Displaying items by tag: ISA
ISA to Seek New CEO Following Retirement of Harry Hermon
Irish Sailing says it will begin a recruitment process for a new CEO soon, following Harry Hermon’s retirement announcement today (Thursday 1 September).
Hermon, who has held the role since 2006, is to retire this December to “spend more time with [his] family”.
During his tenure with Irish Sailing, which began in 1999 in the role of club development officer, Hermon was in the hot seat for four Olympic Games including Annalise Murphy’s historic silver medal in the Laser Radial at Rio 2016.
Commenting on his retirement, Hermon said: “It has been an honour and privilege to work with Irish Sailing over the past 23 years … With COVID-19 behind us and the organisation on a stable footing, I believe it is the right time to retire from Irish Sailing and spend more time with my family at home and overseas. I wish everyone involved in the organisation the very best in the future.”
John Twomey, president of Irish Sailing said: “I would like to thank Harry for all his work with Irish Sailing. He will be missed, and we wish him well in the future.”
Irish Sailing Association Accounts Reveal Assets Worth €3.5m
The ISA’s just-published financial statements reveal it spent €1,642,500 in operational grants in 2021, made up of €589,000 on core activities and €1,053,500 on High Performance. At the end of the year, just over €205,00 of core grants remained to be spent.
Capital Grants received on core activities amounted to €104,150 while €293,000 was received by the High Performance.
Core activities generated a surplus of €140,685 (2020 - €123,095) helped by Special Project Grant of €138k, of which only €38k has been specifically identified as an outlay in the accounts.
Increased sailing activity contributed to increases in;
- Membership income €12K
- Training Income €31K
- Handicap Income €14k
- Competence Certs €20k
Office income fell by €11k, reflecting the fact that the office has been closed for nearly two years due to the pandemic.
In that context, it seems surprising that payroll costs have increased by €76k or 16%, particularly when the accounts acknowledge that €39k in Government Payroll subsidy was received and credited against payroll costs.
The other big increase in costs is in legal and professional fees, which recorded a massive jump from €17k to €45k or 164%.
Communication costs have also grown, from €32k to €44k or 38%.
The High-Performance area experienced a surplus of €36,061 compared with a surplus of €179,044 in 2020 when activities were severely curtailed by Covid restrictions. Apart from special grants towards the cost of the Olympics, Government funding remained at the same level of €800,000. Staff salary costs at €284k for 2 full-time and one part-time staff is a significant proportion of overheads.
There are no details of the Irish Sailing Foundation in the accounts, apart from a note that €14,000 was received as a donation during the year.
The balance sheet shows a trade debtor of €387,658 compared to €743 in 2020. Surprisingly, there is no explanation offered about how this arose or from whom it is due.
The depreciation policy of the ISA means that Fixed Assets are valued at €720k and include the premises in Park Road, at a value of €122k with an open market value probably closer to €2.5m.
The net liquidity of the Association is very good.
- Assuming the Trade Debtor is readily convertible into cash, the ISA has liquid resources of €668k plus €388k making a total of €1,056k
- From this must be deducted designated but unspent deferred Government Grant expenditure of €205k and tangible real creditors and accruals amounting to €221k making a total of €426k.
The true net liquidity is therefore about €630k.
The aggregate real-world value of the Association’s assets is, therefore, closer to €3.5m, made up of €2.5m in fixed assets, plus book value €.5k and net liquid resources €.6k.
Download the 2021 ISA Accounts below as a PDF file
New Book on Sports Governance Launched
Running a sports body has become increasingly onerous. Many sporting entities have become companies and now need to abide by the Companies Act. All entities funded by Sport Ireland must comply with a code of governance, adopted by Sport Ireland, by the end of 2021. In recent years, the sporting world has been rocked by controversies both internationally and here in Ireland, which have had significant repercussions. It is now more essential than ever that all sporting entities, big and small, need to focus on good governance.
Sports Governance: A Guide for Sporting Entities is designed to help board or committee members to understand and address governance issues. The book focuses on three main areas: firstly, an introduction to governance, with a specific look at the governance code for sporting entities and the need for governance; secondly, becoming a board member and the considerations taken by both the person and the organisation before taking on the responsibility; and thirdly the key functions of a board – strategy, risk, accountability, and monitoring. Each chapter ends with essential points for the smaller sporting entity and the club, as well as ten key points.
Sports Governance: A Guide for Sporting Entities is essential reading for anyone involved in running a sporting body, large or small. It will also be of interest to policymakers and auditors. It is available from www.orpenpress.com and all good bookshops for €20.
Anne McFarland is a chartered accountant with a Diploma from UCD in Corporate Governance and a Diploma from the Law Society in Sports Law. She has been a finance director of multinational organisations for many years; she lectures on corporate governance and enjoys working with sporting entities, big and small, to develop strategy and improve governance. This book draws on her practical experience as a board member and as an advisor on governance, as well as her interest in sport, both amateur and professional. She is co-author of A Practical Guide for Company Directors (Chartered Accountants Ireland, 2017).
Covid-19 Update – Irish Sailing Drawing Up Proposals for a Return to Sailing When Restrictions are Lifted
Since the Taoiseach announced full restrictions and closure of clubs and activity centres last month, with the latest update being the continuance of full restrictions until at least May 5th, Irish Sailing has been looking ahead to the process by which we might be in a position to return to the water, and start organising activities once more. The way in which different people access sailing and boating both recreationally and competitively is very varied, and we need to ensure all aspects of the sport are included in any plan to return. We are now working on proposals that will be submitted to Sport Ireland outlining how we might be in a position to adapt our activities in order to remain compliant with restrictions as they are lifted. We will keep you updated.
Harry Hermon, CEO, Irish Sailing
Winners Crowned in Online Irish Sailing Awards Ceremony
Royal Irish Yacht Club skipper Paul O’Higgins has won the Irish Sailing and Afloat.ie Sailor of the Year Award for his outstanding cruiser-racer season at an online awards ceremony tonight.
Dublin Bay skipper O’Higgins was the first double-winner of the Volvo Dun Laoghaire to Dingle race. Racing his JPK 1080 “Rockabill VI”, he also showed consistent form with a series of wins throughout the year, including a class victory at the ICRA National Championships in June, Calves Week in August, and the ISORA title in September.
Read a full profile of the winner and his record-breaking season by W M Nixon here
Eve McMahon of Howth Yacht Club, a trialist for the Tokyo 2020 Olympics, was awarded the Youth Sailor of the Year for her performance internationally in the Laser Radial class.
The Irish Sailing President’s Award was given to Gary MacMahon of the Ilen project from Limerick and West Cork. Gary spearheaded the project to repatriate and restore the historic wooden ketch, which is now used for community-based sailing and educational projects.
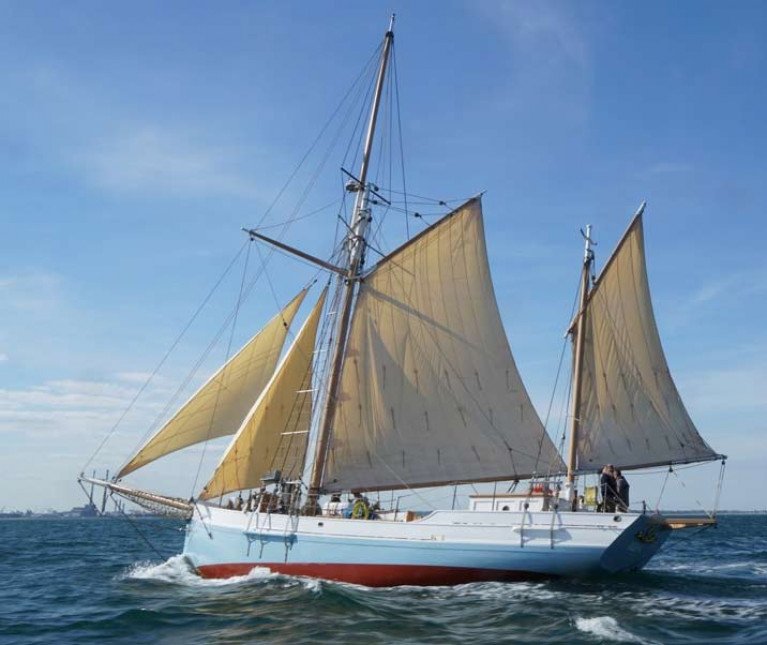 The ketch Ilen
The ketch Ilen
The Sustainability Award was won by two clubs – Bray Sailing Club (Co. Wicklow) and the National Yacht Club in Dun Laoghaire for their environmental work. The Inclusion Award was won by Jon Hynes and his team at Kinsale Outdoor Education Centre.
The Irish Sailing Senior Instructor of the Year Award went to Sam Hennessy of Wicklow Sailing Club.
Malahide Yacht Club took home the popular Irish Sailing Training Centre of the Year award, having been nominated as winners of the Eastern Region. The two other nominees were Galway Bay Sailing Club (West Region winners) and the Oysterhaven Centre (winner of the South Region).
The Irish Sailing Awards are supported by Dun Laoghaire-Rathdown County Council.
In line with social distancing measures in force for the COVID-19 emergency, Irish Sailing announced the winners online.
Following the incident in Dun Laoghaire last year involving Irish Sailing’s High-Performance Optimist Squad and the subsequent investigation and report, Irish Sailing established a working group to consider the recommendations of the report, assess how best Irish Sailing could address them, and to help with the implementation.
The working group comprises David Turner (National YC), Ciaran McSweeney (Monkstown Bay SC & RCYC) Brian Craig (Irish Sailing Board), Harry Hermon (Irish Sailing CEO) and James O’Callaghan (Irish Sailing Performance Director). The group set about developing a simple, practical and fit-for-purpose Safety Resource Pack for ensuring safe coaching events.
The Safety Resource Pack is intended to set the framework for the various functions and principles by which staff, contractors, volunteers and other representatives should discharge their responsibilities as an organiser of coaching events. The objective is to achieve a high standard of safety within Irish Sailing coaching events, without unduly constraining the sailing activities. The aim is not to dictate or restrict activity in any way, but to provide a framework for organisers to identify responsibilities, and make informed and finely judged decisions around safety.
The Safety Resource Pack has been tested by the Irish Sailing Performance squad training, along with club coaching events from three clubs of varying size and resources. The feedback is that the Resource Pack is simple and practical, and has been welcomed by those who have used it so far. The system is now being used by Irish Sailing’s coaching events, and it is anticipated that clubs and classes will adopt it when organising their own coaching activities.
The Safety Resource Pack identifies:
- key functions/responsibilities for organising coaching events
- protocols for dealing with emergencies
- coach pre-requisites for Irish Sailing Coaches
- a practical checklist for planning a coaching event
- a risk assessment to be used for the decision to launch
The Safety Resource Pack (and particularly the risk assessment) will be most effective as an interactive tool maintained as an ‘app’ on a phone, tablet or laptop. In this way, the decision-making process for each coaching event may be recorded online, and negate the need for paper records. Irish Sailing is currently exploring options for using Irish Sailing’s Passport system for this purpose. With some modifications to the software which will be completed in the autumn, it is anticipated that the pack will become available to organisers of coaching events as a live system. In addition, we hope to extend the pack to incorporate racing events in the future.
Irish Sailing says, although the end result is deliberately short and simple, there has been a great deal of research into other systems, both nationally and internationally, along with input from a multitude of people with relevant experience.
Nobby Reilly Details Decision To Resign From ICRA
#ICRA - Norbert ‘Nobby’ Reilly has spoken to Afloat.ie to clarify his comments over his resignation from the Irish Cruiser Racing Association (ICRA) last week.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the Howth Yacht Club sailor and former ICRA commodore left the organisation on the eve of a crucial symposium at the weekend to decide its future, citing disagreements with its direction over the previous year.
Among these were claims that little of its funding boost since signing a memorandum of understanding with Irish Sailing went to new training programmes or recruitment of new members.
Reilly also referred to the decision to make Galway the host venue of the 2018 ICRA Nationals was not passed by the executive, and that the first he learned of it “was on Facebook”.
Commenting to Afloat.ie on Friday, IRCA commodore Simon McGibney said that Reilly had been given a fair hearing regarding his complains, adding that decisions “are always done by majority”.
But Reilly has hit back at assertions that there is “democracy” in the organisation, claiming that no minutes of meeting have been produced where Galway was agreed as this year’s venue.
Following the announcement, Reilly says there was “a storm of protests” from Dublin-based cruiser racers.
A survey was sent out to all members to gauge whether or not they sailed in the 2017 ICRA Nationals at the Royal Cork, the results of which have yet to be officially published.
“All summer ICRA received emails and calls protesting about Galway,” adds Reilly. “I requested that same be made available to [the] ICRA exec but reply received [was] “These were personal to the commodore.’”
Reilly says there was a push within the organisation for an EGM to review the danger of becoming irrelevant to the Dublin fleet, which constitutes the majority of IRCA’s membership.
Instead, a full executive meet was arranged, but Reilly claims that its members had not all been made aware of the complains from the Dublin membership, and that the resulting meeting only saw 50% attendance.
Reilly says his pitch to the executive that IRCA talk with Galway with a view to keeping Dublin as a host venue for the 2018 calendar was voted down — and he was further shot down over his request that Dublin keep a slot by running an East Coast IRC.
“The exec in ICRA is just irrelevant,” adds Reilly on his decision to resign. “Recently two new members [were] added with no discussion or prior notice.”
The historic 70th Anniversary staging of the All Ireland Sailing Championship has seen the famous silver salver depart for a long journey to its new home in Baltimore, as the winner is Baltimore SC’s Fionn Lyden, who was crewed to the win – raced in GP 14s – by Liam Manning.
Although Lyden is currently best known as the 2017 Under 23 Bronze Medallist in the Olympic Finn, he was racing at Mullingar as the nominee of the Irish Team Racing Association, for it was through inter-University team racing that his name first registered nationally as a sailor to watch.
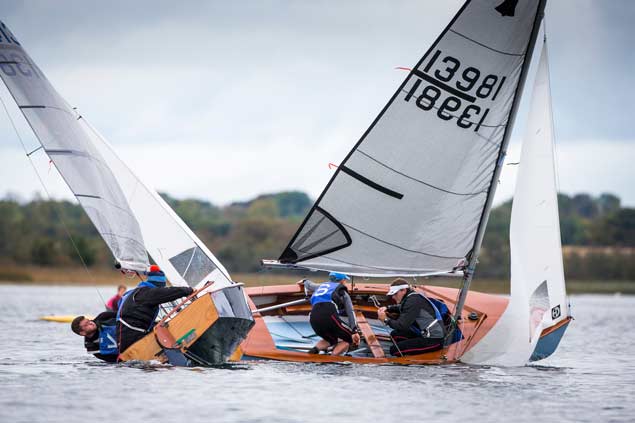 In the final race a strategic decision by Lyden resulted in a two-boat match race between him and Shane McCarthy that took place at one side of the race area
In the final race a strategic decision by Lyden resulted in a two-boat match race between him and Shane McCarthy that took place at one side of the race area
He and Liam Manning had their work cut out against a formidable field in the final, with defending champion Alex Barry of Monkstown Bay and the RS400 class, and GP14 World Champion Shane McCarthy of Greystones, both on top form.
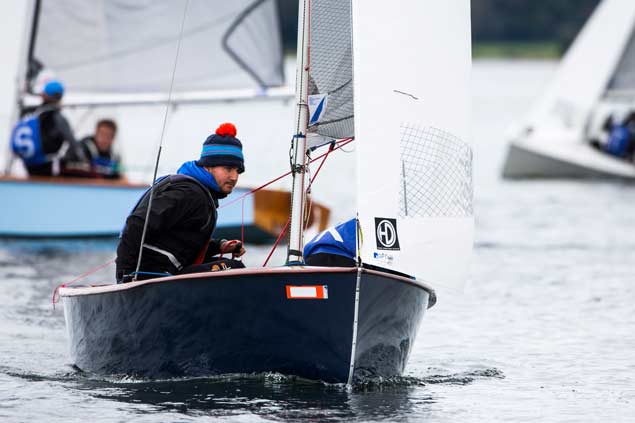 Fionn Lyden was a wild card entry on behalf of the Irish Team Racing Association
Fionn Lyden was a wild card entry on behalf of the Irish Team Racing Association
But Lyden kept his cool and finished the series with 16 points to the 18 of Alex Barry and the 19 of Shane MacCarthy, who came through to third overall in a tie-break with Laser sailor Sean Craig (Royal St George) also on 19.
Read our All Ireland preview by WM Nixon here
Irish Sailng adds (on Monday, October 9 at 1300): Fresh from winning bronze at the U23 Finn World Championships earlier this summer, Baltimore’s Fionn Lyden has won the All Ireland Sailing Championships at Mullingar Sailing Club today.
The series was decided on a knife-edge finale that saw Lyden match-race to the finishing-line with GP14 World Champion Shane McCarthy from Greystones who was denied victory by the tie-break in the series.
Lyden’s crew was fellow West Cork sailor Liam Manning from Schull and the pair represented the Irish Team Racing Association who were Wild Card entries in the championship that is celebrating 70 years.
Two very different days of racing tested the sailors: Saturday was a typical autumnal afternoon on Lough Owel – strong and quite blustery but manageable conditions apart from a few capsizes.
Sunday morning saw the repechage races to decide the last two places in the final, but then the wind dropped and the lake turned into a mirror. Patience from Jack Roy’s Race Management team was rewarded in the late afternoon when a light breeze picked up enough to allow three races in quick succession.
The going was slow, but in the final race a strategic decision by Lyden resulted in a two-boat match race between him and Shane McCarthy that took place at one side of the race area, while the rest of the fleet including last year’s winner Alex Barry battled it out for a podium place.
The final results were Fionn Lyden with crew Liam Manning of Baltimore SC; in second place were Alex Barry with crew Richard Leonard of Monkstown Bay SC , and in third was Shane McCarthy and crew Andy Davis of Greystones SC.
Inaugural Watersports Inclusion Games at the Royal St. George Yacht Club Attracts 220 Participants
The weekend of 24 June saw the inaugural Watersports Inclusion Games taking place in Dun Laoghaire at the Royal St. George Yacht Club with 125 volunteers providing activities for over 220 participants with various abilities on the physical, sensory, intellectual and learning difficulty spectrums and representing all ages, demographics and socio-economic backgrounds. The participants and their families had a chance to try sailing, rowing, canoeing/kayaking and fast boat rides.
Such was the popularity of Day One that Day Two saw many familiar faces and repeat attendees.
The Games aim was not just about showing participants that watersports are accessible, but also to show to watersports providers that with a little bit of training and planning, they can facilitate people of all abilities and backgrounds to get out on the water. The atmosphere during the weekend was fantastic, with participants queuing to sign up for as many different activities as possible – from rowing to 1720 keelboat sailing and yachting, to rib-tripping and kayaking under the piers.
The event would not have happened without the many volunteers who generously donated their time and expertise, and there was enthusiastic feedback from participants and volunteers – both groups saying how much fun the Games were.
The organisers were Irish Sailing, Canoeing Ireland, Dun Laoghaire Sea Scouts, Dun Laoghaire Sailability, Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council, Spinal Injuries Ireland and Royal St George Yacht Club, with generous resource support from National Yacht Club, Royal Irish Yacht Club, Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club, and Adventure Training Ireland. The event was funded by the Sport Ireland Dormant Accounts Sports Inclusion Fund and supported by Dun Laoghaire Rathdown County Council and Dun Laoghaire Harbour Company.
ISA’s Re-Brand as 'Irish Sailing' Gets Mixed Response
We live in a world swamped in acronyms, so much so that even a simple one like ISA has to be explained as “Irish Sailing Association” to all except those involved with or interested in our sport writes W M Nixon.
But we also live in a very crowded world where, if at all possible, the theme of “Less Is More” is increasingly desirable. So the announcement yesterday evening (Monday June 26th) by the Irish Sailing Association, that it is in the process of re-branding itself more simply as Irish Sailing, is in line with a distinct and generally desirable trend.
Like many who have been intimately involved with the ISA in its many manifestations, with it born out of the Irish Dinghy Racing Association and then mutating through the Irish Yachting Association to become the Irish Sailing Association, a first reaction was one of disapproval, but it changed.
There was something attractively personal about an Association, and as its constitution defines “sailing” as an “activity involving engine or sail-powered craft”, it was a recognizable coming-together of people with shared interests in a grouping with its own distinct identity under a very broad umbrella.
ISA provided a sense of belonging, and individual members could cherish their long personal links to it. Yet for outsiders – non-sailors who might be attracted into getting involved with some aspect of our diverse sport – the use of the acronym “ISA” and the defining word “Association” could be off-putting.
For longtime dedicated sailors, these might seem to be decidedly precious, nit-picking and very minor considerations. But you only get one chance to make a first impression, and the modern ideal is that the sense of something being a “movement” as much as an association is a significant factor in making a favourable first impression.
Then too, we’re trying to get away from acronyms, and reduce the number of syllables in a recognisable title to an absolute minimum. ISA as an acronym has only three syllables. But Irish Sailing Association arguably has seven syllables. This makes it quite a mouthful, thereby encouraging reversion to the acronym, which of itself tells us very little of what this organisation is all about
However, “Irish Sailing” has only four syllables. One more than “ISA” perhaps, but still few enough for people to gives it the full title when referring to it, rather than using the much-too-short and possible confusion-causing acronym IS.
So on balance, my response is that the re-branding as Irish Sailing deserves a guarded welcome. But I’m acutely aware that even though the announcement was made only last night, and on a very wet Monday night at that, heated passions are aroused, and there’s an equally tenable argument which sees it differently. That great contributor to Irish sailing afloat and ashore, Monica Schaefer of Greystones Sailing Club and the Wayfarer Class, speaks eloquently for those who feel a special personal link to our national authority:
“I find it incredible to think that the ISA is seriously going to change its name to the same initials/abbreviation as the worlds largest terror organisation. Surely someone must realise that using the initials I and S together will attract all sorts of problems with internet traffic, gaining attention from people not intent on enjoying sailing and from security systems designed to pick up internet / social media traffic that track that sort of thing.
How will racing sailors who are not part of a club now be identified on a race results sheet if they are no longer members of the ISA? Ah yes we can just put down IS instead of ISA, that’ll sort it - LOL
Notwithstanding the problems the initials might attract, surely removing the association makes the organisation so much more impersonal and commercial sounding, if it is no longer an association, does that mean that those who subscribe to it are simply customers and no longer members? Has anyone thought about the fact that If we are not members anymore we will soon lose our sense of belonging? I wonder if we are no longer members of an association will the new organisation be scrapping the membership fee in line with it’s new identity (lol again) presumable the ISA members can now expect a refund of their paid up fee for the remainder of this year.
On hearing this announcement today I immediately feel disconnected with the new identity. I have been a proud member of the ISA since the time of the IYA and now I feel that we the members have just been jettisoned over the side to make way for “progress”, and that we are no longer a part of this supposedly more marketable commercial organisation that has taken over.
Surely a name change requires discussion and debate with the membership and a vote at an AGM or EGM at least? It’s a huge identity change that effects us all so surely we should have a say in it.
This move shouts of commercial interest and does not I believe reflect the interest of the members, but maybe the organisation doesn’t need or want members anymore, and the commercial side of the business wants to follow the lead of ISAF who started this trend with their move from the easily recognised and meaningful ISAF branding to the dull and bland branding of World Sailing.
This really is a shock and not something that ISA members should take lightly.
Regards,
Monica Schaefer”