Displaying items by tag: Dermot Cronin
#Presentation - Friends of Glenua are to hold a presentation entitled: “From the Aegean to the Fastnet Race 2017-Trom agus Éadrom”
The presentation by Dermot Cronin will take place on Thursday 1 March (20:00) at the Poolbeg Yacht & Boat Club, Ringsend, Dublin 4. There will be an entry fee of €5 in aid of the RNLI.
The 2017 Rolex Fastnet Race attracted a record-sized fleet of 362 boats, six more than in 2015. The 605 mile continues to be the world’s largest offshore yacht race, defined by the rounding of the Fastnet Rock with its iconic lighthouse.
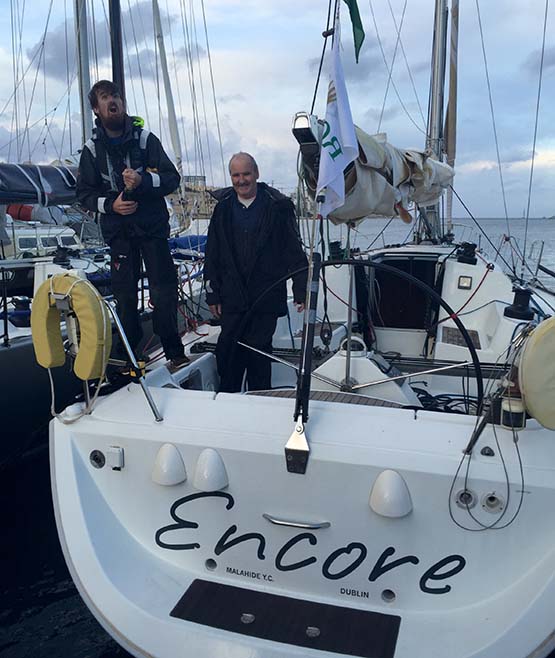
Dermot Cronin of Malahide Yacht Club, competed in the 2017 Rolex Fastnet Race in his yacht, Encore, a First 40.7. The preparations included the 2,500 mile passage of Encore from her winterage in Greece to Malahide, during which she encountered heavy weather both in the Mediterranean and in the Atlantic (the ‘Trom’ of the title).
In his illustrated lecture, Dermot will give a practical insight into the preparation and logistics required to get his boat to the starting line at Cowes followed by the competitive intensity experienced in a huge international fleet. The events of the Fastnet race itself which, although more benign in the weather (the Eadrom of the title), provided some close racing.
Dermot’s first sailing course was with Glenans in Bere Island in 1979. Being an active racing member of Malahide Yacht Club since 1989, he progressed to Round Ireland racing, D2D’s and Fastnet in 2003. He participated in the Middle Sea Race in 2013 and 2014 in his fully crewed Encore. He finally struck gold in 2015 with his son Paddy, winning the Double-handed division of the 2015 Middle Sea Race in Encore.
Dermot & Paddy Cronin Are Afloat.ie Sailors Of The Month: October
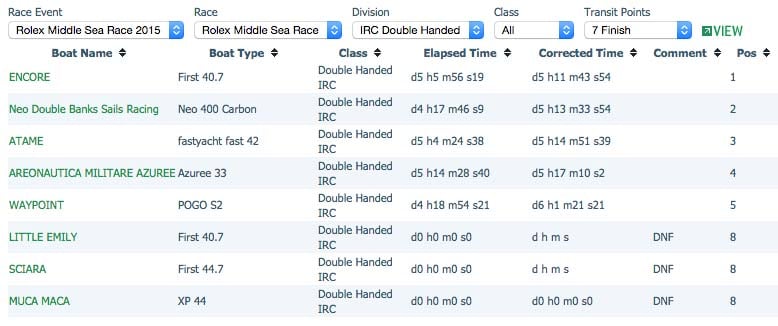
Malahide father-and-son crew of Dermot (63) and Paddy (31) Cronin are the Afloat.ie Sailors of the Month for October after their clearcut win by almost two hours in the IRC Double-Handed Division in the 606-mile Rolex Middle Sea Race.
Sailing their keenly-campaigned First 40.7 Encore, Team Cronin tackled conditions and the opposition as though they were a fully-crewed boat. And though overall it proved to be a race which suited boats around the 50ft mark, the 40ft Encore was very much in contention in her open Class 6 against racers sailed by numerous experienced crews, placing sixth overall out of 18 boats.
This pattern of being a third of the way from the front was continued in the total fleet of 102 contenders, as they placed 37th in an impressive turnout which included all the best offshore racers in the Mediterranean, and such noted international stars as George David’s Rambler 88 (due in Ireland next June in the Round Ireland Race 2016) and the Maxi 72 Momo, which dominated the big boats in the Fastnet Race.
It says everything about the skill and dedication with which Dermot and Paddy raced that we find ourselves easily making comparisons with their showing against the fully-crewed boats, whereas the real story is that they won the Double-Handed Division with plenty of time in hand.

It seemed almost too good to be true, but it really happened……Paddy and Dermot Cronin back in Valetta find they’ve won the Rolex Middle Sea Race Double-Handed IRC Division with nearly two hours to spare.
Malahide Yacht Club's Dermot Cronin sailing with his son Paddy has won the double–handed division of the Rolex Middle Sea Race. The stand out international result for the Irish double–hander was achieved on his Beneteau 40.7 Encore.

Encore from Malahide on her way to overall victory in the double–handed class. Photo: Rolx/Carlos Borlenghi
Cronin is a regular competitor in the 600–mile race but this is understood to be the first time the Irish yacht has been sailed double–handed in the Mediterranean fixture.
The Irish duo, who finished 37th overall beat the UK based Neo 400 Banks Sails Racing by more than two hours on corrected time in a time of five days, 11 hours and 43 seconds.
Malahide YC commodore Graham Smith was one of the first to offer congratulations to the Cronins. 'It's great news, richly deserved and we are delighted for Dermot and Paddy, he said.
The father and son team took just over five days and night to complete the race. Paolo Semeraro's Neo Double Banks Sails Racing had led for much of the race but finished in second place after a strong finish from the Irish team. Beppe Bisotto & Manuel Polo racing Fast 42, Atame was third. This was Beppe's 11th Middle Sea Race and his fifth Double Handed.
Dermot Cronin competed with his First 40.7, Encore, in the last Rolex Middle Sea Race with a full crew but didn't finish the race due to rudder problems in heavy weather. Dermot and his son Paddy have raced double handed before but nothing like the Rolex Middle Sea Race.
“Last year watching the Prize Giving for the Rolex Middle Sea Race, I remember thinking that the only chance I have to get on that stage is with my son Paddy.” commented Dermott Cronin. “Paddy has been tremendously successful racing double handed and I was delighted when he agreed to team up with me this year. I have huge respect for Paddy, I get quite emotional just thinking about that, I call him my master and commander, unequivocally he is the skipper and I am the crew. We have sailed for years and for me it doesn't get any better than this.”
“Probably the stand-out memory of the race was when we approaching Malta.” Commented Paddy Cronin. “We could pick up the tracker again, we knew we were in contention but we had no idea we were leading the Double Handed Class. Initially we thought that would be easy but then we started doubting that, so we put up the spinnaker in strong breeze and the snuffer jammed at the top and we knew that like that we couldn't get it down. So I went up the rig, hoisted by my Dad. It was blowing 25 knots in a confused sea and I was bouncing around and I was thinking we had messed the race up. So to be honest, when we came through the line there was more feeling of relief than anything else. When you finish a race like that it is almost surreal, you are so wrapped up in the race and we only came back to reality when we had a lovely reception from Barry Hurley, who won the Two Handed Class in 2012.”
It will be an emotional moment for Dermot and his son Paddy, when they take to the stage tomorrow, for the Rolex Middle Sea Race Prize Giving Ceremony.
Other Irish sailors competing inlcuded David Kenefick sailing with Artemis in 75th place with Ireland's former Green Dragon, now in Austrian hands, in 76th.
Competing in class four on Xp–act Banks Sails Racing were Andrew Boyle, Philip Connor, Barry Hurley and Kenny Rumball who finished 21st overall.
Meanwhile, Vincenzo Onorato's Italian Cookson 50, Mascalzone Latino, with Northern Ireland's Ian Moore as navigator, corrected out to win the overall prize for the race rating under the ORC Rule. The top three yachts came from three different classes, 57 yachts entered the race under the ORC rating system, which rated the yachts by time over distance. In second place overall was Michele Galli's Italian TP52, B2 with Francesco de Angelis as tactician. In third place overall was Milan Hajek's First 40.7, Three Sisters with a crew all from the Czech Republic.
2015 Maxi 72 World Champion winning navigator, Ian Moore spoke about the Mascalzone Latino victory. “This is the first time we have sailed together as a team for over a year and we put in a great performance. Our team and the boat performed well over a broad range of conditions, and we especially made big gains in the light winds. B2 was always going to be quicker than us in a straight line and they did well in the transition zones at Stromboli and Capo San Vito. We did catch up 14 miles on the first night going past Mount Etna, which was a big gain for us. On the leg from Lampedusa to the finish, there were a lot of thunderstorms and we saw one wind shift of 50 degrees, which we got spot on. This was an exciting race for us and tactically extremely difficult.”
In ORC One, Michele Galli's TP52, B2 was the winner from Hungarian RP60, Wild Joe, skippered by Marton Jozsa. In third place was Vicente Garcia Torres' Spanish Swan 80, Plis play was third.
B2's navigator, Nacho Postigo commented ”I think the 50-52 feet is a good length for this race. The TP52 is an all-round boat, with very little weaknesses, a good compromise between rating and speed. For me this was a typical Middle Sea Race; you struggle to find the wind, and when you do, it happens in excess. This time it was more about managing the light than about strong winds. For me, this is one of the most challenging races in the world. In this race there is a strong association between land and sea, and this drives you to take many important decisions along the way; sometimes, mistakes are really expensive here.”
ORC Two featured three canting keel yachts. Mascalzone Latino was the winner and there was a close battle for second place. Franco Niggeler's Swiss custom 42, Kuka-light, had an epic battle with Guido Paolo Gamucci's Italian Cookson 50, Cippa Lippa 8. Kuka-Light crossed the finish line of the Rolex Middle Sea Race just eight minutes ahead on corrected time to take second place ahead of Cippa Lippa.
ORC Three was won by the Turkish Ker 40, Arkas Flying Box, skippered by Serhat Altay, Arkas Flying Box was also placed 10th overall in ORC. Bastiaan de Voogd young Dutch team racing Sydney 43 Coin Coin was second. Vittorio Biscarini's Italian Mylius 15, Ars Una was third.
“Our Code Zero was a real weapon this race, especially in the wind holes.” commented Martin Watts, Arkas Sailing Team Coach. “There was no end to the enthusiasm from the team in their first major offshore race. Morale was very high on board and the team sailed very well together, I must say they are a real treat to sail with. Our ultimate goal for this year was to win our class at the Rolex Middle Sea Race and our efforts have achieved that, so we are absolutely delighted.”
ORC Four produced a tense battle for the class win, Christopher Opielok's Corby 38, Rockall IV from Hong Kong, corrected out to win the class by under an hour from three Maltese yachts, Christoph Podesta's First 45, Elusive II BOV was second, Sonke Stein & David Anastasi's J/133, Oiltanking Juno was third. Josef Schulteis & Timmy Camilleri’s Xp-44, Xp-Act Bank Sails was fourth by less than five minutes after time correction.
“In the light conditions, we were up against it but once we got into the breeze, this was more advantageous for Rockall, as we have a superior righting moment with a deep heavy keel.” Commented Rockall IV crew, Simon 'Cake' McCarthy. “The team did a great job at Pantelleria, we must have passed about 20 boats with our Code Zero up and at Lampedusa, we knew we were going well. Then the breeze just built and built and in big waves, we were on the edge of control. It was an awesome finish to the race.”
ORC Five produced one of the closest battles of the race. Lee Satariano & Christian Ripard's Maltese J/122, Artie won the class and also placed fourth overall under ORC. Costantin Manuele's First 40.7, Canevel Spumanti from the Yacht Club Adriaco, Trieste was second. Jamie Sammut's Maltese Solaris 42, Unica was third and Laurant Charmy's French J/111 SL Energies Groupe Fastwave was fourth. All four yachts finished within an hour of each other on corrected time.
“Mentally that was a very tough race and at times very frustrating.” Commented Artie's Lee Satariano. “At many stages of the race, if we could have found more wind, we would have done. The crew agree that we probably sailed the boat better this year than we have ever done. We sailed every leg really well and made very few errors. We set out to win our class and we are very happy that we have achieved that.”
ORC Six was won by Three Sisters taking part in their seventh race, the team from the Czech Republic corrected out to beat Grand Soleil 37, Sagola-Biotrading, skippered by Peppe Fornich. The crew are from the Yacht Club Favignana, the Aegadian Island of Favignana marks the northwest corner of the course. Gherardo Maviglia's Beneteau Oceanis 430, Amapola representing Circolo Velico Fiumicino, Roma was third.






























































