Displaying items by tag: Rio 2016
Former 'Queen Of The Breeze' Now Queen Of The Skies As Airline Names Jet After Annalise Murphy
#AnnaliseMurphy - Olympic silver medallist Annalise Murphy has had a passenger jet named after her by an Irish airline, as Dublin Live reports.
But it's not just any aircraft, as its airline's chief pilot is her own father Con Murphy of the National Yacht Club.
A name well known to Afloat readers for his own sailing exploits, Con flies Boeing 757's for ASL Airlines Ireland, which operates both cargo and charter passenger flights.
But it's one of the airline's Boeing 737s plying the charter holiday trade between Ireland and European destinations that's now been rechristened 'Annalise Murphy'.
The touching tribute to Con's medal-winning daughter, who made the Laser Radial podium in Rio after narrowly missing out on bronze in London four years ago, was unveiled earlier this week.
Con was in Rio alongside his daughter earlier this month, but was unable to watch her medal-winning performance as he was fulfilling his own duties as a race official on another sailing course at the time.
Dublin Live has much more in the story HERE.
#Rio2016 - The mother of Irish Laser Olympian Finn Lynch nearly missed seeing him in Rio after failing to secure tickets through the official Irish supplier that's become embroiled in controversy in recent days.
The Irish Times reports on Grainne Adams' interview with Newstalk Breakfast, in which she explained how after great difficulty in contacting Pro10 Sports Management in the run-up to the event, she resorted to a Norwegian ticket resale website in order to attend the opening ceremony earlier this month.
Adams also said that despite the special ticket scheme for friends and family of Olympic athletes, Pro10 told her they did not have tickets for any events in the Olympic sailing regatta, in which Lynch finished a respectable 32nd as he preps for a stronger challenge in Tokyo in four years' time.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, an allocation of unused official tickets for athletes' families and friends was seized from the Olympic Council of Ireland's (OCI) offices at the Olympic Village in the ongoing Brazilian police investigation into alleged ticket touting.
OCI president Pat Hickey was arrested in his hotel last week on a number of charges related to the illicit resale of Olympic tickets, while other OCI members have have their passports, phones and computers seized pending questioning.
Hickey is reportedly sharing a cell in Rio's Bangu Prison with THG Sports director Kevin Mallon, who was arrested on Friday 5 August in possession of hundreds of tickets for high-profile Olympic events.
#Rio2016 - Government ministers have joined in the applause for Annalise Murphy's stunning silver medal win in the Laser Radial at Rio 2016 yesterday (Tuesday 16 August).
Soaking after the race, Minister for Transport, Tourism and Sport Shane Ross said: “I am delighted for Annalise, we all know how determined she was to bring home a medal, after coming so close four years ago this is a fantastic achievement for her.
"Bouncing back from the disappointment of finishing fourth in London 2012 to become European Champion in 2013 to now achieving a silver medal at the Olympics is a wonderful endorsement for what can be achieved through hard work and talent. She has been so determined and she is a fantastic role model for all young athletes.”
Minister of State for Tourism and Sport Patrick O’Donovan added: “Annalise has worked so hard not just for the last week but for the last four years, to overcome the frustration of 2012 and win an Olympic silver medal at Rio is no more than she deserves.
"To become the first Irish female to win an Olympic medal in sailing and Ireland’s first medal in sailing since 1980 is magnificent for Annalise, Team Ireland and the country.
"It was great to hear her brother was able to be there to support her during this achievement. Her family and the sailing club in Dun Laoghaire I’m sure are immensely proud to see her on that podium.
"It has been a great few days on the water for Team Ireland and hopefully there will be many more successes to come.”
#Rio2016 - Annalise Murphy made Irish sailing history this afternoon as she sailed to Olympic silver in Rio de Janerio in the Laser Radial medal race.
Murphy's first Olympic medal, coming after narrowly missing out on bronze at London 2012, is also Irish sailing's first medal triumph at the Olympic Games since 1980.
It all came down to the final push, with Murphy scorching past Denmark's Anne-Marie Rindom into second place behind gold medallist Marit Bouwmeester of the Netherlands.
Expect jubilant scenes in Dun Laoghaire Harbour where her home club the National YC showed the race live on a big screen at the clubhouse platform. Well done Annalise!
 Marit Bouwmeester (NED) won the gold medal (centre) that eluded her four years ago. Silver went to Annalise Murphy (IRL) (left), a sweet reward after finishing an agonising fourth place at London 2012. Anne-Marie Rindom (DEN) took bronze. Photo: Richard Langdon
Marit Bouwmeester (NED) won the gold medal (centre) that eluded her four years ago. Silver went to Annalise Murphy (IRL) (left), a sweet reward after finishing an agonising fourth place at London 2012. Anne-Marie Rindom (DEN) took bronze. Photo: Richard Langdon
Marit Bouwmeester (NED) won the gold medal that eluded her four years ago. Silver went to Annalise Murphy (IRL), a sweet reward after finishing an agonising fourth place at London 2012. Anne-Marie Rindom (DEN) took bronze.
It was a tense Medal Race in light and fluky airs on the Pão de Açucar course in the shadow of Sugarloaf Mountain. Bouwmeester looked to be in a good position during the early stages, but a big split developed in the fleet after the top of the final lap, and the Dutch and Danish contenders were dropped to the back. They could only watch as Murphy and the other front runners sailed away and across the finish line more than a hundred metres ahead.
 Annalise's mum Cathy MacAleavey holding tricolour and her brother Finn (wearing Shamrock tie) celebrate Ireland's historic win
Annalise's mum Cathy MacAleavey holding tricolour and her brother Finn (wearing Shamrock tie) celebrate Ireland's historic win
It was so close between the front five boats on the final run, there was a chance the Irish sailor could steal gold from the Netherlands. But Murphy crossed the line in fifth, yielding the Olympic title to Bouwmeester. With Rindom back in eighth, Murphy had done enough to take silver.
All three sailors celebrated and every one of them looked delighted to have emerged with a medal from perhaps the toughest sailing venue ever seen at an Olympic Games. Bouwmeester now has the gold to go with the silver she took in London 2012.
Murphy Goes For Gold As Medal Racing Resumes In Rio
#Rio2016 - After yesterday's postponement of Annalise Murphy's Laser Radial medal race, this evening all Irish eyes will focus once again on the near-shore Pao de Azucar course – literal translation 'bread of sugar', better known as Sugarloaf, and so called because of its proximity to the iconic mountain that overlooks the natural harbour of Rio De Janeiro.
Using a two-round windward/leeward course with a leeward gate and final reach, race officers will target a 25-minute duration, half the scheduled time of races in the preliminary round.
Today’s forecast on this course is for light to moderate winds at the scheduled start time:
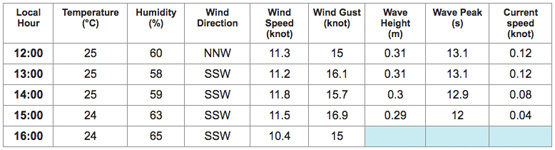
Laser
Finn Lynch’s Olympics finished with the final race in the preliminary series last Saturday, 32nd overall of the 46 competitors.
Rio was always going to be a dress rehearsal for the National Yacht Club sailor, whose real target is Tokyo in four years' time.
It’s not going to be an easy ride, however, as there is an emerging force of young Irish Laser sailors, inspired by Ireland’s recent performances, who will push hard for 2020 selection.
49er
The final three races of the qualification series are scheduled for today, and Irish duo Ryan Seaton and Matt McGovern will be looking to consolidate and hopefully advance towards medal positions prior to Thursday’s medal race.
Currently in fifth place, 12 points behind the Australians in the bronze medal position, the Ballyholme pair will need three good races to catch up.
The gold medal looks to be beyond the rest of the fleet as the ever-dominant New Zealanders Burling and Tuke look set to justify their pre-regatta favourites tag by securing the top honours before the medal race.
49erFx
Ireland's Andrea Brewster and Saskia Tidey will likely need three single-digit results today if they are to feature in Thursday’s medal race.
Lying 12th, but 21 points behind 10th place, the Royal Irish team have shown potential with a third and a couple of sixths in previous races.
The top of the fleet here is very close: only five point separate the top three, with hometown favourites Martina Grael and Kahena Kunze in the bronze position.
World Sailing Struggles With Presenting Rio Sailing Results
#Rio2016 - World Sailing continues to struggle with presenting the results of the Olympic Regatta.
The normally very efficient system that brings the World Cup results seems to have failed at a crucial moment.
The issue seems to be an inability to calculate the overall totals and sort them into leader order.
Interestingly, the workaround that World Sailing has put in place is to direct browsers to the official Rio results site.
Here, too, there are issues as this site does not show how discards figure in the overall total.
However, Afloat.ie has discerned that the World Sailing system seems to be operational again and can be accessed HERE.
Users are advised to save that link, as clicking on the other hyperlinks on this page may take you to the official Rio 2016 results site.
Protest decisions are also available through the same link. However, World Sailing fails to indicate which fleet the protest applies to, so there is a bit of guesswork involved in working out which event is affected by the protest.
Ireland Crews Wait As Weather Forces Rowing Cancellation
#Rowing: The Olympic rowing programme for today, Sunday, has been postponed. The strong crosswinds disrupted a number of races on Saturday and left the Serbian men's pair in the water after a capsize. Ireland single sculler Sanita Puspure had complained about the conditions, saying the boats would not be put out to train in such difficult waters. Two Ireland boats, the women’s lightweight double of Sinead Lynch and Claire Lambe and the men’s lightweight double of Paul and Gary O’Donovan were due to compete in their first race today, but must now wait.
#Rio2016 - World Sailing has provisionally confirmed six Russian sailors for the Olympic Games that kick off next Friday in Rio.
Following a conference call yesterday (Tuesday 26 July) with its board of directors in the wake of the damning McLaren report on doping in sport, the world governing body for sailing confirmed the eligibility of RS:X competitors Stefania Elfutina and Maksim Oberemko, 470 sailors Liudmila Dmitrieva, Alisa Kirilyuk and Denis Gribanov, and Laser helm Sergey Komissarov.
All six are currently in Rio preparing for the games.
Gribranov's sailing partner Pavel Sozykin was denied eligibility based on the findings of the McLaren report, but World Sailing has recommended that the Russian Olympic Committee will have the opportunity to nominate a last-minute replacement.
These provisional confirmations are subject to approval by the Court of Arbitration for Sport (CAS).
"The World Sailing board of cirectors carefully considered all relevant factors in making these determinations, including the guidance provided by the IOC, the results of the McLaren Investigation Report and our own rules and procedures," said Andy Hunt, World Sailing CEO.
"This is unprecedented territory for international sport as, collectively, we work to protect the integrity of sport and remain resolute in our commitment to eliminate doping. These efforts must be balanced with principles of fairness, due process and adherence to established rules.
"There is, however, no room in sailing for athletes who seek to gain an unfair advantage through the use of banned substances or who attempt to manipulate or subvert the anti-doping system. For World Sailing, there is no greater priority than protecting and preserving clean competition.”
The news comes after all but six Russian rowers were barred from the Rio games over the McLaren findings, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Anti-Microbe Suits No Match For Rio Pollution
#Rio2016 - Antimicrobial suits could be an answer to Rio 2016's pollution issues. But are they all they're cracked up to be?
Headlines have made much of the microbe-resistant properties of the new costumes designed for the US Olympic rowing team, as Ars Technica reports.
Comprising two layers, one to wick water from the skin and the other with an antimicrobial finish, the fabric is being talked up for its properties of protection against the water-borne pathogens in Guanabara Bay and the Rodrigo de Freitas lagoon – the latter where rowers will compete next month.
But the textile engineer behind the design says any such claims are "overblown".
Speaking to Vocativ, Mark Sunderland of Philadelphia University confirmed that the antimicrobial finish was an "afterthought" and comparable to athletic wear already on the high street.
Indeed, the primary benefit to rowers is the suit's seamless fit, covering less than half of the body – designed for comfort in high-performance conditions, not for health reasons.
Vocativ has more on the story HERE.
Slick Stains Boats In Rio Olympic Sailing Waters
#Rio2016 - Olympics organisers in Rio have a new headache alongside Zika concerns and rising crime – the city's sailing waters are turning boats brown.
After Chilean 49erFX squad Team Gumucio posted the above video to Facebook, further reports have emerged of sailors getting caught in an oil slick on Guanabara Bay.
"We've never seen anything like this. It was all over the place," Finnish sailor Camilla Cedercreutz told the Associated Press after the slick stained the white hull of her boat brown.
It appears sailors training in Rio's waters ahead of next month's Games now have to add industrial pollution to their list of issues with the Olympic aquatic venue on top of floating debris and high levels of pathogens.






































































