Displaying items by tag: Ocean
The Irish public believes more action needs to be taken to improve the health of the ocean, according to results from Ireland’s first Ocean Citizen Survey.
More than 1,000 people across the island of Ireland completed the Ocean Citizen Survey in 2020 and shared their views on current marine issues and priorities for the protection of the marine environment. The online survey was developed by the Marine Institute and the European Commission to encourage the people of Ireland to contribute to the EU Mission for Healthy Oceans, Seas, Coastal and Inland Waters.
92% of survey respondents strongly agreed that more action needs to be taken to improve the health of the ocean. The respondents strongly agreed (85%) that human actions are damaging the ocean and that the health of the ocean and their own health is connected (67%).
"89% thought the establishment of a European Ocean Agency was a good idea"
“The Irish public care strongly about the ocean and are important stakeholders in planning for its future,” said Dr Niall McDonough, Director of Policy, Innovation and Research Support at the Marine Institute. “It is valuable to have a current understanding of the Irish public’s perceptions and concerns which can be used to inform future research activities associated with these initiatives and policy developments in Ireland, and in Europe.”
The survey also asked the public which 15 marine environmental issues they were most concerned about, and ‘pollution at the coast or in the sea’ was the issue that was most frequently selected amongst the top three. From 14 suggested climate change and marine policy issues, the policy area that was selected the most frequently by the respondents amongst their top three for prioritisation by the European Union was ‘regulating the production, use and disposal of plastic to reduce marine plastic pollution’.
Survey results also indicate that 67% of respondents strongly agreed that economic growth and job generation can be supported by the ocean, seas and inland waters.
Outputs from the Ocean Citizen Survey will be used to inform the preparation of the next National Marine Research and Innovation Strategy, which will commence later this year. Citizen participation is also an important component of the forthcoming Horizon Europe Framework Programme, spanning 2021 to 2027. The information from this survey will feed into the further planning of the Mission on Healthy Oceans, Seas, Inland and Coastal Waters.
Dr McDonough added, “Citizens are crucial to the design and accomplishment of the EU Mission in helping to set objectives and targets and ensuring that missions like this one, make a real difference in everybody’s lives.”
The full report from Ireland’s Ocean Citizen Survey can be viewed online here
Key Findings from Ireland’s Ocean Citizen Survey:
- 85% strongly agreed that human actions are damaging the ocean.
- 92% strongly agreed that more action needs to be taken to improve the health of the ocean.
- 67% strongly agreed that the health of the ocean and their own health is connected.
- 67% strongly agreed that the ocean can support economic growth and job creation.
- 61% said marine pollution was one of their biggest concerns.
- 42% said ‘regulating the production, use and disposal of plastic to reduce marine plastic pollution’ is an issue to be prioritised by the European Union.
- 88% strongly agreed that marine environmental data collection is important.
- 46% consider that a high-resolution map of the ocean seabed is very important to society.
- 89% thought the establishment of a European Ocean Agency was a good idea.
Changing The "Conversation" on the Ocean Environment - Science & Art Combined For Multi-media Exhibition
Combined impacts of sea-level rise, intensification of maritime transport, depletion of coastal ecosystems and deep-sea mining are the theme of a new exhibition planned for the Italian city of Venice which aims to change the conversation about the ocean environment writes Lorna Siggins.
A projected image of Venice in the year 2050 if the global community lives up to the 2016 Paris Agreement forms part of the exhibition, opening in the Spring.
There are predictions that combined sea-level rise and land subsidence will flood the city built on 118 small islands entirely by the year 2100.
Effects of overfishing, bottom trawling, oil exploration and extraction, migration, changing ocean circulations, militarisation and melting ice are also traced by the research project, Territorial Agency, which is hosting the exhibition.
Bathymetry and fishing data from the “black Atlantic”, as in mid-Atlantic, the impact of shipping activity and oil licensing, and a multibeam sonar sounding of Reykjanes Ridge in the Atlantic are among images commissioned for the project.
It also draws on multi-beam sonar data for a view of the Pacific ocean floor, off the coast of Hawaii.
Other images include scenarios of sea-level rise overlaid on the rapid depletion of the coastal ecosystems of the Mississippi delta in the USA, the impact of rapid urbanisation in China on the Yangtze River plume near Shanghai, and fishing and trans-shipment data near the Nazca-Desventuradas marine park off of the coast of Chile.
Territorial Agency was founded by Ann-Sofi Rönnskog and John Palmesino as an independent organisation. It states that it combines “architecture, spatial analysis, advocacy and action” to influence change in the inhabited environment.
The project was informed and “catalysed” by sea-level rise, as the most visible sign of climate change, but investigates the changes in world oceans during the current geological era known as the Anthropocene.
It assesses latest scientific knowledge, based on a consensus that less than 20 per cent of ocean floors have been mapped, to emphasise the critical role of oceans in the planet’s survival.
“The oceans are changing very fast, yet knowledge of them is moving slowly and is enveloped in long-established forms of cultural separation and distinction between human activities at land and at sea,” they state, arguing that “this division needs to be rethought to address the urgent and vast transformations that the seas are undergoing”.
Oceans in Transformation, as the large scale multi-media exhibition is called,“rearranges the maritime space as a stage for human violence, empire and colonial history”.
The organisers will host parallel discussions with key players in environmental conversations and research, including scientists, artists, governmental and society groups, policymakers and conservationists.
The research project is Oceans in Transformation, is led by the architecture team "Territorial Agency’" The exhibition will take place at Ocean Space, Venice, from March 2020, and it is organised and commissioned by TBA21-Academy.
Learn to Skipper A Yacht Offshore
#offshore – Skippering a yacht on an ocean going passage is a serious undertaking requiring significant skills and experience. Getting those skills and experience has always been tricky and every year the rescue services are called out to assist yachts and skippers that have gone beyond their means.
Previously, a skipper looking to build ocean-going experience has had few options other than to join a delivery yacht or maybe crew on the ARC. This gave mileage and some experience, but was no substitute for expert tuition from ocean-going instructors.
To fill this skills gap, a UK sailing school operator, Rubicon 3 has launched a series of three Ocean Crossing Masterclasses, running between October and December 2015.
Based on Rubicon 3's specialised 60' expedition sailing yacht, each masterclass comprises an intensive two weeks of tuition at sea, taught by two instructors. The syllabus has been developed from their skippers' huge experience of expedition and ocean sailing and is a mix of practical and theoretical lessons on how to skipper a boat across an ocean. Every day sees a structured lesson plan, with all critical skills covered. These include route planning; weather routing; yacht preparation; fixes of common problems at sea; celestial navigation and heavy weather techniques, including practical demonstrations of storm sails, tri-sails, drogues and storm boards.
These masterclasses are open to everyone, with ten places on board each one. There are watch leader positions on each masterclass ideally suited for those looking to gain their RYA Ocean Yachtmaster qualifying passage.
Bruce Jacobs, director of the company said, "It's critically important that before skippering a yacht far offshore, you have the practical skills and experience to match your theory. Whether it's how and when to deploy a tri-sail, or conditions are getting nasty and it's time to launch a drogue - the first time you do it should not be the time you really need it. These masterclasses are the very best way to prepare yourself to skipper offshore and to vastly widen your cruising range."
Masterclass dates, routes & prices
Bristol, UK - Baiona, Portugal: October 18 - November 1, 2015. £1,395
Baiona - Madeira - Azores: November 7 - 22, 2015. £1,495
Azores - Madeira - Gibraltar: November 28 - December 13, 2015. £1,495
Kelly Resting Aboard Cargo Ship After Capsize
#ROWING – Ocean rower Aodhan Kelly is travelling the opposite direction to the one he expected this morning – but he is reported to be safe and well after a tumultous 24 hours. The Dubliner and the five other men in the crew of the Sara G were hoping to set a new record for rowing across the Atlantic from Morocco to Barbados, but they capsized at 11 am yesterday 520 miles from their destination.
The six men stayed in a life-raft t until rescued by the cargo ship the Nord Taipei. The 32,000 tonne craft is continuing on to Gibraltar and is due to arrive on February 9th.

The Sara–G at the start of her now ill-fated journey
The Sara G crew, headed up by the experienced skipper Matt Craughwell, were initally hoping to break what they called the “four-minute mile” of ocean rowing by crossing the Atlantic in under 30 days. But winds and sea conditions were much tougher than expected. They had battled on bravely, with the aim of setting a new record but it all went awry on the 27th day of the row.
The present World Record is held by the 2011 crew of the Sara G - including Craughwell and Irishmen Rob Byrne and Adam Burke – who travelled from Morrocco to Barbados in 33 days 21 hours and 46 minutes in 2011. The Hallin Marine had the shortest crossing, travelling from Tenerife to Barbados in 2011 in 31 days 23 hours and 31 minutes in 2011, but because the distance is shorter the Sara G was deemed the World Record holder by the Ocean Rowing Society.
Kelly, a 26 year old from Palmerstown in Dublin, learned his rowing with Neptune rowing club in Islandbridge for whom he won eight national titles, seven junior and one intermediate. In recent years he has been living and working in Reading in England.
Team Sanya Hitches a Ride to Capetown (Photo)
#SANYA– Definitely not as intended but neverthless on her way to Cape Town as our picture shows. The Discover Ireland backed Sanya entry in the Volvo Ocean Race has been successfully repaired and is ready to joing the other six yachts in the fleet. The 70-foot yacht suffered hull damage only hours into the race. Still to arrive is Puma, the third boat in the fleet to have suffered damage in the first leg.

Afloat again and heading for Capetown. Team Sanya is repaired and spotted on a cargo ship
Disaster Strikes as Puma Dismasted in Volvo Ocean Race
The rig onboard PUMA's Mar Mostro failed at around 15:00 UTC in the southern Atlantic Ocean, about 2,150 nautical miles from Cape Town, South Africa.
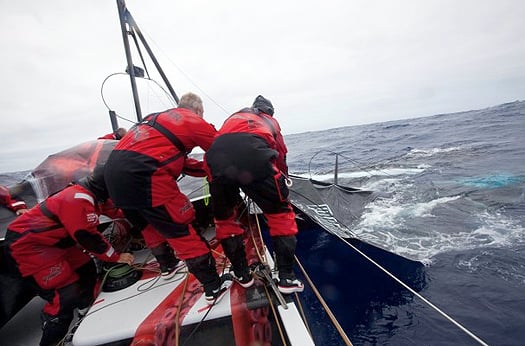
Puma crew try to retrieve the broken rig. Photo: Amory Ross/PUMA Ocean Racing/Volvo Ocean Race
Skipper Ken read reported: "We were sailing on a port tack, beam reaching in 22-23 knots of breeze, heading east northeast with eight to 10 foot waves when the mast failed. There were no warning signs.
"There was no panic onboard, and all crew are safe and well.
"Thanks to amazing seamanship, the three pieces of the mast and all of the sails were recovered. We haven't suspended racing at this point and are weighing up our options.
"At this point we are not using our engine, but are taking some time to clear our heads and evaluate next steps. Our plans may include heading to the island of Tristan da Cunha – about 700 nautical miles from us, nearly on the way to Cape Town.
"This is the saddest and most disappointed 11 people on earth. We were in a comfortable second position, traveling south to get into the final front and head across the southern Atlantic towards Cape Town.
"We were planning to be there in five days. At this stage, my goal is to make sure we get this crew back safely and we will look at options as to how to get back in this race."
The Brazilian search and rescue organization have been informed and are on standby to assist if necessary.
PUMA Ocean Racing's shore team is working on a recovery plan to ensure the yacht can rejoin the race as soon as practically possible and will work closely with Volvo Ocean Race to determine the cause of the dismasting.
Volvo Ocean Race control is in constant contact with the team to establish the full extent of the damage and ensure the crew are given full support to enable them to deal with the situation.
The causes of the dismasting are not known at this stage. However, the rig is of a different origin and manufacture to that of Abu Dhabi Ocean Racing's Azzam which suffered a failure earlier during Leg 1.
Further information will be issued as it becomes available.
Heineken Join Galway's Volvo Ocean Race –Video here!
#VOLVO OCEAN RACE – As plans progress to celebrate the end of the Volvo Ocean Sailing Race in Galway next June Heineken has won the pouring rights and the brewer is expecting to serve over one and a half million people during the course of the event.
They're expecting to attract over 200,000 people per day, for each of the eight days. The world race concludes with an In-Port Race and Pro-Am Race and the Prize Giving Ceremony. Thirsty work? Here's hoping! And Here's Heineken's promo video courtesy of youtube with VOR racer Jerry Kirby comparing the last Galway stopver to 'Woodstock'.
Emotional Walker Tells How Mast Broke (Video)
#ABU DHABI DISMASTING – "I knew there were going to be problems because my feet left the deck" skipper Ian Walker describes the moment of impact when his Abu Dhabi yacht hit a huge wave and lost its mast in the first hours of the Volvo Ocean Race. The team is back in port and are attempting to rebuild the mast and get going again. Hear the latest from an understandibly emotional Ian Walker dockside here:
Puma Skipper Ken Read heard about the dismasting and has chimed in with his take on the disaster, calling it a 'curse' for winning the first In-Port Race in the Volvo, which Abu Dhabi did.
Two races ago Ericsson won the first In-Port only to have keel ram problems and limped into Cape Horn. Last edition, Telefonica Blue won the first In-Port only to break part of their rudder assembly about an hour into the race and had to go in to port to fix it. Now Abu Dhabi.
Marine Minister Ends Up in Choppy Waters
#VOLVO OCEAN RACE – Ireland's Minister of the Marine Simon Coveney jumped ship on Saturday but it was no political volte face instead it was the expediency of Team Sanya's Captain Mike Sanderson who jettisoned the Fine Gael Cabinet Minister shortly after the start of the Volvo Ocean Race in Alicante.
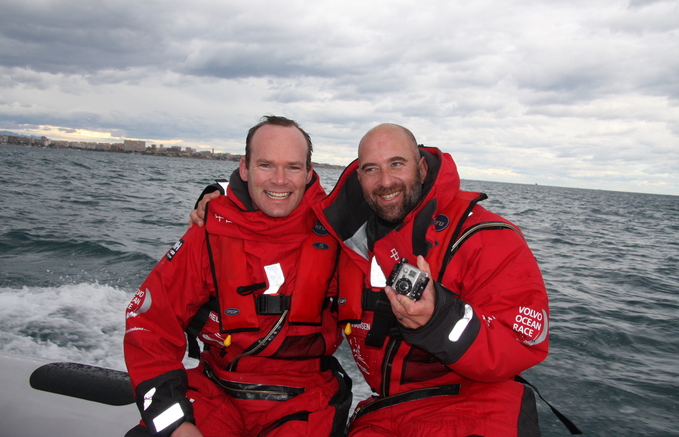

Minister Simon Coveney (left) and Sailing Anarchy Editor Alan Block in good spirits after going overboard from Team Sanya. Photo: Anders Soranio
Onboard Sanya guests for the start on Sanya included Coveney, a racing sailor himself, and Alan Block, Editor of Sailing Anarchy website. After the inshore couple of laps, they had to brave the elements and jump off the boat into the water and both ended up safely on Sanya's team rib.
As it turns out there was no rush and the guests could have sailed on with the Chineses entry. Within hours Sanderson was heading back to shore after suffering hull damage that looks like it's going to take a while to fix.
Coveney got the VIP seat for the race start because Discover Ireland is backing the Team Sanya entry for 25% of the campaign costs. The VOR finishes in Galway next July.
Discover Ireland Backed Yacht Suffers Hull Damage
#VOLVO OCEAN RACE – 24 hours in to the Volvo Ocean Race (VOR) and the fleet is reduced by one third. First Abu Dhabi was dismasted and now news is coming ashore that Team Sanya has suffered hull damage and is heading back for landfall.
Aksel Magdahl, Navigator on-board Team Sanya reported this morning had suffered hull damage on the first leg of the Volvo Ocean Race 2011-12, which began yesterday in Alicante.
The yacht is 25% backed by Irish tourism body Discover Ireland. The damage happened just 24 hours after Ireland's Minister for the Marine Simon Coveney left the boat shorly after the start of the race.
Mike Sanderson, Skipper has confirmed to Volvo Ocean Race Control that "The situation is very much under control, everyone is obviously disappointed but in good spirits as all are safe on-board," he said.
The boat was approximately 30 nautical miles SE of Motril, on the coast of Spain. The wind was blowing 43 plus knots and the waves were around 10.5 metres.
The watertight doors had already been closed as a precaution due to the prevailing conditions and the boat is making its way to Puerto de Motril. After entering flat water, Team Sanya has suspended racing.
Volvo Ocean Race control is in constant contact with the team while establishing the full extent of the damage so that the crew are given full support to enable them to deal with the situation.
Team Sanya's shore team are working on a recovery plan to ensure the yacht can rejoin the Volvo Ocean Race as soon as practically possible.
1300 hours Sunday: Mike Sanderson, CEO/Skipper of Team Sanya, updates us on the latest situation and his thoughts:So close to making it through the worst of the big breeze and then disaster struck. We were looking after the boat nicely when at approx 0900 this morning while going upwind in 35 knots of wind, suddenly the boat went really bow down and immediately we knew it wasn't good. Instantly we slowed the boat right down, got the remainder of the guys in their bunks into life jackets and then set about tacking over to head for shelter.
The water tight bulkhead is doing a great job, the pumps are running and we are nursing the boat with just a double reefed mainsail into port.
Right now we have no idea how major the damage is, we can however see a puncture wound on the port side and streams of carbon peeling off so it isn't good. We are all safe though, as I write this we are just an hour from a safe harbour. The guys are doing a fantastic job, all very positive and working incredibly hard even though you can see the bitter disappointment on all their faces.
Be under no illusion though, we will be back with vengeance.
I will let you all know as soon as we have checked our poor boat out in a few hours...