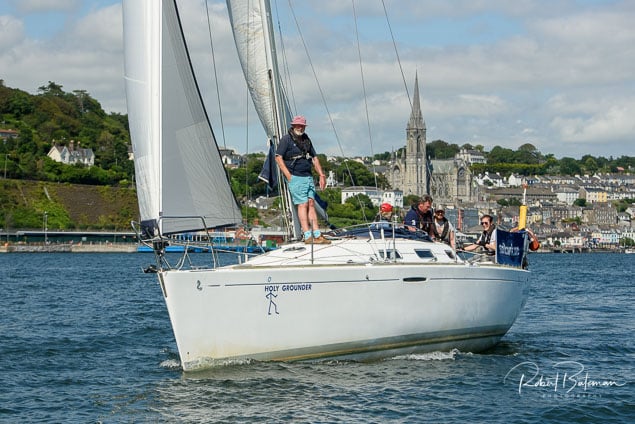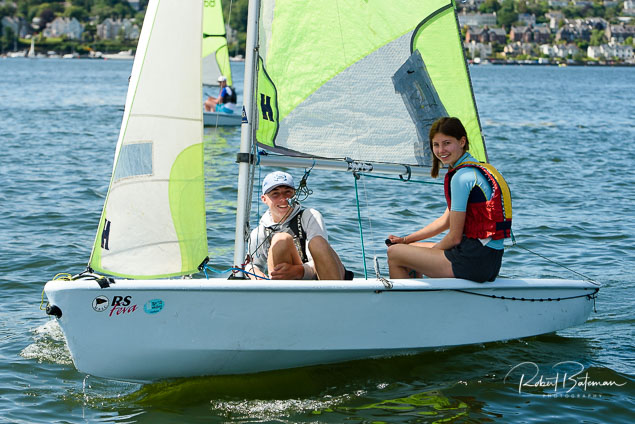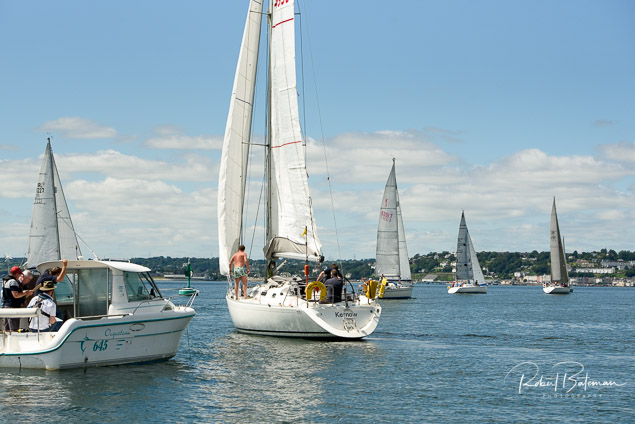Displaying items by tag: Cobh
Crosshaven Lifeboat Crew Assist in Extracting Man With Serious Leg Injury From Cliffs Near Cobh
On Sunday afternoon (15 January) Crosshaven RNLI volunteers were requested to launch and assist the National Ambulance Service and Cobh Fire Brigade to extract a casualty at Cobh.
It emerged that a young man had fallen on cliffs east of the pilot station at Cobh in Cork Harbour and suffered a serious leg injury.
NAS paramedics and fire service personnel were able to access and treat the casualty, but were unable to extract the patient.
Shortly after pagers sounded at 3.35pm, the inshore lifeboat was beached at the cliff base and its volunteers took on board the stretchered patient along with two paramedics for continuation of care.
They were subsequently transferred to Kennedy Quay, where the fire service assisted in extracting the casualty to the awaiting ambulance.
Commenting later, Crosshaven RNLU hailed the “good inter-agency cooperation by NAS, fire service and the pilot launch.”
The lifeboat crew on this callout were Ian Venner, Alan Venner, James Fegan and Caoimhe Foster. Launch crew were Kline Penefather, Conor Barry, Jeff Lacerda, Jennifer Grey, Jonny Bermingham and Kevin McCarthy.
Cobh People’s Regatta to Feature Cruiser Racing
Cobh People’s Regatta, with Cove Sailing Club, is on this weekend with events ashore and afloat.
Sailing races begin with the young sailors of the Optimist fleet on Friday morning, starting at 10 a.m. The cruisers will race that evening at 7 p.m. for the Titanic Trophy. Both are open events as is the Dinghy Racing on Saturday, starting at 2.30 p.m.
The famous Rankin dinghies will race for the ‘Rankin Brothers’ Cup on Saturday. “We expect a great fleet with fifteen boats entered and we hope to have a race mark in by the Promenade in Cobh to increase spectator enjoyment,” Maurice Kidney, one of those who led the revival of the fleet, tells me. First gun for this fleet will be at 3 p.m.
On Sunday, there will be cruiser racing, starting at 1.30 p.m., an open event for all clubs.
Ashore there is a wide variety of events planned.
The coastal town of Cobh on Great Island, Cork Harbour, is after years of waiting, to see plans finally drawn up to build a €100m new road to the town and to replace the only road bridge into the area in order to provide security of movement.
Plans are also being advanced to complete the northern relief road in Midleton and work will get underway next month on the construction of the western relief road in Carrigaline.
 The coastal town of Cobh on Great Island in Cork Harbour Photo: Bob Bateman
The coastal town of Cobh on Great Island in Cork Harbour Photo: Bob Bateman
The population of Cobh (see ship story) and Great Island is more than 13,000 people, and can only be accessed via Belvelly Bridge, which has been subject to closure in the past due to tidal flooding and fallen trees. (See, other Afloat story on the redevelopment of nearby Marino Point).
 Cobh's Belvelly Bridge Photo: Bob Bateman
Cobh's Belvelly Bridge Photo: Bob Bateman
 Cross river ferries - two ferries the “Glenbrook” and the “Carrigaloe” service the River Lee connecting the communities on both sides of the harbour between Cobh and Cork. The ferries can carry 200 passengers and 27 cars. The crossing from Glenbrook to Carrigaloe takes 5 minutes Photo: Bob Bateman
Cross river ferries - two ferries the “Glenbrook” and the “Carrigaloe” service the River Lee connecting the communities on both sides of the harbour between Cobh and Cork. The ferries can carry 200 passengers and 27 cars. The crossing from Glenbrook to Carrigaloe takes 5 minutes Photo: Bob Bateman
Pádraig Barrett, the county council's director of roads, said a tender for a design brief for the upgrading of the R624 into Cobh will be advertised shortly and it is expected the plans will be completed within the next two years.
It is envisaged that the project will be broken up into sections, but the bridge replacement will be given priority.
Cobh could not be accessed by road until the bridge was constructed in 1803.
For further details, Irish Examiner reports on the plans.
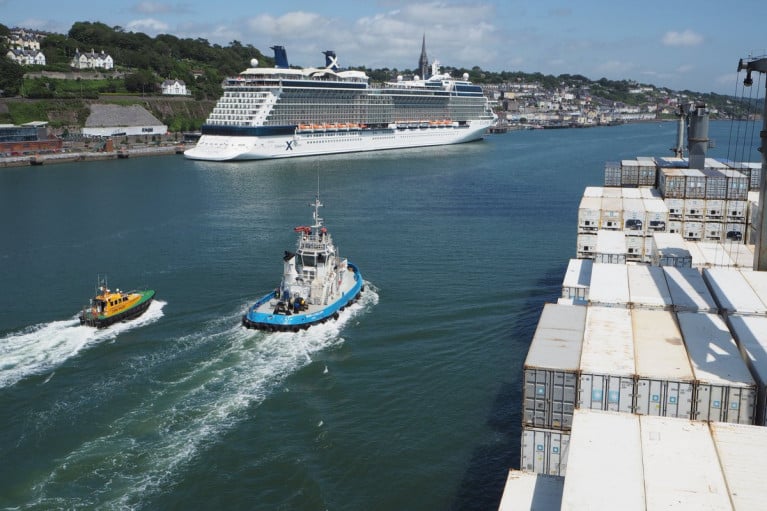
Second Cruise Ship Terminal Port of Cork Plans for Cobh
A second cruise ship terminal the Port of Cork hopes to be operational in Cobh by the end of the decade which will see up to 150 such ships visiting the town every year.
In the interim it's planned to move cruise liners out of Ringaskiddy, due to increased shipping demands there, and berth the larger ships at the existing terminal in Cobh and smaller ones at a new terminal which will be developed at Marino Point (see related story).
A number of businesses are interested in moving into the former Irish Fertilisers Industries (IFI) site at Marino Point and it's expected the harbourside facility will be full and operational by 2023.
Gouldings have already applied for planning permission to move their fertiliser facility from Centre Park Road in Cork city down to Marino Point, and according to Port of Cork chairman John Mullins, another large agri-related business is “in very advance discussions” with the joint venture company, Belvelly Marino Development Company (BMDC), set up by the port authority to develop the site.
More from the Irish Examiner here
Afloat adds that in recent years there has been an increased use of the former IFI jetty at Marino Point, where vessels have berthed, among them tankers, ferries (lay-overs) and visiting naval ships.
While other clubs have found it a big enough challenge simply resuming sailing in a regulation-compliant way, the 101-year-old Cove Sailing Club in Cork Harbour has also been bringing its new marina on stream, and in addition to resuming club sailing, it staged the first open event of the delayed 2020 season, the Squib Southerns, on July 25th-26th. It has been a superb team effort, but all teams need effective leadership, and CSC Commodore Kieran Dorgan has been providing it in a family tradition - his father Barry was in the same role, while on the water Kieran himself is no stranger to the front of the fleet with his First 36.7 Altair.
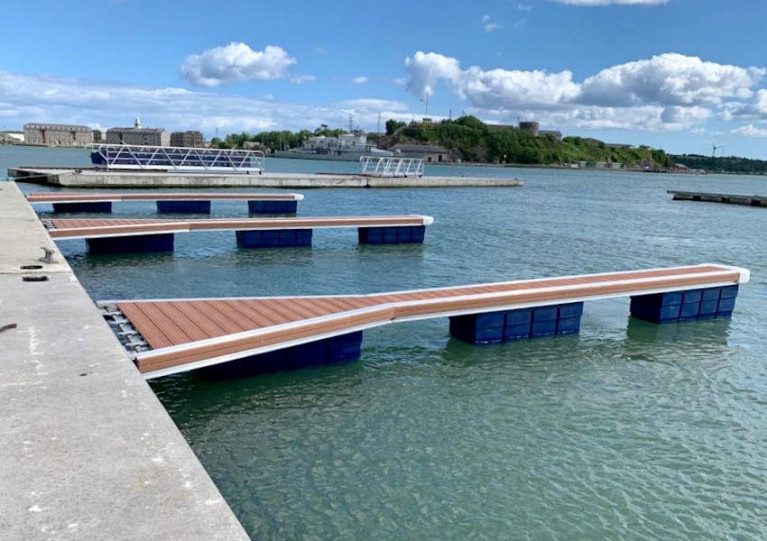
Further Progress On New Cove Sailing Club Marina
Colm McDonagh has shared images of further progress on Cove Saling Club’s new marina pontoons in time for the opening up of sailing activity from tomorrow, Monday 8 June.
Coronavirus restrictions delayed the original expected completion date in April, but the berthing pontoons are now well into assembly before connection to the gangway that was installed earlier this year.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the Cork Harbour club has also been working on upgrades to its dinghy park facilities including a new meeting room, office and kitchen at Whitepoint in Cobh.
What a fantastic addition the @CoveSailingClub marina will be. Really coming together now. @CobhTourism @CobhHarCham @CobhTidy @hashtagcobh2020 @AfloatMagazine @jonathanlee0312 @KENNYTCORK @CathalRasmussen @eucoolroute @royalcork @deshocks @PortofCork pic.twitter.com/cq6n8Gi2gJ
— Cobh Gifts by CMcDonaghPhoto (@C1McD) June 5, 2020
It’s expected the club will shortly provide an update on summer sailing events and courses upon the latest relaxing of restrictions — which allow members within the same county or 20km to visit, and for bigger groups to sail while observing social distancing.
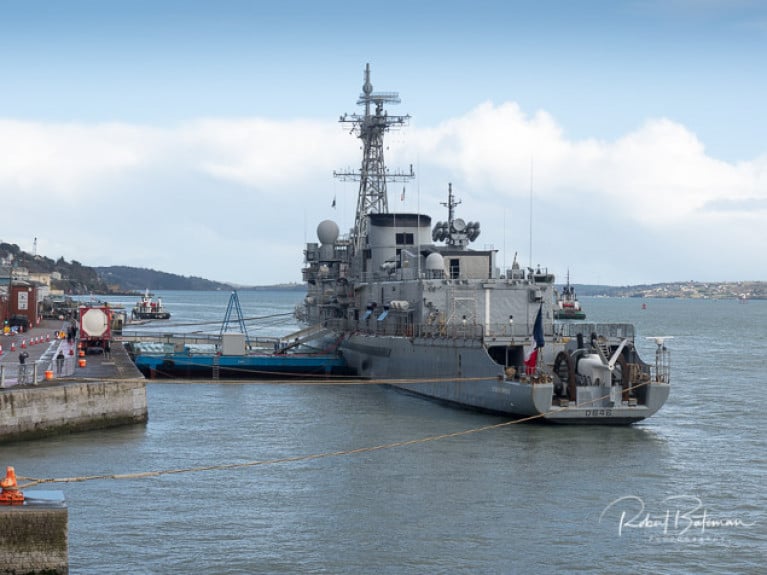
French Naval Frigate Latouche-Tréville In Cork Harbour
The visiting French Naval Frigate Latouche-Tréville was alongside in Cork Harbour at the weekend moored at the Cruise Liner berth in Cobh.
As Afloat previously reported, the frigate and her crew of 244 were in the south coast port in aid of the 'Denim Day 4 Dementia' which took place at the Naval Service base on Haulbowline Island.
The ship is one trio of F70 A SM type anti-submarine destroyers, which the French Navy instead classify as a frigate.
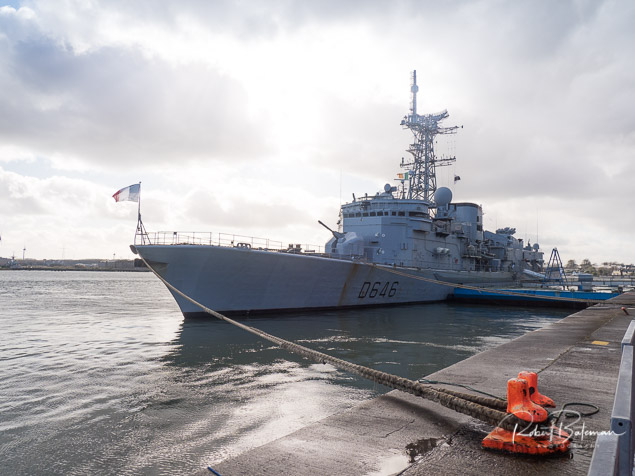 French Naval Frigate Latouche-Tréville alongside in Cobh Photo: Bob Bateman
French Naval Frigate Latouche-Tréville alongside in Cobh Photo: Bob Bateman
Equipped with Excocet surface to air missiles, the frigate commissioned in 1990 has a helideck and hanger that can handle two Lynx helicopters.
In the summer of 2009, she was filmed in stormy seas as part of the documentary Oceans. See vid below.
Cobh Sailing Clubs Getting Back Together in Cork Harbour
With the competitive season now finished on the South Coast, attention turns to club activities ashore which will include annual general meetings and reviews of how the past season went and prospects for the year ahead.
Without a doubt the dominant part of 2020 will be the Tricentenary of the Royal Cork Yacht Club, but across Cork Harbour from that club at Crosshaven there is good news from Cobh, where the Royal Cork was once based before amalgamating with the Royal Munster and moving to Crosshaven.
The RCYC History notes: “By the 1960s changing economic and social patterns made Cobh less and less attractive as a base for the club. In 1966 the Royal Cork and the Royal Munster Yacht Clubs agreed to merge and the Royal Cork moved to its present premises in Crosshaven assuming the title The Royal Cork Yacht Club, incorporating the Royal Munster Yacht Club.”
Last year there were some difficult club movements in Cobh when a new club was formed - the Great Island Sailing Club. That was stated by its proponents to ensure the continuance of sailing at Cobh and that followed difficulties which arose in Cove Sailing Club as it attempted to build a marina at Whitepoint.
New Marina under construction
This year Cove Sailing Club reached and celebrated its centenary and signed the contract for a 30-berth marina at Whitepoint. That has been under construction across the river at Ringaskiddy, with completion and installation targeted for “well in advance of the 2020 season,” according to the club, whose Commodore, Kieran Dorgan, said it will provide “state-of-the-art facilities all-year-round and will accommodate both locals and visitors.”
The two clubs, Great Island and Cove have been discussing joining together again, according to my information and agreement has been reached so that a formal announcement is expected. Despite differences, close contact was maintained between the clubs, “in the best interests of sailing.” Johanna Murphy, who became Commodore of Great Island, also became the first lady elected Commodore of the South Coast Offshore Association where she has led a number of developments to bring clubs closer together.
SCORA is finalising an extensive programme for 2020 which, as well as racing, will include events to develop the social side of the sport, following the success of the Cobh-Blackrock Race, one of the highlights of the season on Leeside.
Dragons at Kinsale
Amongst the positive news from club reviews is that the Dragon Class at Kinsale Yacht Club had “a fantastic sailing season” according to its annual report, with the addition of two more boats to the fleet - TBD – James Matthews, Dave Good and Fergal O’Hanlon is one and the other is Scarlet Ribbons – Thomas O’Brien, Donal Small and Conor Hemlock. This brings the KYC club fleet to 7 and “there is talk of additional numbers joining the fleet next year,” according to the Class Committee.
The project is being completed with the support of Cork County Council, a Sports Capital programme grant, Port of Cork and SECAD. The selected contractor, Orsta Marina Systems Nederland BV, specialises in the design, supply and installation of floating breakwaters and pontoons for berthing of leisure and commercial vessels.
Listen to the Podcast here discussing the growth of interest in sailing.
Cruise Critic awards the highest-rated cruise destinations in 18 cruise regions across the globe in its annual Cruisers’ Choice Destination Awards 2019
Cruise Critic, the world’s leading cruise reviews site and online cruise community, has announced the winners of its fourth annual Cruisers’ Choice Destination Awards, naming the world’s most popular cruise destinations – as well as the best cruise lines to visit each region – based entirely on consumer ratings submitted with reviews on Cruise Critic.
Cobh was recognised as one of the best cruise destinations in the world, winning in the Top-Rated British Isles & Western Europe Cruise Destination category.
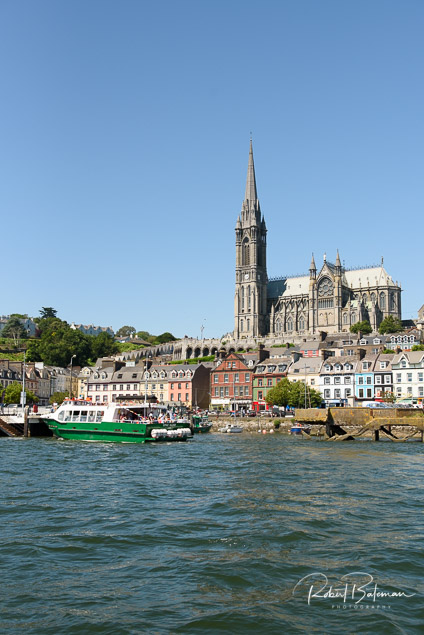 Cobh from the sea Photo: Bob Bateman
Cobh from the sea Photo: Bob Bateman
According to one quote - ‘I just went walking around the town and felt like I was at home there. I ate brunch at a local coffee shop and late afternoon lunch at a small local restaurant. I really enjoyed wandering around and feeling welcomed and happy.’ - Cruise Critic Member GEMarshall
Destinations awarded in this year’s awards received the highest ratings among cruisers who cruised to the destination in the past year and shared their experiences on Cruise Critic.
 Cruise liner Oriana arrives into Cork Harbour this week Photo: Bob Bateman
Cruise liner Oriana arrives into Cork Harbour this week Photo: Bob Bateman
Brendan Keating, Chief Executive of the Port of Cork said: ‘We are blown away that Cobh has secured this top position as a cruise destination. This award is not only testament to the effort by the Port to promote the region but also to the local tourism bodies, businesses and attractions in Cobh who work hard to promote and develop their town.’
“For most travellers, the decision of where to cruise is made before they think about all the other pieces of the cruise planning process,” explains Colleen McDaniel, Editor-in-Chief of Cruise Critic. “And for those looking for incredible cruise destinations, there’s no better way to narrow your options than by seeing which destinations are rated most highly by cruisers who have already been there, done that.”
Cruise Critic boasts the world’s largest online cruise community, with more than 50 million opinions, reviews & photos, covering approximately 700 cruise ships and over 500 worldwide ports.
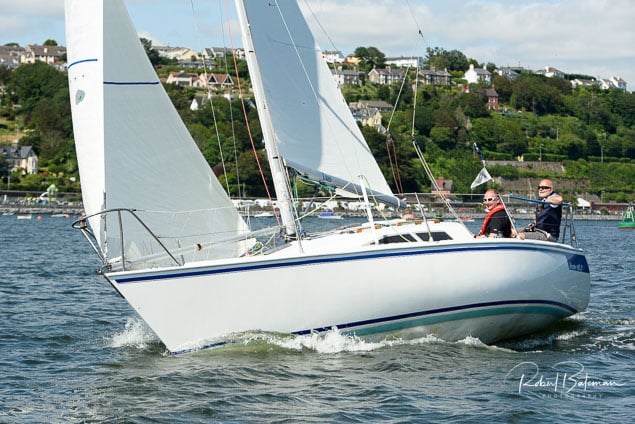
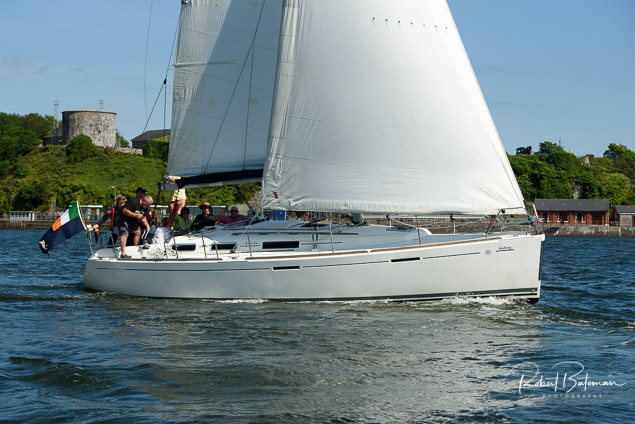
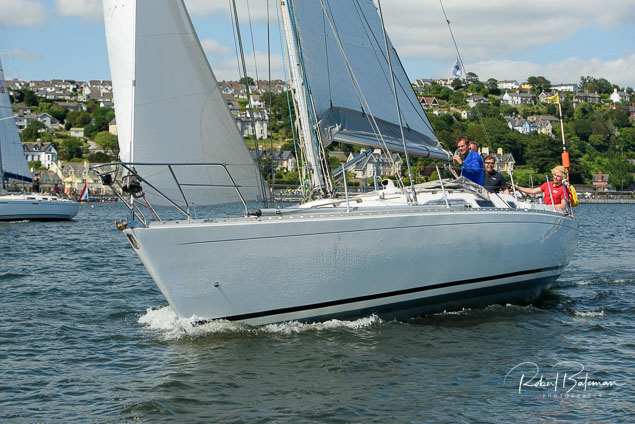
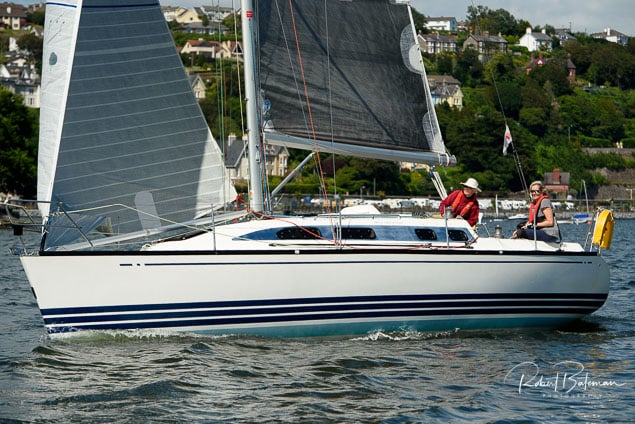
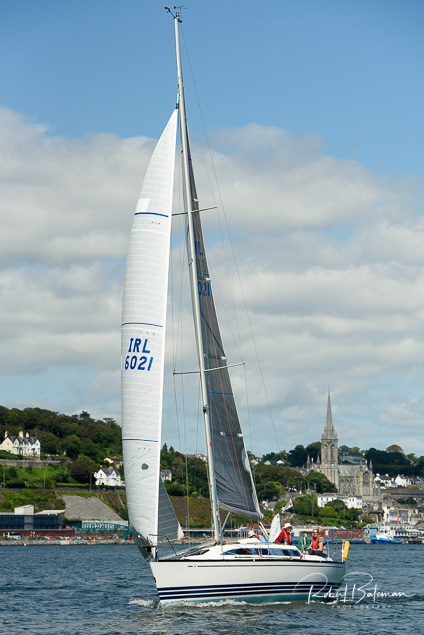
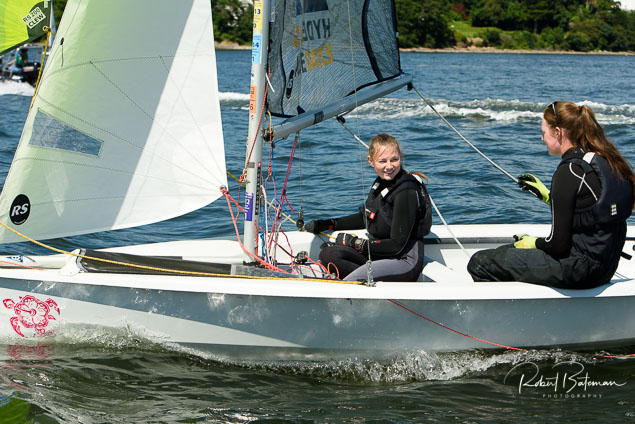
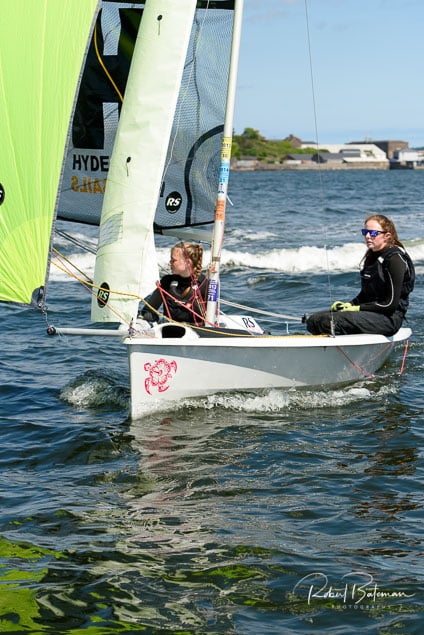
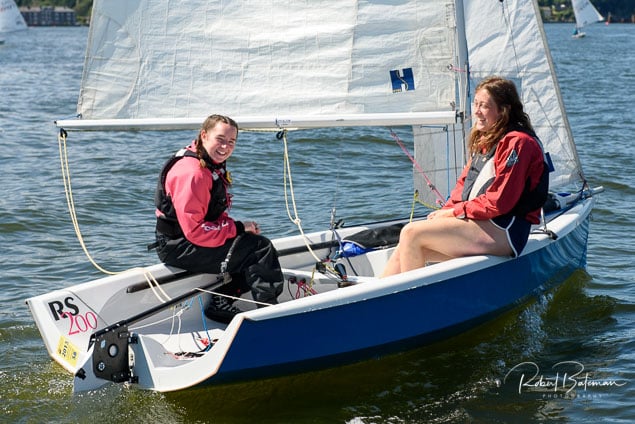
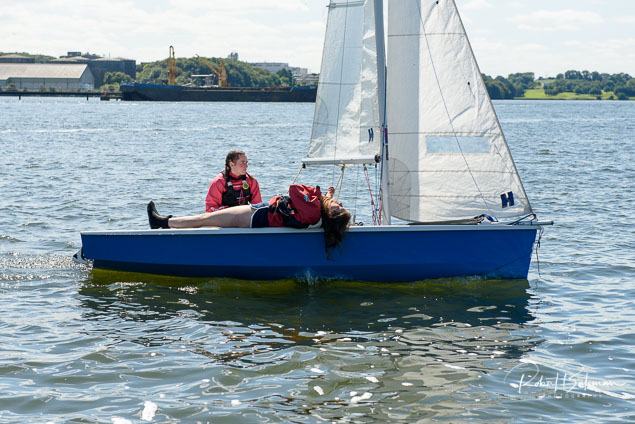
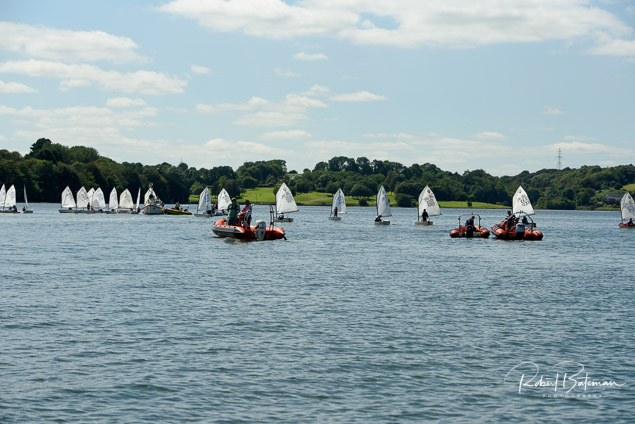
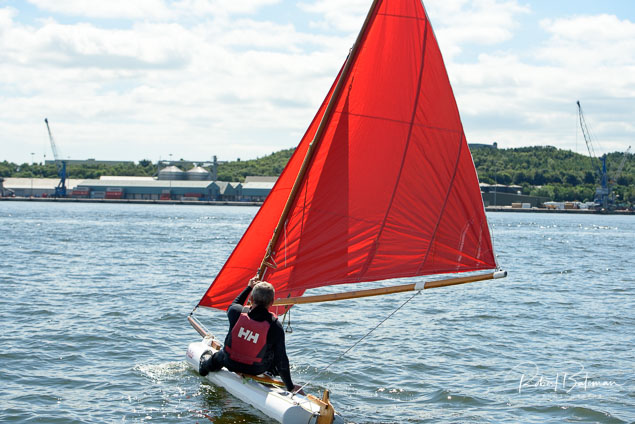
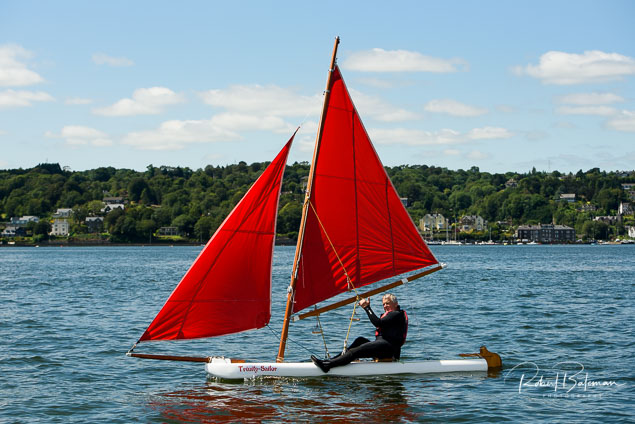
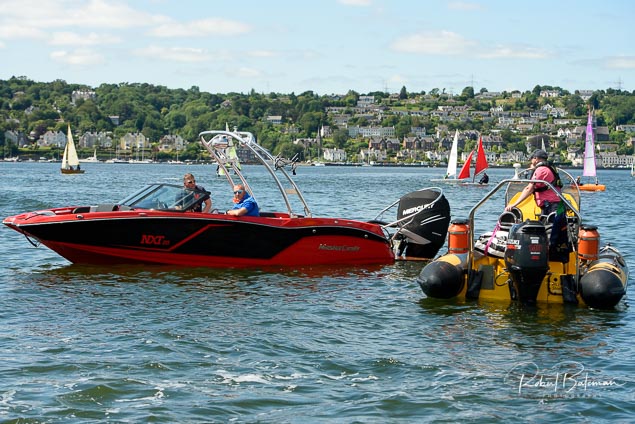
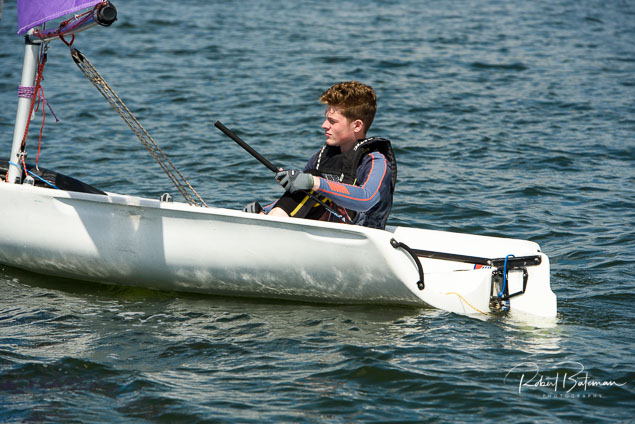
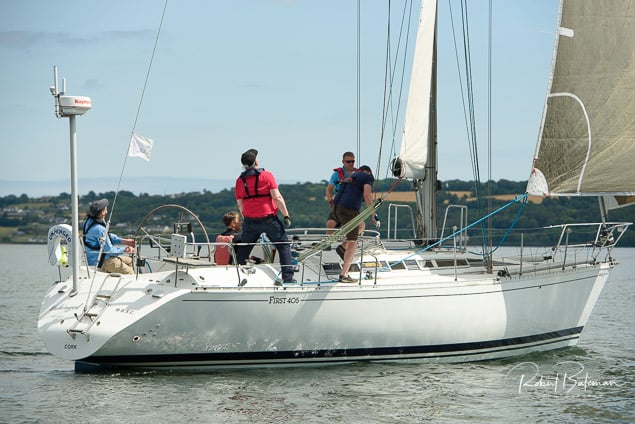
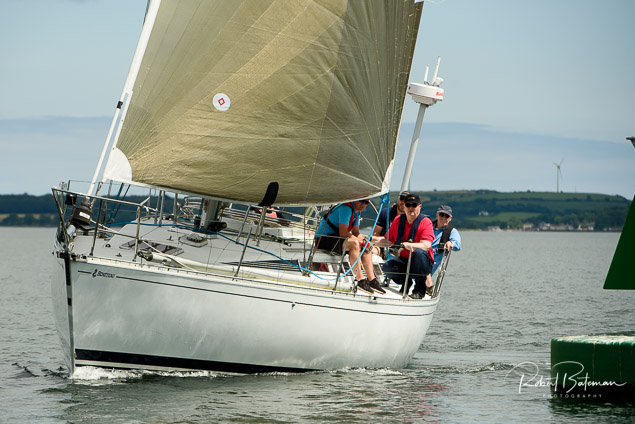
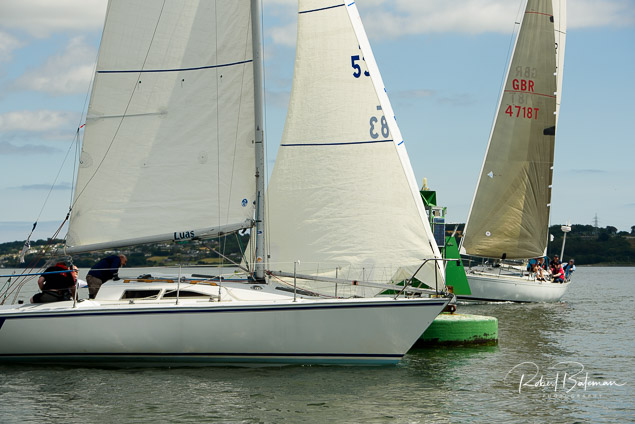
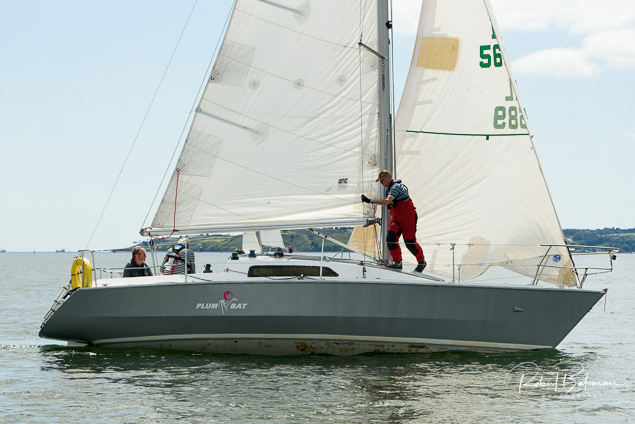
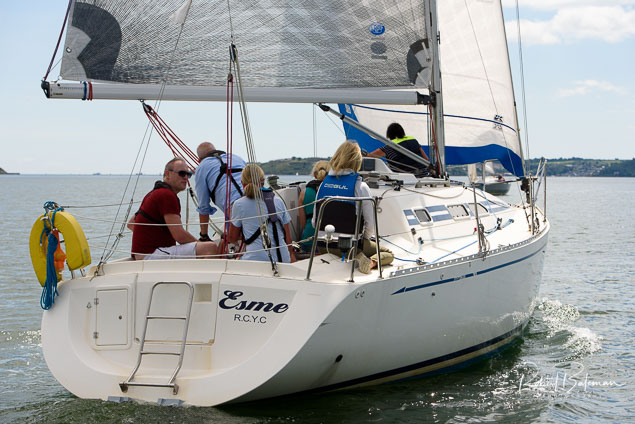
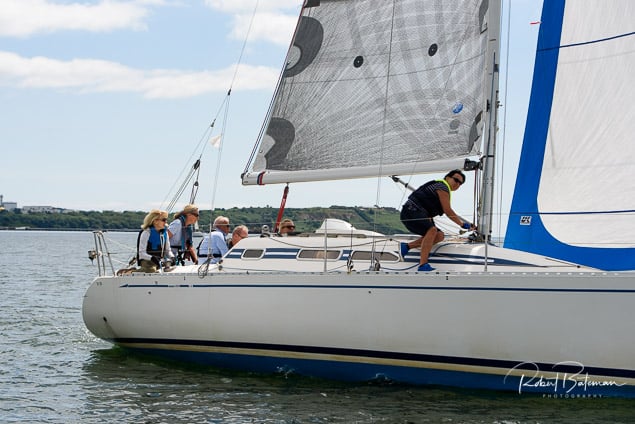
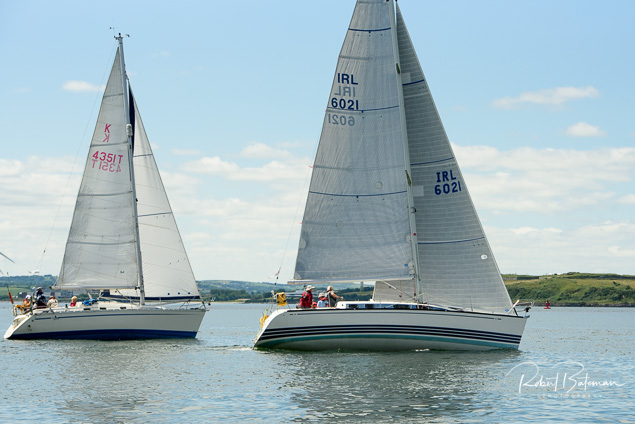
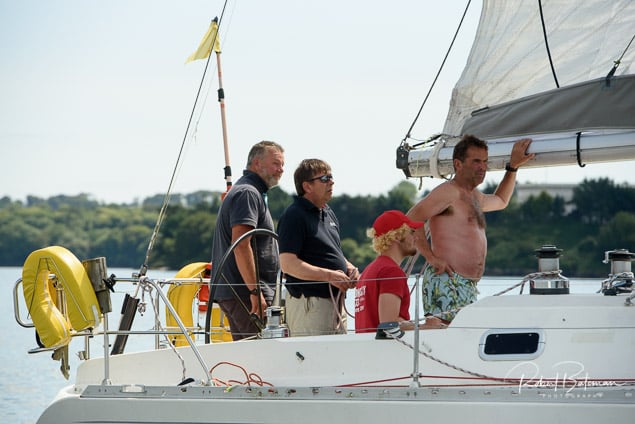
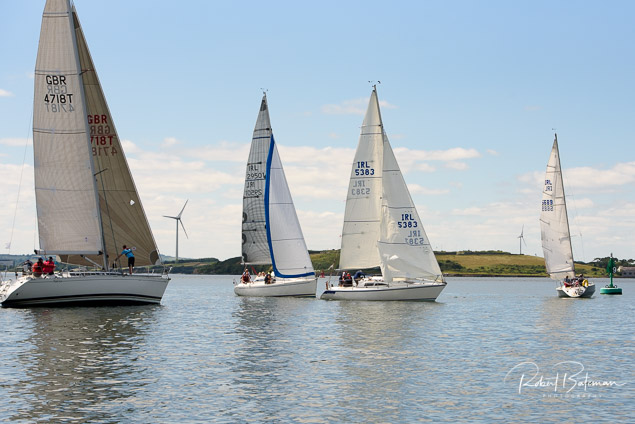
Summer Sails in Cork Harbour for Combined MBSC Cruiser Race
Summertime and the living is easy in Cork Harbour. Despite the postponement of Sunday's Cove at Home Regatta due to the lack of access to landing pontoon at The Quays in Cobh, a combined fleet of nine sailing cruisers coming from RCYC and Cobh (Cove sailing Club and Great Island Sailing Club) and Monkstown Bay Sailing Club for a league race on Saturday as part of 'MBSC at Home' under Race Officer Tom MacSweeney, writes Bob Bateman.
In a lovely summer's afternoon for sailing, the cruiser fleet mixed with an assortment of dinghies.
Cruiser sailors included Ria Lyden sailing an X332, Sean Hanley in a Hunter. Ian Scandrett was sailing the Sigma 38 (with George Radley on board). Eddie English's Holy Grounder and a Hawk 20 also took part.
Photo gallery below