Displaying items by tag: Astrid
Kinsale Lifeboat Volunteer Jailed On Drugs Charges
One of the Kinsale RNLI volunteers honoured for their role in the rescue of 30 crew from the tall ship Astrid in July 2013 has been jailed for seven years on drug distrubution charges.
As The Irish Times reports, Liam O’Connell was sentenced to 10 years with three suspended after pleading guilty to possession of cannabis, cocaine and MDMA for sale or supply at his home just over a year ago.
At sentencing, the judge said O’Connell has exploited his status in the Kinsale community as an RNLI volunteer to participate in the drugs trade.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Altering Passage For 'Promotional Activities' Led to Loss of Tall Ship Astrid – MCIB Report
#astrid – If the initial MAYDAY message from the Sail Training Ship Astrid had been sent out in the correct format the emergency services could have been activated 10 minutes earlier, which could have been critical to the final outcome had conditions been more severe, according to a Marine Casualty Investigation Report (MCIB) published today.
The 95-year-old vessel ran aground on to Rocks off Kinsale during a photocall for the Irish Sailing Association Gathering Cruise promotion, prompting dramatic scenes as 30 people were rescued from rough seas. The vessel ran aground on July 24th 2013.
The main cause of the grounding is that the ship was not operated in a safe manner in compliance with the International Conventions, the report says.
In its conclusions the MCIB states: 'The correct passage planning procedures should have been carried out and the Master should not have altered his passage in an unsafe manner to facilitate promotional activities'.
The report also concluded that passage planning of the voyage from Oysterhaven to Kinsale was inadequate for a ship to navigate a course within 300 (m) of a lee shore in a Force 6 wind. The report says passage planning appears to have been influenced by the 'desire for photograph opportunities' for the Irish Sailing Association's (ISA) 'Gathering' cruise. The report says SOLAS Chapter V Regulation 34 was not complied with.
Mike MacSweeney, a photographer on the media boat that day told Afloat.ie: 'I wish to unequivocally state the following as a matter of record there were no instructions or requests from the media boat to the skipper or anyone onboard the Tall Ship Astrid before or after leaving Oysterhaven on the day in question'.
MacSweeney adds: 'Any actions taken by the Astrid were solely the decision of the Tall Ship Astrid. The first interaction between the media boat and the Tall Ship Astrid was when the ship was in difficulty and the media boat assisted in the rescue'.
The report concludes the immediate cause of the ship grounding and subsequent sinking can be attributed to the loss of power from the main engine. The main engine stopped as a result of fresh water contamination of the fuel. The cause of the water contamination can be attributed to human error when taking on fresh water in Brighton on 12th July 2013. Once water contamination had been found, insufficient action was taken to ensure fresh water was removed from the fuel system.
It went on: 'The operation and condition of the ship did not correspond with the applicable SOLAS Conventions, presenting a danger to the ship and the persons on-board and a threat of harm to the marine environment'.
The ship was not certified as a passenger ship for either EU or international voyages nor were the crew appropriately certified and the ship should not have been at sea, according to the MCIB.
The emergency services responded in a timely manner and effected the recovery of 30 persons without injury.
The MCIB made four recommendations including that the operators of sail training vessels should ensure that they comply with international conventions and European Union law.
It also said sail training ships entering Irish waters and ports must comply with the regulations, and that ships engaged in promotional activities must ensure that the Master has over-riding authority and that the Master must not compromise good passage planning and safety when involved in such activities.
A link to download the report as a (17mb) PDF file is HERE.
Engine Failure Preceded Astrid Incident Says Interim Report
#Astrid - Engine failure led to the grounding of the tall ship Astrid off the Cork coast a year ago, according to an interim report by marine investigators.
The 42m Dutch brig's 30-strong crew, most of them sail trainees, were rescued in a major operation after it ran onto rocks between Oysterhaven and Kinsale in choppy seas during last summer's ISA-organised Gathering Cruise.
Built in 1918 and in service as a cargo vessel till 1975, the tall ship foundered in the same spot where the barque Falls of Garry sank in 1911.
The Irish Times reports on the Marine Casualty Investigation Board's (MCIB) findings ahead of its final report to come after "the natural justice procedure".
Dutch authorities are involved in the Irish-led investigation that began in the days after the Astrid accident. There is as yet no indication as to what caused the vessel's engine to fail.
Rescued Sailors Join Kinsale RNLI Mayday Campaign
#RNLI - Crew members from the training ship Astrid that sank on 24 July 2013 visited Kinsale RNLI lifeboat station to thank volunteer crew and support the RNLI’s Mayday campaign.
Some 30 young people were brought to safety by RNLI lifeboat Miss Sally Anne Baggy when the tall ship hit rocks between Oysterhaven and Kinsale.
Volunteer crew members Liam O’Connell, Nick Searls and Jim Grennan, who were on the Kinsale RNLI lifeboat on the day Astrid sank, were on hand to welcome the visitors and present them with iconic Yellow Welly key rings to mark the occasion.
Undeterred by their experience last summer, the youngsters were taking part on a training exercise on 70ft schooner Spirit of Oysterhaven, the flagship of The Oysterhaven Centre.
The Astrid rescue was just one of more than 40 rescue missions launched by Kinsale RNLI last year.
Voice of Ireland judge and former Westlife member Kian Egan has lent his support to the Mayday campaign which runs from this Thursday 1 till Monday 5 May, when the charity’s volunteers will be selling yellow welly pin badges and key rings for a €2 donation, in cities, towns and villages throughout Ireland.
And as previously reported on Afloat.ie, there will also be a number of welly-themed events held to raise funds for the lifesaving charity in Ireland.
#tallships – Last July, eight youngsters from Ireland that were taking part in a voyage on the Tall Ship "Astrid" got more than they bargained for when the ship got into difficulty near Kinsale during an Irish Sailing Association 'Gathering Cruise' and foundered on rocks. Nine months later, the 100–year–old Dutch ship's journey finally came to an end in a skip when it was cut up for scrap. Here Michael Byrne of Sail Training Ireland relates the outcomes of the ordeal for the 24 trainees from five countries and how the Irish trainees are now back at sea this week on an Irish Vessel, the 'Spirit of Oysterhaven', a vessel that was involved in Astrid's crew rescue.
There were two striking outcomes after the ordeal.
1. How closely the trainees had bonded during their previous ten days at sea, evident in how they cared for each other and how difficult they found it to disband the group when the time came.
2. How anxious they AND THEIR PARENTS were to get them back to sea.
This week that dream came through for some of the Irish Trainees who are taking part in a 5 day voyage on the Cork Coast, largely coordinated by themselves, on Irish Sail Training Vessel "Spirit of Oysterhaven" a 70' Schooner based in Cork. The voyage is part of a "Youth Initiative" project, funded by the EU Commissions "Youth in Action" programme, and overseen by Sail Training Ireland which includes a total of 8 trainees.
The educational programme of activities and workshops is based on environmental awareness and the "Leave no Trace" policy. The trainees are examining the level of rubbish at sea and will be making a public demonstration by building a sculpture out of rubbish they collect.
Sail Training focuses on the valuable life skills that are developed in the participants through the experience of life at sea on a sailing vessel such as; self-confidence, resilience, responsibility and a willingness to rely on each other. Trainees become part of a working crew of the Tall Ship or Sailing Vessel and must work together to operate the ship day and night. Such voyage are excellent opportunities to develop important skills and characteristics and also to develop educational concepts such as environmental awareness, cultural awareness, citizenship and leadership.
Sail Training Ireland, and its members, continue to work to develop more of these programme so that the young people of Ireland have the opportunity to experience life at sea, explore our maritime heritage as a seafaring nation and benefit from the adventure of a lifetime.
There are many more voyages taking place in 2014 both on Spirit of Oysterhaven and on various other Tall Ships that have been arranged to visit our ports.
7 Tall Ships will sail from Belfast to Dublin at the end of May with over 100 young people aged 16-27 years funded to sail on board.
More Honours For Kinsale Lifeboat Crew Over 'Astrid' Rescue
#RNLI - Last Friday (11 April) was a busy night for the volunteer crew of Kinsale RNLI as they collected two West Cork community awards for bringing to safety the 30 crew members of the training ship Astrid that sank outside Kinsale harbour in July last year.
The first honour of the night was bestowed at the 25th anniversary awards ceremony in Bandon’s Munster Arms Hotel, organised by The Opinion magazine and sponsored by Bandon Co-op.
Kinsale lifeboat Miss Sally Anne (Baggy) was first on the scene on 24 July 2013 when the Astrid ran aground. Volunteer crew members Liam O’Connell, Nick Searls and James Grennan worked in treacherous conditions to safely evacuate all 30 crew on board.
They accepted The Opinion/Bandon Co-op Community Award on behalf on the RNLI, along with volunteers from Courtmacsherry RNLI who assisted the rescue.
Next stop was Acton's Hotel for the Kinsale District and Community Awards. Flanked by boat and shore crew and volunteers from the fundraising team, Liam, Nick and James accepted their second trophy of the night.
Lifeboat operations manager John O’Gorman said: “This is a great honour for all the volunteers of the RNLI who give freely of their time to save lives at sea. As volunteers, our only reward is the satisfaction of a job well done and the respect of our community. We have received that in abundance tonight."
This brings to three the number of awards related to the Astrid. Earlier this year the Irish Cruising Club presented Kinsale RNLI with the Waterford Cup, a perpetual trophy dating back to 1953.
What Has Happened to Sailors' Traditional Self–Reliance At Sea?
#safetyonthewater –Can it really be true that lifeboat call-outs in Ireland in 2013 – most of them for recreational boating of some sort - showed a staggering increase of 43% over 2012? W M Nixon discusses the disturbing figures, and considers whether it is possible to re-build the traditional amateur seafaring tradition of competence and self-reliance.
Time was when the most respected sailing folk, the people with the highest standards in their boats and in their use of them for their dedicated style of seafaring, were accustomed to sail the sea on the principle that they would much rather drown than cause any inconvenience or danger to other seafarers in any way whatsoever.
This applied particularly in the matter of being rescued. Being rescued just wasn't done. It was a sign of appallingly poor seamanship. Indeed, having what other people might describe as an adventure of any kind was frowned upon. "An adventure" was looked upon by the pioneers of cruising - just as it was looked upon by their contemporaries, the top explorers - as evidence of incompetence.
It was an admirable if impossibly idealistic attitude, which had its roots in the earliest days of amateur seafaring. In that distant era, the first very few pioneers were venturing forth for pleasure on seas where working people with much less in the way of economic resources were struggling to make a usually poor and often dangerous living as fishermen. To emphasise the difference, pleasure sailors only fluttered about the place in summer like butterflies, whereas those who worked the sea in small boats had to face its ferocity all year round.
Also sharing the sea were the crews of cargo carrying vessels whose demanding owners did not welcome tales of their vessels being delayed and the valuable cargoes put at risk, even for the shortest possible periods, in order to assist or rescue some incompetent amateur. As for the regulators of the sea, the naval ships and the revenue cutters, they were naturally suspicious of people going about their inexplicable business with "pleasure" as their reported objective, sailing hither and yon in their strange little vessels.
They undoubtedly were "little" vessels, as the new sport of cruising with its codes of a high standard was developed by the emerging middle classes of the 19th Century. Unlike the aristocracy and monarchy, who would sail the sea in large yachts with crowds of attendants and everything – including rescue if needs be - done in a very public manner as part of the grand life's rich tableau, the middle classes valued privacy above everything else.
Thus the code of self-reliance in cruising evolved, propounded by folk like Richard Turrell McMullen, who developed the principle of total self-reliance to such an extent that even in coastal waters he cruised single-handed in his final years. And even when pleasure boats numbers and rescue services had developed to an impressive level in the late 20th Century, the "shame of being rescued" was still a very potent attitude which encouraged high standards in boat maintenance and seamanship.
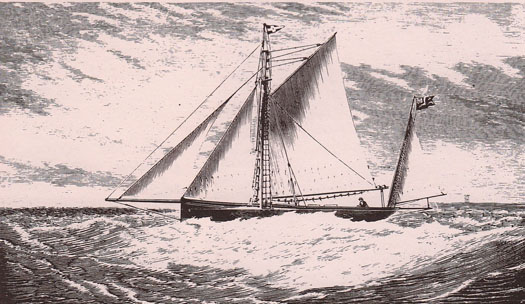
Pioneering seafarer Richard Turrell McMullen in his 42ft Orion, with which he cruised the Irish coast in 1869. McMullen expounded a doctrine of self-reliance and competence in amateur sailors, and would have regarded being assisted by the lifeboats as a matter of extreme shame.
But today, well into the second decade of the 21st Century, the RNLI call-out figures for Ireland do not make happy reading for advocates of rugged seafaring self-reliance. Could it be that the ubiquitous presence of highly-visible lifeboats in our main harbours, with their presence further publicised at major rescues, is creating excessive haste in calling them out for non-emergency reasons?
Admittedly the summer of 2013 was so good that there were many more people afloat in June, July and August than in 2012's grim conditions. Thus many of those rescued will have been casual impulse boaters, rather than dedicated seafarers. But nevertheless a year-on-year increase of 43% in lifeboat launchings, most of them for recreational boating of some sort, is very discouraging for an activity which supposedly prides itself on its capacity for sensible self-regulation, and derives satisfaction from overcoming challenging conditions without assistance.

The Dun Laoghaire lifeboat on exercise in Dalkey Sound. This was Ireland's busiest station in the summer of 2013, with 34 call-outs in June, July and August Photo: David Branigan/Dun Laoghaire RNLI
For the record, Dun Laoghaire was the busiest station with 34 call outs. Portrush in County Antrim was next on 26, just ahead of Crosshaven with 25, while Fenit, Wicklow and Skerries (where their new boat, the Atlantic 85 Louis Stimson, was named and dedicated on Saturday September 7th) were all on 17.

The new lifeboat at Skerries, an Atlantic 85, was dedicated and named the Louis Simson on September 7th. The Skerries station had 17 call-outs during the three summer months.
Of course there are those who will claim that, in many instances, talking of "rescues" would be over-stating the case. When a situation looks like being serious from the outset, the Coastguards – and particularly their helicopter – will get involved. In fact, so many genuinely life-saving events involve helicopters that it's surprising no-one seems to have thought of a rescue helicopter service service funded by charities. Maybe they have, but have found it would be impossibly expensive. In any case, with lifeboats, there's the obvious and stirring maritime link. "Those in peril on the sea" must be one of the most recognisable phrases known to us, and providing charity support to lifeboats is a direct and very satisfying way of connecting with it.
But the fact that the lifeboats receive so much of their funding from charity, and are manned largely by volunteers, adds to the moral overtones when any rescue is successfully carried through. And as we cannot know how even the most minor boat difficulty might go pear-shaped at some future stage, then if the lifeboat gets involved, the perception is that you've been rescued however minor the problem may have been, and notwithstanding the fact that the lifeboatmen themselves may phrase their report to spare the rescued crew's blushes.
The lifeboatmen's attitude is better safe than sorry, and much better safe even if just slightly embarrassed. But an analysis of the incidents in Irish waters is intriguing, and they provided some events with unwelcome publicity. For instance, the ISA's Gathering Cruise-in-Company from Dun Laoghaire towards Dingle in July experienced four different lifeboat call-outs.
The highest-profile incident was the rescue of the crew of 30 from the tall ship Astrid when her engine failed on the short hop from Oysterhaven to Kinsale in fairly rough conditions of onshore winds. One possible story suggests that prior to her arrival in Ireland, one of Astrid's fuel tanks had been accidentally filled with fresh water, which is something that can easily happen in a large and complex old sailing ship during a busy turnaround time in port. In line with their spirit of self-reliance, Astrid's crew had reportedly declined offers of professional assistance in making the tanks diesel-ready again. But despite their best efforts, it seems there might have still been a small quantity of fresh water left, quite enough to cause what became a catastrophic engine stoppage.
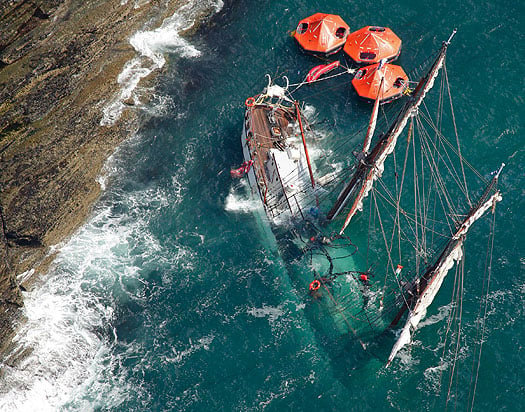

The end of a dream. The sinking of the privately-owned Dutch sail-training tall ship Astrid was a catastrophe, but it wasn't a tragedy as all 30 on board were efficiently rescued by the lifeboats. Photo: Bob Bateman
In fairness to The Gathering Cruise-in-Company, the Astrid sinking was a big ship event with which they became associated almost incidentally. But the three other call-outs were directly linked. The second most serious (after the Astrid) of the Cruise-in-Company's call outs was for the Ballycotton Lifeboat for an injured crewman on a 42ft yacht six miles southwest of the port. Injuries were such that the casualty was transferred by lifeboat to a waiting ambulance at Ballycotton, then as the injured person was a key member of the 42ft yacht's crew of three, the lifeboat returned to the cruiser and escorted her to port.
The other two lifeboat callouts for the Cruise-in-Company were to assist a yacht with her propellor fouled by a fishing pot marker off Kilmore Quay, and to tow in one of the participating boats after her engine had failed off Kinsale.
The hazard of getting fouled in fishing pot lines is even greater in Ireland than other similar places like Cornwall, where Ben Ainslie has written of his family's experience of having their fine yacht driven ashore at the entrance of the Helford River and getting badly holed on rocks, after the propellor had knotted itself in a lobster pot line. The lobsters and crabs along the Irish coast being even more prolific, it's a constant problem when under power, and there are few challenges more daunting than motoring in late afternoon straight into the sun on passage from Carnsore Point to Kilmore Quay, and knowing that the entire route is a maze of pot markers, some quite clearly defined, others lurking just below the surface in the strong tides, and all virtually invisible with the notorious brightness of the sunny southeast right in your eyes.
So for cruising in Ireland, an obvious solution is one of those cunning little cutting devices fitted to the propshaft to slice through any ropes, but even they can be defeated by too much rope. When it does happen, a serrated bread knife with the means of and quick and easy attachment it to the boathook can sometimes work wonders.
But the proliferation of cruisers with SailDrives exacerbates the problem. They may fulfil the designer's dream of having the propellor immersed as deeply as possible, and in clear water too, but it means they're perfect targets for wayward pot lines, and you need a diver or a liftout to get at them if they become fouled.
But do propellers really need to be so deeply immersed? After all, in motorboats they're close under the surface, and often reasonably accessible by long-arm methods from a dinghy. Admittedly with a sailing boat with her extra pitching through having a mast, there is a danger that a shallow-mounted propellor will come out of the water as she punches into a head sea. But for years I'd a share in the Contessa 35 with a high-mounted propellor well aft, and it never came out of the water while motoring in a head sea. Yet thanks to the boat's pintail stern - which had few other merits - you could just about reach the prop from the dinghy, whereas today's wide-sterned boats might preclude that. Whatever, in re-aligning the engine in my current boat, something which just had to be done when I discovered the builders had installed it at an angle of 21 degrees plus, when the manufacturers insist it should be no more than 15 degrees with 7 degrees is an ideal target, I now have a setup where the propellor can be reached by clambering down the stern boarding ladder.
All of which is little enough comfort for a cruising boat with a fouled propellor being rescued by the Kilmore Quay lifeboat during the Cruise-in-Company, but that in turn begs the question: Where were the other cruisers-in-company when this situation arose? The notion behind a cruise-in-company is that there's a feeling of mutual support, and minor problems can be dealt with by assistance from your fellow participants. But even in the companionability of a cruise-in-company, could it be that we've become so accustomed to hearing about the use of rescue services that even with buddy boats presumably near, an everyday get-you-home problem can still lead to an emergency call?
It seems to have happened with the lifeboat going to that engineless boat's aid off Kinsale and more recently the maritime community expressed shared embarrassment when the crew of a cruiser-racer of a notably able type called out the lifeboat when their engine failed as they sat becalmed off Wicklow Head.
But as boat numbers increase, professional privately-run services develop to meet the growing need for assistance like this. In boat-crowded places like Long Island Sound, and indeed on many parts of the coast of the USA, commercial assistance and get-you-home services have been a feature afloat for many decades. And anyone who has been around the Solent will be familiar with the SeaStart service, to which you can subscribe as a sort of insurance, and which now does commercially many of the tasks which used to take up too much of lifeboat time.
{youtube}VrqzFIfV1w4{/youtube}
Even the colours of their boats suggest that SeaStart is the same reassuring presence afloat as the AA is ashore.
Interestingly, SeaStart now sees its role as including the education of its less-experienced subscribers in order to raise their standards of boat and equipment maintenance, and improve their attitudes to sailing the sea. Yet because it's all being done by what is essentially a commercial organisation, those availing of its services don't feel themselves being morally oppressed by a do-gooder organisation or an interfering nanny state.
It works well in a densely-boat-populated area like the Solent region, but we have to face the reality that Ireland has an enormous and often rough coastline, and boat numbers are relatively very few, and often far between. So for now and the foreseeable future, most of us in day sailing, cruising and offshore racing are going to have to rely on self-regulation with a sensible attitude to seafaring, and the use of voluntary services supported by charitable donations in emergencies.
The situation is of course very different in inshore racing, where highly organised club rescue teams with their crash boats, and an admirable ethos of efficiency among their crews, set a standard of self-help and self-regulation which is a credit to our sport. But as soon as the scope of the event spreads from the purely local, and the boat-size goes beyond dinghies, we find ourselves interacting with national emergency and rescue services.
So in seeing the MOD 70 trimaran capsizing in Dublin Bay in June and observing the flurry of helicopter and lifeboat activity – all very necessary as two crew were soon in hospital, one for an extended stay with a severely fractured pelvis – we were seeing a new world. It's a situation very far removed indeed from the schooner America making her unaccompanied way across the Atlantic in 1851, with no contact with anyone until, without fuss or bother, she prepared for the historic race around the Isle of Wight which in its turn was sailed without any expectation of the use of rescue services.
And for those of us in the less exalted areas of personal choice sailing, it really is a matter of self-regulation if we are going to avoid having the authorities impose regulation upon us. In considering this disturbing 43% increase in lifeboat call-outs in 2013, it's difficult to avoid the conclusion that the only reason there aren't threatening rumbles of regulation and inspection from the government is simply because of the dire circumstances of the national finances.
Were we not in a situation of government cutbacks on every front, it's highly likely there'd already be some advisory body looking at ways of making the boating world adopt a more responsible, self-reliant and disciplined attitude towards its activities. That in turn would lead to an increased inspectorate and more supervision, with further erosion of the sense of freedom in sailing the sea. And in the end, it's boat people who would have to pay for it themselves. It's up to us to protect this activity we cherish so much, and to treat it with the respect it deserves.
Tall Ship Astrid Is Cork Harbour Bound For Scrapping
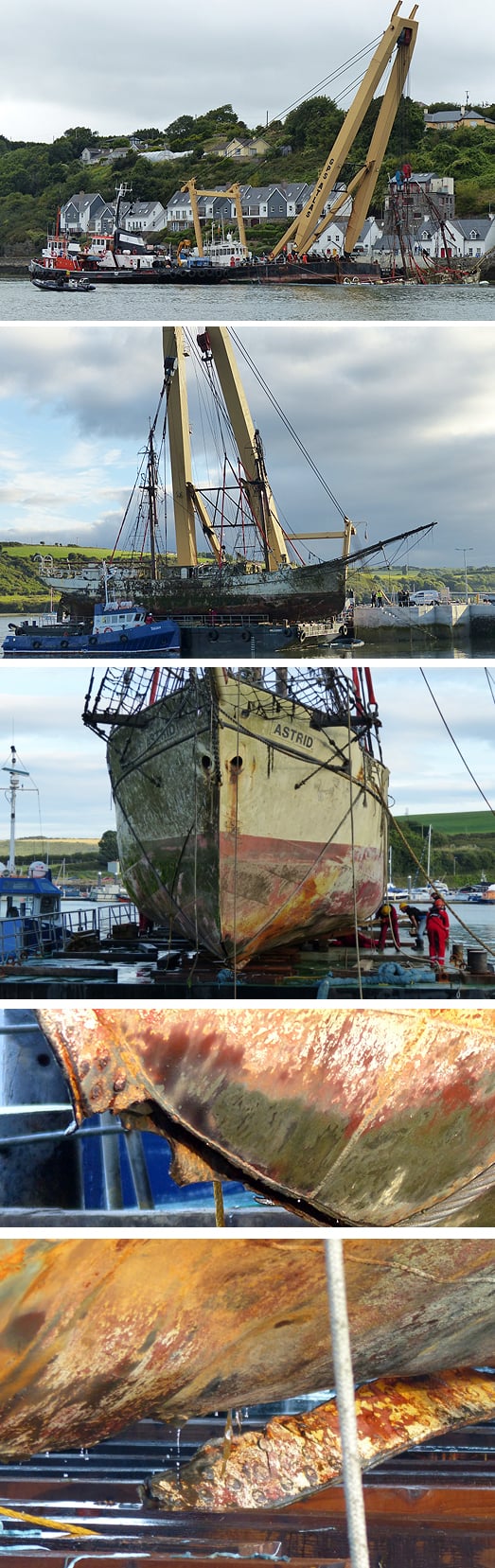
#Astrid - The West Cork Times reports that the wreck of the tall ship Astrid is to be transported to Cork Harbour for scrapping.
Last week the Dutch training brig was recovered from her final resting place on rocks at the mouth of Kinsale Harbour using specialist lifting equipment brought over from the UK.
Though the hull of the 95-year-old ship was in remarkably good condition after she grounded close to the Sovereign Islands, it was decided early on that the severity of the damage she sustained would render her repair and restoration unlikely.
All 30 crew on board Astrid were brought to safety in a major rescue operation on 24 July last when the sail training vessel was blown onto rocks in high wind and quickly took on water.
In the weeks after the incident, items including the ship's bell and compass were recovered from the wreck by divers after they were initially thought to have been stolen in a night-time raid.
Tall Ship Astrid Back From the Deep, Dutch Vessel Successfully Raised in Kinsale
#astrid – The Dutch Tall Ship Astrid that ran aground two months ago has been successfully recovered off the Cork coast today. Using specialist lifting equipment brought in from England, the 100– foot steel hull, now safely atop a massive barge, is remarkably intact as the pictures below, taken by Erskine Tanner at Kinsale harbour, show.
News of the salvage before the arrival of any autumn gales has been warmly greeted. The lift brings an end to the saga for all involved during the rescue of those on board, during her protection while she was on the rocks and in her salvage this week.
A Marine Casualty Investigation Board (MCIB) report is being prepared into the accident.
The 95-year-old vessel ran aground on to Rocks off Kinsale two months ago during a photocall for the Irish Sailing Association Gathering Cruise promotion, prompting dramatic scenes as 30 people were rescued from rough seas. The vessel has been resting on the rocks since the grounding on July 24th.
The vessel hit rocks inside the Sovereign Islands at Ballymacus Point, near Kinsale.
The training ship had lost power and was apparently driven on to rocks by a strong southerly wind at the western entrance to Kinsale Harbour. The grounded vessel quickly took on water and these pictures show where the steel hull was holed.

Salvage of Tall Ship Astrid Begins off Kinsale
#tallship – A salvage operation to remove the wreck of the Tall Ship Astrid from rocks off Kinsale is underway. The operation will involve specialist marine crane equipment brought in from the UK. The 95-year-old vessel ran aground at Rocks off Kinsale last month during a photocall for the Irish Sailing Association Gathering Cruise promotion, prompting dramatic scenes as 30 people were rescued from rough seas. The vessel has been resting on the rocks since the grounding on July 24th.
The operation is expected to take between one and two weeks, depending on weather conditions. A lifting barge and crane are due on site over the next couple of days.
Divers with the company have already completed a survey of the wreck and submitted a report to Coastguard officials on Monday.
For a month after the accident Astrid made a sad picture, still trapped on rocks, her beautiful sails torn and ripped by the sea but amazingly her rig still intact.
The vessel, which was built in 1918 and operated as a cargo ship until 1975, was on a 14-day voyage as part of an EU Youth in Action programme sailing from Southampton to Cherbourg via Kinsale. The Astrid departed Oysterhaven for Kinsale but lost power during a photocall with seven crew and 23 trainees on board.
For more on Astrid's sinking click Afloat's Tall Ship news section.






































































