Displaying items by tag: Newbuild
In an update on Arklow Ranger, the fourth of seven Dutch shipyard completed Eco-Traders of the 6,800dwt / R class cargo ships, departed last month from its inland location to reach a seaport, writes Jehan Ashmore.
An Autumnal launch of the Arklow Ranger, which is just shy of 105m (LOA) length overall, took place in October as Afloat reported at the Royal Bodewes Shipyard at Hoogezand, near Groningen.
Following final works to prepare the Irish flagged cargo ship with a combined hold capacity of 310,000 cubic feet (cbft), the newbuild last month departed the shipyard.
This involved towage from the shipyard on the Winschoterdiep Canal and an onward connection via the Zeehavenkannaal to reach the Port of Delfzijl on the Ems estuary. From there took place the short passage to Eemshaven on 18 December, this in the same week prior to the start of the Festive Season.
It would appear that the last known activity of the Arklow Ranger occured the following day, after arriving at Eemshaven, as the newbuild currently remains at its berth in the Dutch north-eastern port.
As customary with the newbuilds Arklow Shipping have on order to Bodewes, that the shipbuilder's sea trails are conducted offshore of Emshaven. Such trials are carried out in the vicinity of The Frisian Islands, also known as the Wadden Sea Islands, which form an archipelago also off the neighbouring German coast.
Beyond the archipelago is the open waters of the North Sea from where Afloat will have more to report on this newest addition to the Irish Shipping Registrar.
Newbuild Short-Sea 'Coaster' Brings to Eight Out of Ten C-Class Cargoships for Arklow Shipping
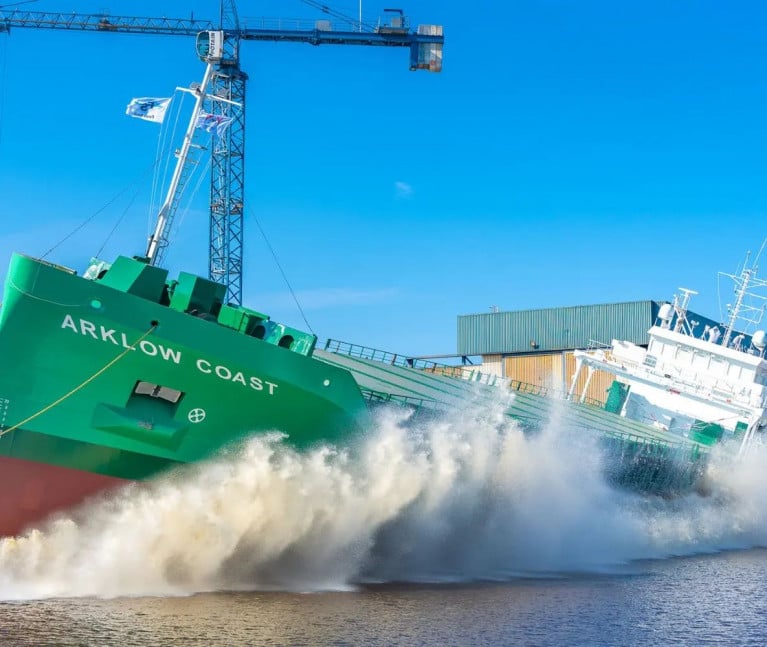
Once again the newest C-class series of short-sea traders for Arklow Shipping, launched in a shipyard in The Netherlands, has been given a ship name first for the Co. Wicklow based shipowner, writes Jehan Ashmore.
On this occasion, Saturday's launch of the 5,054dwat newbuild saw the Arklow Coast take to the waters of the Winschoterdiep canal at Ferus Smit's shipyard at Westerbroek.
The new 87m cargoship will further modernise ASL's almost 60-strong Irish-Dutch flagged fleet, that includes deep sea ocean going bulkers, the largest been a pair of S-class, each of 34,905dwat. In addition to the dwindling R-class of 4,933dwat. Among them the oldest, Arklow Rainbow which Afloat observed depart Dublin Port last week when bound to Northfleet, London.
As for the new Irish-flagged C-Class cargoships, they are given names beginning with the letter 'C'. Such newly created names having differred to previous generations of tonnage dating back to the 1980's. An exception to the nomenclature has been Arklow Castle (see 'European' trader) which follows two predecessors taking this same name.
The previous 'Castle' built for ASL and dating to 1996, was notably a 'containership' which is a rarity for ASL operations, having served a 'liner' service linking the UK, Ireland and Spain. This lo-lo link was discontinued following ASL's disposal of the 532TEU capacity containership.
Whereas, the original Arklow Castle built in 1981 was secondhand tonnage for ASL, until its career ended dramatically when it became wrecked more than a decade later at Sables d'Olonne on the west coast of France.
As for the current Arklow Coast, which represents the 8th of 10 C-class cargoships ordered by ASL and follows Arklow Cloud which Afloat reported late last year also launched at Westerbroek.
A maximized single hold equates to a volume of 220,000 cft and a carrying capacity over 5000 deadweight tons. The newbuild has been given a 1A ice class notation and is propelled by a 1,740 kW MaK engine with a single ducted propeller.
The straight-stemmed bow is equipped with a 275kW electric bowthruster to assist operations in port. Related to that Afloat today tracked several of the C-class cargoships located to ports in north-west Europe, the Baltic Sea and trading in the western Mediterranean.
Irish Lights Look to Future Replacement of Aids to Navigation Vessel ILV Granuaile
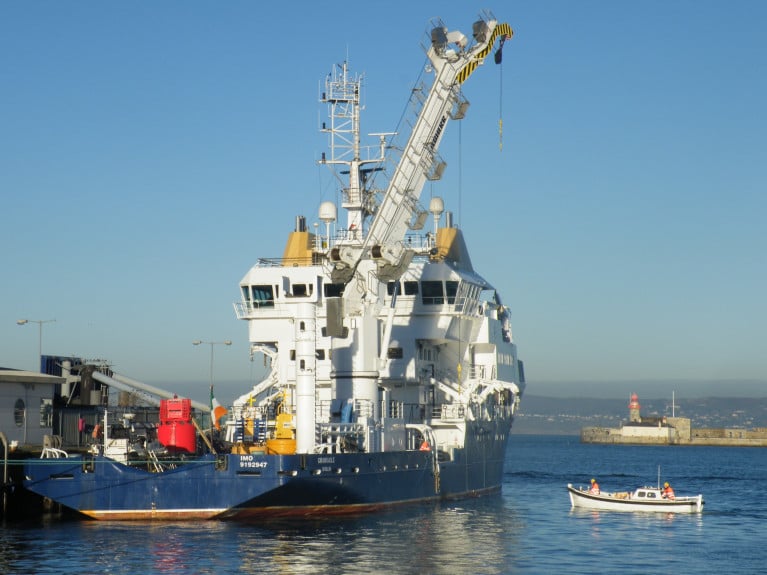
The Commissioners of Irish Lights, the General Lighthouse Authority (GLA) responsible for aids to navigation in waters off Ireland, operates the buoy-laying vessel ILV Granuaile which this year entered its 23rd year in service, writes Jehan Ashmore.
For more than two decades ILV Granuaile has served in its primary function to place and service the 150 offshore buoys of Ireland's long and rugged coastline notablyalong the western seaboard. The bouys warn mariners of the location of sand banks, reefs and other offshore hazards near shipping routes, essential to an island nation given our economic trade is highly dependent on maritime routes connecting Europe and beyond.
ILV Granuaile began service in January 2000, a newbuild that was then one of the most advanced vessels of its type in the world. The newbuild's design, saw buoy operations radically shifted away from the traditional located forward work deck area near the bow to that of the aft-deck.
When ILV Granuaile made its debut in the first month of the millenium, this marked a notable prototype for Irish Lights and would lead to GLA counterparts in England, Wales, Channel Island & Gibraltar (Trinity House) and for Scotland & the Isle of Man (Northern Lighthouse Board) to follow suit with similar vessels. This led to the commissioning of THV Galatea and NLV Pharos respectively.
In addition, ILV Granuaile also formed a prototype for Relume, that initially served the Middle East Navigation Aids Service (MENAS) and in which during last summer, the vessel carried out survey work off the Irish east coast for a windfarm project.
Plans are in place to replace two buoy-laying vessels in the coming years, as Afloat previously reported, Trinity House's ageing THV Patricia (built 1982) and the Northern Lighthouse Board's NLV Pole Star (built 2000). In the same year ILV Granuaile was delivered to Irish Lights, having been built in a Romanian shipyard and with outfitting carried out in the Netherlands.
Irish Lights Statement on replacing ILV Granuaile
Afloat contacted Irish Lights in regards to the operational life-span of the aids to navigation vessel with CIL responding below on the possible future replacement of the vessel.
The Commissioners of Irish Lights is a maritime organisation delivering an essential safety service around the coast of Ireland, protecting the marine environment, and supporting the marine industry and coastal communities. We provide maritime aids to navigation services to meet the State’s legal obligation under SOLAS Chapter V, Regulation 13 and we enhance safety of navigation for all seafarers, including the merchant fleet, the fishing sector and the leisure sector.
In delivering our services we rely substantially on the capability of our buoy tender vessel, the ILV Granuaile; the third Irish Lights vessel to bear the name Granuaile. Built in 2000, the current Granuaile is extremely maneuverable as a Class 1 DP vessel and capable of a wide variety of mission profiles including maintenance of aids to navigation, wreck response and reacting to new dangers to navigation, Search and Rescue/Recovery and response to oil pollution. (See related pollution recovery exercise, as featured in 'Maritime Dalkey' DCC Newsletter, Feb.2015 p. 11 and 13).
Irish Lights operates in close cooperation and mutual support with our sister GLA, Trinity House and the Northern Lighthouse Board. In total, the three GLAs operate seven vessels, of which two vessels THV Patricia and NLV Pole Star (have both Afloat adds shared duties in Irish waters) are approaching end-of-service life and will be replaced in the coming years.
ILV Granuaile has benefitted from all required upgrades and maintenance during her service life, including new bridge navigation and control equipment suite, enhanced sonar capability and upgrades to all critical systems onboard. This has allowed the ship to exceed the requirements for certification by Lloyds and the Flag State. Therefore, it is expected that the ship will continue to operate successfully well into the latter part of this decade.
However, like all vessels she will eventually require replacement and Irish Lights has included this requirement in our strategic planning considerations for the period out to 2030.
It is expected that Irish Lights will benefit greatly from the lessons learned by our sister organisations in Scotland and England in terms of fuel choice and energy efficiency of any new vessel design.
For the moment, we will continue to successfully operate the ILV Granuaile providing maritime services to the State and our user groups, while we begin to work on planning for her eventual replacement in the medium to long term.
Charter Role
The versatile design of ILV Granuaile also makes her ideal for commercial hire, which allows Irish Lights to use any reserve capacity of the vessel to reduce the cost of provision of aids to navigation to the State.
Construction of New Isle of Man Ferry is On Schedule
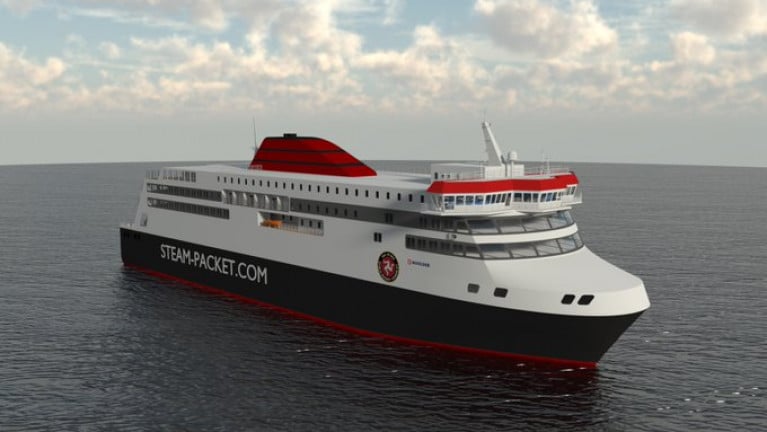
Work on the new Isle of Man Steam Packet Company's flagship ferry, Manxman, is on schedule.
As previously reported on Afloat, the vessel is under construction in a South Korean shipyard and is due to be ready by 2023.
Managing Director Brian Thomson says images of the ferry in its current state will soon be made available.
ManxRadio also has a podcast with the M.D. discussing further details on the newbuild which is to replace Ben-My-Chree on the Douglas-Heysham route.
Scotland & Isle of Man: Northern Lighthouse Board to Replace Aids to Navigation Tender NLV Pole Star
The General Lighthouse Authority (GLA) for Scotland and the Isle of Man, the Northern Lighthouse Board (NLB) has embarked on a project to replace the NLV Pole Star after more than two decades in service.
NLV Pole Star is nearing an end of a career with a newbuild target in-service date of September 2024. This will see the replacement aids to navigation tender meet the ambitious environmental targets set out in the UK Government Clean Maritime Plan, whilst future-proofing NLB’s ability to deliver its vital safety services over the next 25 years.
The new vessel will incorporate contemporary green hybrid energy systems and will be designed to be upgradeable through-life to accommodate emerging power technologies. The vessel will also provide improved sea keeping and heavy weather performance over its predecessor and therefore be able to deliver more effective response to wrecks and new navigational dangers as well as routine operational tasking.
A concept design has been developed in collaboration with OSK-ShipTech of Copenhagen who assisted the project team, which includes ship and shore staff, NLB Commissioners and Caledonian Maritime Assets Ltd (CMAL). This concept design and detailed specification is being used to inform both the business case and procurement exercise.
Mike Bullock, NLB’s Chief Executive said: “This is a very exciting project and we are delighted to have recently received Ministerial and Cabinet Office approval of the Outline Business Case (OBC). This means we can now progress to the procurement phase for the design and build of the new vessel.
“The new vessel will be a step change from what has gone before bringing innovation and new technology to minimise the impact on the environment and ensure that we can continue to protect mariners operating in Scottish and Manx waters. The vessel will also follow a tradition which started in 1892 by being the fifth NLB vessel to bear the name Pole Star.”
The procurement exercise began on 19 May 2021 with the publication of the initial call for interested shipyard builders to respond to a Selection Questionnaire. Subsequently, short listed yards will enter into a detailed tendering exercise which will lead to contract award in mid-2022.
In April, information from NLB’s Industry Engagement events was held and can be found on the NLB website and via the following Industry Event portal here.
This opportunity has been published on Delta eSourcing which is a tool for buyers and suppliers for managing tenders. Interested tenderers must register on the Delta Platform to access key documents and to take part in this procurement activity, click this link.
'Arrow' Brings to Five Arklow Newbuild Bulkers With One More to Follow Suit
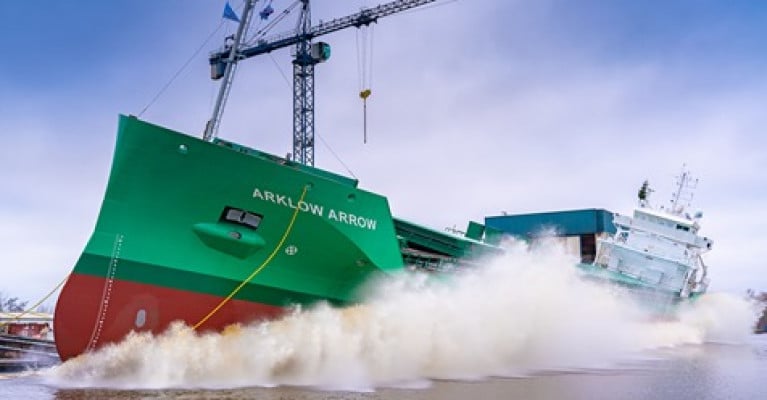
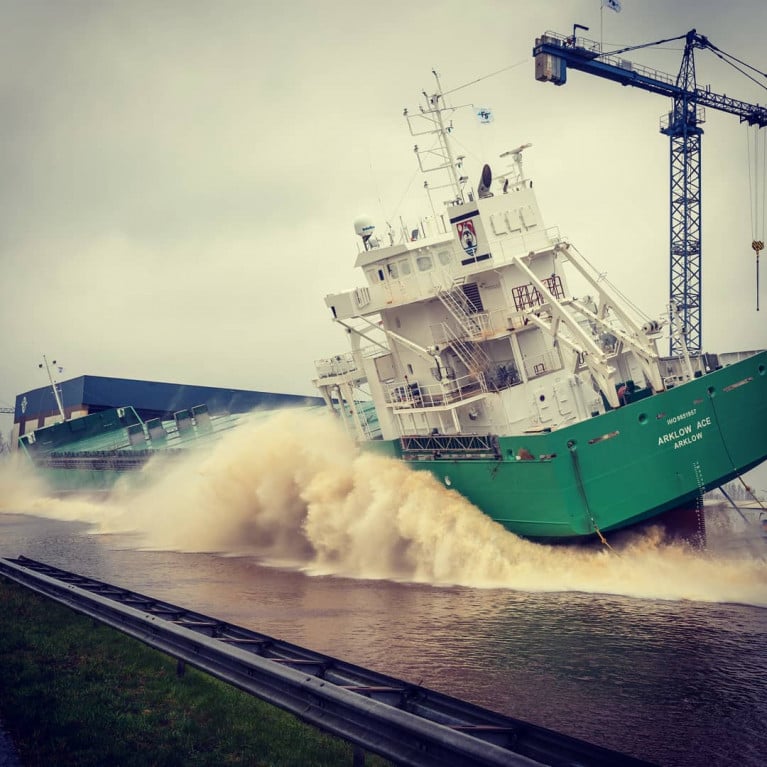
A new bulk oriented general cargoship for Arklow Shipping took to the water for the first time yesterday as the fifth of six ships was launched by shipbuilder Ferus Smit, writes Jehan Ashmore.
The 8,543dwt newbuild (NB.441) bulker was christened in The Netherlands as Arklow Arrow and launched onto the Ems Canal, however due to Covid-19 restrictions the inland shipyard was not open to public.
Ferus Smit is a German shipbuilder that has a second yard located in Westerbroek from where the Arklow A- series 'Arrow' became the first ship to use this name in the ASL fleet.
Arklow Arrow's design is a slightly modified version of the first series of 8,600dwt bulkers of the Arklow B-series also completed by Ferus Smit.
The new design also has an adapted ice class 1A along with a modified bow form and propulsion with a propeller nozzle added. As for the main engine, output has been decreased to 2000kW so to enbable better fuel efficiency.
Following sea trials that will take place in the North Sea, see Arklow Archer' canal transit (following launch in June) the Arrow will join the other A-series ships; Ace, Accord and Abbey which was delivered last year as the leadship.
Likewise of this series the new cargoship is registered at its shipowners Co. Wicklow homeport and will fly the Irish tricolor.
Total hold capacity is 350.000cft and this will see Arklow Arrow be mainly employed in the shipment of corn, wheat and other bulk commodities in European waters.
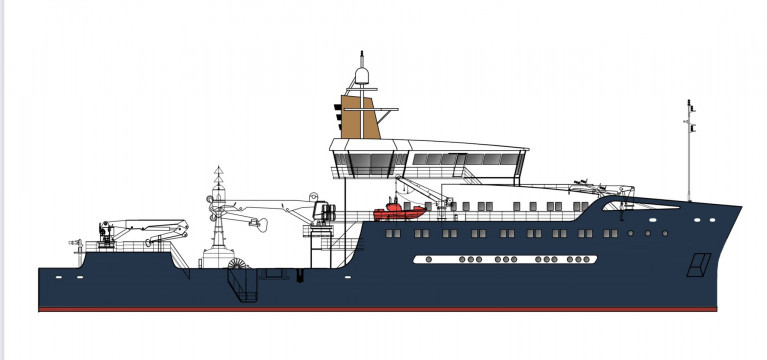
New Multi-Role Vessel (MRV) for Naval Service As Department of Defence Targets €200m
The intention to purchase a new Multi Role Vessel (MRV) for the Naval Service has been confirmed by the Department of Defence.
This could see the vessel be used as a hospital ship and capable of carrying troops and helicopters for amphibious in addition airborne landings.
A spokeswoman for the department said planning is "underway on this project".
It is envisaged that the MRV (as Afloat reported in 2018) will replace the ageing LÉ Eithne as the Naval Service flagship, and could cost up to €200m.
The new ship is likely to be designed to allow it the capability to carry out numerous different types of missions, not just sea fishery patrols.
Military sources have indicated that it could be used to provide humanitarian aid in times of emergency in Ireland and in other countries where conflicts or climate disaster threaten civilian populations.
It could also be used by gardaí, customs, or the coastguard, where required.
The MRV project is being managed by a civil-military project team and work is ongoing on preparing detailed specification requirements for the ship.
For further reading the Irish Examiner reports.
Ferry operator Aran Island Ferries has announced it’s on track to make history this summer – by commissioning Ireland’s largest domestic ferry.
The boat, reports GalwayBayFM, will be a 40 metre vessel with space for 400 passengers, which represents a significant boost in capacity over it’s current largest boats, Music of the Sea and Magic of the Sea.
The new vessel will be the sixth boat in the Aran Island Ferries fleet – though full details or a name for the vessel have yet to be revealed.
Afloat.ie adds as for the names of the larger ferries this is in fact their English translation. The names of these vessels are in Irish, Ceol na Farraige (built 2001) and Draíocht na Farraige (1999) respectively.
Each of the 37m Wavemaster monohull craft can carry 294 passengers.
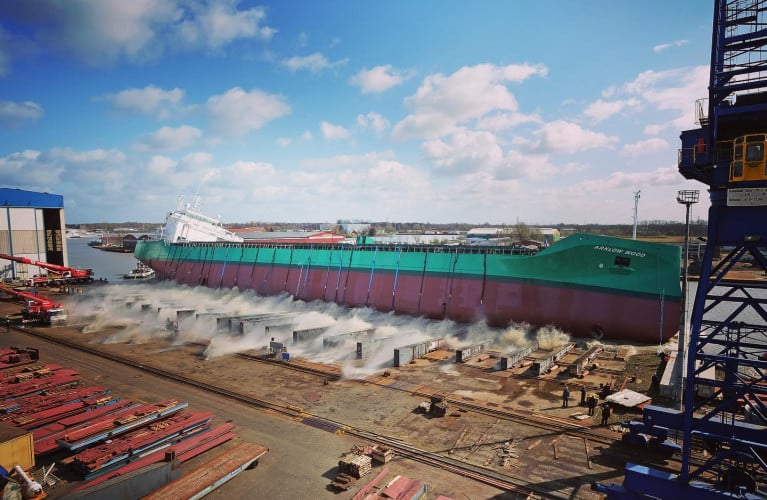
The fourth and final 'W' series of newbuilds for Arklow Shipping was launched earlier this month, writes Jehan Ashmore.
Arklow Wood was successfully launched at the Ferus Smit's shipyard in Leer, Germany.
As Afloat reported a previous sister Arklow Willow was launched last year though the 'Wind' is the first to be used in the owners naming scheme for this series.
The Arklow Wood took to the waters on 3rd April and will fly the Irish flag. As for design the cargoship is an enlarged version of the 8500dwt ships that the shipyard delivered to Arklow Shipping in the past. The cargoship in comparison with these predecessors has almost twice the carrying capacity of 16,500dwt.
As for propulsion the newbuild is equipped with a 3840kW main engine in order to achieve low fuel consumption.
The design features:
– Main dimensions (Loa X B X T) 149.50 X 19.25 X 8.59 mtr.
– 16500 DWT, 700.000 cft hold volume.
– Iceclass 1A with 3840kW main engine.
– 2 box shaped holds.
– Propeller equipped with a duct for enhanced thrust at lower speeds and reduction of maximum installed propulsion power.
A previous 'W' series of a different design and all since disposed had been the first newbuilds for ASL to be ordered from a shipyard outside Europe, having been built in South Korea. This series however only totalled a trio and all using the same ship names now applied to the new series comprising of leadship Arklow Wave, Wind and Willow.
Another recent newbuild, Arklow Ace launched last month and belonging to the 'A' series was also built by the same German group but at their Ferus Smit yard at Westerbroek, The Netherlands. The newbuild has recently left the inland yard under the Irish flag.
The fleet of ASL including its Dutch division totals almost 60 dry-cargo vessels among them deep-sea bulk-carriers.
The latest and third newbuild of the Arklow 'A' class series which is a bulk orientated general cargoship was launched at a Dutch yard, writes Jehan Ashmore.
Arklow Ace (Nb.439) took to the water for the first time as the third of six such ships so far from the Ferus Smit yard at Westerbroek on Friday.
Arklow Ace was christened for owners Arklow Shipping and at the stern the Co. Wicklow town is given as the port of registry. When the newbuild enters service this Irish flagged vessel will expand the fleet to 57 dry-cargo ships including 17 that are Dutch flagged.
Not only is Arklow Ace a new ship but is a first for ASL having this particular 'A' name suffix along with the previously completed sister, Arklow Accord (launched in November). The first of the series, leadship Arklow Abbey (in July) is an exception as the same name was previously used in a vessel dating to 1981 and sold in 1996.
The design of the A series is a slightly modified version of the first series of the 8600dwt bulkers that Ferus Smit built under the name of the Arklow B series.
A modified bow form and hull is adapted for Iceclass 1A conditions. As for propulsion this sees a propeller nozzle added while the main engine output was decreased to 2000 kW for better fuel efficiency.
This ship has the following characteristics:
– Loa = 119.495 mtr
– Lpp = 116.895 mtr
– B = 14.99 mtr
– D = 9.70 mtr
– T max = 7.160 mtr
– Hold volume = 350.000 cft
When Arklow Ace is delivered into service, the newbuild will be primary employed in typical shipments such as wheat, corn and other bulk commodities throughout European waters.