Displaying items by tag: Royal Cork YC
Royal Cork Dinghy Fest Day Two: Photo Gallery
Another day of big breeze for the centreboard classes competing at Royal Cork's DinghyFest 2017 that has attracted over 100 dinghies from foiling Moths to RS 200s, 400s as well as National 18s and 420s.
Photographer Bob Bateman was afloat in Cork Harbour to capture all the action
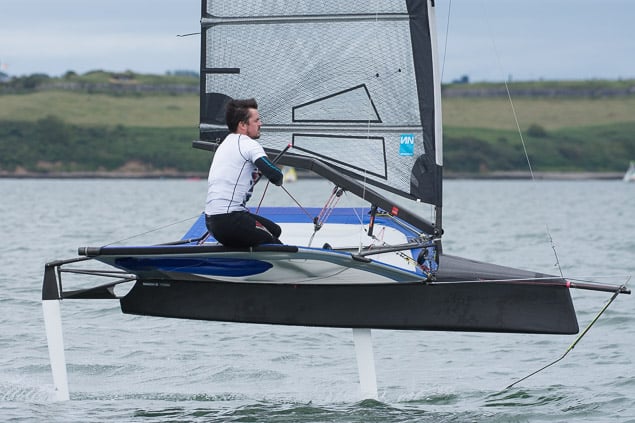
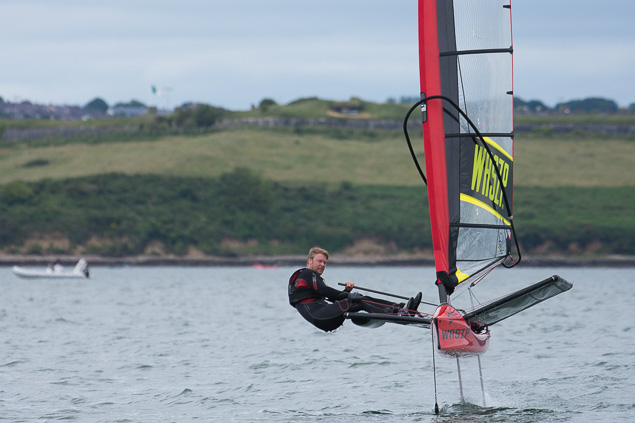
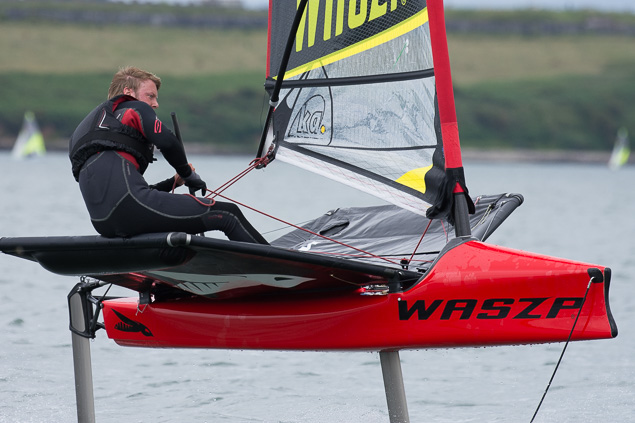
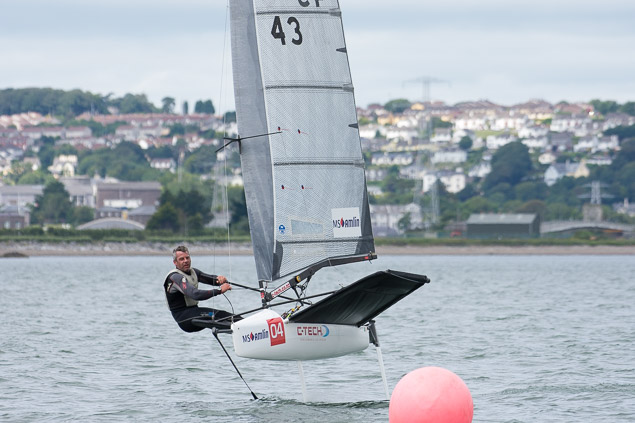
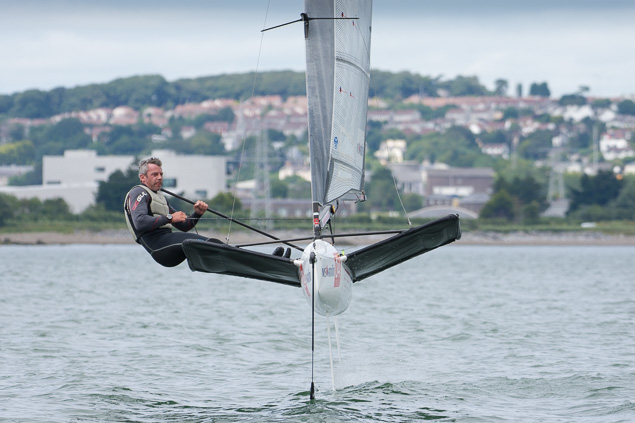
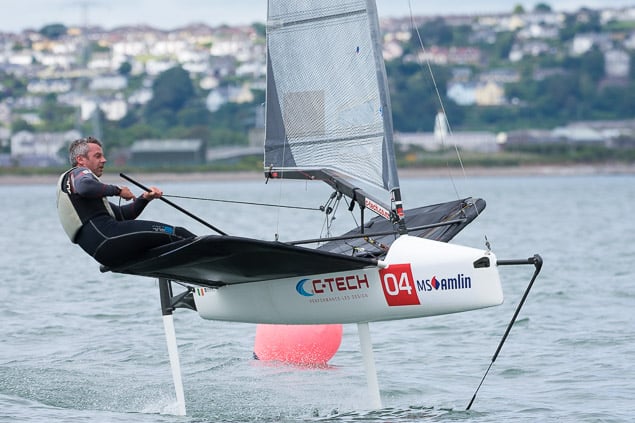
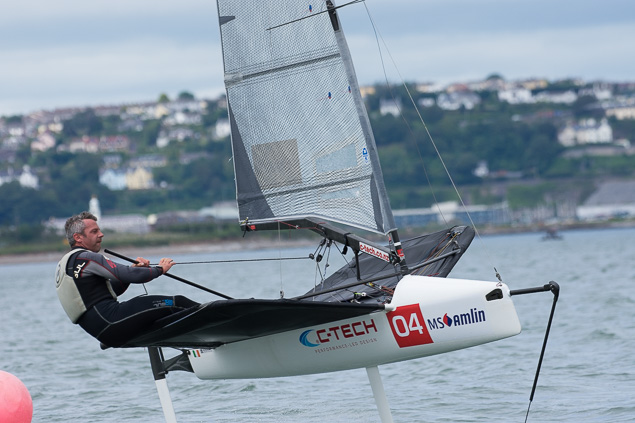
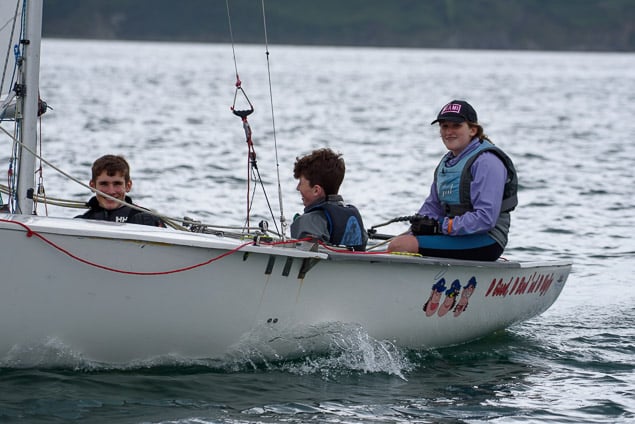
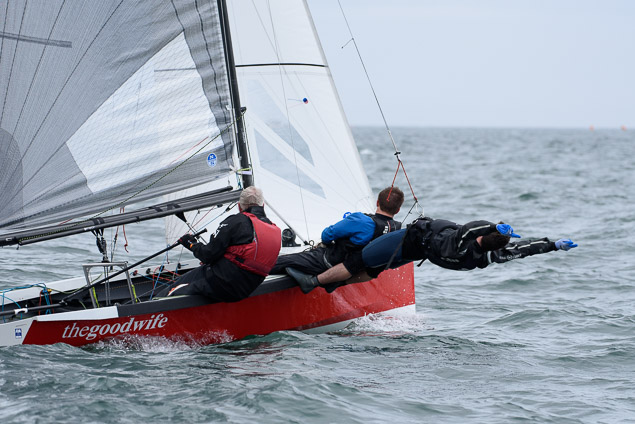
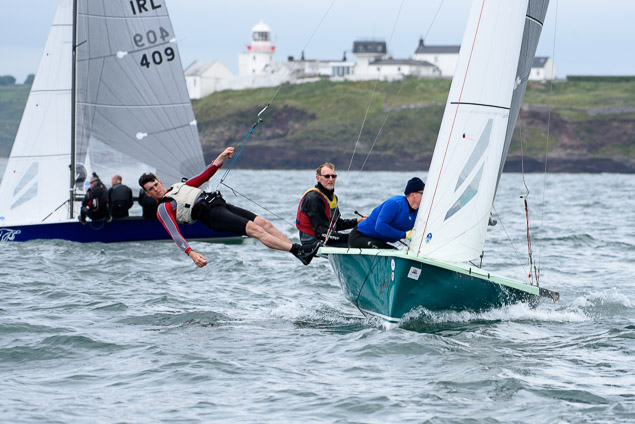
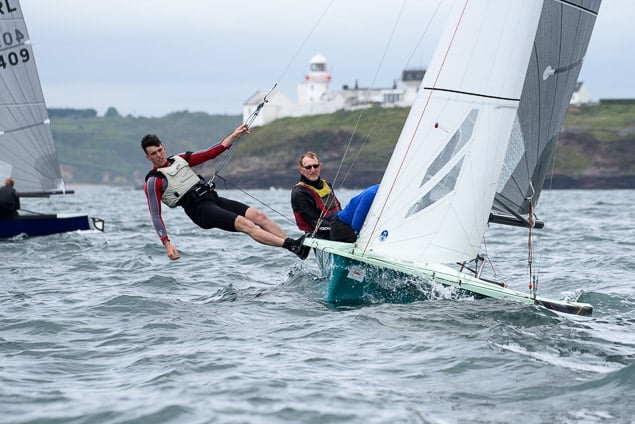
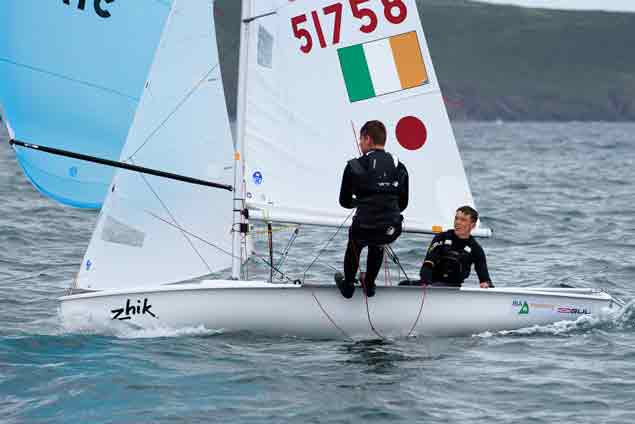
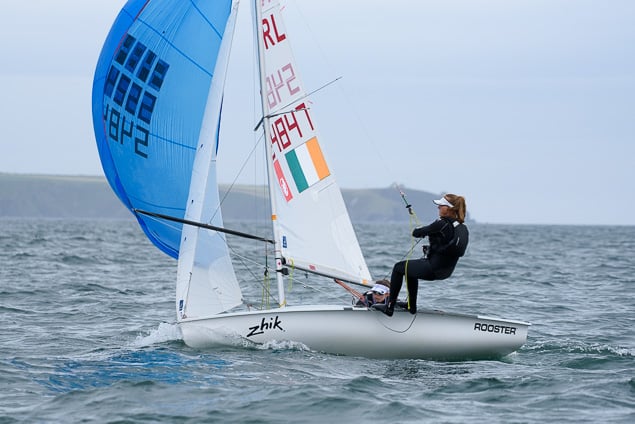
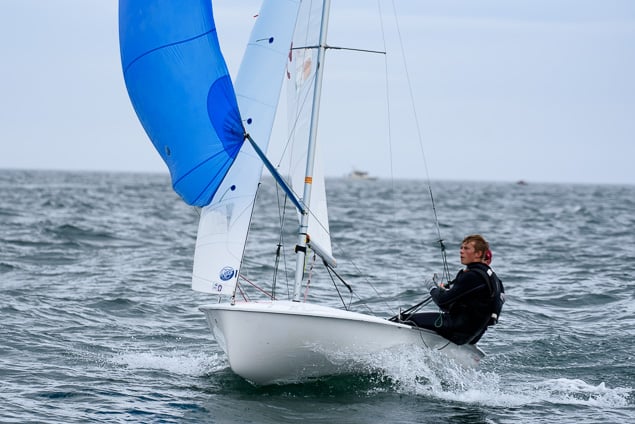
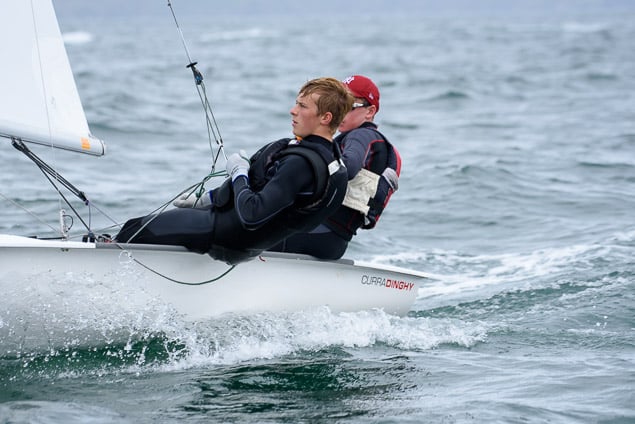
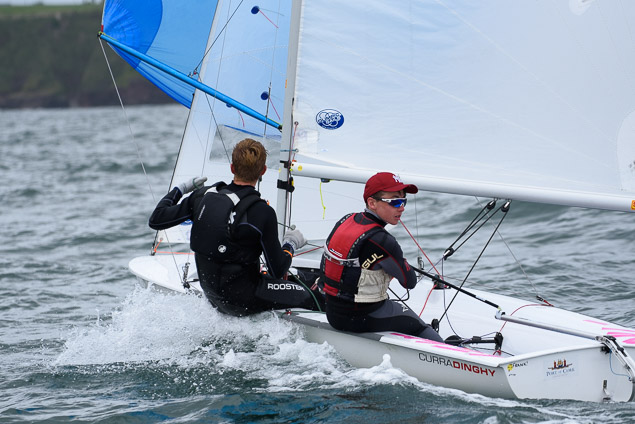
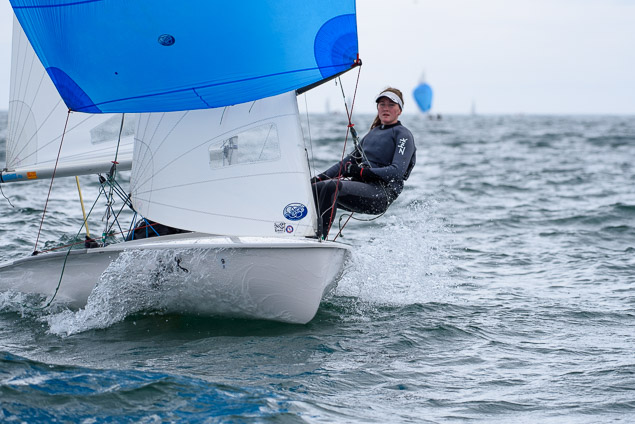
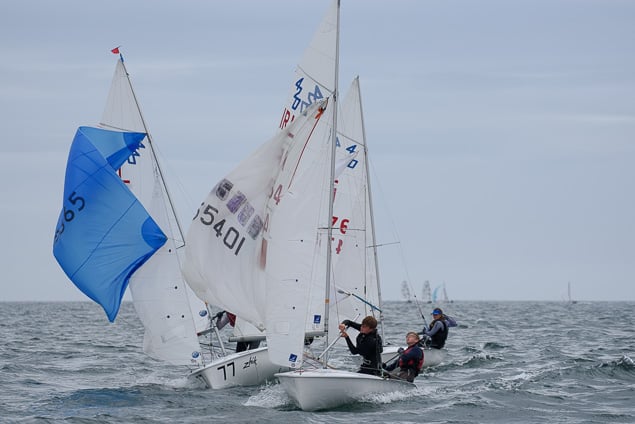
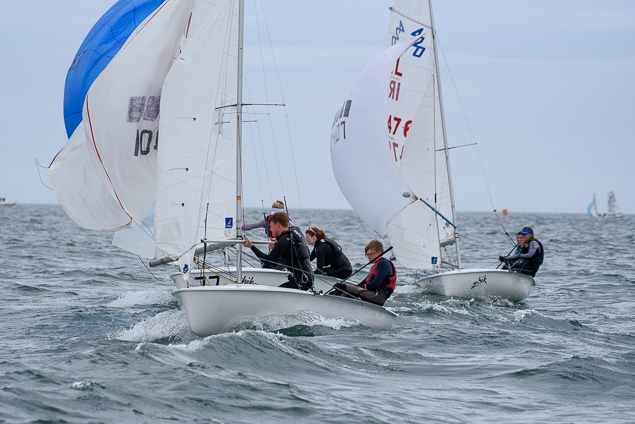
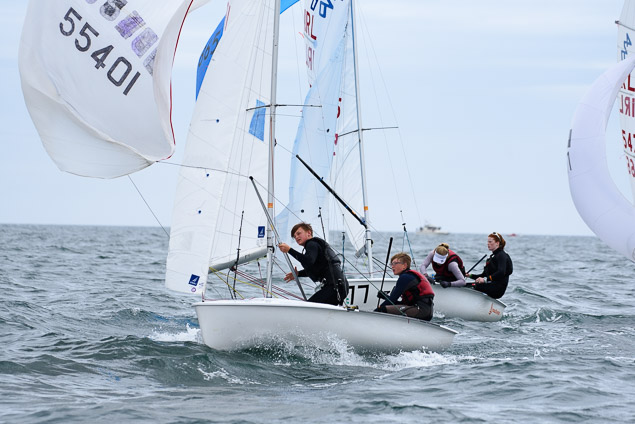
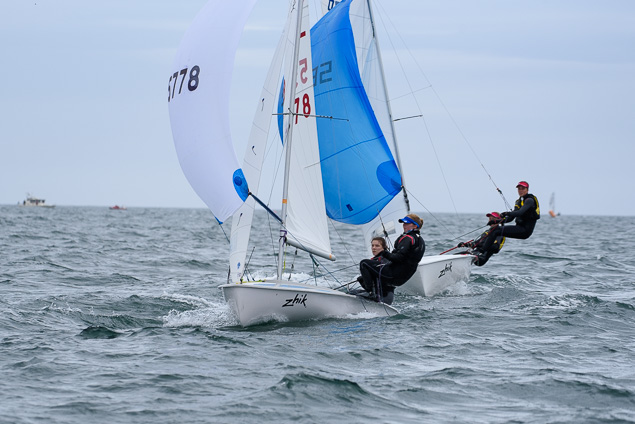
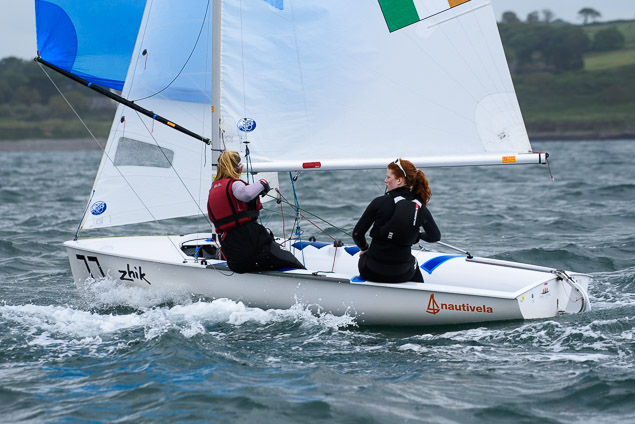
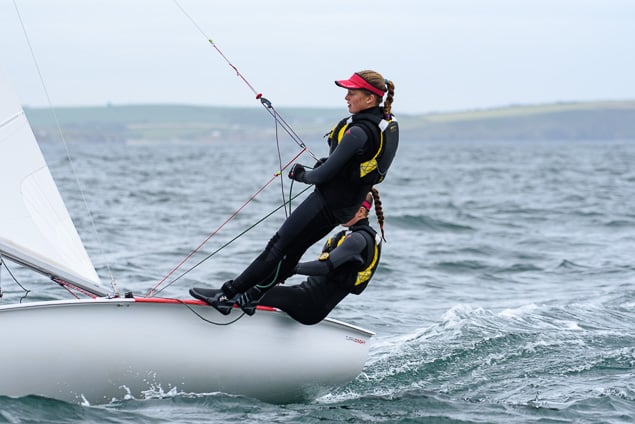
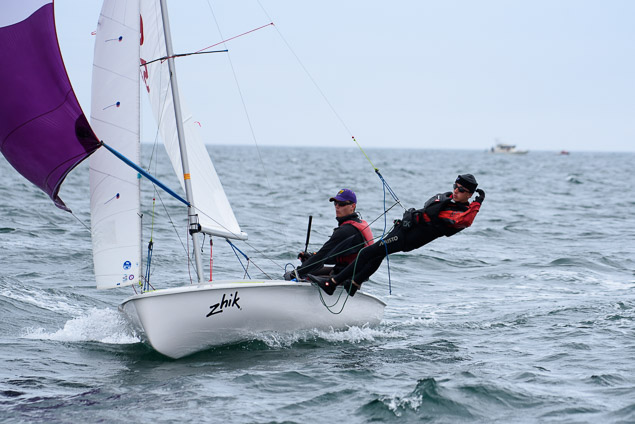
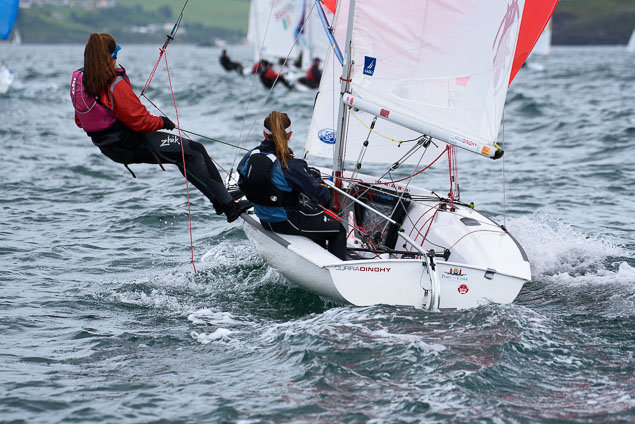
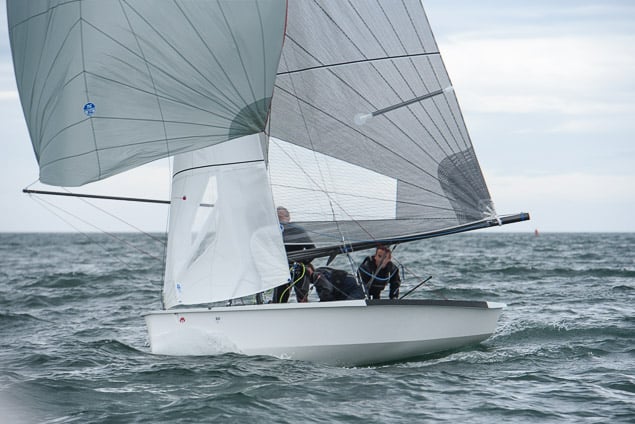
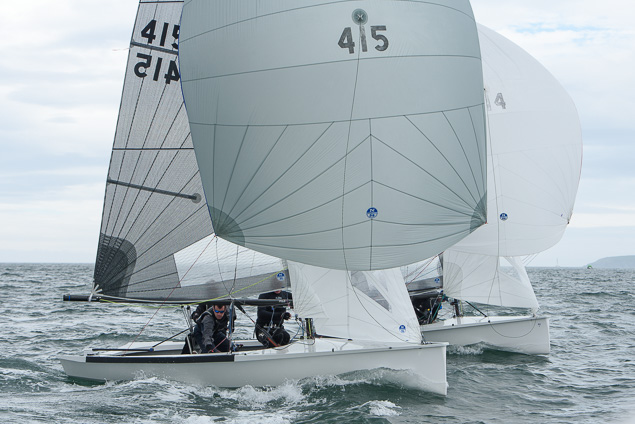
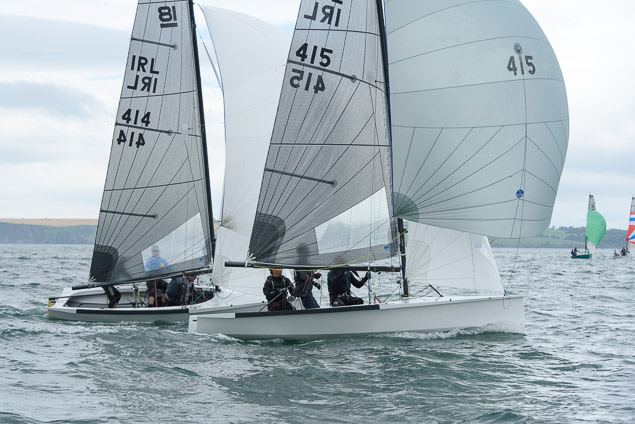
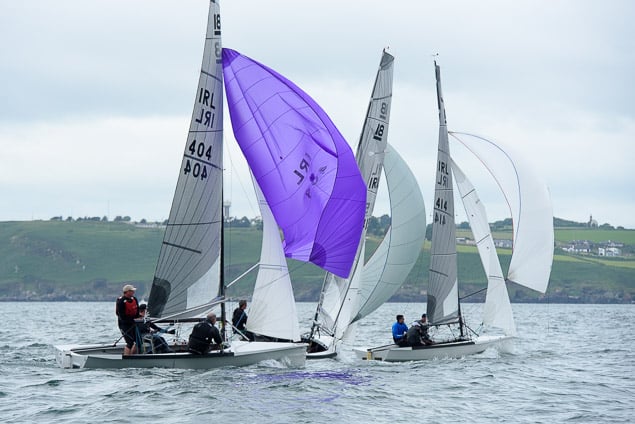
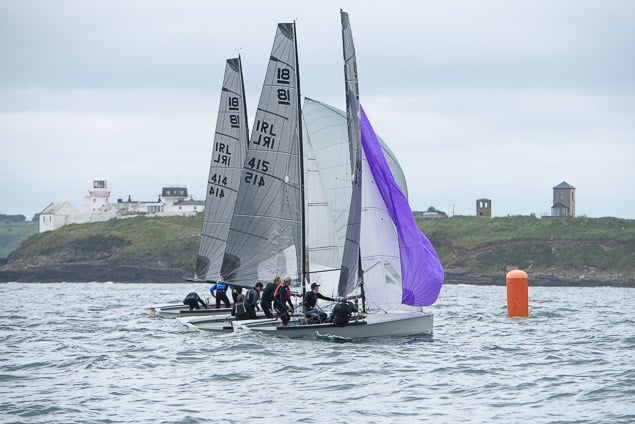
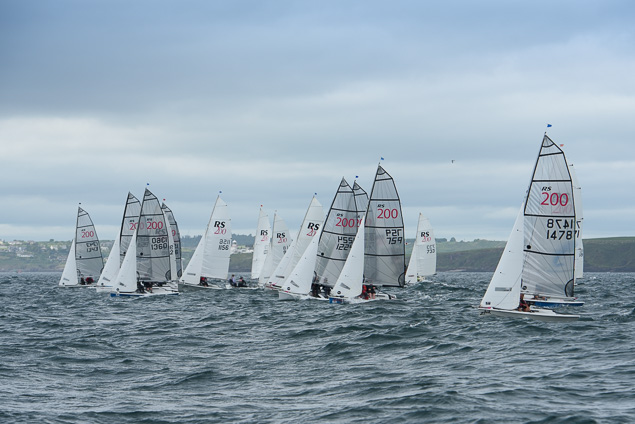
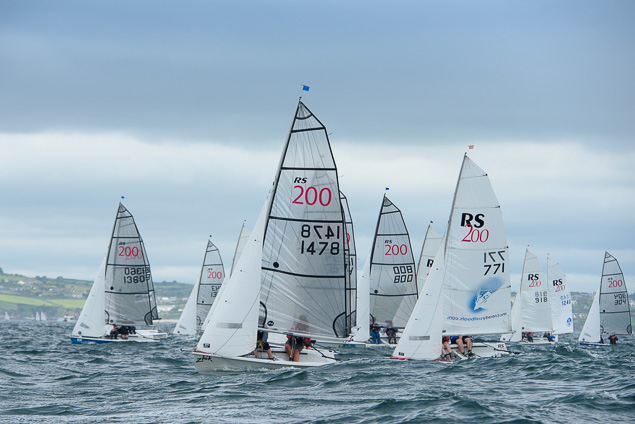
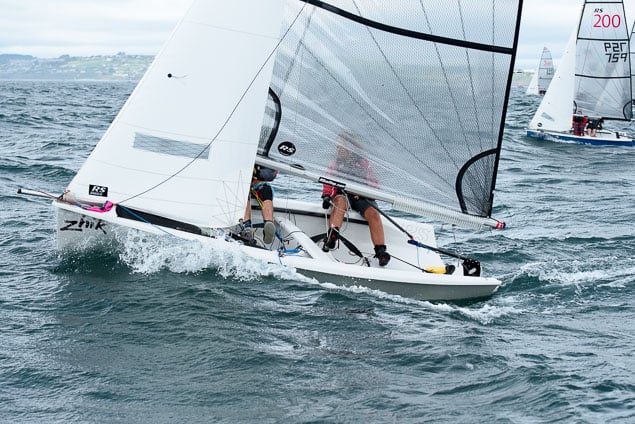
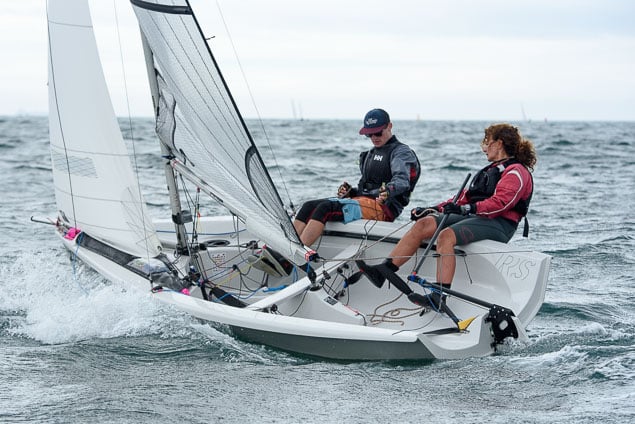
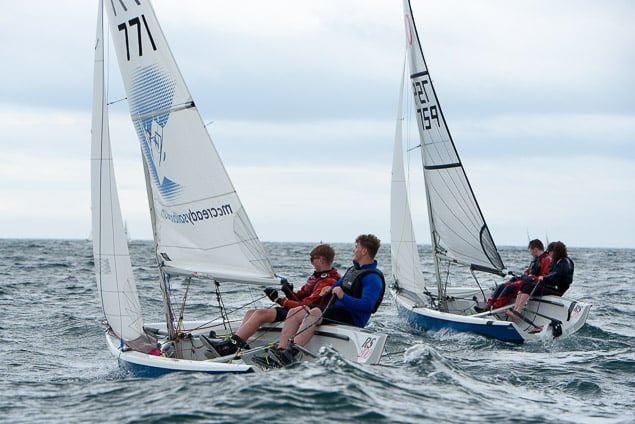
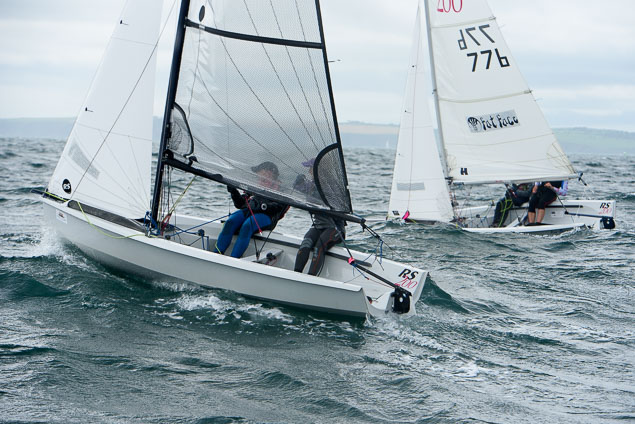
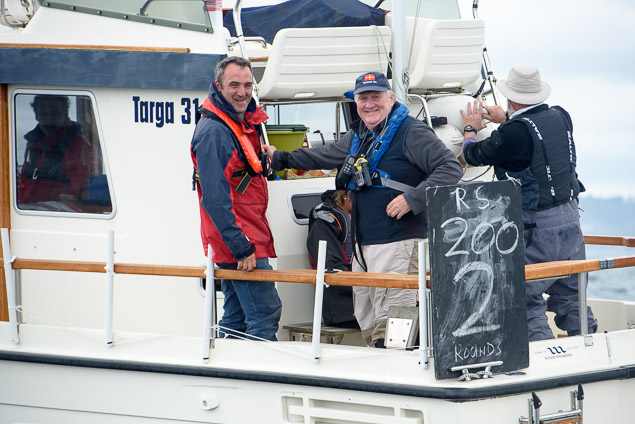
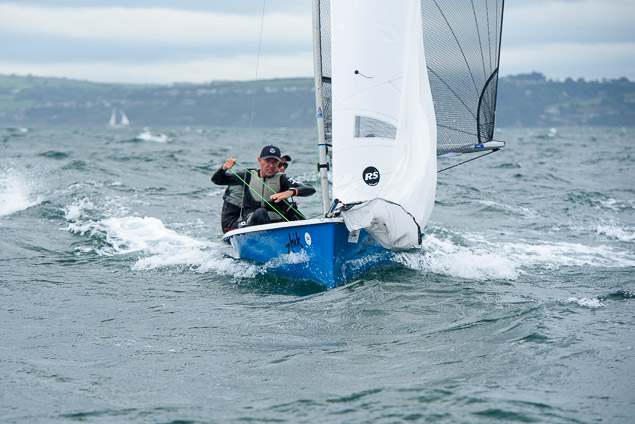
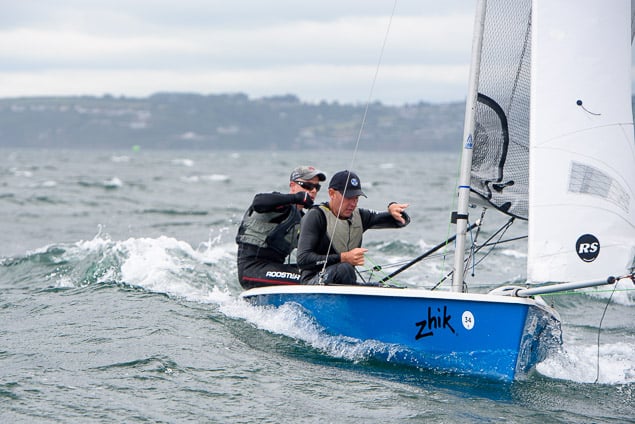
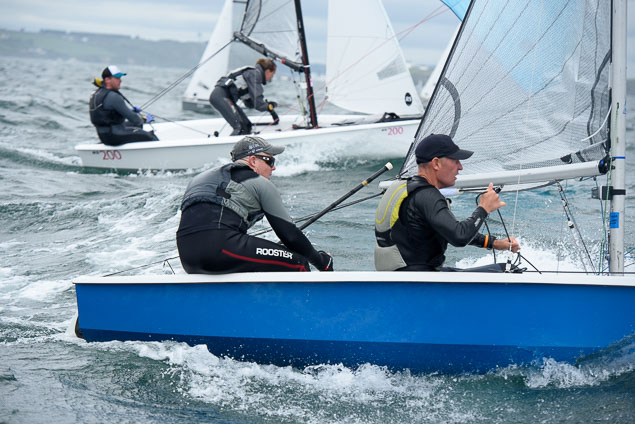
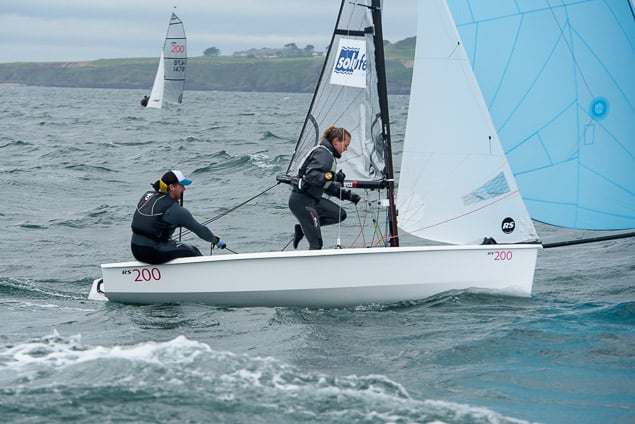
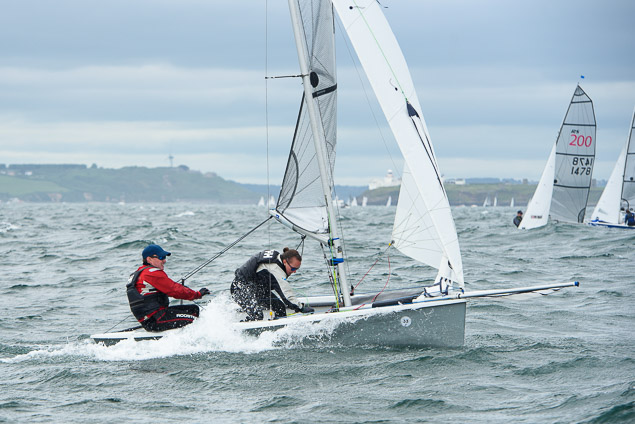
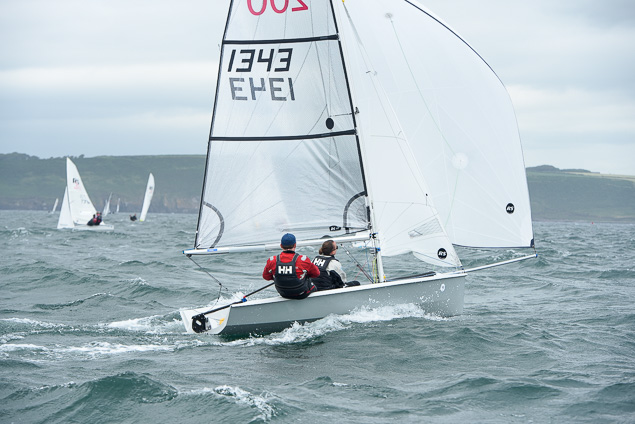
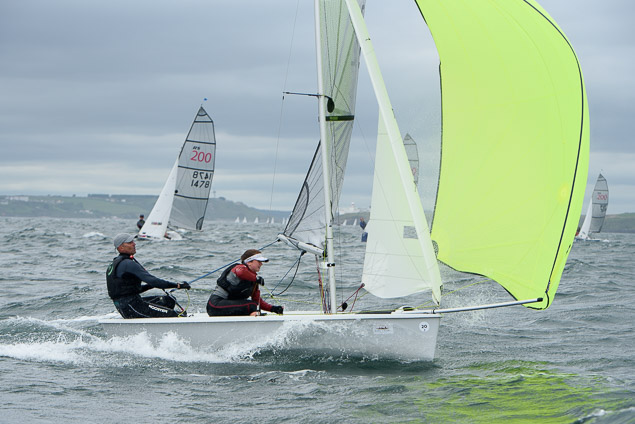
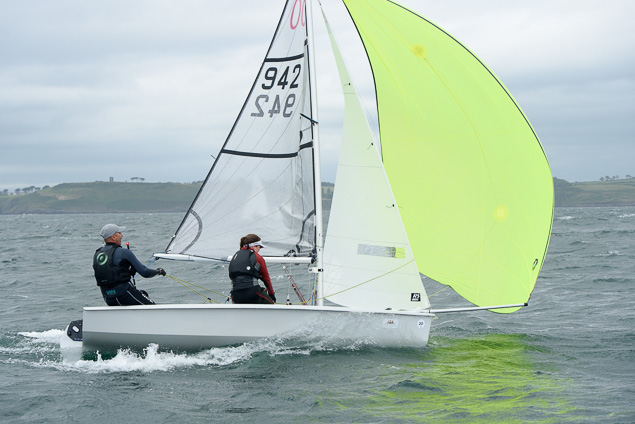
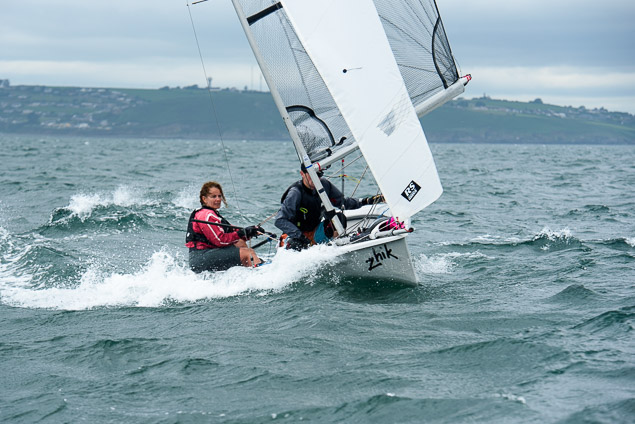
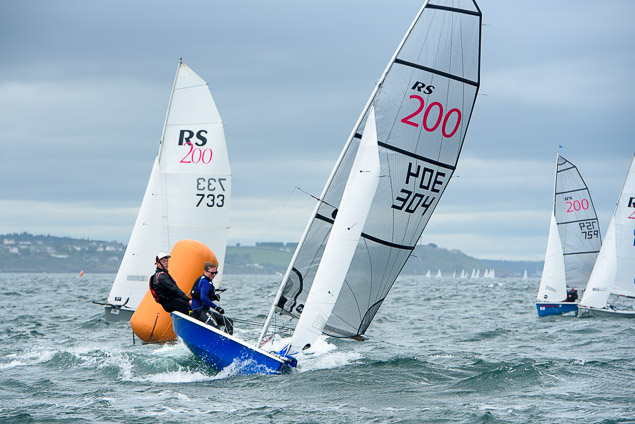
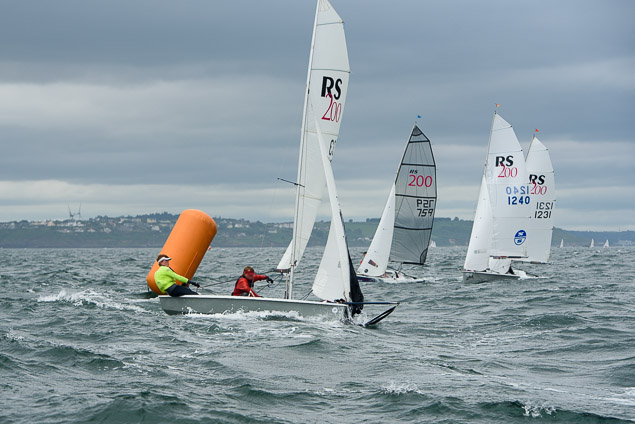
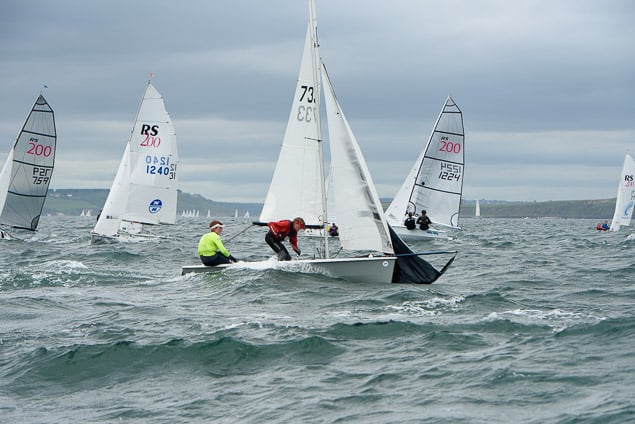
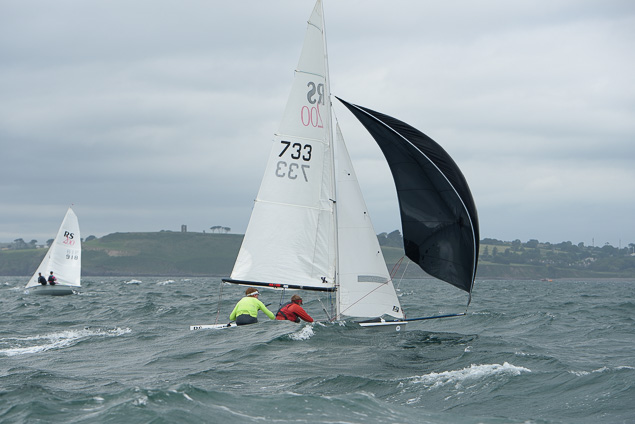
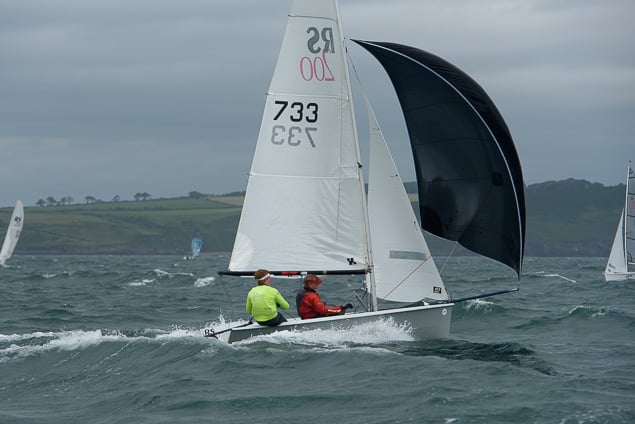
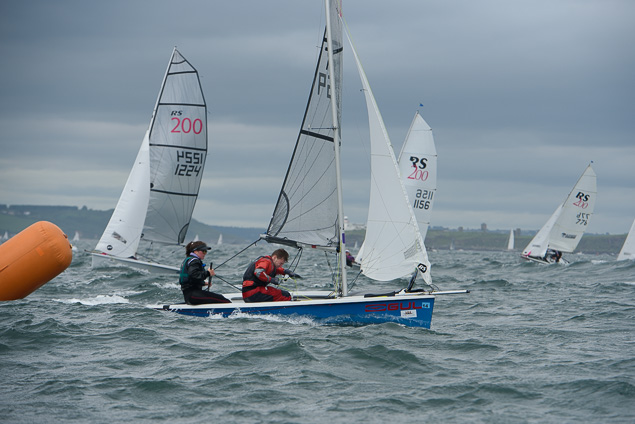
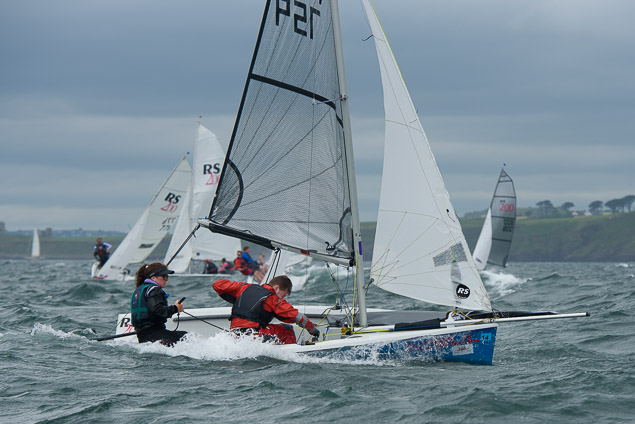
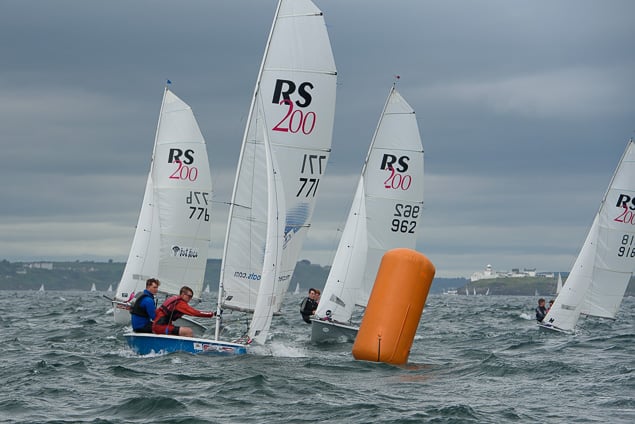
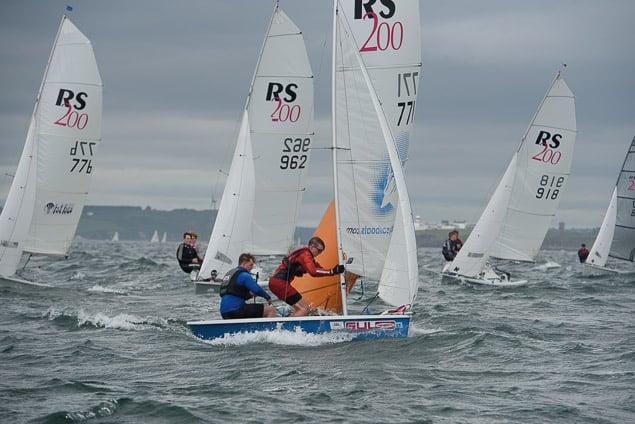
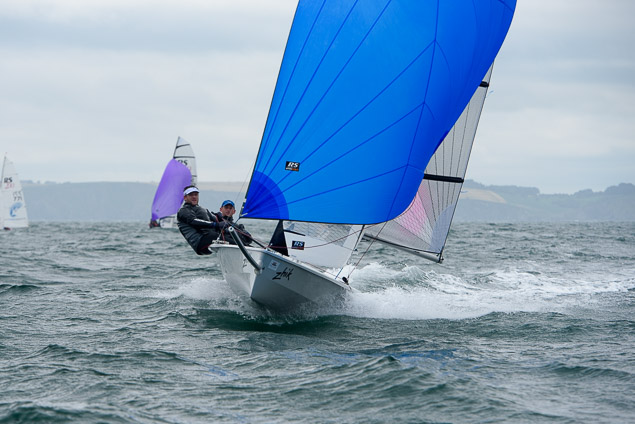
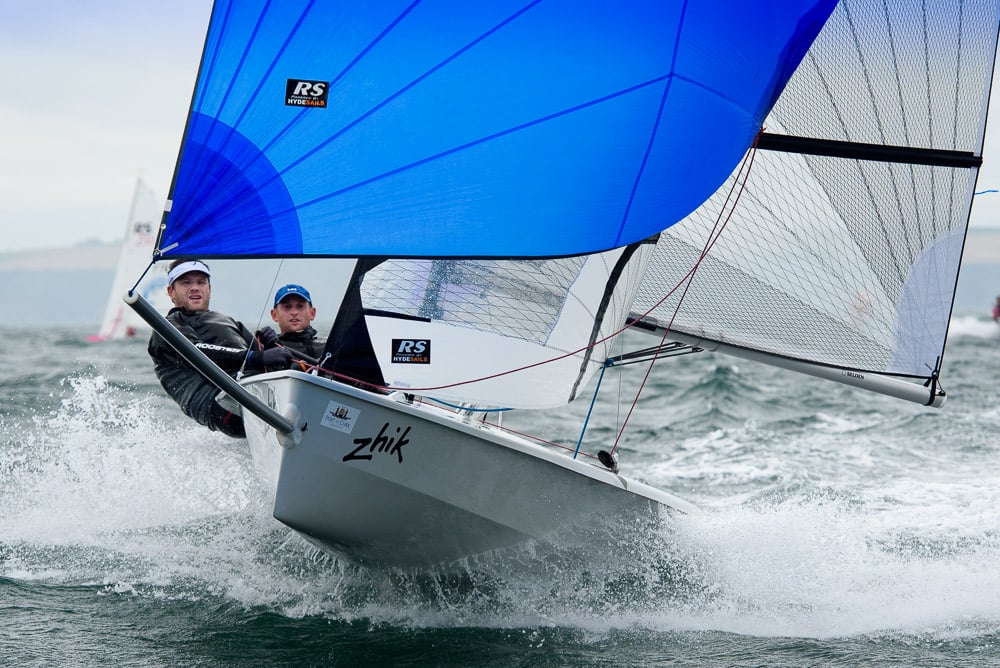
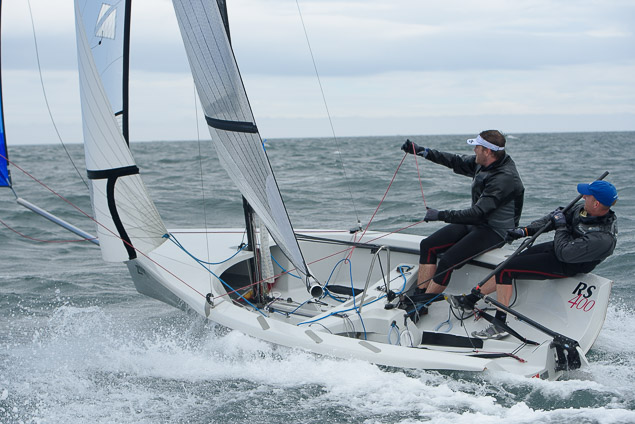
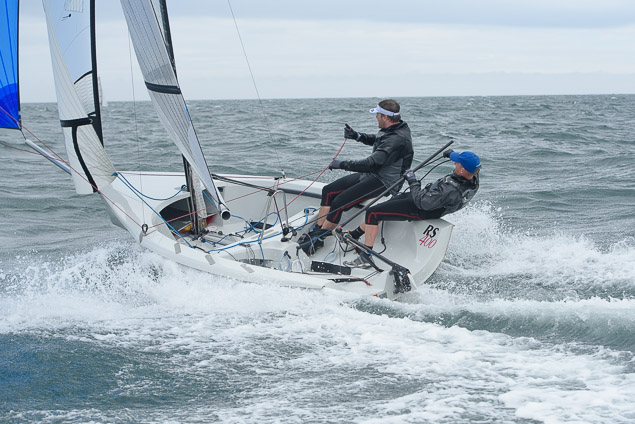
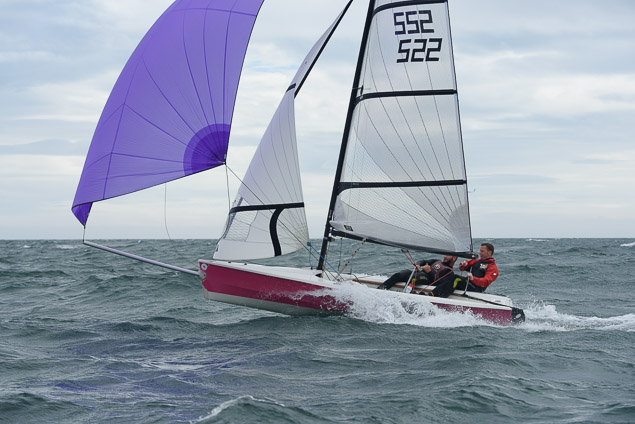
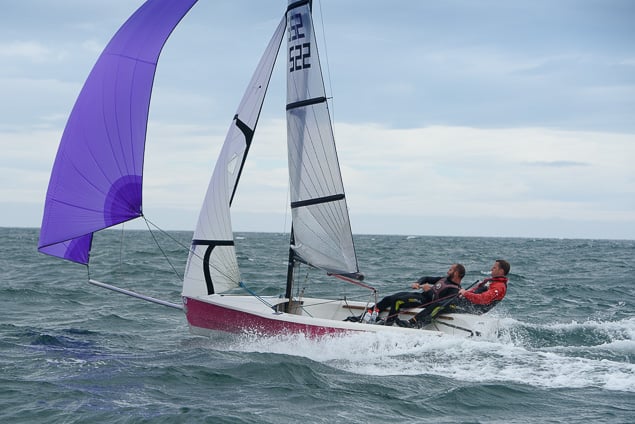
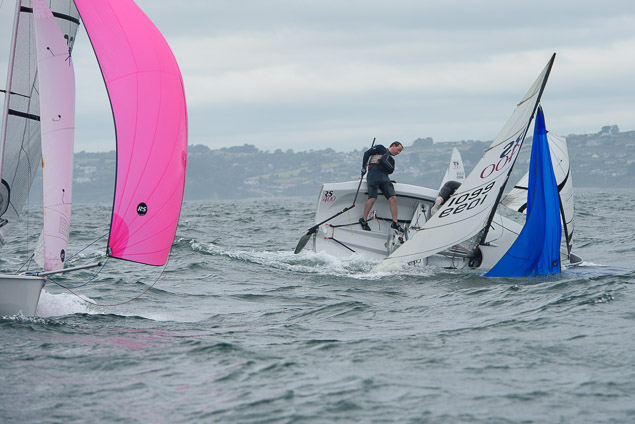
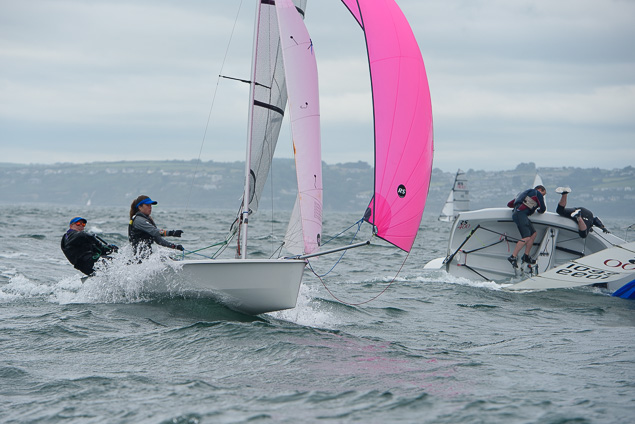
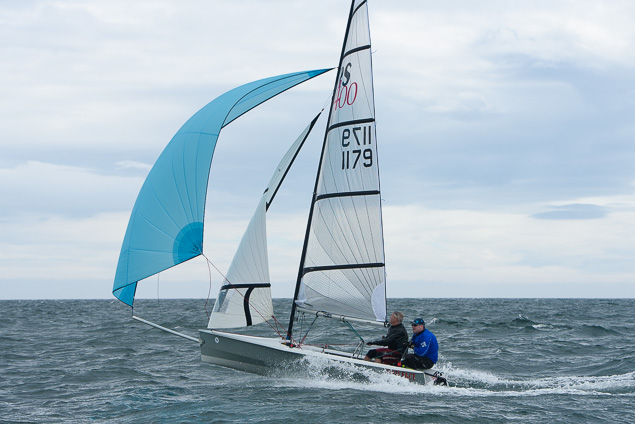
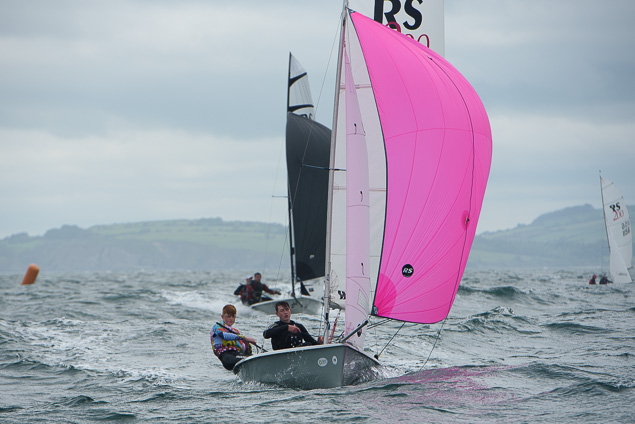
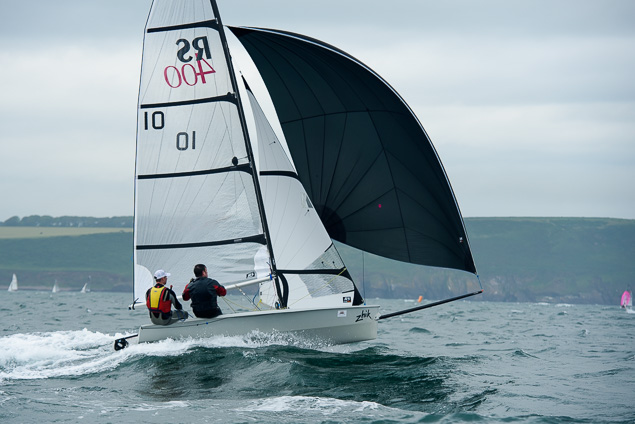
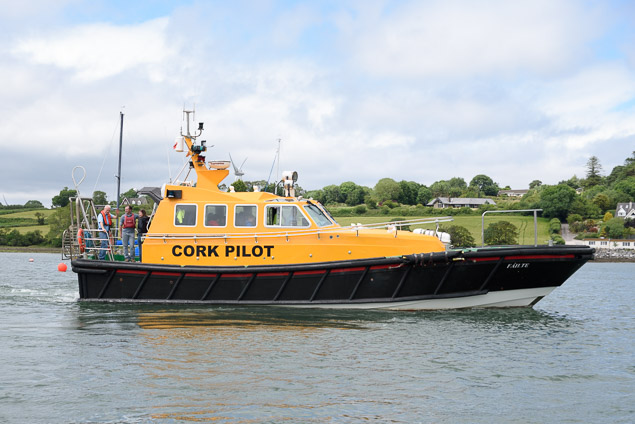







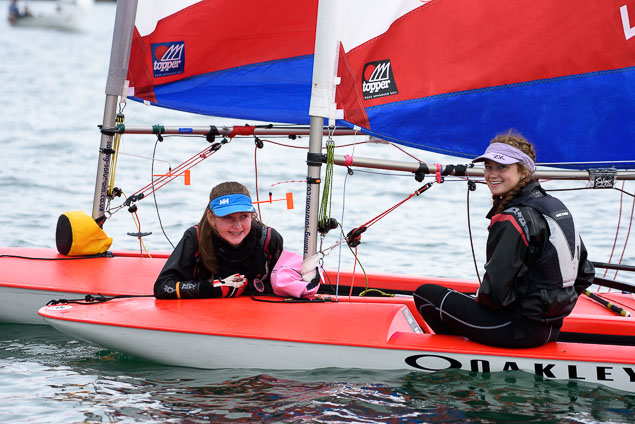

















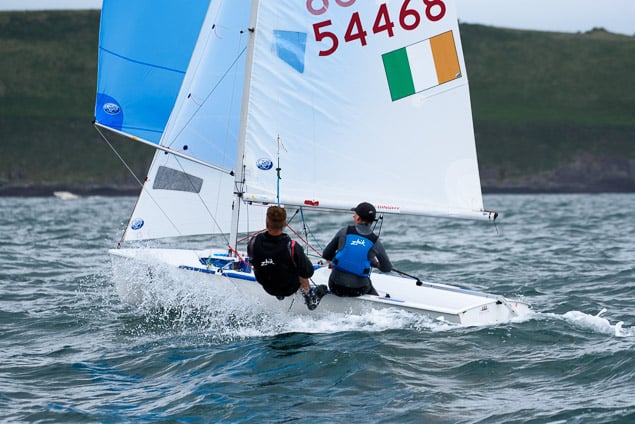













































Royal Cork's O'Leary Tenth in Viper Pan-American Championship
Sailed from March 9-11 as part of Bacardi Miami Sailing Week the EFG Viper Pan-American Championship is the culmination of a year’s worth of qualifying regattas in Australia, Europe, and North America and attracted its regular Irish entry for the week long regatta in Florida.
Royal Cork's Anthony O'Leary, crewed by Ross McDonald from Howth Yacht Club and David Hassett from Cork Harbour (now living in the US) finished tenth in the 23–boat fleet.
A second in race five of the nine race series being the Irish boat's top score.
Royal Cork Yacht Club recently became the first Yacht Club marina in the country to receive the Fáilte Ireland Welcome Standard accreditation for accommodation on its marinas and facilities. “The Club are delighted to have received this accreditation from Fáilte Ireland and we hope the ‘Welcome Standard’ will help attract even more visiting boats from around Ireland, the UK and further afield to visit Cork Harbour. There is plenty to see and do around the harbour as in recent years there has been a huge increase in infrastructural development, with Camden Fort Meagher and Spike Island being two great examples” commented General Manager, Gavin Deane.
Fáilte Ireland's (FI) role is to support the tourism industry and work to sustain Ireland as a high-quality and competitive tourism destination.
With the Quality Assured banner FI have developed new standards to allow for greater innovation, individuality and authenticity in their approved tourist accommodation businesses.
The standards recognise accommodation businesses of all types and styles that are committed to tourism and to maintaining high standards and practices throughout their business. It is targeted at atypical tourist accommodation businesses who do not fit in the existing approval frameworks such as glamping, pods, shepherd huts, yurts, lighthouses and marinas.
The standards identify the strengths of businesses, without taking away any of the character and style of the individual property.
Durcan & O'Shea Win Royal Cork's Inaugural 'Irish Mist' Trophy
The final day of racing in the O’Leary Insurance Group Winter league at Royal Cork Yacht Club was shrouded in a thick blanket of fog. The Race Officer Clem McElligott postponed the start of the race by one hour in the hope that the fog would burn off and the fleet would get racing. With just 20 mines to go to the new start time the fleet made their way out through the thick fog to the start area. As the start approached the fog began to clear, but the fleet were now faced with a new problem there was little to no wind across Cork harbour, forcing the RO to again postpone the start. By two O'clock the RO made the call to fly N over A and the fleet made their way back home for some well-earned mulled wine and mince pies awaiting them in the Club bar.
The final prizegiving was then held to a packed bar of sailors in their Christmas jumpers and hats. Anthony O’Leary and his family were all present to award the winners with beautiful Nash19 Christmas hampers, sourced prepared by Sally O'Leary. But it was the final presentation which really stole the show, when the O’Leary family presented the best performing boat of the league under IRC with the Inaugural Irish Mist Trophy, as previously reported by Afloat.ie, in memory of (Anthony’s father and past Admiral of the Royal Cork Yacht Club) Archie O’Leary. This beautifully hand crafted trophy was won by Tom Durcan and Clive O'Shea sailing their 1720 T-Bone. It was a very fitting end to another great winter league at RCYC.
Royal Cork Keelboat Team Third In Venice 2K
#RCYC -The Royal Cork Yacht Club was represented this weekend at the Venice leg of the international 2K team racing circuit, hosted by the Compagnia della Vela di Venezia.
The mixed Cork crew, who enjoyed a strong finish in Anzio this summer, placed behind Britain’s Serpentine Racing and the winning Dutch-Italian contingent from the Yacht Club Costal Olanda, but ahead of the home team at Compagnia della Vela di Venezia.
The event, taking place from the 4th to the 6th of November, had 11 teams from Italy, Germany, The Netherlands, Britain, Ireland and Sweden competing in generally very light wind conditions. Unfortunately the final day of racing was cut short due to light winds and the results were awarded based on the round robin standings. The RCYC team were beaten by Britain’s Serpentine Racing and the winning Dutch-Italian contingent, known as Yacht Club Costa Olanda.
The team consisting of Fred Cudmore, Lisa Tait, Philip O'Leary, Sonia Minihane, George Kingston, Emma Geary, Sean Cotter and Sarah O'Leary finished in third place.
Wipe Outs at Cork Harbour's CH Marine League (PHOTO GALLERY HERE!)
Clases one, two and 1720’s raced inside Cork harbour today but classes three, four and whitesails was cancelled in what was to be an exhilarating but challenging penultimate day of Royal Cork Yacht Club's CH Marine Autumn Series writes Bob Bateman.
Winds of up to thirty knots greeted competitors and wipe outs and gear failure for some were the order of the day.
Class one were given a harbour course of No5, No11, EF1 no. 20, EF2 No11 no14, EF2 , No11, No 5 and Finish.
Class Two had a course in the same area but shorter. Meanwhile the enthusiastic competitors supplemented from the fleets not sailing had windward leeward courses across the Channel.
In a departure from the normal Autumn Regattas the final day’ racing will be held next Sunday with a Gala prizegiving dinner that evening.
Ostling Wins Women's Match Racing World Championship
Anna Ostling, who first shot to match race fame in Cork Harbour two years ago, with crew Annie and Linnea Wennergren are the 2016 Women's Match Racing World Champions. In the Buddy Melges Challenge, the third event of the 2016 WIM Series, the Swedes defeated Anne-Claire Le Berre, Mathilde Geron and Alice Ponsar of France, in a thrilling final over five matches on Lake Michigan.
Ostling took her first World Championship gold at Royal Cork YC, Iin 2014, and this year's medal is a milestone in a very successful year so far. Her Sheboygan triumph is her third consecutive WIM Series victory, after winning earlier in Helsinki, Finland, as well as in Lysekil, Sweden. With this result Team Anna stretches their WIM Series lead further, as only the regattas in Busan, South Korea, and St Thomas, US Virgin Islands, remain.
After a maternity leave of almost one year, Anne-Claire Le Berre came back to the WIM Series just for this World Championship, aiming for the final and for a medal to put around her neck. This time it's silver, but the gold wasn't very far away.
Final results:
1. Anna Ostling, Annie Wennergren, Linnea Wennergren, SWE, 25 points
2. Anne-Claire Le Berre, Mathilde Geron, Alice Ponsar, FRA, 22
3. Renee Groeneveld, Lobke Berkhout, Mijke Lievens, NED, 20
4. Stephanie Roble, Maggie Shea, Janel Zarkowsky, USA, 18
5. Caroline Sylvan, Louise Kruuse af Verchou, Frida Langenius, SWE, 16
6. Samantha Norman, Carla Holgate, Taylor Holland, NZL, 14
7. Pauline Courtois, Jeanne Courtois, Juliette Le Friec, FRA, 12
8. Nicole Breault, Molly Carapiet, Karen Loutzenheiser, USA, 10
9. Elizabeth Shaw, Madeline Gill, Malin Holmberg, CAN, 8
The Optimist Ulster Championships, hosted by Malahide Yacht Club, saw 120 young sailors compete on the Broadmeadow Water in mixed conditions over two days, with the honours in the Gold Fleets at both Senior and Junior levels going to Royal Cork YC entries.
The event, sponsored by the Grand Hotel, saw Harry Pritchard of RCYC sail consistently throughout to beat clubmate Harry Twomey by just 3 points in the Senior Gold fleet while two other Cork sailors, Michael Crosbie and Justin Lucas, headed up the Junior Gold fleet.
National Yacht’s Club’s Nathan van Steenberge and Jacque Murphy (RStGYC) won the Senior and Junior Silver fleets respectively.
The first day’s racing was notable for fresh westerly and south-westerly winds, with several heavy gusts which severely tested the sailors’ abilities. Conditions improved on the second day and PRO Neil Murphy was able to complete a full 6-race schedule.
Cruisers Called For Survey On 'Cool Route' Project
#Cruising - The Royal Cork Yacht Club is among those partnering a new project to develop and market cruising grounds across Europe's North Western Seaboard from Ireland to Norway.
The Cool Route Project, funded by the Interreg VB Northern Periphery and Arctic Programme, has the involvement of all national sailing organisations in Ireland and the UK, as well as strategic partnerships in Norway and the Faroe Islands.
Wide-ranging research is now being conducted on a transnational collaborative basis by Cool Route on the cruising preferences of sailors along the North Western Seaboard.
"This research, which is incorporating the expert views and priorities of cruising skippers, will be an important input to the future development and marketing of cruising in these waters," say the project organisers, who invite relevant sailors to complete an online survey HERE.
Laser Ace Séafra Guilfoyle wins Royal Cork PY 500
#py500 – Séafra Guilfoyle has won the Royal Cork Yacht Club's PY 500 dinghy prize this afternoon. Only 8 seconds separated 3 dinghy classes at the finish writes Claire Bateman.
Saturday March 14 was the due date for the second annual PY 500 race at the Royal Cork Yacht Club. Well, what a story. The morning dawned with a beautiful blue sky and wonderful reflections in the clear water but alas and alack not a hint of a breeze could be felt and Race Officer Nathan Kirwan had no option but to postpone racing. As the race was to be held in the river, it was hoped to have a start an hour before high water but it was not to be. 'Experts' scanned the skies and ascertained that what clouds were there were moving slightly from the east. And so, when the light fickle breeze did fill in at 11.45am a windward/leeward course was set starting from the club marina with instructions for all boats to sail three rounds.
With a prize fund of €500 for the lucky winner and the ebb tide starting to flow more strongly the competitors were somewhat over eager and a general recall was necessary for the first start but all boats got away cleanly on the second attempt. The race had attracted an excellent entry of 38 but with the light wind morning this was whittled down to 32, still an excellent number. There was a great variety of craft on the water heading for the first mark ranging from National 18's, RS 400's, Lasers full rig, Laser Radials and Lasers 4.7, Toppers, an International 14, a 29er, a Pico, a Laser Stratos, a Finn and a brave Mirror and they all rounded the first mark without any incidents. They completed three rounds of the course and great concentration was needed in the light wind sailing but it proved to be a very enjoyable event resulting in only minor shouting between the competitors
When the results were calculated using the Portsmouth Yardstick only eight seconds separated the first three boats and indeed only three seconds separated the first two boats. Séafre Guilfoyle in a Laser full rig was the popular winner followed by a National 18 sailed by Nicholas O'Leary crewed by Michael O'Brien and Alex O'Connell, in second place and David Kenefick crewed by Grattan Roberts in an RS400 third .
Given the tightness of the results, one wonders what would have been the final placings if the two leading National 18's hadn't decide to concentrate between themselves on having a luffing match approaching the leeward mark in round 2, and who can tell whether or not this was where the vital three seconds between first and second place was lost. Neither they nor we will ever know for sure!






















































































