Displaying items by tag: redevelopment
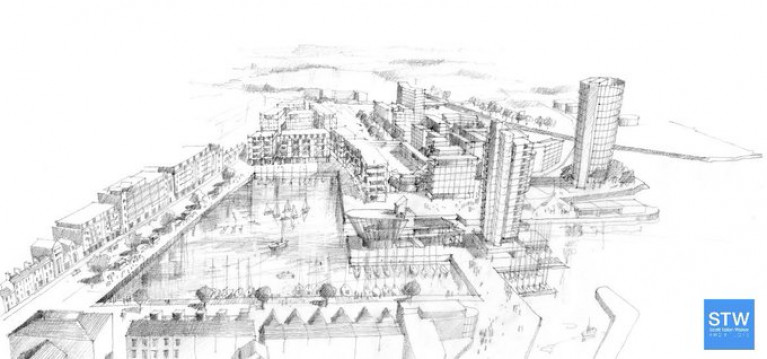
At the Cork Dockyard facility at Rushbrooke, Cork Harbour is where redevelopment plans to service planned offshore wind projects have taken a step forward.
The plan to support offshore windfarm projects is proposed by the Doyle Shipping Group (DSG) which is to redevelop the site as a port infrastructure hub for use by developers of offshore renewable energy (ORE) projects. DSG, the largest port service solutions provider in Ireland with offices in seven ports, has labelled the project, the Cork Dockyard Rejuvenation Project (CDR)
As the Irish Examiner reports, DSG has in recent days issued its tender documents to seek a public relations firm to deliver a strategy for the public consultation process at the site of the former Cork Verolme Dockyard (V.C.D.) shipyard. The current marine engineering facility of Cork Dockyard, carries out ship-repair, survey / dry-dockings including use by the Naval Service.
As the project is large-scale, the ORE falls into the category of a Strategic Infrastructure Development (SID) and as such the application for planning permission lies with An Bord Pleanála.
Approximately 15 hectares is the dockyard site which comprises a graving dry-dock for ship-repair and the adjoining redundant shipyard which was the largest in the Republic. The origins of the shipyard can be traced to its establishment in 1853 and for many decades was considered one of the most significant elements of the harbour's industrial infrastructure.
During the shipyard’s peak, more than 1,100 were employed at the Rushbrooke site as Afloat highlights is where major vessels including those for Irish Shipping Ltd, B+I Line, Sealink/British Rail and the Naval Service including flagship L.E. Eithne were built and launched.
The V.C.D. shipyard however closed in 1984 with the last vessel built, L.E.Eithne for the Navy, noting this ship would also become historically significant, as the last ever ship to be built in the Republic.
More than a decade after the closure of Ireland’s only shipbuilding yard, the site was acquired by DSG in 1995.
Further reading here on the plans for the ORE facility, which will not interfer with the dockyard's ship-repair infrastructure.
In south Wales is where significant progress at Pembroke Dock is being made to create a multi-purpose and future energy-ready port in Pembrokeshire that will create a bright and prosperous outlook for current and future generations.
Physical works on the Swansea Bay City Deal and EU funded Pembroke Dock Marine project began in earnest last August after a breaking ground ceremony marked the start of the construction of a supersize slipway and new workboat pontoons at Pembroke Port.
Since then the landscape of the site has changed dramatically. The slipway is being significantly widened to 68 metres and extended to offer greater flexibility for developers and marine businesses looking to test new marine energy devices, launch and recover vessels, and supply chain companies providing maintenance and engineering services to floating offshore wind device operators in the Celtic Sea. Once complete in Spring 2024, the wider slipway will measure 11,352sqm which is the equivalent of one and half football pitches. Materials from the works to enlarge the slipway are being recycled and used to create much-needed laydown space by infilling the timber pond.
New workboat pontoons are being installed to the east of the existing ferry terminal offering short and long term berthing options for workboats, barges and jack up barges, positioned neatly between Quay 1 and the new slipway. These are already proving popular and will be available to utilise from Autumn 2023.
At Gate 1, the four new annexes attached to the historic Sunderland Hangars are nearing completion. These will offer modern offices and workshops ideally situated for companies in the renewables and marine sectors looking for a new base within a busy commercial port. Brand new office space and workshops allow for a flexible working solution ideal for developers and supply chain businesses. The four hangar annexes are in the final stages of completion and will be ready for occupation this summer. Renamed Oleander House, Catalina House, Falcon House & Erebus House they offer a range of one and two storey office space and workshop areas, with two contracts currently under negotiation.
Commercial Director at the Port of Milford Haven, Steve Edwards, is pleased with the progress being made at Pembroke Port. He said “These works will make a huge difference to the facilities and services that we can offer to the marine sector but also the growing renewables industry that is being attracted here due to the exciting opportunities for floating offshore wind projects in the Celtic Sea. The team at the Port and contractors BAM Nuttall, the Walters Group Walters Group and R&M Williams are keeping the project on track and I am confident we will attract some iconic and innovative companies that want to base themselves at Pembroke Port.”
Councillor Rob Stewart, Chairman of the Swansea Bay City Deal’s Joint Committee, said “The City Deal is making significant progress through the Pembroke Dock Marine project by growing the economy and creating employment opportunities with a particular focus on the energy sector and renewable technologies. The work that R&M Williams and BAM Nuttall are completing in the Hangar Annexes, pontoons and slipway will regenerate Pembroke Port as well as support the blue-green energy economy, which is fundamental for the future of South West Wales. Coupled with the recent success of the Celtic Freeport bid, it strengthens our ambitions to create a prosperous region for businesses to thrive and residents to access well-paid jobs, both now and in the future.”
Pembroke Dock Marine is funded by the UK Government and Welsh Government through the Swansea Bay City Deal, and through the public and private sectors. It is also part funded by the European Regional Development Fund through the Welsh Government.
See the progress being made so far online at: Pembroke Port Developments on Youtube
Submissions numbering 200 in total, have been received from the public on plans for a major redevelopment of Galway Harbour.
The vision for the harbour would involve the transformation of 17 acres of land surrounding the inner port's dock area.
The plan sets out to deliver a sustainable urban living quarter with a key focus on public realm space.
Proposed public amenities include cross-city walking and cycling routes, cultural and event spaces, recreational water sport facilities and a re-imagined street network.
Galway Bay FM has more here
Redevelopment Plans of Marino Point to Be Made Public
According to EchoLive questions regarding plans for the long-awaited redevelopment of Marino Point, the former Irish Fertiliser Industries (IFI) site, near Cobh, will be taken by Port of Cork staff at two events in September.
Two public information evenings are due to take place regarding the Belvelly Port Facility masterplan on September 4 at Belvelly Port Facility office at Marino Point and Thursday, September 5, at Passage West GAA club, both between 4pm and 8pm.
The Marino Point jetty is located in 10m of water, enabling large ships to dock there and a number of companies are set to be located in the 114-acre site.
Port activities will likely be focused on oil, agri-feed, and fertiliser traffic.
The site was previously owned by IFI and UK-based Chemical Industries and closed in 2002 with the loss of over 200 jobs.
For more including comments from a local councillor, click here.
Cork's Tivoli Redevelopment Updated Designs Are Considered
#waterfrontproperty - EchoLive reports of updated design plans in Cork for the redevelopment of the Tivoli docklands that were discussed at a recent meeting in City Hall.
At the Planning Strategic Policy Committee (SPC), officials outlined the proposed development that would see more than 10,000 people living and working in Tivoli.
The Port of Cork is set to vacate the site in the next two years, and plans to create an urban area the size of Blackrock are being prepared.
According to City Hall, Government funding under the Local Infrastructure Housing Activation Fund (LIHAF) to develop the area has been secured.
While Cork City Council does not own the land itself, it is supportive of projects to enhance the city.
More on this story can be read from this link.
#DUN LAOGHAIRE NEWS - Dun Laoghaire's historic Victorian sea baths are to be replaced with a small 'urban beach' under rejuvenation plans for the harbour, the Irish Independent reports.
County councillors for Dun Laoghaire Rathdown voted on Tuesday to green light the construction of a new sea baths facility, part of the 'master plan' development proposed by the Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company that has raised the ire of the harbour's yacht clubs.
The decision is the latest in a long series of ambitious plans for the Victorian baths, which recently received a new coat of paint as part of the Dulux Let's Colour Project but have lain derelict for 15 years.
Under the new plan, all but two of the buildings on the baths site, which was built in 1843, will be demolished to make way for a new jetty and changing area, which is set to include an 'urban beach' in the future.
Only the baths pavillion and a small outbuilding will be retained for an artist's studio, a gallery and café.
The Irish Independent has more on the story HERE.
#GALWAY HARBOUR - Galway Harbour management are looking forward to the prospect of Chinese investment in the port's redevelopment plans, the Galway Independent reports.
“Chinese investors clearly recognise not only the massive potential of ocean tourism, but also the specific potential for Galway as a destination port for cruise liners," said Fine Gael TD Brian Walsh, referring to discussions between the Government and Chinese officials in Beijing last week.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, Galway Bay can expect to welcome at least nine cruise visits thus year, with the first scheduled to arrive late next month.
Walsh added: "Galway is an incredibly attractive city, and if we can make it accessible to the major players in the cruise-line market, the impact on the local economy would be immense.”
Galway Harbour Company CEO Eamon Bradshaw said that the port project had "illicited quite a bit of interest" when the company presented at the recent Chinese-Ireland Relations conference at NUI Galway.
"We’re confident that we do have a lot to offer and we are confident that an investor will come on board."
The Galway Independent has more on the story HERE.
Galway In Talks to Attract Cruise Liners
World tourism bosses and cruise line operators will be headed to Galway next month for high-powered talks aimed at transforming the city into a global destination port.
The Connacht Sentinel reports that execuives from Fáilte Ireland, the Galway Harbour Company and Galway Chamber of Commerce will meet a delegation that will include Jamaica's head of tourism and some of the world's largest cruise line operators to discuss attracting business to the redeveloped port.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the proposed €200 million redevelopment of Galway Harbour - which will increase berthing space to accommodate cruise ships - has received approval to submit a planning application to An Bord Pleanála.
Galway West Deputy Brian Walsh, who helped push forward the development plan and will also meet the delegation at the end of September, said that the Galway Harbour Company has set a target of 50 cruise ships a year - which could bring in an extra €40 million annually to the local economy.
The Connacht Sentinel has more on the story HERE.
As reported previously on Afloat.ie, the Galway Harbour Company's €200 million scheme involves moving the port south onto 24 hectares of reclaimed land in deeper water to accommodate cruise liners, as well as a proposed rail link and marina expansion.
Following the public consultation earlier this year and subsequent discussions with An Bord Pleanála, the scheme has been deemed a 'strategic infrastructure development' and a planning application under this designation is expected to be lodged this month.