Displaying items by tag: Celtic sea
Marine Notice: Winter Geophysical Training and Calibration Survey in North Celtic Sea
The Department of Transport has been advised that a geophysical survey will be undertaken in the north Celtic Sea, south of Co Cork, for equipment testing and training purposes.
The operations are subject to weather and operational constraints but are anticipated to start in early December 2022 and be completed by late January 2023.
The survey will be conducted by the survey vessels Roman Rebel (callsign 2ICA5) and Lady Kathleen (callsign EIXT2), the former on a 24-hour basis and the latter on a 12-hour basis.
These vessels will be restricted in their ability to manoeuvre when surveying due to the deployment of the towed survey equipment, which could be up to 200 metres astern of the vessels. The vessels will display appropriate lights and signals.
All other vessels operating in the area are requested to leave a wide berth. Mariners are advised to keep continuous watch on VHF Channel 16 when navigating the area as outlined by a map and coordinates in Marine Notice No 82 of 2022 attached below, which also has contact details.
Marine Notice: Acoustic Survey in Celtic Sea South of Kilmore Quay
Bangor University will be surveying with hull-mounted and towed acoustic equipment in the Celtic Sea, off the southern coastline of Ireland south of Kilmore Quay, outside the 12 nautical mile limit.
The survey is due to commence on Tuesday 23 August and finish nearly two weeks later on Monday 5 September, weather allowing.
Operations will be conducted by the RV Prince Madog (callsign ZNLJ5). This research vessel will be surveying with hull-mounted and towed acoustic equipment. As a safety precaution, there will be two marine mammal observers on board. No buoys will be used.
Coordinates and a map of the survey area as well as contact details are included in Marine Notice No 56 of 2022, attached below.
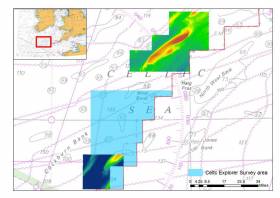
Geophysical Survey Works in Celtic Sea for Voyage Offshore Array
Irish offshore renewables survey company Ondine is undertaking geophysical survey works as part of a scientific data-gathering exercise for the Voyage Offshore Array in the Celtic Sea, south of Co Wateford.
The scope of this survey is the turbine array, which is located outside the 12-nautical-mile zone, and the current plan is to undertake surveys on only 50% of this area.
The works were scheduled to commence earlier this week will continue and will until 15 July, subject to weather.
The survey is being conducted from the research vessel DP1 Kommandor Iona (callsign GAAK) on a 24/7 basis. The vessel is towing geophysical equipment during operations and is restricted in its ability to manoeuvre.
All other vessels operating within the vicinity of the Kommandor Iona are requested to keep their distance and pass at minimum speed to reduce vessel wash. Radio transmissions will be conducted with other seafarers to notify them of the operations.
Further details on the survey area and contact information can be found in Marine Notice No 21 of 2022 attached below.
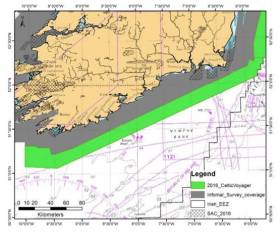
Route Survey Planned for Beaufort Cable System in Celtic Sea
Fugro Germany Marine GmbH plans to conduct a cable route survey outside Irish territorial waters (12NM), but within the Irish EEZ, along the proposed Beaufort Cable System cable route in the Celtic Sea.
Geophysical and geotechnical operations on the planned cable route are expected to be carried out from Thursday 28 April until Sunday 15 May, weather and work progress permitting.
The survey will be conducted by the Fugro Supporter (callsign C6EC3) on a 24-hour basis. As this vessel will be towing survey equipment as well as conducting stationary work, it will be restricted in ability to manoeuvre.
Mariners are advised to keep continuous watch on VHF radio Channel 16 when navigating the area, to keep their distance and to pass at minimum speed to reduce vessel wash.
Details of coordinates for the survey area and contact information can be found in Marine Notice No 18 of 2022, attached below.
Green Rebel Marine in Crosshaven is set to undertake a geophysical survey operation in the Celtic Sea from next week.
The survey from next Wednesday 26 May to 23 June, weather permitting, will be conducted by the Roman Rebel (callsign 2ICA5) using hull-mounted multibeam and sub-bottom profiling systems.
In addition, the vessel will be towing side-scan sonars and magnetometers using dedicated winches at cable lengths dictated by the water depth. Typically, the cable lengths will be about four times the water depth while acquiring data.
The Roman Rebel will display appropriate lights and signals and all survey operations will be conducted 24 hours a day, continuous over day and night.
Full details of coordinates of the survey areas are included in Marine Notice No 32 of 2021, which can be downloaded below.
Geophysical & Environmental Site Survey Off South Coast
A seabed debris clearance, environmental baseline and habitat assessment site survey will take place in licence SEL 1/11 (Barryroe) from later this month.
Barryroe is located in the North Celtic Sea, some 50 kilometres south of the Port of Cork.
The project is scheduled to commence in mid-August 2019 with the survey vessel Kommandor (callsign MCJO2) anticipated to be working on location for 16 days, excluding transit and any weather delays
Survey operations will be conducted on a 24-hour basis in different phases to include towed and non-towed operations. A fisheries liaison Officer will be on board for the duration of the survey.
Throughout the survey operations, the vessel will be displaying appropriate shapes and lights to indicate that the survey vessel is restricted in its ability to manoeuvre.
All vessels are requested to give this operation a wide berth. A listening watch will be maintained on VHF Channel 16, and the vessel will actively transmit an AIS signal.
Full details of the site survey co-ordinates are included in Marine Notice No 27 of 2019, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
New Shark Species Spotted In Irish Waters
A shark species previously unrecorded in Irish waters has been sighted in the Celtic Sea.
A smooth hammerhead shark was reported on the edge of the continental shelf, south-west of Ireland, during a recent fisheries survey on the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer.
The sighting was made by experienced marine mammal observer John Power and bird observer Paul Connaughton during the Marine Institute’s Western European Shelf Pelagic Acoustic Survey (WESPAS).
“While scanning the ocean surface, we sighted a dorsal fin unlike anything we had encountered before,” said Power.
“It was quite different to the fins seen on basking sharks and blue sharks. After consulting available ID keys, we agreed that the shark must be a smooth hammerhead.”
The large, tall and slender dorsal fin of the smooth hammerhead shark distinguishes it from other shark species. The smooth hammerhead also has a single-notch in the centre of its rounded head and is up to four metres in length.
The species gives birth to live young and the pups are usually found in the shallow sandy waters near Florida, the Caribbean and West Africa. However, the species has been recorded as far north as England and Wales.
The smooth hammerhead was sighted during the WESPAS survey, which surveys the waters from France to Scotland and the West of Ireland each year.
Marine scientists collect acoustic and biological data on herring, boarfish and horse mackerel, which is used to provide an independent measure of these fish stocks in Irish waters. Scientists also monitor plankton, sea birds and marine mammals during this survey.
This is an exciting encounter, especially since a rare deep-water shark nursery was discovered by Irish scientists last year
Dr Paul Connolly, director of fisheries and ecosystems services at the Marine Institute, said: “Our Irish waters support a range of marine life and diverse ecosystems, including 35 known species of sharks.
“This is an exciting encounter, especially since a rare deep-water shark nursery, 200 miles west of Ireland, was discovered by Irish scientists last year using the Marine Institute's Remotely Operated Vehicle [ROV Holland 1].”
He added: “This sighting of a new shark species shows the importance of our fishery surveys to monitor our marine environment, and to observe changes in our oceans and marine ecosystems.
“Observing and understanding a changing ocean, is essential for protecting and managing our marine ecosystems for the future.”
The hammerhead shark poses little risk to humans, and there have been no known fatalities from hammerhead sharks anywhere in the world to date.
The species is listed as Vulnerable on the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, and is being increasingly targeted for the shark fin trade as its large fins are highly valued.
Thirty-five species of sharks have been recorded in Irish waters, including the blue shark, porbeagle shark, lesser spotted dogfish and the second-largest shark in the world, the basking shark — a regular visitor inshore during the summer months.
Large Carcass Spotted In Celtic Sea Area Popular With Fin Whales
#MarineWildlife - Naval Service personnel on patrol with the LÉ Samuel Beckett encountered the carcass of a large whale some 50 nautical miles south-east of Ballycotton Lighthouse in the days after Christmas.
The “mystery whale” is neither a sighting (which only counts or living cetaceans) nor a stranding. But as the Irish Whale and Dolphin Group (IWDG) says, the encounter “serves to remind us that the animals that wash up on our shoreline may represent only a small percentage of the total number of cetaceans that expire at sea of presumably natural causes.”
IWDG sightings officer Pádraig Whooley said the location of these whale remains was “interesting as this area of the Celtic Sea has produced the most consistent large-whale sightings in recent months, with fairly regular sightings of fin whales from land-based sites between Ram Head, Ardmore extending east towards the Hook Head lighthouse.”
Survey By INFOMAR to Map Seabed South of Celtic Sea
#MarineScience - Marine Institute's RV Celtic Explorer departed Galway yesterday for the first deepwater INFOMAR survey of 2018 to map the seabed in the region of the Labadie and Cockburn Banks, south of the Celtic Sea.
These areas are of ecological and economic value to the Irish fishing fleet and the data collected will allow better fisheries management decisions.
INFOMAR, the national seabed mapping programme, is a joint programme between the Geological Survey of Ireland (GSI) and Marine Institute. INFOMAR creates bathymetric charts and products for Ireland's coastal and deeper offshore waters using acoustic sonars called multi-beams. The survey team will be led by Vera Quinlan, and include four INFOMAR surveyors / scientists and four marine science students.
Three multi-beam echo sounders on the marine research vessel will transmit beams of sound towards the sea floor. These 'beams of sound' are reflected off the sea floor and both the time it takes to receive the returned signal and the intensity are captured by the on-board systems. This process provides a very clear picture of the shape and texture of the seafloor, such as the bathymetry, and the geological characteristics of the area.
Further studies include the analysis of the radiation patterns of the sonars resulting in increased precision and improved data. This is part of a long-running collaboration between INFOMAR and Professor John Hughes Clarke at the Centre for Coastal and Ocean Mapping at the University of NewINFOMAR survey to map the Celtic Sea seabed Hampshire.
The survey team includes two students from the United States of America, Alexandra Dawson and Treyson Gillespie, from the BEAMS (BEnthic Acoustic Mapping and Survey) Program. BEAMS is an undergraduate-focused training and research program from the College of Charleston's Department of Geology and Environmental Geosciences, and aims to develop a strong and qualified workforce of ocean surveyors in support of the academic, research and operational marine communities.
INFOMAR also welcomes Becky Cronin and Rachel O' Mahoney from the Training Through Research Surveys (TTRS), a collaboration with the Marine Institute. The programme aims to increase national capacity in offshore marine research by offering seagoing placements for students of marine related sciences and technologies on the national research vessels, RV Celtic Explorer and RV Celtic Voyager.
Follow INFOMAR on Facebook and Twitter for updates from the INFOMAR survey team. Also follow scientists@sea blog for some blogs during the survey.
Marine Notice: Hydrographic & Geophysical Survey Off Mayo Coast, Celtic Sea & Irish Sea
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) has been advised that a hydrographic and geophysical survey operation will be undertaken by INFOMAR for the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) off the Mayo coast, in the Celtic Sea and also in the Irish Sea between 21 March and 30 October 2016.
The RV Celtic Voyager (Callsign EIQN), the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), the RV Keary (Callsign EIGO9), the RV Geo (Callsign EIDK6) and the RV Tonn (Callsign: EIPT7) are expected to carry out survey operations and will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
Details of co-ordinates for the survey operations are included in Marine Notice No 11 of 2016, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.