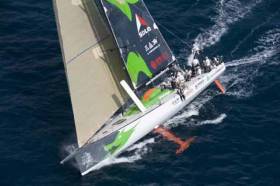
Displaying items by tag: Green Dragon
Green Dragon Galway Youth Crew Take Line Honours Runners Up Prize in Round Ireland Race
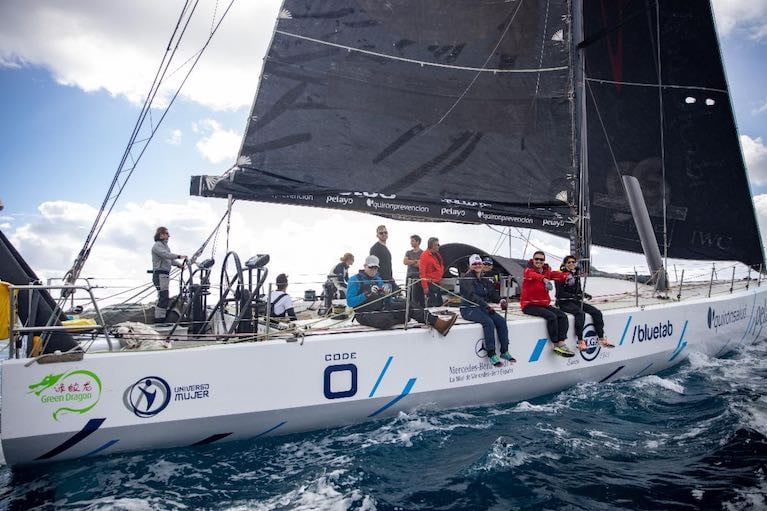
Ten young sailors from Galway Bay who were part of the crew that sailed the Green Dragon in last week's Round Ireland Race from Wicklow finished as Line Honours runners-up and second in Class Zero in the biennial 700-mile race.
As co-skipper Enda O'Coineen previously reported on Afloat, the former Irish VOR boat Green Dragon was entered into June's circumnavigation race to mark the tenth anniversary of the Volvo Ocean Race in Galway.
Green Dragon is currently owned by a yacht charter company based in Vigo in North West Spain.
 Upwind conditions on Green Dragon on the West Coast of Ireland
Upwind conditions on Green Dragon on the West Coast of Ireland
Ten Galway Bay Sailing Club members were aboard for the delivery trip across the Bay of Biscay to Dun Laoghaire. They departed on the morning of June 5th and arrived late June 8th. Following wind and seas, they maintained double-digit boat speeds most of the way. They saw 21kts at one point surfing down the 5m Atlantic swell, which was truly magnificent.
 Cathal Mahon and Rob Talbot from Spiddeal Sailing Club
Cathal Mahon and Rob Talbot from Spiddeal Sailing Club
The owner made young Cathal Mahon (Spiddeal Sailing Club) skipper in the days before the race. A very competent sailor with a calm yet confident manner. He was joined by sailing colleague Rob Talbot (Spiddeal Sailing Club).
 Green Dragon crew (from left) Aaron O'Reilly, Fiona Christie, Iso Inan, Mark Wilson, Paddy Hennelly, Michael Flemming, Cathal Mahon (Spiddeal), Cian Conroy
Green Dragon crew (from left) Aaron O'Reilly, Fiona Christie, Iso Inan, Mark Wilson, Paddy Hennelly, Michael Flemming, Cathal Mahon (Spiddeal), Cian Conroy
The highlights of the race were rounding Fastnet in near calm conditions only to be followed by the very tough upwind leg up the West Coast on Sunday 19th, where there were 38kt gusts and big seas. The tidal gate at Raitlin was also a tricky period. The light winds on the East Coast also proved very frustrating as the boat suffers in light winds. Overall, the crew members had a great atmosphere on board with excellent communication.
 Green Dragon and her Crew for the Round Ireland in light winds
Green Dragon and her Crew for the Round Ireland in light winds
Green Dragon finished in 4 days, eight hours, and 54m 21s. 2nd in line honours and 2nd in Class Z to Kuku 3, a Swiss-registered Cookson 50.
Cathal Mahon (Skipper) Spiddal SC
Rob Talbot (Bow) Spiddal / Galway city
Watch 1
Sammy Burke (Helm/watch lead) Lough Swilly
Jim McGowan (Helm) Lough Swilly
Iso Inan (Pit) GBSC
Michael Starr (Trimmer) Lough Derg YC
Oisin Lyons (Trimmer) Royal Irish YC
Paddy Hennelly (Bow) GBSC
Fiona Christie (Crew) GBSC
Watch 2
Mark Wilson (Helm/watch lead) GBSC
Aaron O'Reilly (Helm/bow) GBSC
Matija Rossi (Pit) Croatia
Michael Fleming (Trimmer) GBSC
David Adley (Trimmer) LDYC
Cian Conroy (Trimmer) GBSC
Barry O'Brien (Trimmer) Kinsale
Volvo 70 Green Dragon's Entry in the Round Ireland Race Marks the Ten Year Anniversary of the Volvo Ocean Race in Ireland
Enda O'Coineen, the (non-sailing) Round Ireland co-skipper of Green Dragon, writes this year's Volvo 70 entry marks the tenth anniversary of the Volvo Ocean Race coming to Ireland.
I am sorry to see the SSE Renewables Round Ireland Race leader for line-honours retiring; my heart goes out to the team. Though on the other hand, I am pleased for the Green Dragon. I say this as a non-sailing Skipper with Conor Ferguson, also non-sailing, who has done a fantastic job helping pull the team together.
We have a great team on the Green Dragon from a select group of 15 from Dublin, Donegal and Belfast. Cathal Mahon is playing a blinder as Sailing Master. Indeed a successful team works without you!!!
 Green Dragon racing in the Round Ireland Race to mark a Volvo Ocean Race anniversary Photo: Afloat
Green Dragon racing in the Round Ireland Race to mark a Volvo Ocean Race anniversary Photo: Afloat
Heading around the top of Ireland tonight, I am delighted with the guys' performance. They are having a ball ...
We brought the Green Dragon back to Ireland to Mark the 10th anniversary of the Volvo Ocean Race in Ireland. And also to mark the arrival of the new Grace O'Malley youth development ship - a legacy from the Volvo and NCB Ireland.
 The new Grace O'Malley youth development tall ship
The new Grace O'Malley youth development tall ship
This 10th Volvo anniversary will be celebrated the weekend of 15 July in Galway, and the 35th anniversary of the NCB Ireland launch around 20 August in Dublin.
Enter the (Green) Dragon - O'Coineen Signs Up Volvo 70 for June's Round Ireland Race
Enter the Dragon. Enda O'Coineen, the Galway man behind the Irish entry in the 2008/9 Volvo Ocean Race is back behind the wheel of the Volvo 70 as the 12th entry into June's SSE Renewables Round Ireland Race.
It's not Green Dragon's first circuit of Ireland either, the Galway Bay yacht was the biggest and fastest of the 38-boat fleet in the 2012 edition of the race.
A year ago, under Johannes Schwarz’s Green Dragon crossed the finish line of the 7th edition of the RORC Transatlantic Race in an elapsed time of 9 days, 18 hours, 53 mins and 40 secs to win the IMA Trophy to take monohull Line Honours in the race.
 Enda O'Coineen - will co-skipper the Volvo 70 Green Dragon in June's Round Ireland Race from Wicklow Sailing Club
Enda O'Coineen - will co-skipper the Volvo 70 Green Dragon in June's Round Ireland Race from Wicklow Sailing Club
The Round Ireland campaign for Green Dragon will be is a joint entry from O’Coineen and Conor Ferguson. The boat is entered as both a Galway Bay Sailing Club and Royal Irish Yacht Club entry.
As regular Afloat readers will know, the original VOR team was captained by Ian Walker and finished the race in fifth place overall (from six starters) scoring 63 points. The boat was designed by Reichel Pugh and built by McConaghy Boats.
Green Dragon's Fast Finish in the RORC Transatlantic Race
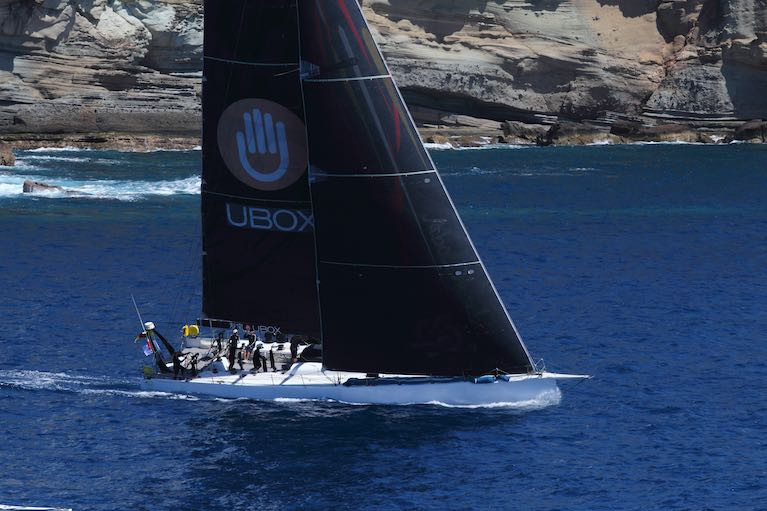
Johannes Schwarz’s Volvo 70 Green Dragon crossed the finish line of the 7th edition of the RORC Transatlantic Race at 04:53 UTC in an elapsed time of 9 days, 18 hours, 53 mins and 40 secs. Green Dragon wins the IMA Trophy and takes Monohull Line Honours for the RORC Transatlantic Race.
Olivier Magre’s Class40 Palanad 3 was less than five hours behind, completing the 2735-mile race in a phenomenal elapsed time of 10 days, 1 hour, 43 mins and 18 secs. For the moment, Palanad 3 have scored the best corrected time under IRC for the RORC Transatlantic Race Trophy.
Green Dragon becomes the seventh boat to win the International Maxi Association’s IMA Trophy. Whilst this year’s race is a different route, Green Dragon is the first monohull to complete the RORC Transatlantic Race in under 10 days. The Secretary-General of the IMA, Andrew McIrvine commented: “Congratulations and best wishes from the IMA to Johannes and the Green Dragon team. We are sorry not to able to greet you, as we would have in more usual times, but we hope you enjoyed the race.”
“It is an honour to win the IMA Trophy, as so many famous boats have done, but to finish the race in such a fast time is incredible. Although we finished in Antigua and not Grenada, the route we took was to the south, so there is not much difference in the miles we have raced,” commented Green Dragon’s Johannes Schwarz.
 Celebrations on board Johannes Schwarz’s Volvo 70 Green Dragon after winning the IMA Trophy and Monohull Line Honours in the RORC Transatlantic. Race. Green Dragon crew: Kees Bos, Alexis Duvernoy, Jonathan Florent, Florian Guezennec, Jens Lindner, Angel Lingorski, Jorge Lorenzo Roman, Elena Malakhatka, Peter Marchal, August Ruckman, Johannes Schwarz (Skipper), Anton Tajiev, Ada Westerinen.
Celebrations on board Johannes Schwarz’s Volvo 70 Green Dragon after winning the IMA Trophy and Monohull Line Honours in the RORC Transatlantic. Race. Green Dragon crew: Kees Bos, Alexis Duvernoy, Jonathan Florent, Florian Guezennec, Jens Lindner, Angel Lingorski, Jorge Lorenzo Roman, Elena Malakhatka, Peter Marchal, August Ruckman, Johannes Schwarz (Skipper), Anton Tajiev, Ada Westerinen.
“In the early part of the race we didn’t push too hard because we are a mixed pro-am crew and there were strong winds on the reach from Lanzarote to Tenerife,” explained Schwarz. “Later in the race we deployed the big kite and the conditions were just so fantastic. It was really special and very emotional for all the crew - we went faster and faster. I have to say that we are deeply impressed by the performance of the Class40s, they were so incredible! When we arrived in Antigua, it was not possible for the RORC team to meet us due to the curfew, but as if by magic, there was a cooler of cold beer on the dock!”
Green Dragon crew: Kees Bos, Alexis Duvernoy, Jonathan Florent, Florian Guezennec, Jens Lindner, Angel Lingorski, Jorge Lorenzo Roman, Elena Malakhatka, Peter Marchal, August Ruckman, Johannes Schwarz (Skipper), Anton Tajiev, Ada Westerinen.
Green Dragon Starts as Favourite in RORC's Transatlantic Race
Ireland's former Round the World race Green Dragon will start as favourite in this weekend's 2021 RORC Transatlantic Race. Run in association with the International Maxi Association, the race is scheduled to start from Puerto Calero, Lanzarote on January 9th, 2021. Ten teams have sailed from European destinations to take part in the 2,735-mile race across the Atlantic Ocean. Due to travel restrictions from the UK, the Royal Ocean Racing Club is operating remotely, relying on the expert abilities of the Calero Marinas’ team and the race officers of Real Club Náutico de Arrecife in Lanzarote.
As regular Afloat readers will know, Ireland's Volvo 70 finished fifth out of seven entries in the 2009 Volvo Ocean Race. Attempts to sell her Green Dragon for two million euros in 2009 after the race did not materialise. She then spent some time in dry dock in Galway, rendered obsolete because her hull was heavier and keel lighter than her rivals.
In spite of the disappointing performance, the boat was welcomed into Galway after the 2009 Transatlantic leg by a huge crowd and a week-long celebration that subsequently set the bar for all other stopover ports in subsequent races.
RORC Transatlantic Race
The RORC Transatlantic Race is a World Sailing Category 1 offshore event with RORC Prescriptions. All competing boats will undergo compliance checks and, in addition, all crew will be required to produce a negative test result for COVID-19 prior to departure.
The monohull line honours favourite is Johannes Schwarz’s Volvo 70 Green Dragon, whilst the multihull line honours will be contested by just one entry, Oren Nataf’s Multi50 Rayon Vert, skippered by Alex Pella. The overall victory under IRC for the RORC Transatlantic Race Trophy is difficult to predict. However, Stefan Jentzsch’s new Botin 56 Black Pearl, skippered by Marc Lagesse, will be difficult to beat. Three teams will contest the IMA Trophy for Maxi Yacht line honours: Green Dragon, Richard Tolkien’s IMOCA 60 Rosalba and Open60 Somewhere London, skippered by Gunther de Ceulaerde. An exciting duel is expected between two of the latest Class 40s from the design board of Sam Manuard; Antoine Carpentier’s Redman and Olivier Magré’s Palanad 3.
Corinthian teams racing under IRC include Benedikt Clauberg’s First 47.7 Kali, which will be talking part in their third RORC Transatlantic Race. Two other teams will be taking on the race Two-handed: Tim & Mayumi Knight’s Pogo 12.50 Kai and Sébastien Saulnier & Christophe Affolter’s Sun Fast 3300 Moshimoshi.
After lengthy consultation with Camper and Nicholsons Port Louis Marina, Grenada Tourism and the competing teams, it was agreed that the safest option was to move the 2021 RORC Transatlantic Race finish to Antigua. It remains the intention of the RORC to finish the 2022 edition in Grenada, as it has done since the first race in 2014.
The veteran Volvo Racer Green Dragon (back mast-less in her old home port of Galway since Sunday) has been sorted. Her spare mast will be stepped today, with the port’s adopted French supersailor Yannick Lemonnier playing a key role in getting this nautical heroine of many a campaign back in full seagoing trim.
Meanwhile, the exceptionally summery weather has provided a warm and welcoming mood for the assembly of fourteen-plus Galway Hookers of various sizes for the Claddagh Festival (which continues until Sunday). The two Viking longships from Ardglass have arrived and been put into full warship mode, the highlight of their visit being the Salthill Raid on Saturday, when they’ll be accompanied by the hookers and a fleet of local yachts.
 The standard of maintenance in the fleet of traditional craft gathered in Galway this weekend is impressively high. Photo: Pierce Purcell
The standard of maintenance in the fleet of traditional craft gathered in Galway this weekend is impressively high. Photo: Pierce Purcell
Afloat.ie’s man in Galway reports that huge credit is due to anchorman Peter Conneely and his team, led by Colin Hermon, who have put in a massive amount of behind-the-scenes work to bring this very special and successful show together. With the quayside thronged last night with Galway, Connemara, Claddagh and Ardglass folk, the festival mood was running very well.
 In the summery weather in Galway, the “raiding” Ardglass Viking longships from County Down seem to exude nothing but goodwill Photo: Pierce Purcell
In the summery weather in Galway, the “raiding” Ardglass Viking longships from County Down seem to exude nothing but goodwill Photo: Pierce Purcell
Green Dragon Back in Galway Looking for a Mast
The Sino-Irish Volvo Racer Green Dragon has been having a somewhat checkered career since leaving Ireland, and though she took Transatlantic line honours in the ARC in December as the beginning of a Portuguese involvement in future Volvo Races, more recently she had the indignity of being dismasted.
Fortunately there’s a spare mast in her old home port of Galway, and she arrived in there yesterday to have it fitted. Afloat.ie will have more on this story as the week goes on.
 “I’m sure we left a spare mast here somewhere.....” Green Dragon returns to her old home port of Galway on a very specific mission. Photo: Pierce Purcell Jnr
“I’m sure we left a spare mast here somewhere.....” Green Dragon returns to her old home port of Galway on a very specific mission. Photo: Pierce Purcell Jnr
Volvo Open 70, Green Dragon, the former Irish Volvo Ocean Race entry has been dismasted in the Caribbean. The yacht made the journey across the Atlantic as part of a Portuguese Mirapuri initiative and was to be sailed in the Heineken St Maarten Regatta by a crew from Sopot YC in Poland.
None of the crew, who all hail from Sopot YC in Poland, were hurt. The unfortunate crew were left looking for crewing opportunities for the Regatta that started last week.
Green Dragon placed fifth overall in the 2008-09 Volvo Ocean Race, coming in 3rd at the Galway, Ireland stopover to the huge delight of the crowds that stayed out until 4am to welcome their boat home.
Mirpuri A Step Closer to Portugal's First Volvo Ocean Race Entry Thanks to Green Dragon
Paulo Mirpuri got a step closer to realising Portugal's first entry in the Volvo Ocean Race 2020 thanks to Ireland's Green Dragon VOR 70 now a training boat for Mirpuri's campaign. As Afloat.ie reported in January, the Portuguese crew made a successful ocean crossing in the former Galway–backed Green Dragon at the weekend.
Ashore in Bridgetown, skipper Mirpuri said: 'My debut on an ocean crossing taught me a lot, especially the importance of the spirit and union of the crew. Now I know exactly how to select the Portuguese sailors for the future Mirpuri Foundation team in the Volvo Ocean Race 2020'.
Ireland's Volvo 70 finished fifth out of seven entries in the 2009 Volvo Ocean Race.
Attempts to sell Green Dragon for €2 million euros in 2009 after the race did not materialise. She then spent some time in dry dock in Galway, rendered obsolete because her hull was heavier and keel lighter than her rivals.
In spite of the disappointing performance the boat was welcomed in to Galway after the 2009 Transatlantic leg by a huge crowd and a week long celebration that has subsequently set the bar for all other stop over ports in subsequent races.
Ireland's 2009 Green Dragon Volvo Ocean Race boat will sail again in a transatlantic race to promote the work of a non profit organsation.
As our photo above shows the famous Irish vessel has been rebranded as 'Mirpuri Foundation', a research body in aerospace and medical domains. The project for the former VOR yacht is 'just at its begining', according to a spokeswoman, but it already counts the support and sponsorship of the Foundation which Mr. Paulo Mirpuri is president.
The project is designed spread the Mirpuri message across the world with a Portuguese crew as ambassadors prior to a future Portuguese Volvo Ocean Race 2020 project.
A transatlantic crossing is planned for January 29th next year.
Ireland's Volvo 70 finished fifth out of seven entries in the 2009 Volvo Ocean Race.
Attempts to sell Green Dragon for two million euros in 2009 after the race did not materialise. She thenspent some time in dry dock in Galway, rendered obsolete because her hull was heavier and keel lighter than her rivals.
In spite of the disappointing performance the boat was welcomed in to Galway after the 2009 Transatlantic leg by a huge crowd and a week long celebration that has subsequently set the bar for all other stop over ports in subsequent races.