Displaying items by tag: Rescue
Relatives Express Delight at Award for Donegal Fishermen, 63 years After Rescue of 18 people
The relatives of a Fermanagh woman who was one of 18 people rescued by two Donegal fishermen have expressed delight that the men are to receive national bravery awards – all of 63 years after the event writes Lorna Siggins
James and Michael “Mickey Red” Gallagher, aged 85 and 80 respectively, will be conferred with State bravery awards today at Farmleigh House, Dublin, and their late father, Michael, will be given posthumous recognition for his role.
The late Jean Morrell, née Mavitty, from Enniskillen, Co Fermanagh, was one of the 18 saved by the Gallagher brothers, after the punt she was a passenger in sank off Roaninish skerries, some five km off Portnoo, Co Donegal.
Jean Mavitty was aged 15 at the time, and had to be restrained by the Gallaghers from trying to jump in again to save her dad after she had been pulled from the Atlantic.
The body of her father, Desmond Mavitty (49), was found three weeks later on Roaninish. He was one of three fatalities.
A young boy, Christopher Chambers, was fatally injured in the propeller of a nearby yacht which had tried to help, while a family friend of the Mavittys, George Warren (55), was taken from the water by the fishermen. In spite of attempts to resuscitate him, he did not survive.
The fishermen, who had set out from Rutland island to fish for lobsters in their father’s half decker, Irine, took the 15 rescued from the water after the punt sinking back into Portnoo.
They also secured the body of Christopher Chambers, and towed in the yacht with three people on board to safety.
There were no VHF radios at the time to contact the RNLI Arranmore lifeboat, and limited communication meant that there were no Gardai at the pier. The fishermen were not notified of the inquest into the three fatalities, which took place that night.
When they got home to Rutland island, which lies between Burtonport and Arranmore, they remember their mother was beside herself with worry, as she had by then heard a report of a sinking and thought her husband and sons had been lost.
Jean Mavitty’s son, Robert, lives in Enniskillen, and said his late mother often talked about the incident, but did not know who to thank. He said she made sure to teach her two children to swim in the sea when they returned on holidays to Portnoo.
“All she remembered at that time was seeing a boathook - none of them had lifejackets when they were pulled out,”Mr Morrell said.
“ My mum had passed her lifesaving awards just a couple of months before, and that was what really upset her about losing her father,,”Mr Morrell said.
Mr Morrell is due to travel to Dublin today (fri) with his sister, Jenny, to congratulate the Gallaghers.
The siblings only learned about the Gallaghers’ involvement two months ago, and visited them recently at their home in Burtonport.
“Together , we feel sure that mum would be proud to acknowledge her personal heroes,” they said. “Without those men, we would not be here...”
The Gallaghers are among 19 recipients of State awards for 12 instances of bravery, and one posthumous award will be conferred on their father, Michael.
The honours will be awarded at Farmleigh House, Dublin, today (oct 18) by Comhairle na Míre Gaile – the Deeds of Bravery Council.
It was established in 1947 to “provide for suitable recognition by the State of deeds of bravery”, and is chaired by the Ceann Comhairle of the Dáil.
Eight serving and one retired Garda are also recipients this year, and the full list is as follows:
Adrian Brennan, Kilkenny; retired Garda Desmond Brennan, Dublin; Garda Pauric Deery, Sligo.; Basil Harte , Sligo; James Hennessy, Cork; Olive Murphy, Cork; Aonghus O’Briain, Dublin; Michael Hempenstall, Dublin; Garda Donal Tully, Dublin; Garda David Currivan, Dublin; Garda Cathal McGeoghan, Dublin; James Gallagher (Snr), Donegal; Mickey ‘Red Michael’ Gallagher , Donegal; Michael Gallagher (Snr),Donegal (posthumous award); Garda Seán Breheny, Dublin; Gary Kennedy, Mayo; Garda Darren Blackwell, Dublin; Sergeant Gavin Coleman, Dublin; Garda M.J. Carroll, Dublin; Garda Jason Walsh, Dublin.
Bravery Award for Sea Rescue of 18 People All of 63 Years Ago
Two Donegal brothers are to receive national bravery awards next week for their rescue of 18 people from two vessels which got into difficulty off Portnoo - all of 63 years ago writes Lorna Siggins.
Retired fishermen James and Michael Gallagher of Burtonport, Co Donegal, were on their father’s half decker, Irine and had set out to check lobster pots when a punt nearby with 15 people on board took a wave across the bow and was swamped.
“It’s as clear in my mind as if it happened yesterday,” James says, recalling the events of August 22nd, 1956 in today’s Irish Independent here
All 15 on the punt ended up in the water with no lifejackets. Among those rescued was Jean Mavitty, then 15 years old, but her father Desmond Mavitty (49) was one of three who drowned, along with George Warren (55) and Christopher Chambers (7). The young boy was fatally injured by the propellor of a nearby yacht.
Those taken ashore by the fishermen included Bruce and Lorna Warren (aged 14 and 17), Robin Chambers (11), David Logan (11), Joe Morton (19), Pat Morton (17), Nevin Kerr (20), Aiden Campbell (15) and Alan Cooper (15). The party had set out to look at the wreck of a coaster, Greenhaven, which had run up on Roaninish island some months before.
Jean Mavitty’s son, Robert Morrell, says his late mother often wondered who she could thank, as she had no memory of who had carried out the rescue. The inquest into the three fatalities was held immediately after the incident, and the fishermen were not present.
The national bravery awards, conferred this year at Farmleigh House, Dublin, on October 18th, are conferred by the Dáil ceann comhairle on people from all walks of life and all sections of society who have “ carried out a deed of bravery with an effort to save human life involving personal risk".
The Gallagher brothers, now aged 80 and 85, will be joined by Jim Gallagher, son of James and nephew of Michael, who has also spent a life at sea and nominated them for the award.
For more see Irish Independent here
NI Coastguard Teams Rescue Pup Cut Off By Tide In Strangford Lough
Coastguard teams from Bangor and Portaferry were tasked to Strangford Lough on Saturday afternoon (17 August) to rescue a young dog stranded by the tide at Island Hill.
The pup’s worried owner “was in the mindset of attempting a rescue himself” but let the coastguard rescuers — one of whom is a dog handler with K9 Search and Rescue NI — handle the situation, according to Belfast Coastguard.
With a little patience to win over the frightened animal’s trust, the dog was soon in the arms of coastguard volunteers and reunited with its owner on dry land.
Belfast Coastguard reminded all pet owners: “Please don’t enter the water after your dog. Dial 999 and ask for the coastguard.”
A member of the US Coast Guard and three of his relatives have been praised by the father of a young girl rescued after she was swept out to sea from a Dublin beach.
As The Irish Times reports, Walter Butler and his relations Eoghan Butler, Declan Butler and Alex Thomson leapt into action when they heard screams for help and saw the girl on a “pink floaty” off Portmarnock beach on Monday afternoon (22 July).
Butler remained on the beach ready to provide casualty care while the others swam out to the girl, who was swept some distance from shore and at one point was struggling to stay afloat after coming off her inflatable.
“We have all been swimming competitively since we were six or seven years old so to say we are good swimmers is an understatement,” said Butler — who noted that it still took half an hour for his relatives to reach the girl and swim her back to the beach, where paramedics and her relieved father were waiting.
The dangers of using inflatables at the seaside were highlighted again just hours later, when Larne RNLI launched yesterday afternoon (Tuesday 23 July) to a report of three people being carried out to sea on inflatable toys in Browns Bay.
At the scene, the volunteer crew found a small fishing vessel had already taken one casualty on board, and they look over to bring the remaining two onto the lifeboat.
RNLI volunteer helm Barry Kirkpatrick said: “We advise you not to use inflatables at the beach as offshore winds can easily sweep you off the shore in a very quick space of time.
“If you do get into difficulty or see anyone else in difficulty, please remember to call 999 or 112 and ask for the coastguard.”
Belfast Coastguard has warned that a number of children have been blown out to sea on inflatable toys in recent days.
“Please remember the safest place for children to play with these death traps is in the back garden,” a spokesperson said.
Wicklow Lifeboat Launched To Search For Missing Dog
Wicklow RNLI's inshore lifeboat was launched at 4:40pm yesterday afternoon (Friday 8 March) to search for a missing dog.
The alarm was raised by the anxious owner after her dog, named Otis, chased some seagulls down over the cliff edge at Wicklow Head and disappeared.
The lifeboat — with helm Graham Fitzgerald and crew Ian Thompson and John Stapleton — was on scene eight minutes after launching and the crew began a sweep of caves and the shoreline at a location known as the Pond, near Wicklow Head lighthouse.
During the search the dog could be heard barking from a cave, so crew member Stapleton was put ashore near the opening and, with some persuading, the dog was coaxed out to climb back up the cliff and into the arms of his grateful owner.
Elsewhere, a young man was recovered from the River Corrib by members of the emergency services in Galway in the early hours of Friday morning following a major rescue operation involving the Galway RNLI lifeboat.
The man has got into difficulty in a canal beside the river around 3.30am, and during the rescue both the casualty and rescue personnel ended up entering the fast-flowing Corrib towards the Spanish Arch, where the casualty was recovered for transfer to Galway University Hospital.
Mike Swan, Galway RNLI lifeboat operations manager, said: “We would encourage all members of the public to respect the water at all times regardless of their activity.
“Be wary of all edges around the sea and watersides. Slips and falls happen in all locations.”
The International Maritime Rescue Federation (IMRF) is calling for outstanding individuals, teams, professionals or volunteers, companies and organisations involved in maritime search and rescues (SAR) – all around the world - to be nominated for an IMRF Award 2019.
"The World Health Organisation estimates that 40 people drown every hour around the world, but without the incredible actions of maritime search and rescue professionals that number would be much higher," says Theresa Crossley, CEO IMRF.
"These Awards recognise those incredible people and the new innovations and technologies that make saving lives at sea possible, even in the most difficult and demanding circumstances.
"The IMRF Awards are now in their fourth year, but each time I review the nominations I am both inspired and humbled by the stories of actions undertaken by maritime SAR professionals around the world," she adds.
Last years' winners included a ship's master who rescued three starving fishermen drifting on a sinking boat, a lifeboat station crew from the Netherlands that had rescued four people from a drifting guard vessel in force eight north westerly winds with ten metre high waves, and a pink rescue buoy flotation device that's saving lives around the coast of South Africa. In addition, two exceptional lifetime awards were presented to two individuals with more than 100 years between them, saving lives at sea in the Caribbean and Bulgaria.
The IMRF is asking everyone to think about those involved in maritime SAR, whether professionals, volunteers, individuals or teams 'who really make a difference', or a 'game-changing' maritime SAR product, service or operational procedure and to consider nominating them for an IMRF Award now.
Nominations are open for the four Award categories:
· Individual: For Outstanding Individual Contribution to a Maritime SAR Operation
· Team: For Outstanding Team Contribution to a Maritime SAR Operation
· Innovation & Technology: For Innovation and Technology in the field of Maritime SAR
· Lifetime Achievement: The Vladimir Maksimov Award for Lifetime Achievement in the Maritime SAR Sector
This year, the Awards ceremony will be held during London International Shipping Week
(9 – 13 September 2019) an event which attracts high-level government representatives and shipping industry leaders from around the world.
The 2019 Awards lunch will take place on an historic vessel moored on the River Thames in London on 10 September.
Visit www.imrfawards.org for more details and to submit a nomination.
#RNLI - Portaferry RNLI’s volunteer crew were paged yesterday afternoon (Saturday 11 August) to go to the aid of two people stranded on Guns Island off Co Down.
The lifeboat launched at 3:20pm in overcast weather with good visibility and a Force 4 south-easterly wind but a rough sea state, and on arrival on scene 20 minutes later it was raining with poor visibility.
Newcastle, Bangor and Portaferry coastguard rescue teams were also in attendance, assisting from the shore.
The RNLI crew approached the scene where they rescued the two people and their dog from the island, where they were stranded after their six-metre punt got into difficultly and was destroyed on nearby rocks.
The casualties were taken to Ballyhornan Beach where they were transferred to the care of the coastguard rescue teams on shore.
Elsewhere, Clifden RNLI added to their busy August with a callout to a yacht with engine trouble both of Slyne Head on Friday afternoon (10 August).
A light Force 2 north-westerly wind made the yacht’s passage to Clifden slow going under sail alone. The Clifden lifeboat crew established a tow to Clifden Bay, which took over an hour, and the D-class lifeboat aided in mooring the yacht.
“Once on the mooring, a rope could be observed caught underneath the yachts hull and an attempt was made to release it. This proved unsuccessful but explained how the yacht had lost mechanical propulsion,” said Clifden RNLI coxswain David Barry.
Why would anyone ignore an offer of a free system that can make sailing, boating, kayaking, canoeing and other water-based activities safer?
I don’t know the answer to that, but maybe there is some reader of Afloat.ie who will tell me why.
I was quite surprised when the man who has led the development of a system which, it is claimed, “fills a critical gap in maritime situational awareness,” is less used in Ireland than anywhere else in the world!
There are more than 170,000 users around the world of a maritime safety and rescue tracking device which has been developed and produced by a Cork technology company. It is in use in Finland, Germany, Holland, Spain, South Africa, Australia, Norway, Cyprus, the United Kingdom and Denmark. Sweden is the latest country that has decided to introduce the Cork-developed system.
 John Murphy of SafeTrx
John Murphy of SafeTrx
SafeTrx is a vessel tracking Smartphone application, Irish-developed and, while it is used in Ireland, John Murphy, CEO of 8 West Consulting, developers of the award-winning SafeTrx Mariner Smartphone-based tracking and alerting system, says he “would consider use low in Ireland in comparison to other countries.”
Overseas countries have run public information/education campaigns about water safety, built around SafeTrx. “They have taken to heart what we have developed,”
he said.
"In an emergency situation it gives rescue authorities quick access to information about the location"
Though the Irish Sailing Association has urged its use here, it is not used as much as overseas. That surprised me when I interviewed John Murphy for my radio programme, This Island Nation. The system has recorded 750,000 hours of use and is sold to national search-and-rescue authorities, so the leisure boat user has no cost to use it.
In an emergency situation it gives rescue authorities quick access to information about the location.
So why is usage low in Ireland?
“Perhaps it is an issue about privacy or confidentiality or not wanting to bother the authorities. That is not prevalent in other countries. In Holland the take-up went from zero to 10,000 registered users in one week. There’s a different psychology, a different acceptance of risk and what people need to do to support themselves in those countries than there is in Ireland,” John Murphy said.
• Listen to the Podcast below of my interview here with John Murphy, a diver and a mountaineer who began developing SafeTrx after discussing with the Irish Coast Guard the need for a safety system for leisure sailors, inshore fishermen, kayakers, canoeists and other leisure water users, to create an ability for the rescue services to track their trips.
Innovative UK approach to Rescue Calls From Stinky Bay & Other Places
I wonder if the example of what FINTAN has done in Britain could be followed in Ireland?
It is an innovative approach to adding to rescue knowledge.
The UK Ordnance Survey and the British Maritime and Coastguard Agency (MCA) have a database called FINTAN, which they describe as helping to create a “vernacular geography” of names known by local people but which have not been listed officially by State organisations.
After five years of work it has built up 6.000 place names known and used by local people, but not until now listed officially. The purpose is that they could be used, if needed, in emergency operations. which could be used both for emergency calls to the Coastguard and to land-based 999 emergency services.
According to the MCA, in emergencies callers can often use nicknames for beaches, rocks and other local areas, for which the names on official maps are different or mightn’t even exist, making the identification of incident locations difficult, so the initiative has been used to close off such loopholes in safety coverage
Some unusual names are listed in FINTAN’S database, including Crazy Mary’s Hole, Nuncle Dicks, Sausage Island and Stinky Bay.
Whatever about the last three of those names, I wouldn’t like to be calling for help and giving the first name as my location to the emergency services! Listen to the podcast below:
Minister Cites Marine Casualties Involving Recreational Craft in Launch of New Code of Practice
Minister for Transport, Tourism and Sport Shane Ross TD, says a significant number of Irish Coast Guard call-outs in recent years have been to assist recreational craft.
The Minister's comments were made as a new Code of Practice was launched for the Safe Operation of Recreational Craft that draws on stats over ten years to 2015.
Reports of the Marine Casualty Investigation Board have also indicated that many accidents and deaths in this sector could have been avoided. The key is to think and act safely, the Minister says.
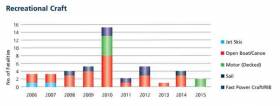
The following extracts from the 2015 Annual Report of the Marine Casualty Investigation Board provide information regarding marine casualties involving recreational craft in the period 2006-2015. The table and chart below give a breakdown of the fatalities by type of craft during the 10 year period up to and including 2015.
Fatalities associated with open boats and canoes have occurred on a regular basis during this period.
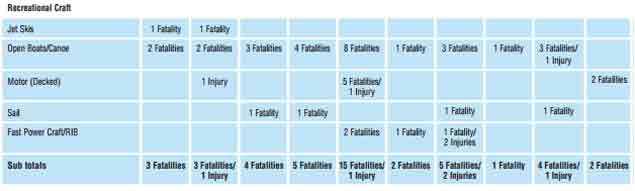 Source: MCIB
Source: MCIB