank Kowalski, managing director of the Cork Harbour boatyard, has developed what the Irish Examiner is calling a “radical” new hull for Thunder Child 2.
Crossing a wave-piercing monohull with a catamaran hull, the new design promises to cut through more than 4,000km of Atlantic seas in under four days.
In May, Safehaven previewed the design of what’s officially the XSV20, which has completed scale model tests ahead of construction of the first demonstrator model due for launch in the new year.
Kowalski says the XSV20 was developed “in one’s endless pursuit of travelling fast in rough seas”.
And he will be putting that statement to the test next summer, between July and September, across the ‘northern route’ from Newfoundland to Killybegs via Greenland and Iceland for refuelling.
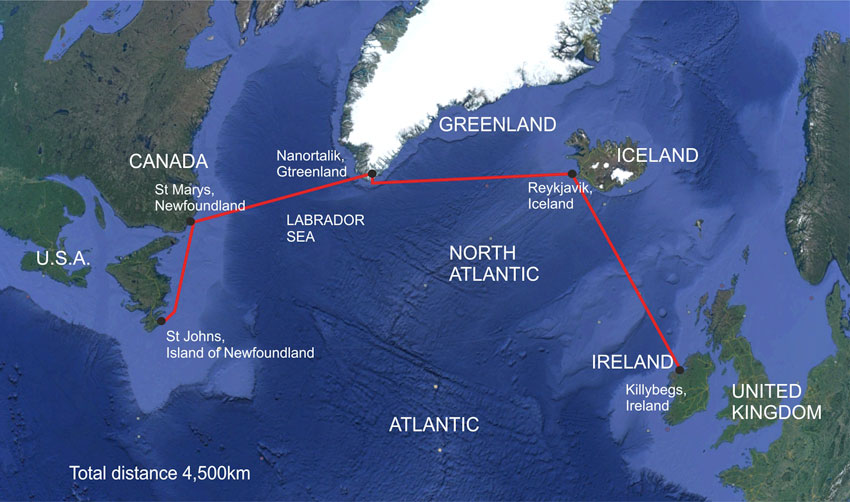
The Safehaven MD and his crew set a new round Ireland record in summer 2017 with the original Thunder Child, a Barracuda XSV 17 interceptor that can reach speeds of 60 knots.
Thunder Child 2 will come with its predecessor’s military-grade navigation technology and shock-dampening seats, and will be powered by four Caterpillar C8.7 650hp engines providing top speeds in excess of 50 knots.
Aside from the company’s record-breaking plans, Safehaven recently launched its third pilot vessel for Malta Maritime Pilots in Valletta.
The Interceptor 48, Juliet, is also the 35th Safehaven pilot boat to enter ports service internationally.
Number 36 is due next month when Safehaven delivers another Interceptor 48 for the Port of Leixões in Portugal under a contract with marine services firm Svitzer.
Safehaven Marine’s latest design concept is the XSV20, which has been undergoing scale model testing out of its Cork Harbour boatyard.
Combining a twin-stepped asymmetrical catamaran hull with a wave-piercing monohull, the hybrid XSV20 aims to set a new standard for high-speed patrol and interceptor vessels.
Safehaven says the 22m hull mould is now complete on the patent-pending design following six months of research and development, during which 12 scale model variants were extensively tank-tested to optimise performance and hydrodynamics.
The first full-scale XSV20 will be powered by four Caterpillar C8.7 650hp engines, ZF gearboxes and France Helises SDS surface drives. The boat will have a maximum speed of well over 50 knots, with a 40kt cruise speed and a range of 800 nautical miles.
The design incorporates all the features of Safehaven’s smaller 11-17m Barracuda range of naval craft, but with greater endurance, payload and crew capacity.
The design has been developed, as Safehaven’s designer and MD Frank Kowalski puts it, “in ones endless pursuit of travelling fast in rough seas” and should allow higher speeds to be maintained in rough sea conditions with greater crew comfort, safety and endurance than conventional designs.
Safehaven says its demonstrator vessel will be due for launch very early next year, when we should expect to see some of the company’s usual extreme testing.
Safehaven Marine’s Latest Pilot Boat ‘Svitzer Oued Rmel’ Put To The Test In Cork Harbour
Safehaven Marine has shared a video clip of sea trials and self-righting testing on its latest Interceptor 48 pilot vessel in Cork Harbour.
Oued Rmel is the first of a two-boat contract with marine services company Svitzer and has been built for operations out of the new TM2 Port in Tangier, Morocco.
The vessel has a positive stability curve to 180 degrees, capable of recovering if capsized by a large breaking wave in the busy shipping lanes of the Mediterranean.
Self-righting test and rough weather sea trials of ‘Svitzer Oued Rmel’ our Interceptor 48 All weather pilot vessel @corkharbour @PortofCork @CorkHarbourWX @RandomCorkStuff @CorkCoast @Coast_Monkey @AfloatMagazine @KENNYTCORK @Deeshocks @captainbob76 @MaryP972 @barrabest pic.twitter.com/TXXTNtqnJi
— Safehaven Marine (@SafehavenMarine) April 4, 2018
Work on the second vessel, a pilot boat for Malta, has been under construction at Seahaven’s Cobh boatyard since late last year, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Irish Boatbuilder Safehaven Set to Launch New UK Royal Navy Vessel
#Boatyard - On Irish shores in Cork a boat being built for the UK's Royal Navy reports the Evening Echo has been named and is only a few weeks away from being launched.
It was revealed in August that Cobh boat building company Safehaven Marine was awarded a contract to build the biggest vessel of a 38 strong fleet for the Royal Navy.
Afloat had previously referred to the survey Wildcat 60 Catamaran, which Safehaven managing director Frank Kowalski said is an “important contract, for the company has been named HMS Magpie and is awaiting module and final installations.
“Pleased to announce our new Motor Survey launch will be named HMS Magpie. The last HMS Magpie was commanded by HRH The Duke of Edinburgh in Malta in the early 1950s. Great to revive such a special link to our Lord High Admiral”, the Royal Navy said.
For more on the story click here.
Afloat adds of another 'royal navy' connection in Cork Harbour took place recently. This involved a courtesy call by the Royal Netherlands Navy submarine HNLMS Walrus which called to the city's central quays last weekend.






































































