Displaying items by tag: RV Celtic Voyager
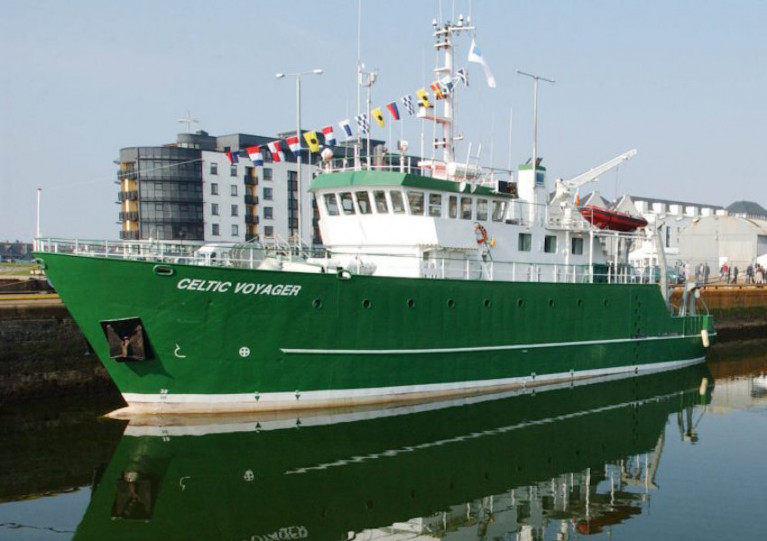
After 25 years in service with the Marine Institute, the RV Celtic Voyager is now going up for sale.
The RV Celtic Voyager came into service in 1997 as Ireland’s first custom-built multi-purpose research vessel. It has been central to the Marine Institute’s work and research, enabling Ireland as a nation to engage in high-quality marine science and to actively contribute to international research programmes.
The vessel has served the nation well over the past quarter of a century, providing marine scientists, researchers and crew members with many years of experience at sea and enabling us to deepen our ocean knowledge.
The research vessel has played an essential role in fisheries scientific research, and a vital role in seabed mapping in Irish waters as part of the INFOMAR programme.
More than 200 shipwrecks around the coast of Ireland, including the RMS Lusitania, have been mapped by the Celtic Voyager. In 2007, the survey of Galway Bay revealed for the first time a detailed seafloor and geology of the bay, confirming the location of the Galway Bay Fault.
The vessel is currently lying afloat in Howth, Co Dublin. Interested parties can contact the sole agent, Hanseatic Offshore Brokers (details below), to register interest and to arrange viewing. The closing date for registration of interest is Friday 1 September 2023.
Hanseatic Offshore Brokers GmbH
Große Bleichen 32,
20354 Hamburg, Germany
Mobile: +49 173 1 555 351
Email: [email protected]
Web: www.hanseaticoffshore.com
Survey of North Celtic Sea Next Month to Support Research on Carbon Capture
The Irish Centre for Research in Applied Geosciences (iCRAG) at University College Dublin will undertake its InStor survey to acquire data for leakage monitoring for carbon capture and storage in the North Celtic Sea next month.
Supporting ongoing research at iCRAG, the survey’s aim “is to investigate and characterise the existing seabed morphologies which are related to passive and active seepage of fluids, such as pockmarks and mounds, and to provide new high-resolution geophysical datasets along with geochemical data, which will be used to create an integrated baseline geological model and form the basis for understanding the current status of complex processes in the survey area.”
Weather depending, the survey will be carried out between 19 and 26 March by the RV Celtic Voyager (callsign EIQN) which will display appropriate lights and signals. Work will be performed in accordance with safe operating practices regarding MMO procedures and cognisant of fishing gear.
Coordinates of the survey area as well as contact details are included in Marine Notice No 13 of 2022, which is attached below.
Marine Notice: Multibeam & Side-Scan Sonar Survey Off South Coast
The Department of Transport advises that an analogue survey consisting of multibeam, side-scan sonar and magnetometer will be carried out off the South Coast of Ireland by the Marine Institute on behalf of Providence Resources from Saturday 23 to Sunday 31 October, weather permitting.
In addition to the analogue survey, seabed samples and camera imagery will be acquired at approximately 10 stations in the survey area.
The survey will be conducted in Block 48/24 Barryroe, in the North Celtic Basin, around 45–50km from the south coast of Ireland, and will be undertaken by the RV Celtic Voyager (callsign EIQN). The vessel will be towing a side-scan sonar and magnetometer from time to time with cables of up to 300m long.
As this vessel will be restricted in its ability to manoeuvre when surveying, other vessels are requested to keep a wide berth. The vessel will display appropriate lights and signals.
For details of coordinates of the survey area, see Marine Notice No 55 of 2021 which is available to download below.
SeaMonitor Survey Deploying ‘Listening Stations’ to Track Marine Wildlife in North Channel This Week
The next SeaMonitor survey will be carried out by the RV Celtic Voyager in the North Channel from tomorrow, Wednesday 29 September.
This latest stage of the project aims to deploy 80 acoustic listening stations (ALSs) across the North Channel from Malin Head in Ireland to the Isle of Islay in Scotland between over four days, concluding on Saturday 2 October.
These stations will allow recording the presence of tagged marine wildlife including salmon, seals, cetaceans, basking shark and skate species, and provide evidence for conservation measures.
The SeaMonitor project is already ahead of schedule, as previously reported on Afloat.ie, with researchers from Nova Scotia in Canada carrying out expert field work using large-scale acoustic telemetry equipment.
This week’s survey operations will be carried out during daylight hours to facilitate a safe deployment of acoustic receivers on the seabed. The RV Celtic Voyager (callsign EIQN) will display appropriate lights and signals throughout.
For details on relevant locations and contact information, see Marine Notice No 54 of 2021 which can be downloaded below.
Call for 2022 & 2023 Applications for Ship Time on Ireland’s Research Vessels Now Open
Applications are currently being accepted for ship time in on Ireland’s national marine science research vessels in 2022 and 2023.
In addition to the RV Celtic Explorer and RV Celtic Voyager, placements will also be available on the new RV Tom Crean which is expected to be operational in mid 2022 and will replace the RV Celtic Voyager.
The ROV Holland I as well as the Marine Institute’s Slocum Glider submersibles Laochra na Mara and Aisling na Mara are also offered.
Applications must be submitted using Research Vessel Operations’ online Survey Planning System by Thursday 16 September. Contact Research Vessel Operations at [email protected] to obtain a username and password.
Each application will be reviewed and the applicant will be informed as soon as possible whether the ship time they requested is available. If the requested timing is not available, alternative dates may be offered.
The Vessel Charter Guidelines should be read carefully before submitting the ship-time application form.
Further information, technical specification and contact details for the Slocum Gliders are available on the Glider webpage.
Applicants may seek grant-aid to cover all or part of the vessel charter costs for Research Surveys or Ship-Based Training Programmes in 2022. The closing date for receipt of grant-aid applications is 5pm on Thursday 16 September.
Applicants for ship-based training are advised to consult with the Strategic Marine Alliance for Research and Training (SMART) at [email protected]. SMART aims to standardise and optimise ship-based training for undergraduate and post-graduate students and develop nationally accredited ship-based training activities for national higher education.
Applicants are advised that survey schedules can change during the year; contact Research Vessel Operations at [email protected] to check whether any survey slots remain for 2021 and/or request to be notified if any dates become available.
The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport advises that INFOMAR will undertake a hydrographic and geographic survey operation in the Celtic Sea and Atlantic Ocean for six months from this April.
The massive operation will involve research vessels from Geological Survey Ireland (Keary, Geo, Lir, Gale and Mallet) and the Marine Institute (Celtic Voyager and Celtic Explorer) in a variety of surveys — along the South-West Coast from Roaringwater Bay to Kilkee, and offshore south of Mizen Head and between Kerry Head and the Aran Islands.
All vessels will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the survey, and will display appropriate lights and markers. The RVs Celtic Voyager and Celtic Explorer will also be towing a magnetometer sensor with a single cable up to 200m in length, and a moving vessel profiler cable of variable length up to 200m.
Full details of the surveys, including dates, maps and coordinates, can be found in Marine Notice No 10 of 2021, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
RV Celtic Voyager of the Marine Institute, Ireland's national agency for marine research, development and innovation, has been working in south Dublin Bay this week, writes Jehan Ashmore.
The 31.4m ship to be replaced next year by a Spanish newbuild, to be named the RV Tom Crean (52.8m), has since the start of this week carried out ship-based training albeit for 'land-based' marine biology students given the lock-down restrictions.
Despite that, Dr. Simon Berrow and Mr. John Boyd of the Galway-Mayo Institute of Technology (GMIT) have been 'live-streaming' from on board the RV Celtic Voyager to their students at home.
According to a tweet on the M.I. website, the work has been an excellent run down of what's involved in offshore surveys. As close as the real thing as you can get, less the swell and the rain!
The scene was observed by Afloat as the RV Celtic Voyager was in a south Dublin Bay prior to returning to the temporary base of Dun Laoghaire Harbour this afternoon. According to Met.ie, gale force 8-9 winds forecast tonight on the Irish Sea and Storm Force 10 off Wicklow Head and further south.
Already in port at Carlisle Pier, the UK registered, Spanish owned trawler Magan D which had been adrift that arrived at the weekend. Also berthed but since yesterday, Dublin Array's proposed wind-farm project related ship, Fugro Mercator having been busy on geophysical surveys.
The GMIT has a Marine and Freshwater Research Centre where among the specialist research staff is Dr Simon Berrow, responsible for Marine mammals, seabirds and Environmental impact. Also on board, Mr. John Boyd's specialising in fisheries, seagoing operations and maritime training.
The vessels six day (at 'sea') training programme is scheduled to end this Saturday.
While today, the M.I. other larger research vessel, RV Celtic Explorer (65.5m) is working in waters considerably further offshore in the North Atlantic Ocean.
Afloat tracked RV Celtic Explorer some 400 nautical miles offshore of the western seaboard to the ship's homeport of Galway.
The deployment of the vessel is to support an Ocean & Climate survey across south Rockall Trough with the vessel due back to its homeport in around a month's time.
Marine Notice: Survey for Fibre Optics in Site Investigations in North Irish Sea Next Month
The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport advises that a survey to investigate the use of fibre-optic cables in site investigations will be carried out in the North Irish Sea next month.
This survey from 16-25 March is being carried out in support of ongoing research at the Irish Centre for Research in Applied Geosciences (iCRAG).
The equipment and techniques to be used include:
- Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) using fibre-optic cables: A 1000m length of fibre optic cable will be placed temporarily on the seabed in order to carry out the survey. The position of the cable will be marked using surface buoys.
- OBS deployment: Two ocean bottom seismometers will be deployed and will remain in position until retrieval at the end of the survey.
- Sparker seismic profiling: This will be carried out as mobile work towing a transducer a short distance behind the work vessel.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Voyager (Callsign EIQN) and Fionn Mac Cumhaill (Callsign EIDN2). The two vessels will work close by each other and the latter is assisting with marine mammal observer work.
The vessels will display appropriate lights and signals. Mariners should note that seismic surveying using DAS equipment will be performed during daylight hours.
Further details including relevant coordinates can be found in Marine Notice No 08 of 2021, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
Marine Notice: SeaMonitor Survey in North Channel Sets Sail Later This Month
The Loughs Agency advises that it will carry out the SeaMonitor-EU Interreg Project (Survey CV21003) from Saturday 27 February to Friday 5 March.
The survey is being carried out in the North Channel in support of EU InterregVA project SeaMonitor.
A total of 108 Acoustic Listening Stations (ALS) are planned to be deployed at different locations covering a total of 63km between Malin Head in Co Donegal and Portnahaven on the Isle of Islay in western Scotland.
The first ALS on the Irish side is located 0.5 nautical miles from Inishtralhull Island at a depth of 20m. On the Scottish side, the first ALS is located 0.5nm from the shore at depths of 20-30m.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Voyager (Callsign EIQN) which will display appropriate lights and signals. Operations will be carried out during daylight hours to facilitate a safe deployment of acoustic receivers on the sea bed.
Further details including relevant coordinates can be found in Marine Notice No 07 of 2021, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
Sediment Wave & Sand Bank Survey Continues In South Irish Sea
The next legs of the Mobility of Sediment Waves and Sand Banks in the Irish Sea (MOVE) Survey begin tomorrow, Wednesday 23 September, according to the latest Marine Notice from the Irish Maritime Administration.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the survey is being carried out in support of ongoing research at the Irish Centre for Research in Applied Geosciences (iCRAG).
The latest two legs of the survey will take place from 23-28 September and from 7-19 October in the south Irish Sea.
Works will be carried out by the RV Celtic Voyager (callsign EQIN) using a variety of equipment and techniques, including ADCP, multibeam sonar and sediment sampling.
All works will be performed on a 24-hour schedule and the vessel will display appropriate lights and signals.
Details of all works entailed and the survey areas are included in Marine Notice No 43 of 2020, a PDF of which is available to download below.