Displaying items by tag: iPhone
New Mobile Guide to Lough Derg Trails
#INLAND WATERWAYS - A new mobile app that guides visitors around the trails of Lough Derg has gone live, the Clare Champion reports.
More than 20 trails are included in the app, from walking to cycling, driving, cruising and canoeing.
The app - developed in partnership between Shannon Development and US firm EveryTrail - uses Google Maps and the GPS system in smartphones to pinpoint trails near the user's location.
Users can download route descriptions, images and notes, get directions to the starting point and follow the the pre-plotted course.
The Lough Derg Trails app is available for iPhone and Android devices.
The Clare Champion has more on the story HERE.
Navigating With the IPhone
Dag Pike talks us through the fact the ubiquitous IPhone will do nearly anything that you ask it to and it even makes phone calls. Much of what it does is related to land-based applications but now the boundaries are becoming blurred and the IPhone can become a wonderful navigation device for use at sea.
I am sure that many of you have already discovered the virtues of the IPhone and the more I use it for navigation, the more I discover what it will do. The problem is to narrow down what you want the phone to do rather than being distracted by the wide variety of applications on offer that will run your life if you let them.

It sounds too good to be true and in some ways it is. Being a small portable package makes it vulnerable. You might drop it, you might loose it, you might have a flat battery, or it might just stop working, so you could be vulnerable if you put all your trust into this one unit. For many, there has been safety in the philosophy of having each navigation requirement contained in a separate unit, then if one fails then you still have the other to keep you going. I would be very nervous about putting all my navigation requirements into the one IPhone when I was out at sea but where the IPhone would perform very well would be as a back-up to the conventional navigation systems and it would still remain working if all your electrics failed.
Let's have a closer look at each navigation requirement that can be provided by the IPhone and this will give a better picture of what can and cannot be done with the IPhone.
Communications
You can make phone calls and send text messages and have Internet access using the IPhone wherever there is coverage for the provider that you are using. If you want to get sophisticated, then you need the 3G coverage and that tends to be less extensive, particularly out at sea. For normal phone coverage, you can be pretty certain of coverage up to 5 miles offshore and in many areas up to 10 miles but after that it can be a bit hit and miss. There will always be dead spots that the signal cannot reach, particularly along a rocky coastline where there are cliffs, but this can be a problem with marine VHF as well.
Whilst there are detailed maps showing the mobile phone coverage on land there are none for sea coverage so you can only learn what is available when you are out there. You should have a VHF radio on board as well as an IPhone so that you can hear distress messages and send out your own if you are in trouble but more and more these days boaters are using mobile phones to communicate for routine matters such as organising a berth in a marina and you certainly don't want to be thinking about using the VHF to book a table in a restaurant.
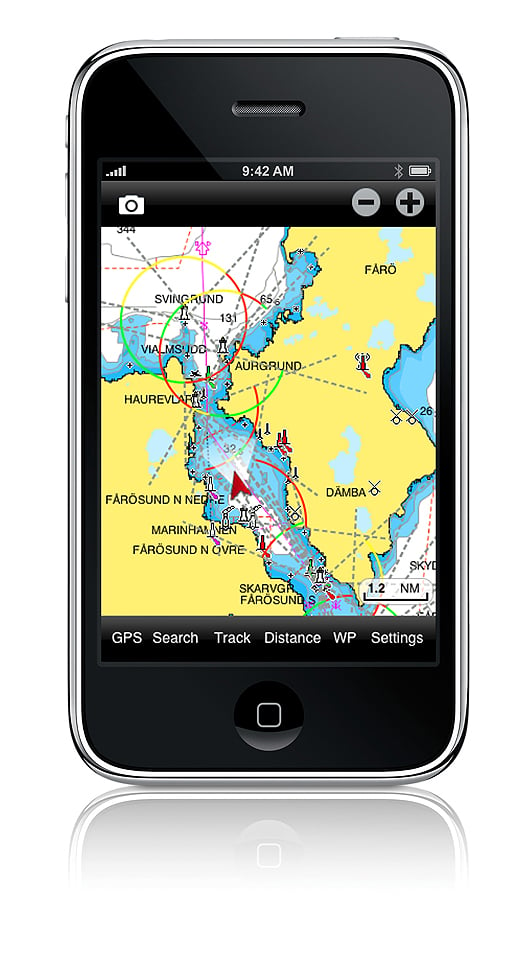
With the Navionics navigation package on your IPhone, I love the way that you can just tap on a port or marina and up will come the telephone number. One more tap on the screen and the phone is ringing.
GPS Reception
GPS is the key to position fixing and the IPhone has a built in receiver that should know where you are all the time. However, you will notice that your conventional chart plotter has its GPS antenna located outside the boat to ensure continuous reception. Your IPhone GPS will have its antenna inside the boat most of the time so you will need to check whether the GPS is working here. It may work under the windscreen and it should certainly work in an open boat or on the flybridge but GPS reception is certainly something to check out before you commit yourself to IPhone navigation. I use the Pocket GPS World App because this shows you the reliability of the position information being produced by the GPS and you should consider this vital information.There are very cheap or free GPS Apps that you can download that will show your position, speed course etc, which you could use in conjunction with paper charts if you just want to simplify your IPhone navigation.
Navigation
There is no doubt in my mind that that the Navionics App is the best one both for route planning and for navigation itself. This system has rave reviews and it works extremely well by offering most of the facilities that are found on mainstream chart plotters on the small screen of the IPhone. There is virtually worldwide chart coverage and you simply download the App that is relevant to the area you plan to sail in. For instance you can get chart coverage of the whole of the UK and Northern Europe for the price of a couple of bottles of wine.
It is the compact size of the screen that can make things difficult but you soon get used to this. When you are plotting a route, you need to take extra care that the route you have chosen is free from dangers and this can only be done by expanding the scale and then carefully studying the route in detail. I found it too easy to set the waypoints out and then find that the chosen route passes over a rock or a shoal that does not show up too well on the small screen or the scale that you are using.
You set the waypoints by selecting WP and then simply tapping the screen and with big fingers, it is not easy to set them accurately. However, they are easy to adjust, again by simply touching the way point and dragging it to where you want it to be. It took me 5 minutes to plot a route involving 10 waypoints and that including checking it out afterwards.
Once plotted all you need to do is keep the 'own ship' icon on the course line to follow the route. You can set the track plotting mode so that you have a record of where you have been and you get a heading vector and a speed read-out provided that you are doing more than 5 knots. That might be a handicap for sail boats because that heading vector is particularly useful to see where you are going in relation to the plotted route.
Don't take for granted that the GPS plot is giving accurate information. As mentioned above, I like to get a check on the quality of the GPS fix because when I was testing the IPhone, there were a couple of times when it plotted over the land and I was confident that I was on the water.
The Navionics App also has tidal and current information for 7 days ahead for a variety of locations around your position. There is so much information built into the system that you have virtually everything at your fingertips. However, there are some things that it will not do such as showing you the total distance of a route you have plotted and the courses and distances of each leg of the route. That said, the Navionics App has to be one of the most useful for those who want to navigate on the water.
AIS
You cannot get a direct read-out from the AIS transmitters around you because you need VHF for that but the next best thing is the Ship Finder App. With this App you can go to nearly any location around the world and it will show you the ships and boats that are transmitting their AIS signals. Tap on any one of the ship icons and it will show you all the details of the ship including its size, destination and course and speed. This function is more of interest than a serious navigation tool but it could be useful to indentify a ship out at sea and to give some idea of where it might be heading.Compass
The IPhone has a built-in compass but there are also a number of Apps available with alternative compass displays. The standard display shows both an analogue and a digital read-out of the heading and checking this out at sea, it seems to be reasonably accurate, say to within 5°. The reason it is hard to get better accuracy is that the heading shown is the way that the IPhone is pointing and it is hard to get this lined up exactly with the bow of the boat. It only wants a slight movement of the phone to change the heading by several degrees. However as an emergency compass it works and you have the choice of the readout in either true or magnetic headings.
Weather
If your IPhone is connected to the Internet then you can access all the web sites that offer weather information. However I use an App called Weather Pro that will give you detailed 7 day weather at any port you programme in. The forecast is given for every 3 hours and details thing like wind strength and direction as well as predicted wind gust speeds. However, you do need to be aware that these are basically land forecasts and the conditions at sea could vary a little.
Comments
Every time that I have used the IPhone for navigation I have been amazed at its capabilities. It gives you so much information in such a small package that you will wonder how you ever managed without it. This really is the problem because in time you will take everything the IPhone can do for granted and you will no longer check that it is giving good quality navigation information. The biggest worry is the quality of the GPS position information because much of the navigation depends on this. I used the App that tells you the quality of the GPS fix but that means switching over to this at frequent intervals. It would be much better to have an automatic system that throws up an alarm when the GPS position is poor. I am sure that will come with time.
I would be nervous if the IPhone was my only source of navigation information. It is easily dropped, it is not waterproof and the battery has only a limited life. Of course, you can mount it into a holder and you can keep the charger plugged in to overcome the battery life problem and you can get extra life batteries. Where the IPhone scores is that it makes a great back-up system that will cover most of your navigation needs. In this respect, it could replace the hand held GPS and the hand- held VHF to a certain extent but before you throw these items away, I would suggest that you get a lot of experience with IPhone navigation. Only then will it become the true navigation friend that this remarkable piece of equipment is.
iPhone Co-Ordinates Save Stricken Vessel
A stricken vessel was located in trouble on Lough Erne using lat/long data from an iPhone.
A 999 call from the Motor Cruiser ‘Wee Rascal’ on Lough Erne in the early hours of this morning called on all the investigative powers of Belfast Coastguard as the vessel wasn’t even close to its reported position.
The vessel was on passage from Kesh to Enniskillen in windy, wet conditions when it called 999 to ask for assistance. Despite an extensive search of the area around its reported position neither the Enniskillen RNLI Inshore Lifeboat nor Erne Coastguard Rescue Teams could find the vessel.
Because the vessel had no flares, flash lights or VHF Radio on board to show rescuers where it was, Belfast Coastguard resorted to mobile phone technology. A locator i-phone application finally gave rescuers the vital latitude and longitude they needed to locate the vessel
The vessel was finally located 25 miles away from its reported position, dangerously amongst the rocky shoreline off Eagle Point. It was carefully brought away from the rocks by the skill of the Enniskillen RNLI Inshore Lifeboat crew and taken to the safety of Beleek marina.
Coastguard Watch Manager Steven Carson said:
“A combination of luck and technology saved these four people from imminent danger this morning. They had charts onboard but obviously no real idea of how to get to their destination or how to report their position in an emergency.
“Vital hours were wasted eliminating one possible location after another, time that we wouldn’t have had if the vessel had struck the rocks and sunk. I hope that this experience will help the crew to realise why navigation training is essential for all mariners, whether you’re on a Lough or the open sea.”
New App Shows the Racing Rules
American firm DP Associates has announced the launch of You-Tack! Pro, The Racing Sailor’s Illustrated Guide. Easily understood, it has extraordinary 3D animated quizzes and brilliant illustrations. You-Tack! Pro is available at the iTunes Store for $19.95. (You-Tack! Lite, a free demo, highlighting the major features, is also available – on the iTunes Store by 06/30).
Major Features:The Official ISAF Rules and Definitions with colorful clear illustrations, simple, direct explanations and hyperlinked citations, that make the rules easy to understand. Included for quick reference are all the rules from Part 1 through Part 7, with the appendices A thru D.Forty-two quizzes with vivid “you are there” 3D animations, in seven distinct categories: The Start, Sailing Upwind, The Upwind Mark, Sailing Downwind, The Downwind Mark, The Finish, and Signals.
Each quiz contains: a fact-based Situation, an Illustrated Question, and a 3D Animation. Answer the quiz to find out if you’re right, and review the rationale behind the answer, while a Scoreboard tracks all your answers, and points you to a list of the rules you missed.After completing a quiz, the specific rules and definitions discussed in each quiz are displayed for review.All the racing signals are explained in detail with brilliant graphics, including images of all the international signal flags.No other Racing Rules app comes close!
You-Tack! Pro could be used as a teaching tool for junior programs (run it on the iPod), and a fun clubhouse method for crews looking to build rules knowledge. You-Tack! Pro makes learning the Racing Rules of Sailing easy, and fun. Created by racing sailors for racing sailors, whether the boat you sail is a maxi-yacht, a beer-can racer or a one-design dinghy, You-Tack! Pro is the quickest and most convenient way to build racing confidence, with increased rules knowledge.
To purchase You-Tack! Pro, or to download the demo, You-Tack! Lite, please visit the iTunes App Store.
It highlights and examples the features and functionality of You-Tack! Pro - including a fully indexed listing of all the rules, (displaying the specific details, illustrations and explanations of Rules 1 to 13). Featured are two 3D animated quizzes, all the signals, and all the definitions. It’s a free and easy way to see how the quizzes and the 3D animations function, and how the rules are illustrated in the Pro version.
More on: [email protected], 212-941-1441, or 917-417-3728
































































