Displaying items by tag: Sisk
The Sisk family are a remarkable tribe around boats as around everything else with which they get involved. But perhaps the most remarkable of them all was John Sisk (1911-2001), who spearheaded the family construction company’s move from being a regional leader in Cork to a frontline national firm in Dublin, a quiet behemoth of a company which has continued on to international prominence.
He must have been one of the best-organised people on the planet. Despite a workload which would have felled a team of half a dozen super-talents, he always said that he was going to retire at the age of sixty. And he did exactly that, enjoying thirty years of pursuing other interests which fascinated, entertained or simply amused his always-active brain.
 Lines of Cheerful Maid. Faced with John Sisk’s powers of quiet persuasion, London-based designer Robert Clark drew them in 1943 even as World War II raged about him.
Lines of Cheerful Maid. Faced with John Sisk’s powers of quiet persuasion, London-based designer Robert Clark drew them in 1943 even as World War II raged about him.
And although there were times when keeping the company afloat in the economically-depressive days of the 1930s, ’40s, and ’50s must have required iron determination and enormous self-belief, he was able to pursue an interest in getting afloat for recreational purposes. But being John Sisk, this was no trivial pursuit – he wanted to build boats to the plans of the leading international designers of the day.
 Cheerful Maid in the West Pier yard in Dun Laoghaire around 1962 – she was an almost-perfect example of the Robert Clark designs of that era. Photo courtesy Hal Sisk
Cheerful Maid in the West Pier yard in Dun Laoghaire around 1962 – she was an almost-perfect example of the Robert Clark designs of that era. Photo courtesy Hal Sisk
Thus even though World War II was at its height, he was in correspondence with Robert Clark in London, and in 1943 persuaded Clark to design a 40ft cruiser-racer sloop which was to emerge in 1949 as the very handsome Cheerful Maid, built at the Sisk-backed Dalkey Shipyard at Bulloch Harbour, it was a yard which subsequently went on to acquire a name for the series-production of Folkboats.
Meanwhile, the busy Sisk mind was pursuing another Scandinavian line of interest. While other Irish owners were beginning to incline towards James McGruer in Scotland for boats to the new International 8 Metre Cruiser/Racer Rule, John Sisk was in a fruitful exchange of ideas with the Swedish designer Knud Reimers.
 The pans of Marian Maid as featured in the Yachting World Annual 1954. Design novelties included an aft-facing auxiliary engine
The pans of Marian Maid as featured in the Yachting World Annual 1954. Design novelties included an aft-facing auxiliary engine
The result was the Reimers take on this new concept which the designer so liked that two boats were built to the design, a sloop-rigged version in Sweden for the designer himself and – unusually - a yawl-rigged one, Marian Maid (it being the Marian Year of 1954) for John Sisk built by Dalkey Shipyard, his business setup which seems to have been a moveable feast spread between Bulloch Harbour and Dun Laoghaire’s West Pier.
Although John Sisk was a longtime member of the National Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire, as his son Hal recalls, he was too busy to be a really “clubbable man”. Thus he hadn’t had the time to cultivate a sufficiently seasoned crew to race and cruise Cheerful Maid despite getting her an RORC rating, but after she was sold away and became Sainte Anne under noted offshore sailor D H F Williams in the south of England, she made more of a mark for herself.
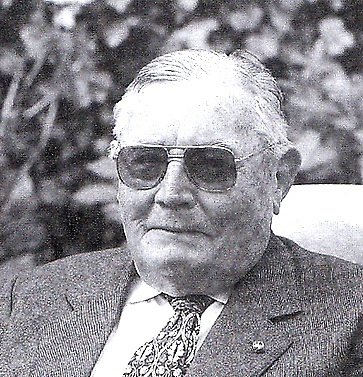 John Sisk – despite being accustomed to a prodigious work rate, he retired exactly when he said he would, at the age of 60, which allowed him thirty years of active retirement. Photo courtesy Hal Sisk
John Sisk – despite being accustomed to a prodigious work rate, he retired exactly when he said he would, at the age of 60, which allowed him thirty years of active retirement. Photo courtesy Hal Sisk
Equally, with Marian Maid the light use for family sailing purposes made for little impact on the Dublin Bay sailing scene, even if like Cheerful Maid she’d featured as an interesting design in a major sailing publication, with Cheerful Maid in The Yachtsman in 1945, while Marian Maid had something of a splash in the Yachting World Annual of 1954, which would have been published in December 1953.
 As to how and why Dalkey Shipyard included The Turkish Republic among its key customers we can only guess, but what’s for sure is that despite his name appearing nowhere on the letterhead, John Sisk was the main man behind the company. Courtesy Hal Sisk
As to how and why Dalkey Shipyard included The Turkish Republic among its key customers we can only guess, but what’s for sure is that despite his name appearing nowhere on the letterhead, John Sisk was the main man behind the company. Courtesy Hal Sisk
As the years went by, John Sisk’s correspondence with noted designers moved up a step further with an exchange of letters with Olin Stephens in New York. Sisk was looking for a boat around the One Ton size with added competitive potential for his growing sons, and in the mid-1960s, Stephens revealed that the company’s new design for a 36ft race-oriented fin-and-skeg fibreglass sloop would actually be in production in Italy as the Gaia 36 before she was due to appear as the much-heralded Swan 36 from Finland.
 Thanks to John Sisk’s continuing correspondence with Olin Stephens, the Italian-built Sarnia was in action in Ireland long before her Finnish-built hull sister, the Swan 36, was seen here
Thanks to John Sisk’s continuing correspondence with Olin Stephens, the Italian-built Sarnia was in action in Ireland long before her Finnish-built hull sister, the Swan 36, was seen here
Thus Sarnia arrived from Italy in Dun Laoghaire to introduce the new era of very stylish fibreglass cruiser-racers, and she has been in Ireland ever since. As for the first of the Sisk performance cruisers, it’s only known that by 1980, when the last of the Lloyd’s Registers was published, Sainte Anne (ex-Cheerful Maid) was no longer in it. But for someone with the time, a fast-moving computer, and the USB with all the Lloyds Registers which was created by the Association of Yachting Historians with Hal Sisk as Chairman, it might be possible – perhaps with additional resources - to find out what became of this remarkable product of late 1940s Bulloch Harbour Yacht building.
 Marian Maid in Dublin Bay after her 2002 restoration. Photo: W M Nixon
Marian Maid in Dublin Bay after her 2002 restoration. Photo: W M Nixon
 The classic Marian Maid – designer Knud Reimers liked the look of her so much in 1954 that he had a sister-ship built for himself
The classic Marian Maid – designer Knud Reimers liked the look of her so much in 1954 that he had a sister-ship built for himself
Meanwhile, Marian Maid is back in Dun Laoghaire, owned by George and Hal Sisk and Hal's son Owen, and immaculately restored by Jimmy Murphy and Peter Sweetman and Sisk boat specialist Ian Squire with the team at Rossbrin Boatyard in West Cork, where the up-dating mods have included the installation of an electric auxiliary engine.
It’s not the first time Marian Maid has undergone a major restoration. Back in 2002 she arrived in Dun Laoghaire after a restoration commissioned by Patrick McHugh in northwest England. But when he became ill, a prolonged period for the Maid in the boatyard at Holyhead Marina – where all the winds of heaven seems to blow with extra vigour – put everything back to Square One.
 Jimmy Murphy of Rossbrin Boatyard in West Cork – his team’s restoration of Marian Maid has included the installation of an electric auxiliary engine
Jimmy Murphy of Rossbrin Boatyard in West Cork – his team’s restoration of Marian Maid has included the installation of an electric auxiliary engine
However, with the standards set by the late Edmund Kreugel at Rossbrin continuing, Maid Marian is completely herself again, ready to be the flagship in the Parade of Classics at Dun Laoghaire on the morning of Sunday, July 2nd to introduce the week-long Coastival, leading into the Volvo Dun Laoghaire Regatta from Thursday, July 5th to Sunday, July 9th.
As an event, the VDLR is – let’s face it - the ultimate in clubbability. Were he still with us, John Sisk would probably much prefer to be away from its mega-partying, alone at his desk in email communication with some rising international design star, and bouncing around fresh ideas for a new boat which would be so good the designer would want one for himself.
Historic Sarnia is Classic Irish Sailing Saga
Some boats just come and go, leaving little trace in the Irish sailing community’s consciousness. But others quickly become an integral part of our enduring mental and physical furniture, and our story at the weekend about the 1966-vintage Sparkman & Stephens-designed 36ft Sarnia and her first owner John G Sisk rang many bells.
Not least is the discovery that her name means “Star of the Sea” in an ancient alternative Roman language. It has a lightness to it which compares favourably with the official Latin of “Stella Maris”, for in naming a boat Stella Maris, you saddle her with a certain duty of piety, whereas there’s a sense of freedom about “Sarnia”.
This tells us even more about John G Sisk, the man who in 1949 called his new Robert Clark-designed Dun Laoghaire-built 38ft sloop Cheerful Maid at a time when cheerfulness was not at all high on the Irish agenda.
Be that as it may, Sarnia engendered hope when she arrived newly-built from Italy in Dublin Bay in 1966, and her first major challenge, raced by George, Hal and John Junior - the next generation of Sisks – was the RORC Beaumaris to Cork Race of June 1967.
The young Frank Larkin of Limerick was part of the youthful crew, and his memories of this experience 53 years ago arrived with us bursting with life as soon as the Sarnia story was posted on Saturday. It’s further proof, were it needed, that sailing is the secret of eternal youth, for recently Frank has acquired a Laser – not the first by any means – to let him sail when he wishes on Lough Derg from the KSC base close north of Killaloe.
 You guess his age…….Sarnia veteran Frank Larkin with his newest Laser at Killaloe Sailing Club
You guess his age…….Sarnia veteran Frank Larkin with his newest Laser at Killaloe Sailing Club
Recollecting sailing events of more than five decades ago, he wrote of the great memories of how Sarnia came to be in Dublin Bay, and explained that he’d been on the University College Dublin Intervarsities Team racing squad with John Sisk Jnr, and it was after he’d returned to Limerick that a call came asking him would he crew on Sarnia in their first major offshore race, the RORC Beaumaris-Cork event of June 1967, an offer which he took up with enthusiasm.
Yet it was quite a leap in the dark, as Sarnia was new, the Sisks and their young sailing friends were new too as offshore racers, and the forecast was for a real sluggeroo out of the Irish Sea, round Carnsore Point and on still to windward past the Saltees and the Coningbeg for that often seemingly endless beating to Cork, where the headlands off West Waterford and East Cork all look so similar that you feel you’re in a Groundhog Day of endless windward work.
As expected, the already legendary Denis Doyle with the handsome big 47ft white Moonduster was soon in the lead, and steadily pulling away in stately style in this race back to his home port. But the much smaller Sarnia was like a terrier to windward, while providing a very rapid tutorial in offshore racing for her young crew.
 The “stately Moonduster” at the Rock in the 1969 Fastnet Race. In 1967, she took Line Honours in the RORC Beaumaris to Cork Race, but the new Sarnia won on corrected time
The “stately Moonduster” at the Rock in the 1969 Fastnet Race. In 1967, she took Line Honours in the RORC Beaumaris to Cork Race, but the new Sarnia won on corrected time
The evening and night were the second day, as the good book says, as they got to Crosshaven in the gathering dusk without another boat in sight ahead or astern. After mooring up in those pre-marina days, they were taken ashore by the club launch to what everyone still thought of as the Royal Munster YC, even if for the three months since March 1967 it had been the Royal Cork Yacht Club incorporating the Royal Munster Yacht Club.
Whatever the name, Denis and his crew from Moonduster were comfortably at dinner in the club as Sarnia’s exhausted young team came into the clubhouse “looking like drowned rats” as Frank recalls. “Denis immediately realised that we had beaten him, and brought the six of us dripping wet to the bar, and bought us a congratulatory drink. A true gentleman and a great sportsman”.
Apart from the classic Crosshaven welcome, another important part of a visiting winner’s reception was the mandatory photo for what was then The Cork Examiner, and thus we have this enduring record of Sarnia’s young crew, now well tidied up but still somewhat bemused by the extraordinary capabilities of this new boat that John G Sisk had found for them.
But the late 1960s were a time of very rapid design development, and while Sarnia was fine for the Irish Sea, in Cowes the likes of English owners like Max Aitken and Derek Boyer had now adopted Sparkman & Stephens designs with full chequebook yachting ferocity, and the resulting one-off high-spec “Terrible Twins” – Roundabout and Clarionet – were pretty well unbeatable in the Solent One Ton Class Challenges.
 Raw power. The new Finot-designed Half Tonner Alouettte de Mer for the Sisk family arrives in Dun Laoghaire unpainted – and she sailed her first season to win the Irish Sea championship without a lick of paint
Raw power. The new Finot-designed Half Tonner Alouettte de Mer for the Sisk family arrives in Dun Laoghaire unpainted – and she sailed her first season to win the Irish Sea championship without a lick of paint
 Alouette de Mer painted a bright red for her second equally successful season
Alouette de Mer painted a bright red for her second equally successful season
But in any case, having tasted one leap forward in design development, the Sisk brothers were keen to try another, and Hal, in particular, was bringing to the following of the development of new designs the same dedicated research he now devotes to yachting history (he’s the Chairman of the International Association of Yachting Historians), such that in June 1971 the brothers took delivery of the very new Finot-designed Half Tonner Alouette de Mer which - very appropriately - translates as Sea Lark.
Built in France in aluminium, she was so new that there hadn’t been time to give her a lick of paint, but in her raw state they raced her to the overall championship winner in the Irish Sea, a boat so interesting that one Sunday in July 1971 I’d made a point of sailing over to Dun Laoghaire to have a proper look at her.
This was suitably rewarding, but even more rewarding in retrospect was that James McAsey, owner of the 1894-built Peggy Bawn since 1919, was taking her out for what may have been his first sail of the season, for Mr McAsey was well stricken in years, and didn’t believe in rushing things. And it meant that by purest chance, we were witness that day at the same time to the most innovative offshore racer with which Hal Sisk was ever involved, yet we also saw the already ancient Peggy Bawn sailing three decades and more before Hal took her over and created one of the finest classically authentic yacht restorations ever seen.
 This page from the August 1971 Irish Yachting & Motorboating (the direct predecessor to Afloat Magazine) has the remarkable coincidence of featuring the Sisk family’s new Half Tonner Alouette de Mer, and the 1894-built Peggy Bawn being taken for a sail in Dun Laoghaire by then-owner James McAsey, her “custodian” since 1919. In 2005, Hal Sisk’s award-winning restoration of Peggy Bawn was completed in Dunmore East by Michael Kennedy
This page from the August 1971 Irish Yachting & Motorboating (the direct predecessor to Afloat Magazine) has the remarkable coincidence of featuring the Sisk family’s new Half Tonner Alouette de Mer, and the 1894-built Peggy Bawn being taken for a sail in Dun Laoghaire by then-owner James McAsey, her “custodian” since 1919. In 2005, Hal Sisk’s award-winning restoration of Peggy Bawn was completed in Dunmore East by Michael Kennedy
The Sisk brothers subsequently went through several very fine offshore racers including the great Imp, and Frank Larkin raced on them all. But meanwhile, Sarnia was ploughing her own proud furrow, and after she’d been owned for a while by Dennis O’Sullivan of Monkstown on Cork Harbour (since noted as a Laser Grand Master-plus), she was bought by Sam Dix of Malahide in 1975 and based at Howth. There, the young Robert Dix frequently sailed her to many successes, though he does admit that participation in the hyper-light 1977 Fastnet Race with a crew of his father Sam, himself, his brother David, Richard Burrows, Jock Smith, Graham Smith, and Vincent Wallace definitely came under the “learning experience” category. But they finished nevertheless with a boat which had become part of the family, and as Robert Dix went on to win Class 1 and lead all the Admirals Cup boats in the 1981 Fastnet Race with Ken Rohan’s Regardless, it was undoubtedly a learning experience of real value.
 A youthful Robert Dix helming Sarnia to a neat pier start off Howth Harbour on a Wednesday evening cruiser race in 1976. Despite several significantly larger boats racing that night, Sarnia was comfortable first on the water at the first mark. Photo: W M Nixon
A youthful Robert Dix helming Sarnia to a neat pier start off Howth Harbour on a Wednesday evening cruiser race in 1976. Despite several significantly larger boats racing that night, Sarnia was comfortable first on the water at the first mark. Photo: W M Nixon
Becoming part of the family seems to be the key to Sarnia’s seemingly effortless longevity, and in modern times it is the Creedons of the National Yacht Club – Michael Creedon father and son – who have happily taken on the custodianship. The TLC which Sarnia relishes was particularly in evidence in Dingle in 2005 when she won the Cruisers Class in the Dun Laoghaire to Dingle Race, for she was positively and deservedly glowing in the Berth of Honour at the entrance to Dingle Marina.
 Sarnia in 2005 in Dingle, glowing with success after winning the Cruiser Division in that year’s National YC Dun Laoghaire to Dingle Race. Photo: W M Nixon
Sarnia in 2005 in Dingle, glowing with success after winning the Cruiser Division in that year’s National YC Dun Laoghaire to Dingle Race. Photo: W M Nixon
Now she is afloat again, and ready for her 55th season. Those who feel there won’t be a proper season at all until mid-August if at all, what with all the COVID-19 cancellations, would do well to close in on that little bit of copy in the August 1971 Ireland Afloat. If we could make it up as we went along way back in 1971 because the weather was better than it had been for three years (now there’s a problem), then surely we can do the same now, provided we accept that crowds ashore indoors won’t be part of the package? Here it is in close-up:
 We should be so lucky – back in 1971, the programme was being adjusted at very short notice because of exceptionally good weather in the best summer for three years
We should be so lucky – back in 1971, the programme was being adjusted at very short notice because of exceptionally good weather in the best summer for three years
The generally accepted view of the 1950s in Ireland is of an economically grim period when everything - including the spirit of the inhabitants - withered in the face of a seemingly permanent financial recession, with desperate emigration the only solution for many young and sometimes not-so-young people. And in sailing, even though the early years of the decade had seemed a time of hope, with the new vision of the 1946-founded Irish Dinghy Racing Association still in the ascendant and people like Douglas Heard and Freddy Brownlee of Dun Laoghaire ordering the exciting new offshore racers Huff of Arklow and Flying Fox from the design board of the innovative Uffa Fox, the underlying trend was soon going downwards.
The nadir was reached in 1954-1956, when the American dollar was high against the pound that was then the Irish currency, and a connection to America saw the disposal for short-term profit of what was virtually an entire flotilla of some good Dun Laoghaire-based yachts to new American owners.
Baltimore-built 6-ton yawl Evora
Inevitably there was a typically Irish upside to this, as the decidedly individualistic businessman Dermot Barnes, having found a lucrative American buyer for his attractive John Kearney-designed 1936 Baltimore-built 6-ton yawl Evora, reckoned that the most economical way to comply with the purchase requirement for the boat be shipped to America was to get a keen young crew to sail her across the Atlantic.
 Dermot Barnes 30ft John B Kearney yawl Evora in Dun Laoghaire in 1954 shortly before she sailed for America under the command of Michael O’Herlihy of Hawaii Five-O fame. Photo: Dick Scott
Dermot Barnes 30ft John B Kearney yawl Evora in Dun Laoghaire in 1954 shortly before she sailed for America under the command of Michael O’Herlihy of Hawaii Five-O fame. Photo: Dick Scott
The delivery skipper was a determined guy called Michael “Styx” O’Herlihy, who had ambitions in showbusiness. Having reached the Promised Land with Evora, he promptly headed on west for Tinseltown, and became a huge success in television as a producer and director with Gunsmoke, Maverick, Star Trek, Hawaii Five-O, M*A*S*H, the A-Team and other top shows which one daren’t acclaim out loud for fear of age-recognition.
Meanwhile, Evora stayed on America’s East Coast for a while, but then someone with the west in their eyes took her away to sail round the world. The little Baltimore-built boat did well, as she got right across the Pacific to north Australia. But there the funds ran out, for in 1991 an Irish crew - voyaging round the world in some comfort in a Hallberg Rassy 46 – came upon her looking rather sorry for herself in Darwin.
It was a sad sight, yet it was also a reminder that back in the later 1950s, for most people all of Ireland was reckoned to be a sad sight. Yet when you consider some of the international businesses which were building on hard-earned success from a narrow Irish base during the 1950s, you can’t help but think this gloomy view of Ireland resulted from an unnecessarily negative groupthink which definitely wasn’t shared by everyone, yet was shared by enough for significant numbers to up-sticks and seek their fortune elsewhere.
Sparkman & Stephens-designed Gaia 36 Sarnia
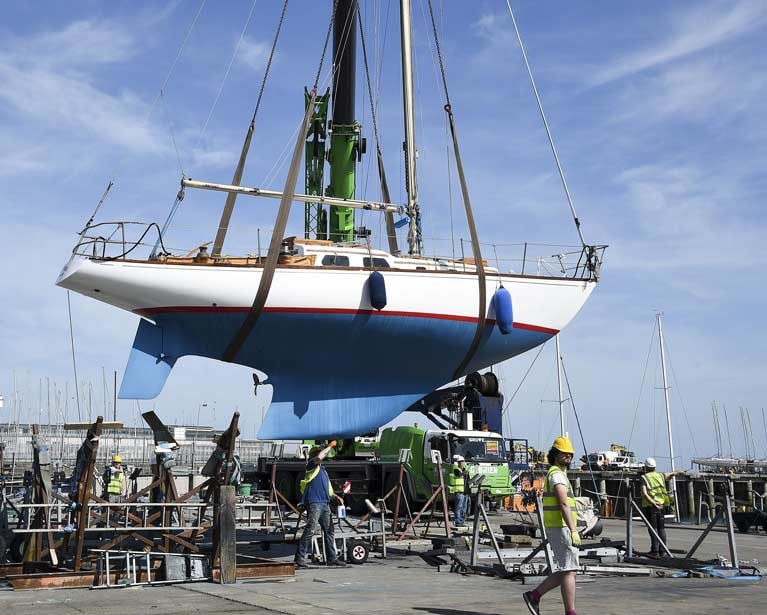
As for those who stayed behind and made their way as best they could, we can see them as either dully unadventurous or quietly heroic. The quietly heroic were those who managed to build up businesses in that arid time, and it was as the photos by Michael Chester of last weekend’s lift-in at the National YC came up on the screen that there came a vivid reminder of one of the quiet heroes. For among the forty boats being heaved afloat in a remarkable day’s work, there was the 36ft Sparkman & Stephens-designed Gaia 36 Sarnia, now all of 54 years old, yet looking better than ever under the caring ownership of Michael Creedon.
 Class shows. Michael Creedon racing Sarnia.
Class shows. Michael Creedon racing Sarnia.
John Sisk
She was built as part of a series-production in Livorno in Italy by Cantieri Benello in 1966 for John G Sisk (1911-2001). He wasn’t quite the father of all the Sisks, for there were Sisks of significance in the building trade from the mid-1800s in Cork, where they built the majestic City Hall in 1930. But it was this John Sisk who, in the difficult business climate of the later 1930s at the age of just 26, decided to move the company’s main focus of operations in 1937 to Dublin, where he’d been in school at Clongowes Woods.
Gradually he built the business through the patient winning of major contracts for hospitals, cathedrals and bridges, such that by the late 1940s the company was the first in Ireland to sign major construction contracts for more than a million pounds apiece.
Yet it wasn’t all work. In Cork the family had been into boats and even when Dublin-resident they continued to holiday at Crosshaven. But while his father and grandfather had been content with commissioning new pleasure craft from local boatbuilders around Cork Harbour, in Dublin young John G Sisk became an investor in a yacht building enterprise called the Dalkey Shipyard Company, which despite its name was based at the head of the West Pier in Dun Laoghaire.
 A beacon of hope in wartime. The plans of the 38ft Cheerful Maid designed in 1943 by Robert Clark for John Sisk, as published in London in the Spring 1945 issue of The Yachtsman
A beacon of hope in wartime. The plans of the 38ft Cheerful Maid designed in 1943 by Robert Clark for John Sisk, as published in London in the Spring 1945 issue of The Yachtsman
 The classic profile of an offshore racer until the benefits of a separate vertical rudder were appreciated, as seen in the hull profile and accommodation of Cheerful Maid
The classic profile of an offshore racer until the benefits of a separate vertical rudder were appreciated, as seen in the hull profile and accommodation of Cheerful Maid
Robert Clark-designed sloop-rigged Cheerful Maid
Subsequently, it became the Dalkey Yacht Company and was best known for building a number of Folkboats long before the class became ubiquitous in Ireland. But in 1949 and again in 1954, it also built two substantial yachts for John G Sisk himself, the 38ft sloop-rigged Robert Clark-designed sloop-rigged Cheerful Maid in 1949, and the 41ft 6ins Knud Reimers-designed yawl Marian Maid in 1954.
The order for the design of Cheerful Maid was placed with Robert Clark in London in 1943, when there certainly was a world war going on. But John Sisk and Robert Clark seemed determined to maintain some semblance of a more normal life, so much so that the completed design appeared in the London-published Spring 1945 edition of the then-quarterly magazine The Yachtsman.
 Cheerful Maid ashore for the winter in Dun Laoghaire in 1951
Cheerful Maid ashore for the winter in Dun Laoghaire in 1951
This was all of six months before World War II ended in Europe, but such things were encouraged to a limited extent by the authorities as morale-boosting, for we can be quite sure that those fighting by sea and land would have devoured any information about the new boat as a harbinger of peacetime sailing.
 Despite the acute post-war shortages of material, the yacht-builders of Dun Laoghaire managed to build Cheerful Maid to the high standards required for her topside to be varnished
Despite the acute post-war shortages of material, the yacht-builders of Dun Laoghaire managed to build Cheerful Maid to the high standards required for her topside to be varnished
Knud Reimers-designed yawl Marian Maid
Cheerful Maid, when she finally appeared in Dublin Bay in 1949, was classic Robert Clark, a witch to windward but a bit of a handful downwind with that heavily-raked rudder. For his next boat Marian Maid. John Sisk went for a less-raked rudder with some flat along the bottom of the keel, but the main interest in this new Dun Laoghaire-built Maid was that she was designed by Knud Reimers of Sweden to the new International 8 Metre Cruiser-Racer Rule, which had been mainly devised by James McGruer of Scotland.
 John Sisk’s 8 Metre Cruiser-Racer Marian Maid was designed by Knud Reimers of Sweden, and built in Dun Laoghaire in 1954
John Sisk’s 8 Metre Cruiser-Racer Marian Maid was designed by Knud Reimers of Sweden, and built in Dun Laoghaire in 1954
Another Dublin Bay owner, Peter Odlum, had gone to McGruer for his boat to the new class, Namhara which was number 5, but John Sisk had a very European outlook, and getting a Swedish design was typical of his approach. However, although he sailed from the National Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire, and continued to maintain his membership of both the Royal Cork and the Royal Munster in Cork, he was a busy man in work and somewhat reserved too, with a strong focus on family life.
Thus the energetic social and sporting scene of Dun Laoghaire sailing wasn’t really his thing, and his time afloat was largely a private affair, such that his son Hal observes that while he loved sailing, he wasn’t all that keen on racing despite having competitive racing boats, as he felt it sometimes brought out the worst in people.
Yet although he could be a prodigiously hard worker, he’d a company rule that all senior managers and specialists in the now-large Sisk organization should retire at the age of 60. So by the time the 1960s had arrived, he was in the count-down phase of handing over the reins to his oldest son George, with key roles in the company also being fulfilled by his other sons John and Hal, with the latter bringing a special marine expertise through spending his college years at the University of Delft in The Netherlands.
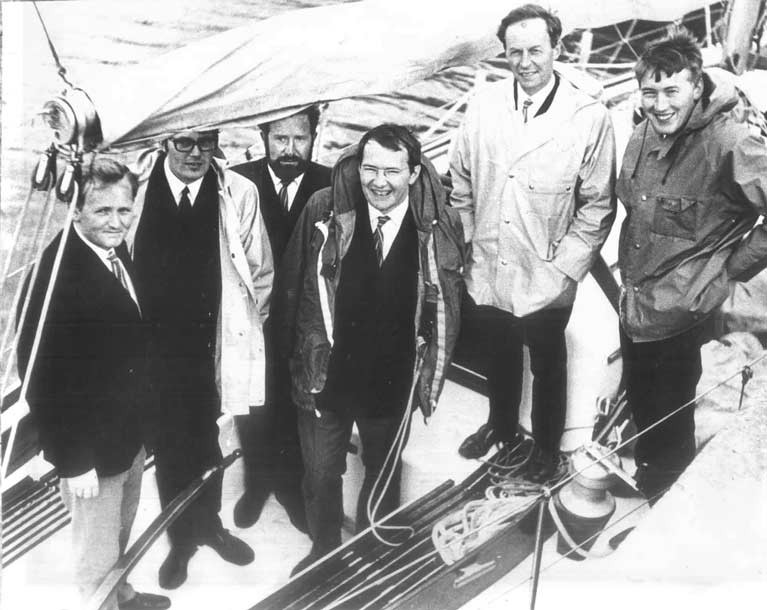
 John G Sisk (second left) with his sons John, George, and Hal on the occasion of his receiving the Lifetime Achievement Award of the Institute of Building. At the age of just 26 in 1937, he had moved the main focus of operations of the Sisk company from Cork to Dublin and had gone on to build it into one of the largest construction companies in the state with extensive international operations. But despite his exceptional work ethic, he retired at age 60, as he always said he would.
John G Sisk (second left) with his sons John, George, and Hal on the occasion of his receiving the Lifetime Achievement Award of the Institute of Building. At the age of just 26 in 1937, he had moved the main focus of operations of the Sisk company from Cork to Dublin and had gone on to build it into one of the largest construction companies in the state with extensive international operations. But despite his exceptional work ethic, he retired at age 60, as he always said he would.
Thus it was something of a joint family enterprise in selecting a new Sisk yacht for the mid-1960s, but the head of the family was ahead of the game in that he’d been in correspondence with designer Olin Stephens of New York, whose work he greatly admired.
Olin Stephens
The relationship between Sparkman & Stephens of New York and the offshore racing scene in Britain (and Ireland by extension) had not always been smooth. For although the very young Stephens brothers Olin and Rod and their indomitable father Roderick Senr had brought the all-beating Dorade to England in 1931 to win the Fastnet Race - which the brothers on their own then won again with Dorade in 1933 - no useful European design orders resulted from the campaign.
On the contrary, the result was less than pleasant. In 1933-34, Yachting World magazine ran a competition for a substantial yacht to the new 55ft rating rule of the Royal Ocean Racing Club, and the winner was a 72ft yawl designed by Olin Stephens. The detailed winning plans were published in the magazine in the best Yachting World style, and a Scottish whiskey magnate and notorious big game hunter after ivory (he proudly claimed to have killed more than a thousand elephants) promptly lifted the plans and took them to the noted steel trawler builders Hall, Russell of Aberdeen, and asked them could they build this boat in steel.
Trenchemer as she was to be called – named after William the Conqueror’s flagship of 1066 – was virtually finished, with her enormous spars well on their way to completion by McGruer’s on the Gareloch in their renowned spar shop, by the time Olin Stephens got to hear about it all. He felt badly done by, for apart from his rather shabby fee-avoidance treatment, he said that he could already think of several improvements he would have made to the design had he been involved in the building from the start.
 Olin Stephens at the height of his success in the 1960s. In 1934 while still building his career, he had felt rather bruised by the way he had been treated over the “abducted” designs for the 72ft Trenchemer
Olin Stephens at the height of his success in the 1960s. In 1934 while still building his career, he had felt rather bruised by the way he had been treated over the “abducted” designs for the 72ft Trenchemer
The big game hunter claimed that as the design had been published as the result of an open public competition, he felt it was in the public domain, for use by anyone. In time, some sort of settlement must have been reached, for when the new Trenchemer’s details were eventually published in Lloyd’s Register, Olin J Stephens was acknowledged as the designer. But the whole business left an unpleasant taste, which meant that when the Stephens brothers brought the new Stormy Weather to England for the 1935 Fastnet, they took quiet satisfaction from clearly beating all the newest British designs, although they probably had mixed feelings from trouncing Trenchemer too, but her navigation was all over the place as the compass adjusters had been unable to fully offset the effects of the big steel hull.
 The 54ft Zeearand was Sparkman & Stephens first proper European design commission and won owner Kees Bruynzeel of The Netherlands the 1937 Fastnet Race
The 54ft Zeearand was Sparkman & Stephens first proper European design commission and won owner Kees Bruynzeel of The Netherlands the 1937 Fastnet Race
After this third Fastnet win, they did finally get a proper design commission from the European side of the Atlantic, but it was from the Dutchman Kees Bruynzeel who was building a plywood manufacturing empire, yet found the time to commission and campaign a handsome new 54ft S&S design called Zeearand in the 1937 Fastnet race, and he duly won.
By this time Sparkman & Stephens were so busy with the expansion of their business in America and elsewhere that they didn’t need to expend unnecessary energy on cultivating a British clientele, and in Europe while they had a presence with a few boats in the Mediterranean, in northwest Europe they weren’t really centre stage again until 1959, when discerning Dutch owner Hendrik van Beuningen ordered the 35ft Hestia (she was S & S Design 1478, business was booming), and cut a mighty swathe through RORC racing and Cowes Week.
 Business is booming, The good-looking and very fast 35ft Hestia of 1959 was design number 1478, and put down a serious marker for the new range of S&S designs in Europe
Business is booming, The good-looking and very fast 35ft Hestia of 1959 was design number 1478, and put down a serious marker for the new range of S&S designs in Europe
 Hestia’s hull profile provided a very potent windward performance, but she was a handful downwind, and during the period 1962-65, Sparkman & Stephens developed a more manageable fin-and-skeg profile for their new production 36 footer
Hestia’s hull profile provided a very potent windward performance, but she was a handful downwind, and during the period 1962-65, Sparkman & Stephens developed a more manageable fin-and-skeg profile for their new production 36 footer
But by this time, yacht design was going into a fast-development stage, with the fin-and-skeg designs of Dick Carter coming successfully down the line in the wake of pioneering work by Ricus van der Stadt. Although the first S&S fin-and-skeg was the 43ft Deb (later Dai Mouse III, later Sunstone) in 1963, the skeg-hung rudder in this case looked like an afterthought rather than an integral part of the design.
Thus the traditional closed profile shape with the rudder now at an almost ludicrous angle was still the norm when the S&S-designed 43ft Clarion of Wight won the Fastnet Race for English owners Derek Boyer and Derek Miller in 1963.
So it was that, having first made their mark with the Fastnet win in 1931, after 32 years Sparkman & Stephens had become an overnight success in England. They were finally making their mark with the British offshore racing establishment, for although the difference between the RORC and Cruising Club of America rating rules had been seen as a barrier, ever since Bruynzeel’s Zeearand in 1937 the S&S team had shown they could create winners for European owners racing under the RORC rule.
 Hull profile of the 1963 Fastnet Race winner Clarion of Wight, “bringing overnight success to Sparkman & Stephens in Britain after only 32 years….” The main part of the race involved heavy windward work, so the downwind disadvantage of her much-raked rudder was not a significant problem
Hull profile of the 1963 Fastnet Race winner Clarion of Wight, “bringing overnight success to Sparkman & Stephens in Britain after only 32 years….” The main part of the race involved heavy windward work, so the downwind disadvantage of her much-raked rudder was not a significant problem
 Clarion of Wight racing for Ireland under Rory O’Hanlon’s ownership in the 1971 Fastnet Race, when she won the Philip Whitehead Cup. By this time – as is just visible - she had been changed to fin-and-skeg configuration
Clarion of Wight racing for Ireland under Rory O’Hanlon’s ownership in the 1971 Fastnet Race, when she won the Philip Whitehead Cup. By this time – as is just visible - she had been changed to fin-and-skeg configuration
Yet it wasn’t until the mid-1960s that this was finally accepted, and it was accepted for other rules as well. From Scotland, Peter Wilson ordered a new 8 Metre Cruiser-racer, to be called Nan of Gare, from Sparkman & Stephens. Fortunately, relations had already been smoothed with McGruer’s building the S&S designed Deb in 1963, for they were also to build Nan. But it may well be the Trenchemer bruising of 1934 still rankled, for having completed the design with Nan of Gare getting her first of many wins, Olin Stephens wrote a somewhat waspish critique of the International 8 Metre Cruiser/Racer Rule
For John Sisk in Dublin, this sudden rush to acquire a Sparkman & Stephens design threatened to de-rail his own developing relationship with Olin Stephens, but he needn’t have worried. The great designer wrote personal letters to Dublin revealing his concerns at making a proper change from an angled rudder on the back of the keel to a vertical and much more effective skeg-hung rudder which nevertheless looked as though it was an integral part of the whole concept, and he told of how they were working on a 36ft hull working on the basic canoe body which had proven such a success with Hestia, but with a new concept in the way the skeg-hung rudder blended with the whole.
 John G Sisk in retirement. As planned, he retired at 60, and had thirty years of retirement, “always interested in life and often rather amused by it”.
John G Sisk in retirement. As planned, he retired at 60, and had thirty years of retirement, “always interested in life and often rather amused by it”.
He further revealed that a new company in Finland was hoping to mould boats to this design, but meanwhile his long-established relations with Italy meant the design – which in Finland was to become known as the Swan 36 – was coming into production in Italy as the Gaia 36 at an earlier date, albeit with a different coachroof and a special highly-engineered foam sandwich construction, and might John Sisk be interested in one of these?
For John Sisk in conference in Dublin with his sons George, Hal and John, this was all music to their ears. Their engineering outlook much preferred the greater rigidity of the foam build, they liked the sound of the builders, they were all for Italy, and by 1966 they were owners of the new 36ft S&S instant classic Sarnia, a very handsome yacht in an attractive shade of emerald blue, and a brilliant all-round performer.
Sarnia has been one of the most cheering things in Irish sailing ever since. It is good to know that such boats are among us, and it as entirely appropriate that she should emerge in such style from among the crowd last Saturday at the National YC, John G Sisk’s Dun Laoghaire club. Michael Creedon deserves every credit for being such a devoted custodian of a true classic.
Sisk's Wow Sails to Victory in DBSC Race
George Sisk's new Wow sailed to success in the Crusiers Zero divison of the Dublin Port sponsored Dublin Bay Sailing Club race this afternoon. The new J111 that sailed its first race in July's Volvo Dun Laoghaire regatta beat Vincent Farrell's Tsunami, a Beneteau 40.7, for the Bay's big boat IRC honours. Full results for the entire Dublin Bay Sailing Club race (for 23 JULY 2011) are below:
BENETEAU 31.7 Echo- 1. Fiddly Bits (Kevin Byrne et al), 2. Thirty Something (Gerry Jones et al), 3. Attitude (D.Owens/T.Milner)
BENETEAU 31.7 - 1. Prospect (Chris Johnston), 2. Magic (D.O'Sullivan/D.Espey), 3. Thirty Something (Gerry Jones et al)
CRUISERS 0 - 1. Wow (George Sisk), 2. Tsunami (Vincent Farrell)
CRUISERS 1 - 1. Gringo (Tony Fox), 2. Jalapeno (Dermod Baker et al), 3. Xtravagance (Colin Byrne)
CRUISERS 1 Echo - 1. Jura (Barry McCabe), 2. Gringo (Tony Fox), 3. Jalapeno (Dermod Baker et al)
CRUISERS 2 Echo - 1. Cor Baby (Keith Kiernan et al), 2. Smile (O'Connell/Healy/O'Sullivan), 3. Bendemeer (Lindsay Casey Power)
CRUISERS 2 - 1. Jawesome 11 (V.Kennedy/M.Dyke), 2. Smile (O'Connell/Healy/O'Sullivan), 3. Cor Baby (Keith Kiernan et al)
CRUISERS 3 - 1. Supernova (K.Lawless et al), 2. Asterix (Counihan/Meredith/Bushell), 3. Jammie Dodger (J.H & D.O'Neill)
CRUISERS 3 Echo - 1. Taiscealai (Brian Richardson et al), 2. Jammie Dodger (J.H & D.O'Neill), 3. Asterix (Counihan/Meredith/Bushell)
DRAGON - 1. Phantom (D.Williams/P.Bowring), 2. Susele (Michael Halpenny), 3. Sir Ossis of the River (D Bergin)
FLYING FIFTEEN - 1. Deranged (C.Doorly), 2. As Good As It Gets (Alan Balfe), 3. Snow White (Frank Burgess)
FLYING FIFTEEN - 1. Fflogger (Alan Dooley), 2. Snow White (Frank Burgess), 3. As Good As It Gets (Alan Balfe)
GLEN - 1. Glenroan (Terence Moran), 2. Glencree (J.Bligh/H.Roche), 3. Glenluce (D & R O'Connor)
IDRA 14 FOOT Race 2- 1. Dunmoanin (Frank Hamilton), 2. Squalls (Stephen Harrison), 3. Doody (J.Fitzgerald/J.Byrne)
IDRA 14 FOOT - 1. Squalls (Stephen Harrison), 2. Dart (Pierre Long), 3. Dunmoanin (Frank Hamilton)
MERMAID Race 2- 1. Jill (P.Smith/P.Mangan), 2. Kim (D Cassidy), 3. Aideen (B.Martin/D.Brennan)
MERMAID - 1. Kim (D Cassidy), 2. Jill (P.Smith/P.Mangan), 3. Aideen (B.Martin/D.Brennan)
PY CLASS - 1. R Tate (Laser), 2. Desmond McCarthy (Laser 1), 3. Orla Callender (Laser 1)
PY CLASS Race 2- 1. R Tate (Laser), 2. Desmond McCarthy (Laser 1)
SHIPMAN - 1. Macro One (Joseph Murray), 2. Whiterock (Henry Robinson), 3. Euphanzel lll (Louis McSherry et al)
SIGMA 33 - 1. Popje (Ted McCourt), 2. Leeuwin (H&C Leonard & B Kerr), 3. Gwili Two (D.Clarke/P.Maguire)
SQUIB - 1. Kookaburra (P & M Dee), 2. Little Bird (N Barnwell), 3. Pintail (M Muldoon & B Stevens)
SQUIB Race 2- 1. Little Bird (N Barnwell), 2. Nimble (Brian O'Hare), 3. Kookaburra (P & M Dee)
WHITE SAIL CRUISERS Echo - 1. Nirvana (Bernard Neeson), 2. Persistence (C. Broadhead et al), 3. Act Two (Michael O'Leary et al)
WHITE SAIL CRUISERS - 1. Act Two (Michael O'Leary et al), 2. Persistence (C. Broadhead et al), 3. Arwen (Philip O'Dwyer)

























