Displaying items by tag: Upper Lough Erne
Waterways Ireland advises masters of vessels and waterways users on the Erne System that the Upper Lough Erne Predator Challenger boat pike angling competition will take place this Saturday 13 and Sunday 14 April.
The event will take place from the Share Centre Activity Centre on Upper Lough Erne, with around 50 boats taking part from 9am to 5pm each day.
Waterways users are reminded that the slipways at Corradillar and Derryadd will be busy with fishing boats launching for event.
Masters are requested to keep wash to a minimum when passing fishing vessels, the cross-border body for Ireland’s inland waterways adds.
Upper Lough Erne: Crom Jetty Reopens After Repair Works
Waterways Ireland advises masters of vessels and waterways users on the Erne System in Northern Ireland that Crom jetty on Upper Lough Erne has been reopened as of Friday 2 June after repair works.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the jetty had been closed last week due to fire damage being sustained at the facility, while a vessel was also sunken adjacent to the jetty.
Waterways Ireland advises masters of vessels and waterways users on the Erne System in Northern Ireland that Crom jetty on Upper Lough Erne is closed until further notice. This is due to fire damage being sustained at the jetty, while a vessel is also sunken adjacent to the jetty.
Erne System: Remedial Works on Corradillar Jetty
Waterways Ireland advises masters of vessels and waterway users on the Erne System that remedial works are planned for Corradillar Jetty on Upper Lough Erne on Friday 21 April and from next Monday 24 to Friday 28 April.
Access to the Co Fermanagh jetty and slipway will be limited during the above dates with the site closure on Monday to include the jetty, slipway, quay and car park, the cross-border body for Ireland’s inland waterways adds.
Mechanical equipment will be operating on land and on the water. Masters of vessels and waterways users should proceed with additional caution in the vicinity of the works and adhere to instructions from works crews and signage.
Upper Lough Erne: Refurbishment Works on Geaglum Jetty Walkway
Waterways Ireland wishes to inform masters of vessels and waterway users on the Erne System that works will commence on Monday 24 October to refurbish the walkway connecting the car park to the floating jetty at Geaglum on Upper Lough Erne.
The floating jetty will remain available for mooring. However, the walkway will be closed for the duration of the works and subsequently access to the car park for boaters will not be available.
The works are expected to last approximately three weeks, the cross-border body for Ireland’s inland waterways adds.
Carrybridge Lifeboat Assists Two People and a Dog on Vessel Aground Near Belle Isle Estate
Carrybridge RNLI’s inshore lifeboat Douglas Euan & Kay Richards was launched on Sunday evening (28 August) at the request of Belfast Coastguard to assess a vessel with two people and a small dog on board, which had run aground on Upper Lough Erne in Northern Ireland.
The volunteer crew launched at 9.40pm headed for the reported location around a mile south of Belle Isle Estate and quickly located the casualty vessel, which had been refloated and taken under tow by a smaller RIB.
As the lifeboat approached both vessels, the tow was stopped to allow the helm and crew to come alongside the casualty vessel. They assessed the situation and the wellbeing of the two people and small dog on board and found they were all OK.
A full check of the casualty vessel was carried out to make sure that there was no water ingress after the earlier grounding, and none was found.
Due to the darkness of the hour, the helm deemed the safest option would be for the lifeboat and its crew to take over the tow, and to bring the vessel back to its private marina some two miles from where it was currently positioned.
The tow was successfully transferred and the lifeboat proceeded in towing the vessel to its private marina. The crew of the RIB were thanked for their assistance and they returned to their own private mooring.
Speaking following the callout, Chris Cathcart, volunteer helm at Carrybridge RNLI advised all boat users: “Before setting out on your journey, please plan your route using the relevant charts and carry out regular checks of your position whilst you proceed.
“Also allow extra time for your journey, due to the evenings getting darker earlier as autumn approaches.
“Have a means of calling for assistance if you find yourself in trouble and have lifejackets for all on board. If you see someone or something in trouble on the water or are in difficulties yourself the number to dial is 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
Upcoming Inspection & Repair Works on Erne System
Inspections and repairs will be taking place on the Erne System later this month, according to Waterways Ireland.
On Upper Lough Erne, inspection work on the underside of Lady Brooke Bridge in Co Fermanagh will begin next Monday 11 October, continuing until Friday 22 October.
Pontoons will be in used to carry out the inspections and the bridge will be partially closed off to vessels during this period.
Masters of Vessels and waterways users are also advised that Corradillar Slipway and jetty will be used for assembly of the pontoons on 11 October and for disassembling the pontoons on 22 October.
Elsewhere, on Lower Lough Erne, major works will be taking place at Portora Lock gates outside Enniskillen on Thursday 14 and Friday 15 October.
The lock gates will be closed over these two days, from 8am on the Thursday to 7pm on the Friday.
Carrybridge Lifeboat Assists Two After Cabin Cruiser Breakdown
Carrybridge RNLI’s inshore lifeboat was launched yesterday afternoon (Friday 10 September) to assess a cabin cruiser with two people on board which had broken down some two miles southeast of Knockninny in Co Fermanagh.
Once on scene on Upper Lough Erne, the volunteers established that the casualty vessel had suffered fuel issues and drifted into reeds in a small bay.
After a full review of the situation, lifeboat helm Chris Cathcart deemed the safest option was to carefully tow the vessel into deeper water, and then to proceed to tow it back to the nearest safe berth which was Knockninny public jetty.
With the owner’s permission, a stern tow was established from the lifeboat to the casualty vessel, and it was taken back to Knockninny where it was safely secured at the jetty.
Speaking following the callout, Cathcart echoed his previous advice for boat users, many of whom will be making the most of the remaining weeks of the 2021 cruising season.
“Before setting out on your journey, please plan your route and carry out regular checks of their vessels prior to going afloat and also throughout your journey,” he said.
“Have a means of calling for assistance if you find yourself in trouble, have lifejackets for all on board and plan their journey using the relevant charts.
“If you see someone in trouble on the water or are in difficulties yourself the number to dial is 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
Carrybridge Lifeboat Assists Vessel Adrift Near Island In Upper Lough Erne
Carrybridge RNLI’s inshore lifeboat launched yesterday afternoon (Tuesday 12 November) to a vessel adrift close to an island in Upper Lough Erne north-east of Knockninny Marina.
Winds were north-westerly Force 2 when the lifeboat Douglas Euan & Kay Richards arrived on the scene and slowly proceeded to the location of the vessel, with one man on board.
With the owner’s permission, and due to weather conditions pushing the boat onto the island, the lifeboat crew set up a tow line to being the casualty vessel into deeper water and then onwards to the safety of the marina.
Speaking following the callout, lifeboat operations manager Stephen Scott advised all boat users: “Before setting out on your journey, please plan your route and carry out regular checks of their vessels.
“With the constantly changing water levels at this time of year, please be vigilant for floating debris in the water. Also have a means of calling for assistance if you find yourself in trouble.
“If you see someone in trouble on the water or are in difficulties yourself the number to dial is: 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
Carrybridge RNLI is currently seeking new crew members to join its search and rescue service in Co Fermanagh, and will be hosting an open evening for all interested candidates at the lifeboat station next Thursday 21 November from 7pm.
Waterways Ireland has issued Marine Notices related to a number of events taking place on Ireland’s inland waterways this weekend.
On the Royal Canal, a Junior Canoe Polo Competition will take place at Kilcock Harbour from 10am to 6pm tomorrow, Saturday 22 June.
Passage will be possible between 1pm and 2pm. Masters of other craft are requested to proceed at slow speed and with minimum wash and note any directions issued by the stewards.
On the Shannon-Erne Waterway, masters and owners of vessels are advised that they may experience short-term delays between Lock 1 at Corraquill and Ballyconnell Marina between 1pm and 6.30pm tomorrow due to the waterway’s 25th anniversary event.
Masters are requested to proceed at slow speed and heed any instructions issued by the event marshals.
Elsewhere on the River Shannon, the swimming element of a triathlon event will take place in Tarmonbarry on Sunday 23 June between 9.30am and noon.
Tarmonbarry lock will be closed to traffic during this time, and the N5 Shannon lifting bridge will also be closed, requiring large airdraft vessels to berth north of the bridge for the period.
A children’s swimming event will take place at 6pm on Saturday in Tarmonbarry, but this will not affect vessels in the navigation.
Masters are requested to proceed at slow speed and with minimum wash when approaching this section of the river and heed any instructions issued by the event marshals.
Meanwhile, on Upper Lough Erne, masters and owners of vessels are advised that dredging works are due to commence at Kilmore Quay on Monday 1 July and last for approximately nine weeks.
The map below shows the area to be dredged and the route the vessels will be taking in order to bottom-dump the material.
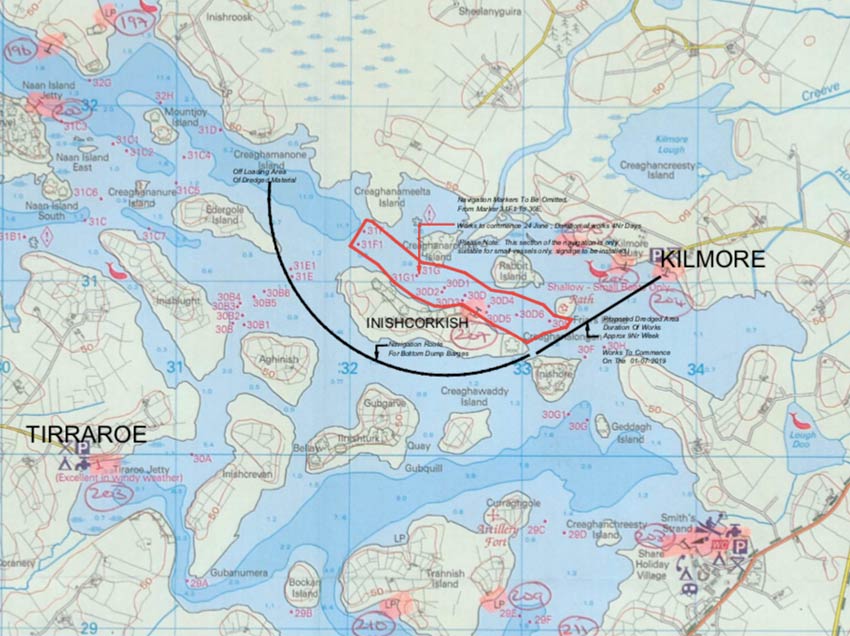
Masters of vessel are requested to proceed with additional caution in the vicinity of the dredging operations and dredging vessels.
Waterways Ireland thanks its customers for their co-operation in this and all other matters.































































