Displaying items by tag: Marine
Killybegs Report Shows Maritime Jobs Potential
#JOBS – 250 jobs could be created over a three year period across five key maritime areas in Killybegs according to a report launched by the Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine, Simon Coveney TD,
Minister Coveney set up the group on the 3rd June this year following the Economic Report for the European Commission, which assessed the status, development and potential diversification of Killybegs as a fisheries dependent community. The Group comprising of representatives from the Irish seafood sector, tourism, education, enterprise and the Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine were tasked to identify potential jobs across key areas including seafood, ancillary services, offshore supports, tourism and marine leisure and green economy/renewable energy.

Minister for Agriculture, Food and the Marine, Simon Coveney with Sean O'Donoghue, Chairman, Chief Executive, Killybegs Fishermen's Organisation Ltd, Cecil Beamish, Assistant Secretary, Department of Agriculture, Food and the Marine, Seamus Neely, County Manager, Donegal County Council, Jason Whooley, Chief Executive, Bord Iascaigh Mhara (BIM), Paul Hannigan, President, Letterkenny Institute of Education, Jim Parkinson, Representing Offshore and Ancillary Services, Niall O'Gorman, Representing Donegal Fish Merchants Association and Conor Fahy, Regional Director, Enterprise Ireland at the launch of a report on Job Creation in the Killybegs Region.
Minister Coveney commented at the launch; "I set ambitious targets for the group and I am very pleased to see that the group has not only clearly outlined how 250 jobs can be achieved but has also identified new areas where additional jobs can be created into the future. The importance of the seafood sector to Killybegs region cannot be overstated as it is responsible for 68% of the workforce. The Group has identified that through greater diversification and adding value to our existing resources, 130 jobs will be delivered in this sector. The Group are to be commended for working together to complete this task in the allocated time and I am looking forward to seeing the actions from the report completed and the benefits that they will bring to the people of Killybegs".
The report outlines 250 jobs to be created over a three year period across five key areas. In total, 130 potential jobs were identified within the seafood sector. The expected increased access to raw materials such as blue whiting and boarfish present the most significant opportunities, along with a concerted focus on value adding opportunities. Within the ancillary services, 24 jobs were identified if collaborative opportunities between various companies can be enhanced and their abilities promoted. The offshore sector could generate 20 jobs, however competitive service provision and appropriate skill resources are deemed fundamental to achieve this. Approaching 50 jobs were identified within the tourism/marine leisure area if a co-ordinated marketing strategy is developed, whilst the green economy and renewable energy area offers the potential to create up to 40 jobs.
The Minister added "This pilot approach of co-ordinated developmentally focused activity which is concentrated on natural resources has delivered results that will drive economic development and job creation in the Killybegs region. An example of this is the partnership between BIM and LYIT to address seafood value added activities. As a direct result of this jobs initiative, the College of Catering in Killybegs will become a focus for industry activity beginning with a workshop on new product development for crab suppliers is already planned for the 30th November".
Members of the High Level Group are:
Sean O'Donoghue, Chairman, Chief Executive, Killybegs Fishermen's Organisation Ltd
Cecil Beamish, Assistant Secretary, Department of Agriculture, Food and Marine
Seamus Neely, County Manager, Donegal County Council
Jason Whooley, Chief Executive, Bord Iascaigh Mhara (BIM)
Paul Hannigan, President, Letterkenny Institute of Education
Jim Parkinson, Representing Offshore and Ancillary Services
Niall O'Gorman, Representing Donegal Fish Merchants Association
Conor Fahy, Regional Director, Enterprise Ireland
Marine Federation agm for Dun Laoghaire
#BOATSHOW–The Irish Marine Federation (IMF) holds its Annual General Meeting at 18.00 on Wednesday, 30th November at the National Yacht Club, Dun Laoghaire.
Top of the agenda, in these challenging times, is the staging of next year's boat show which the board are keen to press ahead with in spite of the downturn. Options being discussed are a scaled back show as well as an on the water focus.
The AGM is open to all members of the IMF, whose subscriptions are up to date.
The meeting will be followed by drinks at the NYC bar.
Discovering our (Underwater) Past

Map of the Aran Sound in Galway Bay
Speakers at this annual seminar of the INFOMAR (INtegrated Mapping FOr the Sustainable development of Ireland's MARine Resource) programme will discuss the discovery of new and historic underwater wreck sites, the application of seabed mapping in the selection of sites for generating wave energy, the protection of fish spawning grounds, and the planning of fish farm sites.
The INFOMAR programme is a jointly managed programme between the Marine Institute and the Geological Survey of Ireland (GSI) and is funded by the Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources (DCNER).
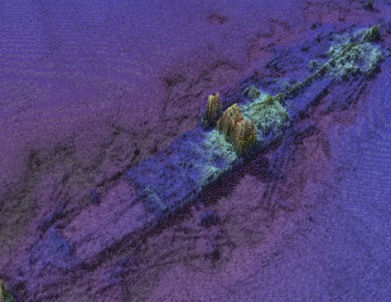
Wreck of the SS. Manchester Merchant
The event will also feature the latest results from a range of EC funded marine mapping initiatives and stunning underwater footage from the recent Irish mission to the volcanic vents of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge over 3,000 metres below the surface of the sea.
Opening the seminar Dr. Peter Heffernan, CEO of the Marine Institute said, "Ireland is leading the way for Europe in marine mapping and in laying the foundations for the sustainable management of our ocean space. Surveying the gateways to our ports, mapping our fish spawning grounds, finding routes for marine telecommunications cables and selecting the best sites for ocean energy generation all rely on accurate seabed mapping capability, which Ireland now possesses."
In addition to its large scale marine mapping remit, INFOMAR's Value Added Programme is co-ordinating an integrated multidisciplinary approach to the handling, processing and application of its ever-expanding marine data set.

Deepwater photograph from the mid-Atlantic Ridge
As a result of its latest call for research proposals, INFOMAR received 32 submissions for studies on such subjects as the appraisal of seabed data for tidal energy generation, the integration of satellite and marine data for coastal mapping and the use of new graphic animation techniques to integrate environmental information into seabed mapping displays.
"INFOMAR is a key mechanism to unlock the economic potential of our ocean territory," said Koen Verbruggen of the GSI. "By linking industry and academia to the realisation of our government's objectives and requirements around sustainable ocean development we will strengthen Ireland's position on this new frontier and expand our capability to deliver services and solutions to all marine sectors – in Ireland, in Europe and across the world."

Wreck of the sunken Guinness ship W.M. Barkley off Dublin Bay
As well as looking to the future, Ireland's maritime past will be explored in a presentation by the Underwater Archaeology Unit of the Department of Arts, Heritage and the Gaeltacht on the discovery of a probably late 16th century wreck off Rutland Island, Co. Donegal. The wreck, which may have been an armed merchant ship, a pirate or naval vessel potentially associated with the local Gaelic lordships or the Spanish Armada of 1588, is an extremely important find that could add greatly to our understanding of Ireland's maritime heritage.
Shillington's Quay in Portadown Set for Revamp
Shillington's Quay in Portadown is set for redevelopment thanks to a significant grant from the European Union.
The Portadown Times reports that half of the borough's £200,000 (€230,000) funding will be used for a new floating jetty and environmental improvements for the Newry Canal quay area, which was last used as a working port in the 1930s.
A total of £2.5 million (€2.9 million) has been earmarked by the EU for promoting tourism in the cross-border East Border Region, which aside from six Northern Ireland council areas also includes the Irish counties of Louth, Meath and Monaghan.
Other improvements to marine and waterway facilities include a £125,000 (€145,000) investment for the Eisenhower Pier in Bangor, on the southern side of Belfast Lough.
The Portadown Times has more on the story HERE.
Celebrations for Five Decades of the Barcelona Boat Show
In June 1963, a group of personalities who are linked to sports and the nautical industry, with Juan Antonio Samaranch at the forefront and the support of Fira de Barcelona, set up the first edition of the Barcelona Boat Show. The event, which is celebrating its 50th anniversary, has had a long and successful run and is, today, the sector's biggest commercial platform in Spain, its main meeting point and an international leader.
The Barcelona Boat Show is created in 1963 with the aim of boosting the sports and recreational nautical industry and promoting nautical sports. At the time, there are only a few specialised companies and marinas and an absolute lack of knowledge among the Spanish population about the possibilities of navigation. Nonetheless, thanks to the enthusiasm and drive of a group of people passionate about boating and the few professionals that existed at the time, the show manages to open its doors successfully with the participation of 150 exhibiting companies in hall 1 of Fira de Barcelona's Montjuïc exhibition centre.
After the success of the first edition, which took place within the framework of the very popular Feria de Muestras, it was agreed that the show would be an annual monographic event. In 1965, in the international category, it starts to exercise its role as a voice for the concerns of the sector, a function it has maintained until today.
Only two years later, in 1967, the nautical industry's first major boom takes place: new ports are opened, boats are built with their own design or under licence from foreign shipyards, boats can be seen in the sea, wood starts to give way too fibre glass and ranges grow considerably. In line with this development, the show sees a significant increase in exhibitors in 1969 and its organising committee prioritizes the growth of young people's enthusiasm for the sea -the appearance of the Optimist in '68 being crucial to this.
The sector undertakes actions to raise the government's awareness of the importance of carrying out reforms on registration procedures and taxation, with the aim of boosting an industry and trade that are forecast to grow and generate wealth and jobs for the country. The same year, the Law of Marinas is enacted; this is a basic toll for the expansion of the nautical industry in Spain and is considered to be one the Boat Show's most important contributions to the sector.
The 70s: the boom of tourism and nautical sports
The sector becomes more and more professional and, in the 70s, there is a notable increase in enthusiasts, although the figures show a big gap between Spain and other countries. For example, while in Spain the ratio is one boat for each 1,500 inhabitants, in Italy it is one per 192 and, in Scandinavian countries, it is one per 62. In any case, the government gives signs of its interest in the sector and the show; and in 1973, it grants it the golden plaque for tourist merit, aware of the importance of nautical tourism in Spain.
The show also continues to reinforce its sports aspect as a complement to its commercial side. Boat Show Trophy Races are organised and awards are given to the best sportspersons of the year, such as the Spanish Optimist team, which become World Champions in the races held in Sweden.
Ecology starts to make an appearance with the exhibition of the Dephins, the first electric engines. In 1976, the event receives the name of "International Boat and Sports Show" and opens up to the camping and caravanning sector. Samaranch, who has been president of the show since its beginnings, leaves the post in 1978, having been appointed Spain's ambassador in the Soviet Union and Outer Mongolia. He is replaced by Jacinto Ballesté, also member of the founding team. In 1979, the Asociación Española de Puertos Deportivos y Turismo is founded and its secretariat is installed in the Boat Show with Jorge Salvat at the helm. This represents one further step in the sector's development.
The 80s: the popularisation of nautical activities
The 80s bring many changes and innovations: the foundations to make the show more international are laid, it is split into sectors and the dates are brought forward in order to allow shipyards to programme their purchases and production. These changes are positive for the event, which sees the number of exhibitors and exhibition floor space grow, up to the middle of this decade. New nautical sports, such as windsurfing, take off and the first solar panels to be installed on board are exhibited. Boat charters and hire start to have a place in the show, with proposals to attract a public eager to navigate but unable to afford a boat of their own.
The number of new products presented by exhibitors also increases. Electronic equipment becomes smaller and cheaper and bow propellers for medium-length boats are introduced, making it easier to dock and cast off.
Activities to bring the public into contact with the nautical world increase, with navigation courses, steering with a tow, submarine photograph contests, navigational simulators, announcement of races, etc. Associations, federations, and institutions hold more and more assemblies, juntas and meetings within the setting of the show. In short, the show, which receives the Creu de Sant Jordi (Saint Georges' Cross) from the Generalitat de Catalunya in 1988, is confirmed as the sector's meeting point.
The 90s: the first on-water show
The 90s start with optimism. In 1992, the Barcelona Olympic Games are held, which represents a turning point for tourism, including the nautical industry: charter companies are consolidated and new marinas are built.
The number of motor boats at the show increases, especially large units and fisher-cruisers, as do new products presented by exhibitors; new materials, such as the composite, the latest design and equipment proposals and the latest technological advances, above all in the field of electronics, are exhibited. The concepts of sustainability and ecology take hold in the nautical world, even in recreational fishing.
The show is also consolidated as the meeting point for the sector, which is more and more professionalized, taking its concerns to the administration via the new associations that continue to arise. It also becomes a setting for the announcement of important races.
Nonetheless, during this decade, the show's main new feature is its arrival at the sea. As an addition to the Montjuïc exhibition centre, in 1995, Port Vell is set up for the first time to provide the setting for the On-Water Show with larger national and international boats. The same year, Jordi Montserrat takes over from Miguel Rafart as director of the show. In 1998, Fira de Barcelona's Administrative Board appoints Jorge Salvat as President Emeritus, after having been the show's president for 19 editions. He is replaced by the well-known impresario Enrique Puig.
A new century: the number of nautical enthusiasts grows
Enthusiasm for nautical activities multiplies and the show begins to develop in spectacular fashion. One of the highlights occurs in 2002, coinciding with the disappearance of the peseta and the introduction of the euro: the event moves to the new, modern Gran Via exhibition centre, maintaining the On-Water Show in Port Vell. In response to sector demands, the dates are also changed to the first week in November, in order to give continuity and avoid coinciding with other international shows.
Between 2002 and 2007, the Boat Show continues to grow, boosting the leisure activities and nautical sports sectors and showcasing national and world premiers. It is also the venue for meetings of international organisations with the presence of personalities related to the nautical industry from around the world, such as the International Sailing Federation (2003). New organisations are created within the show's framework, such as the Asociación Española de Clubes Náuticos and the Asociación Nacional de Empresas Náuticas, ANEN (2006). In 2007, Jordi Freixas is appointed new director of the show to replace Jordi Montserrat.
After years of optimism, the sector begins to show signs of recession in 2008, which leads to concern that a world scale economic crisis is on the horizon. That year, Enrique Puig, the show's president, passes away and, for that edition, the president emeritus, Jorge Salvat, steps in. In 2009, Luis Conde is appointed the new president.
From that year, the effects of the crisis are heightened. Until now, the show has been carrying out actions to support companies, reinforcing its role as the main platform for energising trade and the sector's main setting, from which to express its needs and look for solutions to tackle the difficult economic situation.
Despite the recession, nautical companies have stood out for their efforts and commitment to technological innovation with the development of new, safer, sustainable and environmentally-friendly products. At the same time, lovers of the sea, who continue to grow in numbers, are looking for new formulas via which to enjoy the sea, and interest in charter and shared property is growing.
Ferry Stops, 'Sea Water Baths' on the Way for Dun Laoghaire
The last Stena line ferry sailing from Dun Laoghaire featured on the RTE News headlines last night. The ferry link is stopping because of a decline in passenger numbers and the high cost of fuel, say the operators, Stena.
The report by John Kilraine, interviewed Harbour Boss Gerry Dunne who spoke about the master plan for the harbour, how the harbour company hoped that Stena could rebuild the route, the bid to attract cruise ships and the east coast port's future as a marine leisure centre.
The masterplan is to go through the planning processs piece by piece and harbour yacht clubs have concerns over aspects of the plan.
Last night's bulletin also reported the harbour company intends to open a 'sea water baths' in the harbour next year and a diaspora centre in 2013. The RTE report is here.
See also:
Dun Laoghaire Yacht Clubs Voice Concern Over Plan
Dun Laoghaire Yacht Clubs are voicing concerns about the impact on sailing if a 'cruise ship jetty' is constructed as part of the recently published harbour masterplan.
Dublin Bay Sailing Club, Dun Laoghaire Motor Yacht Club, National Yacht Club, Royal Alfred Yacht Club
Royal Irish Yacht Club and Royal St George Yacht Club. are also concerned about access to the water if a proposed 'pedestrian walkway' in front of the waterfront clubs was completed.
The clubs have engaged 'professional help' to prepare a submission to outine the concerns.
Also seen as a problem is the 'lack of sufficient facilities in the masterplan for hosting significant international sailing events'.
A survey in 2009 by the Irish Marine Federation (IMF) calculated a €3million spend by participants connected with the 500-boat Volvo Dun Laoghaire regatta. The clubs have previously stated they see the harbour's future as a leisure facility.
A masterplan model was on display by the Harbour Company in the month of August.
Writing to members in the current edition of the National Yacht Club's newsletter commodore Paul Barrington says the clubs 'hope to further engage with the harbour [company] to find a mutually acceptable way forward'.
Water Rat: Harbour Plan is a Curate's Egg
While it might be an exaggeration to say that all of the 21 crew members of Rambler 100 owe their lives to the Irish Search and Rescue service, there are certainly five people whose future prospects were greatly improved by the operation off the Fastnet Rock on August 15th. A lot of media focus has been on Coxswain Kieran Cotter and the crew of Baltimore Lifeboat as well as lifeboat mechanic Jerry Smith, whose dive boat, on charter to the media team of one of the competitors, was on hand to search and recover the five drifting crew. There is no question that this focus is appropriate. RNLI crews all over the UK and Ireland deserve the attention, not only because of their extraordinary voluntary dedication to the cause, but also because such publicity helps swell the coffers of the charity. The service could not operate without the generosity of the donors and incidents such as these help fill the blue boat-shaped boxes held by even more RNLI volunteers.

Saved: Ireland's Rescue Services Answered the Call of the capsized Supermaxi Rambler 100 off the Fastnet Rock. Photo: Team Phaedo
The dramatic stories and pictures dominating the media show the front line of a quite wonderful resource that is Search and Rescue in Ireland today. Baltimore Lifeboat was at the coal face of an intricate network of operations, triggered by the crew's EPIRBs. Irish Coast Guard radio officers in Valentia responded almost immediately tasking the rescue resources, working the phones and computers to confirm that this was not an accidentally triggered EPIRB, contacting RORC HQ, determining search patterns and relaying the information to the scene. It was the backroom contacts between RORC and the Coast Guard in endeavouring to contact Rambler 100 using satellite phones that confirmed the possibility of a catastrophic incident involving the Supermaxi. The subsequent tasking of the Shannon and Waterford based Sikorsky helicopters led to the medevac of crew member Wendy Touton and timely treatment of her hypothermic condition, initially by the on-board paramedics and later at Tralee General hospital. And Coast Guard involvement didn't end with the successful rescue – the shoreside operation to provide food and shelter in Baltimore was coordinated by Coast Guard personnel and the salvage operation of the hull of Rambler 100 was overseen by the Irish Coast Guard.

Rambler crew are recovered from the water after a SAR operation by the Irish Coastguard Photo: Team Phaedo. More photos here.
That Ireland has probably one of the best Search and Rescue services in the world goes back to the campaign initiated in 1988 by Joan McGinley, following the death, within sight of land of Donegal fisherman John Oglesby, whose leg was severed in a trawl winch. Eamon Doherty, the late former Garda Commissioner chaired the review group established in response to the campaign and his report led to the establishment of the Irish Marine Emergency Service, subsequently the Irish Coast Guard. Under the guidance of Director Capt Liam Kirwan, the new service moved quickly to become not only the central co-ordinating body for Search and Rescue, but developed its own resources, notably the helicopters, previously tasked in from Irish Air Corps and UK SAR.
Another element that will feature in the Rambler 100 incident is the Marine Casualty Investigation Board (MCIB), set up from recommendations arising from a review of the handling of investigations into marine casualties.
It might be thought that the incident is now closed, but there are many unanswered questions and the investigation will be looking at these and making recommendations that should improve safety in this sector. These questions will include EPIRB performance, liferaft deployment and grab bag usage, but perhaps the key issue yet to be determined is why the response from fellow competitors didn't appear to happen. Even if Channel 16 wasn't being actively monitored, and if not why not, shouldn't the Mayday set off by the Coast Guard have set off the DSC alerts on the radios of Rambler 100's fellow competitors? Had the incident occurred several hours later or earlier when Rambler 100 could have been up to 100 miles from the nearest land, when conditions worsened, we could be looking at much more serious consequences.
It is heartening to think that, in this small country of ours in troubled times, not only do we have a shining star in our search, rescue, recovery and restore system, involving professionals and volunteers cooperating for the greater good, we also have a system that determines the nature of incidents so that we can all learn from the experience.
And let us not forget those people and services, such as the Gardai, Navy, Army and the community of Baltimore who are outside the media spotlight who contributed to this happy ending.
Afloat's Latest Coastguard News
Afloat's Latest RNLI Lifeboat News
Afloat's Latest MCIB News
Tall Ships 2011: Young Sailors 'Buoyed' with their Successes
Not only has their ship, The Moosk been placed third in class in the first leg of the race, but they were awarded the youngest crew trophy and won their skipper's weight in food and drink having been the first 2011 tall ship to arrive at Unst.
Eighteen of the St Budeaux School's 14-19 year olds have been involved in the international event which started in Waterford, Ireland and included ports of call at Greenock, Scotland and Lerwick in the Shetland Isles, continuing to Stavanger in Norway before finally dropping anchor at Halmstad in Sweden at the beginning of August.
The 18 students who successfully completed a rigorous selection before finally becoming crew for a section of the race on the tall ship Moosk were split into three groups.
The first six sailed from Plymouth to Waterford where six more Marine Academy students took over and raced in the first leg, Race One, from Waterford to Greenock. Once in Greenock, the crew changed again and the final six students sailed to Lerwick before returning home this weekend.
The young sailors are buoyed up with their successes.
In their latest messages on Facebook they say: "Wahoo just arrived in Lerwick, we've had an amazing time already. We've been to Unst and rounded Mukkle Flugga, the most northern point in Britain. We won the Captain's Weight in Unst - proud - and had a parade with Vikings. All in all it's been amazing so far."
Marine Academy Plymouth is planning a celebration evening in September for the students who joined hundreds of other youngsters crewing ships from Russia, Belgium, Germany, Sweden, Lithuania, Poland, Norway, Denmark, Colombia, Spain and France.
Helen Mathieson principal at Marine Academy Plymouth said: "The success of all our young people taking part in the fantastic event which is the Tall Ships Race is a very fitting end to the Marine Academy Plymouth's first year.
"All the students who have taken part have learned so much - about themselves, what they can achieve and how they can make success happen by working with others. All of them have been part of winning teams and have felt the joy of making it happen for themselves; their horizons have been widened by the whole experience."
Public Consultation on Cork Harbour's Future
A public consultation on the future of Cork Harbour is open until 15 July.
Copies of the 300-page Cork Harbour Study are currently available at Cork County Council offices and online at www.corkcoco.ie, The Southern Star reports.
The study outlines possibilities for the long-term future of the coastline in and around the harbour, including but not limited to the development of disused or under-used areas, and sustainable patterns of settlement and industry.
Ideas the report puts forward for public debate include a new marina for Cobh, more shoreline pedestrian and cycleways, a new container terminal at Ringaskiddy and initiatives for marine-related employment.
"A balance between the development and amenity roles of Cork Harbour is only likely to be maintained if there is public support for this," said outgoing Cork Mayor Kevin Murphy. "Greater use and better public access to its amenities and recreational facilities will make this more likely."







































































