Displaying items by tag: Lough Corrib
Forum for Challenges Facing Lough Corrib Called For
Ireland’s second largest lake, Lough Corrib, faces so many challenges that it requires a forum for stakeholders, a weekend workshop has agreed.
This would facilitate co-operation between the many State agencies and voluntary groups working to protect the lake and river system, the workshop in Claregalway, Co Galway, agreed.
The “Who’s Who in the Corrib” workshop involved over 40 representatives from Galway city and county councils, the Environmental Protection Agency, Inland Fisheries, National Parks and Wildlife, universities and angling groups and Corrib Beo.
The workshop was facilitated by Dr Trish Murphy of Inishowen River Trust and Mark Horton of the Rivers Trust, with support from the Local Authority Waters Programme (LAWPRO).
Dr Bernadette White of LAWPRO discussed catchment plans and the potential for catchment forums in the new River Basin Management Plan for Ireland, due out by the end of 2023.
Corrib Beo says the workshop “discussed the challenges facing Lough Corrib - these included a loss of water quality, invasive species, climate change, lack of public awareness of the lake and a confused mosaic of State bodies”.
“People just don’t know ‘who is in charge’ of Lough Corrib,” the group notes.
“Based on the feedback, there was a strong sense that we need an entity with a holistic view, to mobilise the resources towards a common vision for the Corrib,” it says.
John Gibbons of Oughterard said at the public session that “the Owenriff River is dying before our eyes - we are on a race to the bottom of the Corrib!”.
Billy Kavanagh, East Corrib Alliance, stated that it was established by four angling clubs with the aims of improving water quality in our rivers, enhancement and restoration of habitat around these rivers, and trout stream development.
“We felt we had to do something as a matter of urgency, and we feel that the involvement of farmers/ landowners is of the utmost importance,” he said.
Micheál O Cinneide, co-chair of Corrib Beo, heralded the importance of a Corrib Forum, where agencies, council staff and voluntary groups could “share experience, set priorities and work on a long- -term plan for the management of the Corrib”.
Gerry Lydon of Corrib Beo thanked LAWPRO for the initiative.
“Corrib communities have been working locally for years, but we need a collective approach, leadership and shared learning,” he said.
The Corrib information day included an open session, where members of the public were able to meet the participants at their stands and learn about the many groups and projects working towards the protection of the Corrib.
“ The turnout showed a strong level of public interest and a mandate for LAWPRO to continue its work with Corrib groups and agencies,” Corrib Beo says.
Kayaking & Open Water Swimming Projects Get Funding Under €3.5M Scheme for Adventure & Rural Tourism
Kayaking in Carlow and swimming in Lough Corrib are among some 189 projects to benefit as part of a €3.5 million investment in adventure and rural tourism.
The State funding being rolled out in partnership with Fáilte Ireland under the Outdoor Recreation Infrastructure Scheme (ORIS) promises to further enhance Ireland’s natural amenities and support rural Ireland as a destination for adventure tourism.
Projects across every county have been chosen for investment of up to €20,000 under Measure 1 of the scheme. Funding for larger projects under Measure 2 and 3 of the scheme will be announced by Minister for Rural and Community Development, Heather Humphreys in the coming weeks.
Among the projects being funded in this round are improvements to river access to enhance the overall experience at Tullow Kayaking Club in Co Carlow (€20,000) and maintenance of the swimming area, including provision of lifebuoys, at Annaghdown Pier on Lough Corrib in Co Galway (€20,000).
River Habitat Enhancement Works Announced for Lough Corrib Catchment
Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) has announced details of 31 locations prioritised for river habitat enhancement works in the wider Lough Corrib catchment area.
Each of the 31 river channels has been prioritised for enhancement works based on its hydromorphological condition, which considers how far the state of the river had departed from its natural condition.
The prioritisation follows extensive consultation by the State agency with responsibility for the protection and conservation of freshwater fish and habitats with stakeholders, including local angling clubs, the National Parks and Wildlife Service and the Office of Public Works.
In addition to surveys of the river channels, a review of the physical and ecological characteristics of the watercourses in the catchment were carried out, including water quality and fish status analysis.
A high priority was given to channels with moderate and good water quality; as well as those with low fish status.
Speaking about the announcement, Barry O’Connor, director of IFI’s Development Programme, said: “Following significant research and consultation by IFI, this prioritisation list of 31 river channels sets out where the most urgent habitat rehabilitation works are required in the Lough Corrib catchment area, and will allow us to focus our resources on the areas that are in most need of help.
“This is in addition to the annual maintenance of priority salmonid habitats being conducted by IFI staff throughout the catchment, along with stock management, and weed control operations.
“All prioritised works will be included in our medium-to-long-term management plan for the Great Western Lakes, which is currently under development.”
It is proposed that the enhancement works will be completed over a five-year period, with some already underway at a number of top priority habitat sites.
Extensive preparations will take place for the remaining sites, subject to the availability of resources. These include:
- Landowner consultation and securement of consent.
- Preparation of a development plan for each site, followed by appropriate assessment to ensure that sensitive species and habitats are not adversely affected by the proposed works.
- Undertaking of fish surveys before works are undertaken and in the year after the works are carried out. Further monitoring surveys may also be carried out.
- Application for consent to the relevant authorities, followed by procurement of contractors and materials.
New Film Shows How Tree Went From Oak to Boat in Iron Age Replica Project
An oak tree’s transformation from trunk to replica iron age boat on Connemara's Lough Corrib has been filmed as part of a University College Cork (UCC) project.
Entitled "A New Logboat for Lough Corrib: The Pallasboy Project", the film was made over 20 months and documents how the logboat was modelled on a 2,400-year-old vessel found at the bottom of Lough Corrib.
The original was partially excavated and recorded by Karl Brady of Ireland's National Monuments Service's Underwater Archaeology Unit.
Photographer and former archaeologist Brian Mac Domhnaill’s film begins with the felling of an oak in the Vale of Clara, Glenalough, Co Wicklow in November 2017.
It closes with the boat’s maiden voyage at Knockferry, Lough Corrib in Galway in July 2019. The boat launch was hosted in partnership with Moycullen and Oughterard Heritage, and drew national media attention.
UCC archaeologist Dr Benjamin Gearey noted that the film documents the painstaking process of converting around two tonnes of oak tree into a close replica of a 2000 year vessel, and its joyous maiden voyage onto the waters beneath which the original still lies".
As Afloat reported last July, the replica was modelled on the sunken boat that measures some 7.5m long, 0.61m wide and 0.4m deep.
It was created by Mark Griffiths, as part of the Pallasboy Project, an international collaborative study established at UCC to investigate the crafting of prehistoric wooden objects and involving archaeologists, woodworkers and artists.
After the log was felled and the trunk prepared, Griffiths carved the replica over a period of 18 days at the Meitheal Mara community boatyard in Cork City, using a combination of replica prehistoric and modern tools.
The project was funded by the World Wood Day Fund via the International Wood Culture Society. The replica log boat has since been gifted to Moycullen Heritage Society.
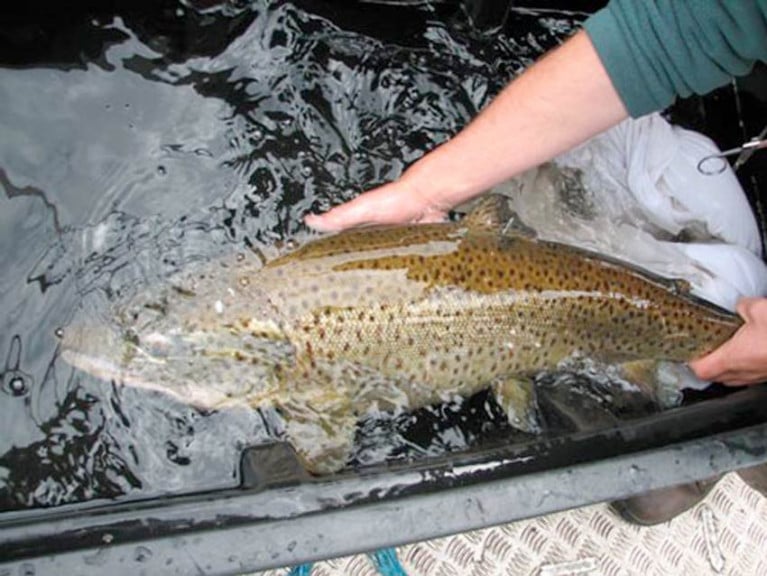
New Research on Ferox Trout Highlights Its Importance to Lough Corrib & Lough Mask
A newly published research paper co-authored by experts in Ireland highlights the importance of ferox trout to the fisheries of Lough Corrib and Lough Mask.
Ferox trout are highly prized by trophy anglers, and Loughs Corrib and Mask have recorded the majority of Irish specimens since angling records began in the 1950s.
The large, long-lived, fish-eating trout are normally found in deep lakes and are believed to be genetically distinct from normal brown trout, having evolved after the last Ice Age 12,000 years ago.
Little was known about the spawning location of Irish ferox trout compared to normal brown trout, and a radio tracking study was initiated in both catchments in 2005.
Local anglers and Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) staff helped catch large ferox trout on both lakes in order to insert radio tags.
The fish were released after tagging and then tracked with help from the Irish Air Corps helicopter unit and by walking spawning streams with a radio tracking antenna to determine in which streams ferox spawned.
Scientists from Inland Fisheries Ireland worked with colleagues at the Norwegian Institute for Nature Research on the data collected in this study.
Results from radio tracking showed that the majority (92%) of ferox trout tagged in Lough Corrib spawned in a single spawning stream, the Cong River, while the majority (76%) of ferox trout tagged in Lough Mask spawned in the Cong canal and Cong River.
These results, as published in the Journal of Fish Biology, indicate that these streams are most likely the principle spawning locations of ferox trout in both lakes.
Dr Paddy Gargan, senior research officer at Inland Fisheries Ireland and lead author on the publication, said: “The occurrence of ferox trout predominantly in single spawning rivers in both catchments highlights the vulnerability of the ferox populations with estimates of their population size thought to be small”.
IFI’s head of research Dr Cathal Gallagher welcomed the findings and said: “It was important that conservation measures, based on this research, have been introduced in the Corrib and Mask catchments continue to protect ferox trout.
“These conservation measures have reduced the number of ferox trout being killed and claimed as specimens and support the conservation of this unique trout.”
Life was simpler back in 1882 when the sailing folk of Galway Bay and the stunningly beautiful Lough Corrib inaugurated the Galway to Cong race the length of the great lake writes W M Nixon. People didn’t have cars, and still less had they efficient road trailers. So if you raced the whole way from Galway up the lake to Cong, you then had to expect to sail back again, and you’d have covered at least 60 miles by the time the day was out, though it’s likely they made at least two days of it.
But now with modern road trailers and dinghies dominant, complex logistics enter the equation. Since its revival in 1972, the race has been just one way – southwards from Cong to Corrib Village in Galway city. In order to ensure a smooth state of affairs after the finish, competitors are offered the option of leaving their boats by road at Lisloughry beforehand, then leaving their cars and trailers at Corrib Village where a bus will be on hand early in the Saturday morning to get them back to their waiting boats in Cong.
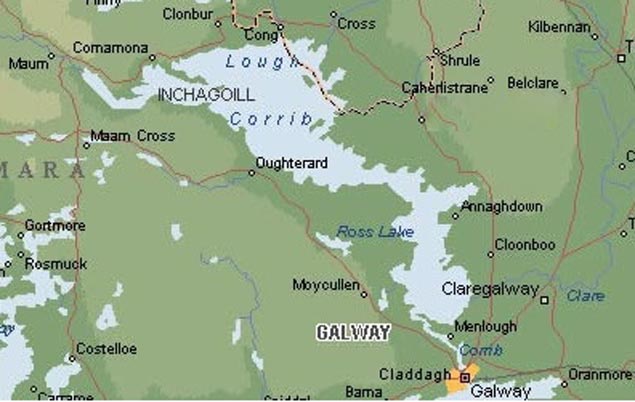 The basic shape of Lough Corrib indicated in this plan gives some idea of the length of Saturday’s race, but doesn’t fully reveal the lake’s island-studded nature (below) Photo: W M Nixon
The basic shape of Lough Corrib indicated in this plan gives some idea of the length of Saturday’s race, but doesn’t fully reveal the lake’s island-studded nature (below) Photo: W M Nixon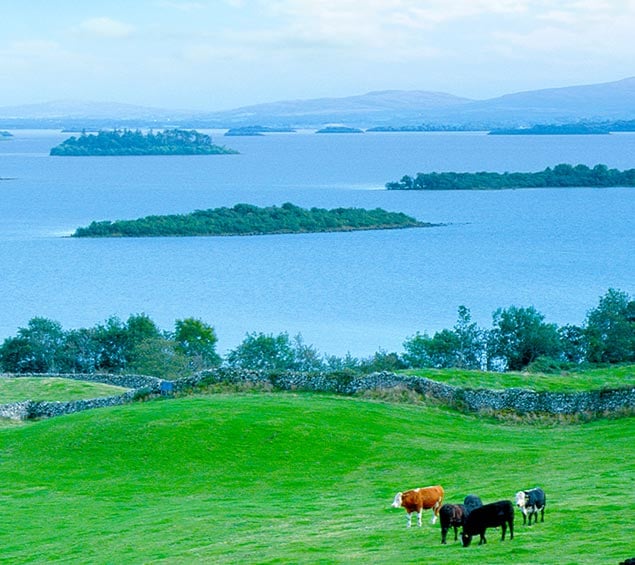 Not only is the race now a convenient half size in length (though still all of 30 miles), but there’s a pit stop for lunch and conviviality at Kilbeg, more or less halfway down the lake where the expansive Corrib is at its narrowest, and there’s a pub nearby. But the very fact that your car and trailer are waiting at the south end of the lake is a real spur to completing the event
Not only is the race now a convenient half size in length (though still all of 30 miles), but there’s a pit stop for lunch and conviviality at Kilbeg, more or less halfway down the lake where the expansive Corrib is at its narrowest, and there’s a pub nearby. But the very fact that your car and trailer are waiting at the south end of the lake is a real spur to completing the event
On the other hand, with people making last-minute decisions based on the fickle weather of 2019, maybe the handiest contact is direct to organiser John Barry, Rear Commodore (Dinghies) Galway Bay SC, at 086-8111269 – he reports that entries already in range from 420s to a selection of RS dinghies, participant ages are from 15 to 85, and there’s a strong female contingent taking on the challenge.
Meanwhile, the GBSC cruisers are recovering from their Summer Solstice Cruise to the Aran Islands at the weekend, which had a dozen boats taking part. While the sail round Inishmore on Saturday enjoyed Mediterranean conditions, Sunday brought driving easterly rain and a very damp beat home - all very character-building stuff.
Two Anglers Plead Guilty To Illegal Fishing Methods On Cong River During Annual Closed Season
Two anglers recently appeared in court on charges relating to illegal fishing methods on the Cong River and fishing during the closed season.
On Thursday 23 May, Mindaugas Jenkus of Claremorris, Co Mayo and Dalius Bureninas of Birr, Co Offaly appeared in front of Judge Mary Fahy at Clifden District Court in respect of breaches of fisheries legislation on the Cong River which occurred on 9 September 2018.
Both defendants represented themselves and pleaded guilty to strokehauling (using a weighted instrument or device with a rod and line or otherwise to foul-hook fish) and fishing out of season on the Cong River.
Bureninas also pleaded guilty to a further charge of obstruction under Section 301 (7) of the Fisheries (Consolidation) Act 1959.
Fisheries officer Paul Reynolds outlined the facts of the case to the court, while assistant fisheries inspector Barry Kelly also told the court that the Cong River was a very important salmonid fishery with has a large run of Atlantic salmon and a good stock of brown trout.
It is also of particular conservation interest in relation to ferox trout, for which the river is renowned.
The Cong River is one of the main tributaries of Lough Corrib, and is one of the most important salmon rivers in the west of Ireland
Fisheries inspector Pat Gorman stated that these offences were very serious due to the conservation status of the Cong River, when asked his opinion by Judge Fahy.
The judge commented on how serious a matter these offences were and referred to Bureninas giving a false name and address when lawfully demanded. She also noted that Mr Jenkus had a recent conviction for a similar fisheries offence.
Judge Fahy stated that if both defendants paid costs of €600 each to the court at a sitting of Clifden District Court on 26 September, she may deal with the matter by way of a somewhat reduced fine.
She also warned both men to be on their best behaviour and not to come to the attention of Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) again as there was a risk of a custodial sentence being imposed.
“The Cong River is one of the main tributaries of Lough Corrib, is one of the most important salmon rivers in the west of Ireland and provides habitat for a very unique salmonid sub-species, ferox trout,” said IFI chief executive Dr Ciaran Byrne when commenting on the case.
“The Cong River is closed to angling during September as a conservation measure relating to both Atlantic salmon and ferox trout. The river attracts many anglers and tourists annually to fish for these unique wild salmonid species.”
Galway Boating Clubs Unite For Historic Cong-Galway Sailing Race Across Lough Corrib This June
Sailors and boating enthusiasts from Galway’s sailing and boating clubs are coming together next month to follow their forebears in Europe’s oldest and longest inland sailing race.
On Saturday 29 June the fleet of dinghies will pit their wits against the elements and each other on the historic route along the length of Lough Corrib from Lisloughrey near Cong to Galway city.
Since 1882, sailors have raced the length of Lough Corrib. While the origin of the wager which prompted the first races is shrouded in myth and lore, the early races were hotly contested and a great social occasion.
They were very much a test of stamina as well as skill, with competitors completing a round trip of over 60 nautical miles from Galway to Ashford Castle and back again. It was raced annually until 1914 and the outbreak of World War I.
The race was revived in its current format, sailed in one direction from Lisloughrey to Galway, in 1972 and again became a stable in the Galway maritime calendar.
However, the weather gods have not been good to the race in recent years.
So, to ensure a successful event this year, the boating and sailing clubs around Galway have come together and moved the event to an earlier slot in the calendar.
It will take place this year on 29 June and follow the traditional steamer channel through the lake.
Full details of the race and the online registration are available on the Galway Bay Sailing Club website.
Transport will leave Corrib Rowing and Yacht Club and the Galway Commercial Boat Club at 8am to bring sailors to the start line in Lisloughrey. From there, the boats will make their way to Kilbeg for lunch and then continue on to the finish line in the lower Corrib.
However, the challenges don’t end there, with the Quincentennial Bridge providing a final obstacle to be negotiated — usually with the mast, sails and sailors in the water!
Following the race, there will be the chance to relive the decisive moments of the race at a reception hosted by the Commercial club after the historical silverware has been presented at CRYC.
Galway Bay Sailing Club has a link to the Notice of Race and Sailing Instructions, as well as the online registration form. For more details about the 2019 Cong-Galway Sailing Race, see the Facebook event page HERE.
Angling Centre Owner Convicted For Illegal Netting On Lough Corrib
The owner of an angling centre from Moycullen was convicted at Galway District Court last Tuesday 5 February for the illegal use of a net and for possession of an unlawfully captured trout.
The court heard that Michael Canney, with an address at Portarra Lodge, was approached by Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) fisheries officers on the morning of 25 June 2018 as he was hauling an illegal net into a lake boat on Lough Corrib.
Diorai Ford, solicitor acting for IFI, outlined to the court that fisheries officers had covertly kept the illegal net under surveillance throughout the night.
The net had been fishing since the previous evening when it was discovered during a routine fisheries patrol.
Canney was accompanied in the boat by a foreign student who was staying with him where he operates an angling centre.
When Canney retrieved the net into the boat, it contained one dead brown trout. While in the act of lifting the net, Canney was approached by a fisheries officer on a personal water craft.
Canney was co-operative throughout. The equipment used in the commission of the offences was seized and included a lake boat and engine.
Solicitor for the defendant, Sinead Fitzpatrick, stated in his defence that Canney had a group of Italian anglers staying with him at the time and he was undertaking a survey to see what fish stocks were in the area.
Judge Mary Fahy commented that she knew several people who fish legally on a regular basis on Lough Corrib and that Canney was a mature man and that he knew that what he was doing was illegal.
Judge Fahy convicted Mr Canney on both counts, and imposed a fine of €500 for the use of an unlawful net, along with a fine of €500 for the possession of an unlawfully captured trout.
Costs of €600 were awarded to IFI’s solicitor. The boat and engine that Canney used in the commission of the offences were also forfeited.
IFI chief executive Dr Ciaran Byrne said: “Lough Corrib is considered Ireland’s finest wild brown trout fishery and is also a Special Area of Conservation (SAC) designated for the protection of numerous aquatic species including Atlantic salmon.
“Lough Corrib attracts a vast number of anglers from all over the world who enjoy the unique angling for wild brown trout, Atlantic salmon, pike and coarse fish that the lake offers.
“This conviction reflects the long hours that dedicated fisheries officers spend on a daily basis in protecting our valuable fisheries resource.”
Fish Kill Confirmed On 5km Stretch Of Dublin’s River Tolka
#Angling - Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) has confirmed a fish kill on the River Tolka that was reported earlier this week.
Fisheries investigators found dead fish over a 5km stretch of the river in the Tolka Valley Park area, following the report on Tuesday 18 September.
According to IFI, a “significant source of polluting material has been identified” and samples were taken for analysis.
In the meantime “relevant parties are undertaking appropriate remedial action” as the investigation continues.
Also this week, Minister of State for inland fisheries Seán Kyne committed €300,000 for the removal of an invasive waterweed in Lough Corrib.
IFI will begin operations in 2019 to remove the aquatic plant Lagarosiphon major from the lough, after successful cutting and picking operations over the summer months this year.
In addition to these management operations, IFI commenced a research project last month which aims to establish the current distribution of L major in Lough Corrib.
New innovative methods are being trialled to survey the aquatic plant as part of this research. These include unmanned aerial drones, sub-aquatic remotely operated vehicles (ROVs) and modern remote sensing techniques.
Speaking as he visited IFI’s stand at the National Ploughing Championships, Minister Kyne also asked the fisheries body and his department to continue liaison with the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS), who have responsibility for the legislation covering Alien Invasive Species (AIS).