Displaying items by tag: Marine
Water Quality and Marine Score Lowest In Report Card on Government Climate Commitments
Water quality and the marine scored the lowest in a “report card” commissioned by Friends of the Earth on Government progress on its own climate and environmental promises.
This year’s grading of “C plus” represents “moderate progress” and is a “small improvement” on the C grading awarded last year.
The grading was carried out for Friends of the Earth by experts who annually assessed the Government’s implementation of commitments in the Programme for Government.
The group said there was a significant improvement in the “Energy” category, one of nine subject areas.
The Government’s highest scores came in the categories of “Waste and Circular Economy” (7.5 - down from 8.5 last year), “Energy” (7 - a significant improvement from 4 last year) “Buildings” (7 - up from 6 last year) and “Air Quality” (7 - same as last year).
The lowest scoring categories were “Agriculture and Forestry (4 - same as last year) where the Government is now “flirting with failure”, the group says, and “Water and Marine (5 - marginally up from 4.5 last year).
Commitments on drinking and waste water are “in danger of not being achieved by this Government”, the group says.
It notes that Ireland’s water quality worsened in 2022 compared to 2021, with dangerous nitrate and phosphate concentrations in many of Ireland’s river sites, estuarine, and coastal water bodies.
Chair of the assessment panel, Dr Cara Augustenborg from UCD said that “we’re accustomed to hearing nothing but bad news when it comes to Ireland’s environmental record, but taking a deep dive inside the Government’s work since 2020 provides clear evidence that progress is being made to improve Ireland’s environmental health in most areas”.
“It’s frustrating that this work is not yet apparent in people’s lives and we’re not seeing the transformational changes needed to address the climate and biodiversity emergency,”she said.
“However, if the Government doubles down on their efforts through intense and sustained effort, we could be living in a more sustainable Ireland within the decade. The question is whether or not the Government’s will is strong enough to accomplish this in the short time remaining.”
Dr Paul Deane from University College Cork said the review “gives us cause for hope but not a reason for celebration”.
“Ireland’s greenhouse gas pollution has reduced marginally this year, but we are still massively addicted to fossil fuels. However, we are seeing a positive foundation for a cleaner future being put in place,” he said.
Dr Diarmuid Torney from Dublin City University said that “three years on from the formation of the Government, we see a mixed picture”.
“Although a good foundation is being laid, and there is solid progress in some areas, overall delivery is slower than I would have liked to see approximately two-thirds of the way through the Government’s term in office,” he said.
Oisín Coghlan, Friends of the Earth chief executive who commissioned the assessment, said that it showed that “time is running out fast for this Government to fulfil its climate and environmental commitments”.
“The coalition leaders need to be upfront with people that a certain amount of inconvenience and disruption is unavoidable now, in order to prevent climate chaos and destruction down the line,” he said.
“My fear is party leaders will become more timid as elections approach, when what we need now is honesty and courage,” Coghlan said.
Fish Farmers Challenge Marine Minister
Despite numerous requests for support with rising costs, Irish aquaculture has been ignored, according to the representative body for the country’s fish farmers, IFA Aquaculture.
It has taken issue with a claim by the Marine Minister that he has supported the sector through the Ukrainian crisis.
The Minister’s appearance on RTE’s Prime Time has been criticised, where he said he had supported the Irish seafood sector during the Ukraine crisis. Teresa Morrissey, Executive of IFA Aquaculture, has made a strong riposte: “He hasn’t. As ever, Irish aquaculture has been ignored, despite numerous requests for support with rising costs.
“Some fish feed costs have almost doubled recently. Electricity costs will increase by an average of €100.000 this year for some operators. Raw materials costs have increased. Some of our members estimate they will spend an extra €350.000 over coming 12 months. This is not sustainable for Irish Aquaculture operators and their businesses will no longer be profitable unless there are significant supports during this time of crisis to assist with spiralling input costs.”
Irish Aquaculture has huge potential, says the IFA.
“The State needs to believe in the sector.”
Listen to Teresa Morrissey of IFA Aquaculture below.
Students Showcased their Projects in the Marine Institute's Headquarters in Oranmore
Thirteen undergraduate students, participating in this year’s Marine Institute’s Summer Bursary programme, recently showcased their projects at a poster presentation day, held at the Marine Institute’s Headquarters in Oranmore.
The Bursars presented the outputs of their projects to the staff of the Marine Institute and answered questions about their project work. This year’s bursaries comprised a broad range of projects that are linked to the work undertaken by the Marine Institute. The project areas include Fisheries, Molecular Chemistry, Aquaculture, Marine Infrastructure Asset Management, Oceanographic analysis, Ocean Economics, Research Office, Human resources, Library and Marine Communications.
“The presentations showcased the diversity and high standard of work our bursary students are involved in,” said Helen McCormick, Bursar Programme Coordinator and Senior Laboratory Analyst at the Marine Institute.
A panel of judges, drawn from a range of Marine Institute staff, reviewed the posters, selecting three winners based on the student’s knowledge of their work, the presentation of their project information and their answers to a variety of questions.
Éabha Gaughan (NUI Galway) was awarded first place for her outstanding work on Human Resources Support which showcased her restructuring of the Marine Institute’s internal staff intranet using SharePoint software.
Éamonn-Joeín MacDonnachá (University College Cork) and Sara Ellis (NUI Galway) were both awarded second place for their creative work on analysing crayfish historic records and how they can be used as validation for the molecular detection of crayfish pathogens.
Hadia Mahmood (Munster Technological University) was awarded third place for her informative presentation on Ireland’s marine economy, in which she gathered data from various sectors and identified specific marine-related state investments.
“Each student showcased their work with energy and clarity and a great strength of the bursary scheme was to see students undertaking projects that were unrelated to their undergraduate degrees” said Dr Paul Connolly CEO of the Marine Institute. “Our Bursary scheme is a great introduction to the diversity of marine science and having undertaken four such bursaries many years ago, I am so proud to see the scheme continue to flourish.”
The Marine Institute Summer Bursary Programme has been running since the 1960s. A highly sought-after work experience programme in marine science, the programme continues to offer a promising gateway for students into the expanding world of marine science and research in Ireland.
The programme is aimed at undergraduates who have completed two years of study in a relevant discipline and is advertised on www.marine.ie in February each year. The scheme will continue in 2023.
Floating Nuclear Reactors & Reducing Shipping Carbon Emissions Theme of International Conference
The role of the marine environment in the push towards “net zero” carbon emissions is the theme of an international marine engineering conference running online later this month.
The challenges involved in using offshore wind energy and the feasibility of “floating nuclear reactors” to reduce emissions will also be discussed at a fortnight-long online conference opening later this month.
The conference from June 28th to July 9th is hosted by the Institute of Marine Engineering, Science and Technology (IMarEST) - an international body for marine engineering, science and technology professionals which has charitable status and is based in Britain.
Clean energy and transport in relation to ship-based research expeditions will be addressed by National Oceanography Centre associate director of national marine facilities Leigh Storey.
Setting a benchmark for decarbonising operations and maintenance vessels attached to offshore wind farms is the focus of a talk by economic analyst Dr Anthony Gray of ORE Catapult.
Using asset leasing models to encourage energy-saving technologies in reducing carbon emissions from shipping with be discussed by BMT naval engineer Nick Williams.
Soon Heng Lim, founder of the Society of Floating Solutions will focus on the controversial topic of floating nuclear plants – as in small modular reactors to reduce carbon emissions.
“We have an exceptional roster of speakers for this year’s annual conference, exploring many of the most pertinent subjects across marine engineering, science and technology,” IMarEst chief executive Gwynne Lewis said.
Attendees can register for the event via the IMarEST’s website here
Atlantic Seaboard Harder Hit Than East Coast by Economic Affect of Pandemic, Report Says
Dublin may have the highest number of cases of Covid-19 infection, but it is least exposed of all Irish counties to the economic impacts, a new report says.
The Atlantic seaboard reliance on tourism and recreation, including the marine sector, and service industries is making it more vulnerable, with Kerry has been identified as the hardest hit, the report by the Northern and Western Regional Assembly says.
It identifies Galway as the city most likely to be severely affected, followed by Waterford, Limerick, Cork and Dublin in that order.
The report bases its information on numbers of commercial units operating in sectors which are likely to be worst affected, including mining and quarrying, construction, non-essential retail and wholesale services, food and accommodation, arts, recreation and entertainment, hairdressing, beauty and fitness.
It notes these are sectors which rely on human interaction and have been forced to close or downsize dramatically, due to social distancing measures. The nature of their business largely prevents them from operating remotely.
The report calculates that Kerry has 53.8 per cent of its commercial units operating in the sectors, and is likely to be hardest hit as a county.
It is followed by Westmeath at 51 per cent, Donegal at 50.6 per cent, Cavan at 50.5 per cent and Clare at 50.4 per cent, the report estimates.
The report says that exposure is “generally lower in more urban-based counties” as “such counties rely more on economic activities that are capable of operating remotely” – as in activities such as finance, ICT and professional and technical services.
It says the county with the lowest “Covid-19 exposure ratio” is Dublin, with 39.4 per cent of its commercial units operating in the sectors likely to be worst affected.
It calculates Cork is also cushioned, with 44.4 per cent of its commercial units in worst affected sectors, while Carlow is at 44.7 per cent, Waterford is at 45.8 per cent and Wicklow is at 46 per cent.
It says that in “absolute terms”, Dublin has the highest number of commercial units operating in the most exposed sectors at 14,360 units, followed by Cork at 8,144 units, Galway at 4,253 units, Kerry at 3,263 units and Donegal at three.
It says that Galway city and suburbs have 46.1 per cent of commercial units operating in the sectors likely to be worst affected, “in line with the corresponding ratio for the State as a whole”
The report for three regional assemblies by economist John Daly was prepared to identify which geographical areas in Ireland are more likely to be exposed to economic disruption caused by the necessary measures to prevent the spread of COVID-19.
It uses information from the GeoDirectory commercial database, as of September 2019.
Analysing the impact on a regional basis, it says the northern and western region has the highest “COVID-19 exposure ratio”, with 48.6 per cent of its commercial units operating in the worst affected sectors.#
The southern region has 47.2 per cent of its commercial units operating in the most affected sectors, while the eastern and midland region has the lowest “COVID-19 exposure ratio” at 43.6 per cent, the report says.
It notes that in absolute terms, the eastern and midland region had the highest number of commercial units operating in the sectors likely to be worst affected at 29,637 units, followed closely by the southern region at 27,583 units and the northern and western region at 16,515 units.
Maritime Organisations Should Speak Out at Election Time
The first people arrived on the shores of this island some 10,000 years ago… according to history …. but as the Irish people of today listen to the campaigning of those who want to be elected as our rulers - those political hopefuls do not prioritise the maritime sphere and, in national debates on television, radio and in the print media, they have not referred to it.
What does that indicate?
That the marine does not rank as a priority matter, even though it is a vital channel of transport, food supply, energy, communication and leisure. You'll have to dig deep to find political manifesto commitments to maritime affairs.
Afloat has done that for you in its assessment of how the main parties perceive maritime matters. The conclusion reached is that: “This island nation still doesn't have a marine policy or a dedicated marine department. It’s a ship of state without a captain or a rudder.”
This is despite some commitments, such as ‘harnessing our ocean wealth..” though that seems to have stalled somewhat.
I actually like the fact that politicians and political parties, even Government Ministers and leaders of industry refer these days to “this island nation” a phrase I can claim some justification for promoting during my years of broadcasting, but I'm getting very fed up with politicians, government and all political parties in this General Election for their attitude towards the marine sphere.
 Is it because of lacking an outspoken approach that the maritime sphere is neglected?
Is it because of lacking an outspoken approach that the maritime sphere is neglected?
The third biggest country in Europe, by virtue of our seabed territory of 220 million acres, as I’ve often heard quoted, but as fishermen will tell you, most of that was given away by the Government. That was put well this week by John Nolan, 37 years in the fishing industry and Managing Director of Castletowbere Fishermen’s Co-op, when he said Ireland was wronged, robbed of this huge economic resource and he blames politicians and the Civil Service administration.
The Irish Islands Council – Comhdhail Oilean na hEireann and fishing organisations – have called on election candidates to publicly pledge commitment to the offshore islands and to the fishing industry… but I haven’t heard a single other maritime organisation make any calls, nor speak out as strongly as John Nolan has done…. Is it any wonder then that successive governments got away with removing a dedicated marine department in an island nation and dividing the marine sphere into the responsibilities of six Departments… That was a divide and conquer policy motivated by civil service advice, I was told. It certainly removed a maritime focus at the Cabinet table.
But while politicians can generally be berated for their lack of maritime interest – the maritime sphere – all of it – perhaps needs to look at itself – and to speak out the maritime sector more loudly….
More on the podcast below.
Marine Garden Promoting Clean Oceans Wins Gold at Bloom
A marine garden containing almost 30,000 cubic litres of Atlantic seawater and brimming with sea life from different types of seaweeds to fish species native to Irish waters has been named the overall winner in the concept garden category at Bloom 2019 today. As previously reported by Afloat, the Bord Iascaigh Mhara sponsored garden, Aquamarine, supported by the European Maritime and Fisheries Fund, was designed by wife and husband team Liat and Oliver Shurmann and highlights the need to protect Ireland’s marine environment against plastic waste.
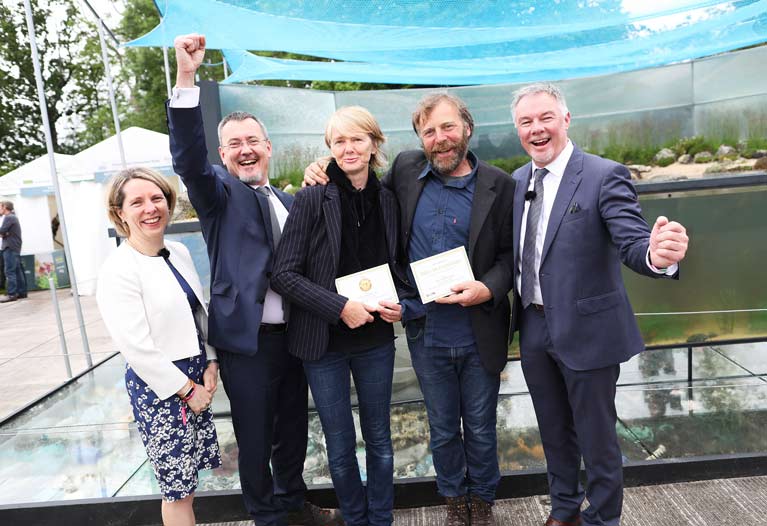 Gold Bloom winners - l-r, Tara McCarthy, CEO Bord Bia; Jim O’Toole, CEO BIM; Liat Shurmann; Oliver Shurmann and Gary Graham, Manager Bloom, Bord Bia Photo: Julien Behal
Gold Bloom winners - l-r, Tara McCarthy, CEO Bord Bia; Jim O’Toole, CEO BIM; Liat Shurmann; Oliver Shurmann and Gary Graham, Manager Bloom, Bord Bia Photo: Julien Behal
Jim O’Toole, CEO BIM said: “ Marine, human and all other life is contingent upon a marine environment that’s clean and free from pollution and plastics. Every item of plastic that surrounds the garden at Bloom is a real example of marine litter that has been collected by fishermen and members of the wider fishing and seafood industry in Ireland. Sustainability is central to BIM’s strategy and it’s the driving force for men and women working in the seafood industry in Ireland.”
The fish species and water will be returned to the sea when Bloom ends on Monday and all of the materials used in the garden have been either salvaged or recycled and will be reused.
Oliver Shurmann spoke about the design of the marine garden and said: “It’s designed to look like a scientific cross-section of a landscape with layers of plastics visible underneath it. That’s what we [Liat and I] wanted to achieve. We wanted to create an atmosphere and to combine something beautiful with something that was repulsive. This will shock people. Children will see this and wonder, ‘what are we doing?’”
The garden has been designed to highlight the problem of plastics in our oceans as part of the Clean Oceans Initiative that was launched by the Minister for Agriculture, Food the Marine, Michael Creed earlier this year.
Catherine Morrison, Sustainability and Certification Manager at BIM, spoke of how the marine garden aims to raise awareness of the impact plastic is having on the marine environment and how fishermen and fish farmers in Ireland are working together to address the problem. She said:
“ It’s hard to quantify how much plastic is in our oceans but the average adult in Ireland uses roughly 60kg of plastic every year, one of the highest rates of any country in the European Union. Not all of the plastic ends up in the oceans, but the plastic that does causes a problem.”
Aquamarine is open to visitors each day of Bloom from Thursday 30th May until Monday 3rd June.
Maritime Priorities In Transport’s Statement Of Strategy 2016-2019
#Maritime - ‘Safe and sustainable’ marine transport and ‘delivery of emergency management services’ have been made a high level goal in the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport’s Statement of Strategy 2016-2019, published this week.
Identifying Ireland’s maritime sector as “a critical gateway” for trade and tourism, the statement calls for “an efficient and effective competitive ports sector [that] can foster job creation” via trade, infrastructure developments and “opportunities in other areas such as offshore energy, cruise and marine leisure and recreation.”
Reduced ship emissions and safety at sea are also priorities within the Maritime Safety Strategy, which “includes a range of actions to be implemented or begun by 2019” such as flag state and port state regimes, and the IMO’s Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers.
Key services in this strategy include the delivery of a 24/7 marine emergency response and management service by co-ordinating the response to SAR incidents and pollution threats at sea.
Progress on these goals will be monitored by various indicators, such as the transfer of regional ports to local authority control by the end of 2018, the imposition of a new ‘ports performance’ measurement system by the end of 2017, the development of a web portal for SeaSafe Ireland by the middle of next year, as well as a minimum 90% availability of Irish Coast Guard units ahead of “full interoperability” of marine rescue co-ordination by next winter.
The full Statement of Strategy 2016-2019 can be downloaded HERE.
What's New on Afloat's Marine Marketplace?
A new Tohatsu outboard engine (2.5HP 4-stroke Short Shaft (15") at €726, Mirror dinghy spars for a fiver, a maritime painting of the ARC fleet at €200 by artist Pete Hogan are just a few of the offers currently on Afloat's Marine market.
You can also find a range of charts and cruising guides from Todd Navigation in Belfast, bilge pumps and anchors from O'Sullivan's Marine in County Kerry plus Rick Tomlinson's sailing calendars and a lot more besides. Seller Gary Elisson wants a project boat to do up as a live aboard. 'It must be cheap', he says. Waterford seller Niall Power has a carbon fibre spinnaker pole (3.5 Mtr long) for sale at €700.
Recent section updates now include space for boatyard services such as engine repairs, marina berths, boat hire, sailing school courses, crew and much more.
Check out the latest items here and list your own items, services and events in Ireland's dedicated maritime marketplace.
The idea behind the platform is to give focus to the Irish marine market through a definitive portal.
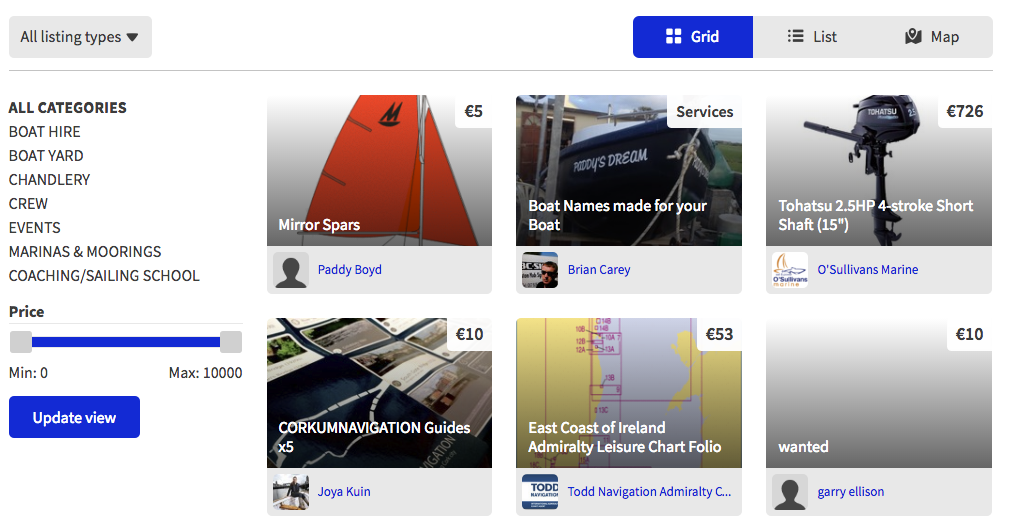 Some of the latest items on Ireland's marine marketplace. Click for more.
Some of the latest items on Ireland's marine marketplace. Click for more.
Marine Plan Could Deliver An Additional 29,000 Jobs
#oceanwealth – Addressing the second 'Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth' Conference today, in Ringaskiddy, Co. Cork, Simon Coveney TD, Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine outlined new economic research that indicates the Government's blueprint for the marine which could deliver more than 29,000 additional jobs and an additional €2.7bn in economic growth by 2020. Downloasd speech below.
Minister Coveney said that "Ireland is now firmly on what I believe is an unstoppable journey of marine expansion. We are experiencing a significant period of 'blue growth' with a 9% increase in growth in Ireland's marine sector over the last five years and the ocean economy now valued at 1.3% of GDP. Today we are building on this progress with the publication of a development framework for the marine sector, coupled with the clear commitment from Government to introduce a marine spatial planning process for the country, which will underpin the achievement of these economic targets as the Harnessing Our Ocean Wealth strategy is implemented."
Ireland's Ocean Economy report and associated research on the downstream impacts of the marine, produced by the Socio Economic Marine Research Unit at the National University of Ireland states that if HOOW targets are met, 29,300 new jobs could be created by 2020, with 16,100 projected to come directly from the marine sector. An additional growth of €2.7bn in the wider economy is also expected.
The report also confirms the current value of the blue economy. In addition to the 18,400 individuals currently directly employed in our marine industries, a further 13,000 are employed indirectly across the wider economy, creating an additional €3.3bn in turnover. For every €100 turnover created from our ocean economy, a further €78 is created indirectly in other sectors.
The Minister encouraged members of the public to attend the Seafest 2015 open day on Saturday in Ringaskiddy "Members of the public will be able to access a state of the art stimulator that is used to train ships' captains and visit seafood cookery demonstrations. They will also be able to experience what it's like to be exposed to hurricane force winds through the BIM Beaufort Scale Hurricane Experience. There will be an extensive seafood fair and cookery demonstrations and multiple other activities on and off the water. This event is free of charge for every age group with lots of family activities planned."
The Conference included contributions from Minister Coveney, Alex White, T.D., Minister for Communications, Energy and Natural Resources; Sean Sherlock, T.D., Minister for Research & Innovation; and Mr Paudie Coffey T.D., Minister of State at the Department of the Environment. Commissioner Karmenu Vella, Environment, Maritime Affairs and Fisheries European Commission and Rt. Hon. Darin King, Minister of Business, Tourism, Culture in the provincial government of Newfoundland and Labrador also spoke at the Conference.
This second annual Conference which reviewed ongoing progress on implementation of the Government's Integrated Marine Plan (published in 2012) was attended by over 500 delegates from the public and private sector with an involvement in the marine sector.
In concluding his address, Minister Coveney said "I believe that the outlook for the sector is really exciting and the possibilities are endless. The challenge now is to make the marine sector a leading contributor to the Irish economy and to recognise the potential we have as an island nation to be a major player in the sector internationally."



































































