Displaying items by tag: plastic
Discarded plastic is the predominant form of litter on Northern Ireland’s beaches, according to a new survey by a local environmental group.
As the Belfast Telegraph reports, the survey by Keep Northern Ireland Beautiful estimates that plastic — most of it single-use, such as bottles or food wrappers — accounts for nearly four-fifths of more than three million items of rubbish on NI beaches at any one time.
The figure is projected from on-site surveys in 2019 which recorded an average of more than 500 pieces of litter per 100 metres of beach.
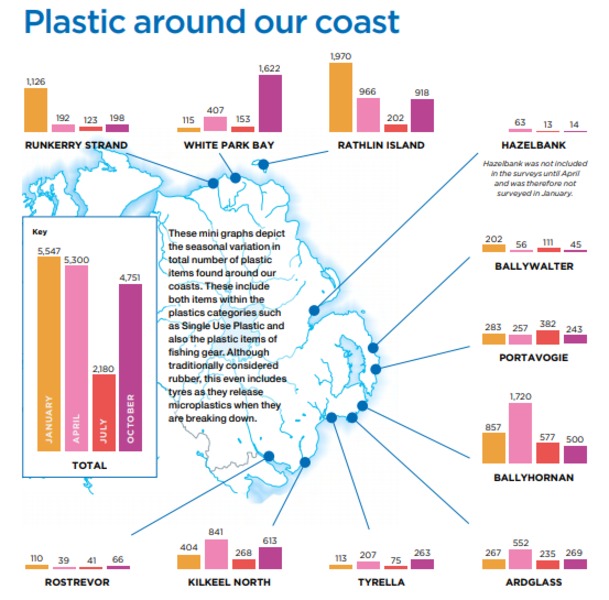
Commenting on the survey, NI Environment Minister Edwin Poots said: “The figures reveal the stark reality of litter on our beaches, with over 22,000 pieces of litter collected across 11 beaches, with 78% of this made from single-use plastic.”
The Belfast Telegraph has more on the story HERE.
Marine Minister Thanks Trawler Owners For Playing Their Part In Ireland’s Clean Oceans Initiative
Marine Minister Michael Creed has welcomed the increase in trawlers and other fishing boats now signed up to Ireland’s Clean Oceans Initiative.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the initiative involves fishermen storing and returning to land marine plastics that come up in their nets daily as they fish, thereby removing this pollution from the marine environment.
The minister launched the Clean Oceans Initiative in January this year at Union Hall, setting a very ambitious target for the participation of the entire Irish trawl fishing fleet in the scheme by 31 December.
To date, 168 trawlers and 56 other fishing boats have signed up with 12 ports registered and involved in the initiative.
“It is heartening to see the numbers that have come on board and that we are now at 70% participation. I would like to thank every boat owner who has joined up,” said the minister.
“We need to get every single trawler on-board for this. This is good for the fishing industry and good for the environment.”
He added: “I’m delighted that the fisheries producer organisations endorsed this initiative and are encouraging their members to sign up and get involved.”
Protecting our oceans is one of 17 Global Goals that make up the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
By the end of the third quarter this year, approximately 70 tonnes of marine plastic waste had been collected from 12 of Ireland’s busiest fishing ports and 25.5 tonnes of used fishing nets have been collected for recycling by Bord Iascaigh Mhara’s (BIM) mobile shredder, the ‘Green Machine’.
Minister Creed expressed his thanks to BIM and to those leading the early brigade: “I must commend all those currently involved in the Clean Ocean’s Initiative being run by BIM and the longstanding commitment many in the fishing industry have to bringing ashore plastic waste from the sea.
“I look forward to seeing 100% participation by our trawling fleet by the end of this year.”
Applicants are advised to sign up on the BIM website or by contacting BIM directly at 01 214 4100.
Plastic fibres released during construction on the Dun Laoghaire baths site last year have again washed up on nearby beaches, as The Irish Times reports.
The plastic shards were washed into the water during a concrete pour at the development last November, prompting a safety advisory for swimmers and beach-goers between the West Pier and the Forty Foot.
A clean-up operation was launched at the time which recovered 50kg of the 70kg of plastic strands released.
Now a volunteer clean-up group says some of the unrecovered plastic reappeared at Sandycove on Thursday ahead of Storm Lorenzo.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Sea Change At Seafest: Ireland’s Largest Free Maritime Festival To Raise Awareness Of Plastic Pollution
An interactive hut made up of 60kg of household plastics — the average amount used by an adult in Ireland each year — will be unveiled at SeaFest this weekend, highlighting the problem of plastics in our oceans.
Ireland’s largest free family-friendly maritime festival begins at the Port of Cork from today, Friday 7 June, and continues to this Sunday 9 June with over 100 free events celebrating our oceans.
More than 100,000 visitors are expected to attend SeaFest, which is presented by Cork City Council and the Inter-Departmental Marine Coordination Group (MCG).
Raising awareness of the need to protect our marine environment against plastic pollution, Bord Iascaigh Mhara's centrepiece at SeaFest is the Clean Oceans Experience.
Funded by the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund, the installation includes a 60kg plastic hut sculpture, representing the total plastic packaging waste produced per person in a year.
This installation will be accompanied by a specially commissioned artistic performance, Fantastic Fishermen Go Fishing for Litter, on how the fishing sector is reducing plastics in our seas.
Members of the fishing sector taking part in BIM's Fishing for Litter scheme, which encourages fishermen to take ashore waste they encounter at sea, have collected over 330 tonnes of marine litter since it began in 2015.
“Environmental stewardship of our oceans is something we need to instil in our children”
“Environmental stewardship of our oceans is something we need to instil in our children,” Lord Mayor of Cork, Councillor Mick Finn, said. “This will ensure the problems facing our oceans are addressed, and hopefully, reversed.
“I’m delighted to welcome SeaFest to Cork for the next three years, as it serves an important role in this education. SeaFest is a brilliant illustration of our unique and unrivalled maritime history.
“In a fun and interactive way, this national annual festival is helping those of all ages to think about their connection with the water and how the actions they make today can make a difference tomorrow.”
Engaging exhibitions and workshops to turn plastic into art also feature at SeaFest, open daily from 10am to 6pm.
A Flock of Sea Gulls will see 1,000 young visitors transform 1,000 plastic cartons into an installation of seagulls, while the Port of Cork and MaREI’s 3D exhibition, Maintaining a Healthy Harbour, is also on display, with marine litter artworks from local school children.
Showing how our oceans and climate are linked, the Marine Institute’s Wild Atlantic Theatre features talks from Met Éireann’s head of forecasting Evelyn Cusack and wildlife cameraman Doug Allan.
Doug, who has worked alongside Sir David Attenborough on BBC’s Blue Planet and Frozen Planet, will discuss how changing climate is affecting Earth's north and south regions.
Sustainably sourced Irish seafood plays a starring role at SeaFest
Sustainably sourced Irish seafood plays a starring role at SeaFest with demos from top chefs Nevin Maguire, Rory O'Connell and Martin Shanahan.
The Bord Bia and BIM Seafood Experience also features fishmongers Pat O’Connell and Hal Dawson on seafood preparation.
Encouraging responsible activity on the water, SeaFest will hold free sailing, kayaking, and currach boats sessions, along with interactive displays exploring the marine world.
Speaking ahead of SeaFest 2019, Marine Minister Michael Creed said: “SeaFest is part of Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth, the Government’s integrated plan for the marine sector. A key aspect of this plan is to significantly increase our level of engagement with the sea.
“As we welcome the festival back to Cork from Galway where it has been thriving over the past three years, once again, SeaFest has delivered a fantastic line-up of free, educational and fun events to engage both the public and policy makers alike and emphasise the importance of Ireland’s marine economy.”
Providing education on our oceans, the Marine Institute's RV Celtic Explorer is open to the public, following its oceanographic data collection voyage from Galway to Cork.
There will also be vessel tours of Commissioners of Irish Lights’ ILV Granuaile and tall ship Phoenix.
MFV Allanah Riley, a white fish trawler that fishes out of the port of Castletownbere, will be open to visitors throughout SeaFest. Its crew will be on hand to explain the sustainable fishing practices of the Irish fishing fleet.
Market traders will be using compostable packaging across the weekend
As part of Cork City Council’s commitment to green initiatives, Cork City Council environmental awareness officer Mary Walsh highlighted that market traders will be using compostable packaging across the weekend.
“There will also be pirates on site, keeping SeaFest free from single-use plastics. If someone has brought a plastic bottle with them, the pirate will show them how, and where, to dispose of it,” she said.
SeaFest 2019 is a culmination of a weeklong celebration of Ireland’s rich maritime heritage, as the annual Cork Harbour Festival runs until Sunday 9 June.
The Our Ocean Wealth Summit takes place in Cork on Sunday 9 and Monday 10 June. The summit will hear from global leaders including environmental activist and former US Secretary of State John Kerry.
To view the full festival programme visit SeaFest.ie. Follow SeaFest on Facebook, Twitter and Instagram and use the hashtag #SeaFest19.
SeaFest is proudly supported by Cork City Council, BIM, Marine Institute, Port of Cork, Cork Harbour Festival, Commissioners of Irish Lights, Defence Forces, Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine, Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Bord Bia, Sea Fisheries Protection Authority, Pure Cork and by media partners Today FM and RedFM.
Seafest is co-funded by the Government of Ireland and the European Union under Ireland’s European Maritime & Fisheries Fund Operational Programme for the seafood sector.
Target for 100% of Irish Trawlers to Recover Plastic Waste from the Oceans on Every Fishing Trip
Minister for Agriculture, Food & the Marine, Michael Creed T.D., today announced Ireland's Clean Oceans Initiative and called for the participation of the entire Irish trawl fishing fleet in the scheme by 31st December 2019. His ambition is to have all Irish trawlers at every pier and every port actively participating in Ireland’s first coordinated initiative on land and at sea to collect, reduce and reuse marine litter and clean up our marine environment. Building on the very successful Fishing for Litter campaign the Minister has challenged BIM to work with the fishing industry to ensure participation of 100% of Irish trawlers in the Clean Oceans Initiative by the end of 2019. BIM will report to him quarterly on the progress being made to meet that target.
Speaking at the launch of Ireland’s Clean Oceans Initiative in the fishing port of Union Hall today Minister Creed said:
“I recognise that co-ordinated action is required on land and at sea to address the serious issue of pollution of the Oceans with plastics. This threatens our fish stocks, the wider marine environment and the future of our fishing industry. I am setting out a challenge for our fishing industry to set a world first by having all of our fishing trawlers cleaning and removing plastic from the ocean every day, as they go about their activity at sea. This is good for the marine environment, fish stocks and our fishing industry. This is a challenge which I am confident our fishing industry will rise to and succeed in setting an example for other nations.”
Creed went on to say “We can only solve the problem of plastics in our oceans by working collaboratively. Ireland’s “Clean Oceans Initiative” which I am launching today, aims to mobilise every member of the Irish seafood sector and its wider communities – every fishing port, fishery harbour and pier in Ireland - to take action. I believe that our fishing industry will build on the good work they have been voluntarily doing to date on marine litter, to get every trawler in the Irish fleet involved, to show how we can begin to address this great global challenge of our time. Everyone has a responsibility for marine litter and we intend to take on that responsibility through Ireland’s “Clean Oceans Initiative” .”
Fishermen have been living in harmony with the marine environment since the beginning of time, they share Minister Creed’s concerns and they have a key role to play in recovering discarded plastics from the oceans. Our fishing vessels are towing nets through the waters around our coast on a daily basis and often find debris, including waste plastics, when the nets are hauled. Minister Creed wants to facilitate our fishermen to bring this waste home from their fishing trip and he is encouraging our fishermen to recover as much plastic as possible from the seas around Ireland. He has made funding available under Ireland’s European Maritime and Fisheries Fund (EMFF) to support the new “Clean Oceans Initiative” to provide on-board storage facilities and on-shore infrastructure for environmentally friendly disposal of all plastics, waste, ghost fishing gear, etc. recovered at sea. The on-shore infrastructure will also be available to fishermen and aquaculture operators to dispose of unwanted fishing gear and other items with plastic content.
In addition to the “Clean Oceans Initiative” Minister Creed has asked BIM to assemble a collaborative team representative of all stakeholders to focus on solutions for marine litter prevention and removal. The team will include fishermen and fish farmers, net makers, harbour authorities, fish processors, community groups, Fisheries Local Action Groups (FLAGs), academics and NGOs. He has also asked BIM to include a broader outreach to the wider coastal community, of which the seafood community are a vital and intrinsic part and to report back to him by the end of 2019 with proposals for further innovative solutions for the prevention and removal of marine litter.
Contamination in the marine environment is not a new phenomenon and up to 80% of marine debris is made up of plastics. Total World production of plastics reached 335 million metric tons in 2016. Plastics do not biodegrade, they photo-degrade, breaking up from recognisable items of all sizes and shapes into tiny particulates. The risks posed to marine wildlife by waste plastics has motivated research to assess the extent of the problem and this is welcomed but we cannot afford to delay remedial actions so the Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine, Micheal Creed T.D. has decided to act now and promote all possible measures to prevent plastics from entering our marine environment and to remove as much plastic from the marine environment as possible.
Flossie Donnelly's New Years Day Killiney Beach Clean Up
Dublin Bay youngster Flossie Donnelly made a great start to the New Year with a Killiney Beach Clean Up as part of her ongoing campaign to rid Dublin Bay of plastics.
As Afloat.ie previously reported, young coastal litter crusader Flossie Donnelly celebrating in May the installation of Dun Laoghaire Harbour’s first Seabin after a successful fundraising campaign.
The New Year's Day Killiney Beach Clean up was organised by "Flossie and the Beach Cleaners" and supported by Dalkey Tidy Towns.
Grand Canal Clean Up
Meanwhile, on the Grand Canal in Dublin a litter picking group will meet this Saturday, January 5th at 10 am by Leeson Street Bridge. Pickers, bags, and gloves all provided. Coffee compliments of Starbucks to finish.
Viking Marine's Shout Out on Plastic in Dun Laoghaire Harbour
Viking Marine is promoting presents with a conscience this Christmas with one such gift being Viking Marine reusable water bottles. It's part of a drive in Dun Laoghaire on Dublin Bay to make 2019 the year that moves on from being 'aware' to being 'active' about removing the plastic threat in our seas.
While out in the harbour this week, Viking Marine's Ian O'Meara observed the not unusual sight of plastic waste build up, an ongoing issue which, sailors at least, are all very aware of. He spotted a seal at the West Pier chewing on plastic (pictured above). 'A sad sight', Ian told Afloat.ie
In a shout out to all harbour users, O'Meara says "leisure, commercial, everyone - Save Our Seas". And the chandler adds, "to us as retailers to provide our customers with choices in sustainable reusable and recyclable plastics".
Biodegradable Bow Stickers For Greener Racing
The scourge of bow stickers stuffing rubbish bins and polluting waters the world over could soon be a thing of the past thanks to a new biodegradable variant.
YachtRacing.life reports on the new stickers from race boat supplier PROtect Tapes, made from bioplastic film and designed to be durable enough for regattas of seven to 10 days.
There is also an existing short-term bow sticker for shorter events made of paper from sugar cane cellulose.
Both are made of compostable materials so they can go in the brown bin straight after racing — but if they come off while on the water they will degrade completely within a year.
The development will be good news for Martin Byrne and his fellow Dragon sailors, who raised the issue of plastic pollution from bow stickers at Volvo Cork Week this past summer.
Safety Advisory For Swimmers Over Plastic Pollution At Forty Foot
#Safety - Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown County Council has posted a safety advisory for swimmers in Dun Laoghaire over an incident of plastic pollution between the West Pier and the Forty Foot.
According to the local authority, “small strips of plastic” that have washed ashore in recent days may be present in bathing waters.
While the plastic poses no chemical danger, it could be a nuisance or at worst a physical risk to swimmers.
As The Irish Times reports, contractors working on the redevelopment of the Dun Laoghaire baths site are launching a clean-up operation in the affected area after “a quantity of fibres” was washed into the water during a concrete pour.
It follows community efforts led by local environmental hero Flossie Donnelly, who recently donated a second Seabin for cleaning surface debris in Dun Laoghaire Harbour to the National Yacht Club.
New Web Series Follows The Riptide Movement As They Discover The Impact Of Plastic In Our Oceans
The Riptide Movement’s Plastic Oceans is a three-part web series that hopes to add to the urgent and important debate about how to solve the global plastic crisis and the devastating effect it is having on our marine life.
The Clean Coasts programme took Dublin rock band The Riptide Movement along the incredible Irish coastline and met with some of Ireland’s leading marine biologists, researchers, campaigners and Clean Coasts volunteers to discover the real impacts of plastic in our oceans and what it means for the future of all life on our planet, including us.
The Clean Coasts programme engages communities in the protection of Ireland's beaches, seas and marine life and currently has over 650 volunteer groups working along our Irish coastline, carrying out beach cleans and coastal protection work.
The band also visit a number of locations leading the way in tackling plastic waste including University College Cork, a Green Campus awarded site; chatted with Amanda Byram at the launch of Sky Ocean Rescue in Ireland; and sat down with the Minister for Housing, Planning & Local Government Eoghan Murphy to see what actions the government are taking and what can be done to address the issue at policy level.
Regarding wildlife, a visit to Ireland’s only seal sanctuary and a panel discussion with filmmaker Sophie Darlington highlights the impact our love of plastic is having on our marine animals.
The result is a web series aptly titled ‘The Riptide Movement’s Plastic Oceans’. Narrated by Jerry Fish, this web series highlights the extent of the plastic crisis in Ireland in an informative, artistic and engaging way, whilst also showcasing the small changes we can make to help stem the tide of single use plastics.
Talking about the web series and the bands’ collaboration with Clean Coasts, lead singer Malachy Tuohy said: “We hope this web series and our music can help raise more awareness around one of the greatest environmental challenges of our time.
“Our reliance on single use plastics is destroying our oceans, a reality so poignantly highlighted by David Attenborough in Blue Planet 2. Through our web series we wanted to learn about the issue of plastic pollution here in Ireland and what small changes we can make to help stem the tide of single use plastics.
“Our oceans are drowning in plastic and it is not the legacy we want our generation to be remembered for.”
Speaking about the web series, Clean Coasts manager Sinead McCoy said: “Litter and particularly marine litter has a huge long term negative impact on our environment. Raising public awareness is incredibly important when it comes to reducing marine litter which we see washing up on our coastline on a daily basis.
“So, the Clean Coasts programme is delighted The Riptide Movement are using their influence to bring attention to not only the issue of marine litter but the incredible work being done by Clean Coasts groups and our Clean Coasts stakeholders.”
For more information on how to get involved in Clean Coasts programme see cleancoasts.org







































































