Displaying items by tag: Tasmania
For Irish Offshore Racing Sailors, 'Tis The Season To Be Sailing To Hobart
#rshyr – Tasmania is a medium-sized island in the Great Southern Ocean which is sheltered to the west only by South America. And as Tasmanians reckon skinny little New Zealand doesn't really provide a proper lee, they'll tell you their island is also sheltered to the east only by South America. So although it is at the same latitude in the south as Bordeaux in southern France is in the north, Tasmania's weather conditions – particularly the winds – can be much more extreme than they are in Bordeaux.
For sure, this lovely island can have some beautiful summer weather. But equally, it can serve up some very demanding sailing conditions. Thus the annual 628-mile Rolex Sydney-Hobart Race inevitably brings the fleet into increasingly hostile seas the further south they progress down much of the course. And the Bass Strait between Australia and Tasmania is a notoriously rough bit of water which has claimed lives in this event.
But then the twist in the tail is the final ten or so miles from the Iron Pot up the narrowing and increasingly flukey Derwent Estuary to the finish at the Hobart waterfront. This concluding crawl can test any sailor's sportsmanship as he or she sees a good position, hard earned over hours and days on a very rough sea, wafted away in calm spots and fickle zephyrs. Indeed, some hardened Hobart race veterans reckon the real contest finishes not even at the Iron Pot, but rather as you enter Storm Bay in the approaches to the Derwent Estuary, saying that it's just a lottery thereafter. But despite such criticisms, the race is one of sailing's great events. W M Nixon takes a look at this year's 70th staging of the classic, which starts in traditional style on Sydney Harbour in less than six days time.
If the annual Rolex Sydney-Hobart Race didn't exist, then world sailing would have to invent it. But happily, it's there already for our absorption and enjoyment. And in 2014 for its 70th staging, it's more relevant than ever in an era of instant global communication. When we remember that much more than half of humanity lives in the Northern Hemisphere and many of them are now in the depths of winter, the fact that there's this glorious and accessible sailing spectacle all ready to roll on screens worldwide, just as we're finally sated with Christmas and all its trappings, is a sanity-preserver for anyone interested in boats and sport.
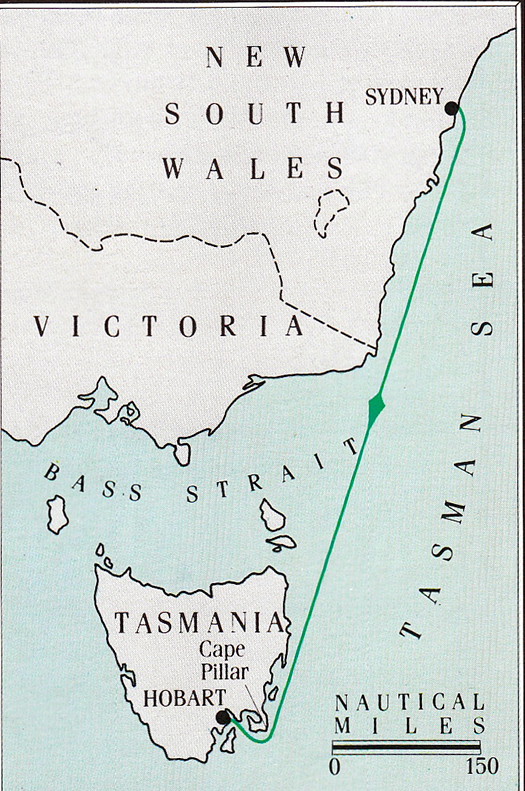
The great race's 628 mile course takes the competitors ever deeper towards the Southern Ocean with every mile sailed.
Of course there's Irish involvement in it at a specific level, with two boats in particular carrying our special interest. But at a more generous level, anyone who has the slightest interest in sailing cannot but be fired up by the wonder of an event in which some of the most advanced hundred footers in the world are swept up in a contest in which they will not only be in cut-throat competition with each other for line honours, but at the end, when all the calculations have been done, for dyed-in-the-wool offshore racing enthusiasts the real competition will be for the Tattersall's Cup, the hugely prestigious trophy for the overall handicap winner.
With 117 expected starters of all sizes from 33ft to 100ft, as the race gets under way each boat will have its own ideal set of conditions and circumstances to suit crew hopes. But as the contest continues, there'll be those who start to emerge in the leading group on handicap, and by the time they're in the final approaches, it is usually whittled down to about a dozen boats or even less which are in there with a shout for the Tattersall's.
But the line honours race for the Illingworth Cup – named in honour of the great British offshore racing skipper and innovator John Illingworth who first suggested the race in 1945 and won it too – now that's a different animal altogether. It's a real death or glory battle. And there's something specially entertaining and attractive about a no-holds-barred contest between boats you could like a lot, just at the time when the word is that the current flotilla of Volvo Round the World Racers may not be very likeable boats at all.
For we hear that the Volvo 65s are twitchy beasts, and not really fun to sail. To have a boat which turns round and looks at you is unfortunate. To have a boat which lies on its back and waves its legs in the air is unfortunate. But a boat that does both....? Oscar Wilde's Lady Bracknell said everything about such a situation.
So we'll return with relief to the crazy guys with the glorious big boats at the front of the fleet in the race to Hobart, for after the Volvo 65s, they're like a breath of fresh air. This is definitely not the territory of careful accountants and penny-pinching save-a-dime boatbuilding. We're looking at the stuff of legend. And the people's favourite has to be the veteran Wild Oats XI, marvellously campaigned by Mark Richards and his team of all the talents with the full support of the veteran owner Bob Oatley (86), whose wine brand of Wild Oats – one of many business interests – doesn't suffer any image problems at all when his boat of the same name wins yet again.
They talk of the Reichel Pugh designed super-slim Wild Oats XI as a "beloved old boat", but in truth she has been so continuously modified that you'd be hard put to say just what is original. The word is they've made her waterlines even narrower up forward – she used to be skinny, but now she's anorexic. As for last year's secret ingredient, the horizontal hydrofoil which, when deployed to lee, reportedly improved performance by up to 4% by making the boat better able to carry sail, for this year's race they tried making it even longer, such that it didn't entirely retract into the housing. But it seems that with a bit sticking out permanently on the weather side, it created more fuss than it was worth, so it has been shortened back to disappear entirely when not in use.

Wild Oats XI has so many bits and pieces sticking out of her hull that she has been compared to a Swiss Army Knife. This is skipper Mark Richards standing on the horizontal hydrofoil which, when deployed on the lee side, gives sufficient lift to significantly improve sail-carrying power. However, it has been shown that it has to be completely retractable into its housing when on the weather side, otherwise it causes unacceptable turbulence.
This conclusion on the downside of making the hydrofoil even longer emerged from some serious heavy weather sailing by Wild Oats off Sydney recently, when she was getting her final pre-Hobart race test and crew training. Heading back to port, with only about a quarter of the mainsail set in a very big wind, the silver arrow was making up to 33 knots. That will be food for thought for the four other hundred footers, the most challenging of which is of course Jim and Kristy Hinze Clark's new Comanche, just out of the wrappings, a hundred foot of total racer with Kenny Read as skipper.
The new girl on the block. American Jim Clark and his Australian wife Kristy Hinze Clark will debut their new hundred footer Comanche in the Rolex Sydney-Hobart 2014.
The same Kenny Read endeared himself to the Irish sailing community during the first Volvo visit to Galway five years ago, when he exited the dock somehow managing to look cool wearing a Paddy Hat that no-one else would be seen dead in. The boy is still busy, as he's worldwide president of North Sails, while his current main commitment afloat is to campaign the very extreme Comanche to the limit, with the Rolex-Sydney Hobart Race 2014 the first outing for real.
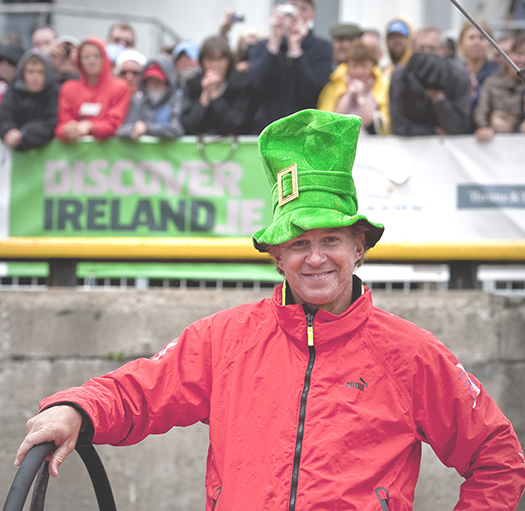

God be with the days.....five years ago, Kenny Read endeared himself to the people of Ireland by managing to look cool in this hat while exiting Galway Docks during the Volvo stopover. Photo: Failte Ireland/David Branigan
The hundred footers did have their first encounter a couple of weeks ago with the CYCA Solas Big Boat Challenge in Sydney Harbour, but racing boats this size in such relatively restricted water gives a somewhat skewed picture. Nevertheless the very experienced tacticians on Wild Oats still managed to finish first, as they did last year, but it was Comanche second quite a bit clear of Anthony Bell's Perpetual Loyal.
Once upon a time, Perpetual Loyal was very well known in Ireland, but that was in 2011 when she was George David's Rambler 100, and upside-down off West Cork. Until Comanche's appearance, Perpetual Loyal was reckoned the potentially fastest hundred footer of them all if she just could get enough wind in the right direction. But now the hundred footer field is wide open as a number of them have been undergoing major modifications of the kind you might expect to see on model yachts, but not on thirty metre hulls.

Can you see the join? The entire aft half of Rio 100 is entirely new, thanks to several months of major surgery in Auckland.
Thus the former Lahana, now American-registered, owned by Manouch Moshayedi and re-named Rio 100, simply had her entre aft half cut off, and replaced with a new wider stern section. Just like that. But you ain't heard nuthin' yet. The irrepressible Syd Fischer, shaping up to do his 50th Sydney-Hobart at the age of 87, decided that the hull of his hundred foot Ragamuffin needed some mods. A lot of mods. So he has just kept the deck and rig, but cut off the original hull, and replaced it with a new one from the same designer, Andy Dovell.

The incredible Syd Fischer, a sprightly 87-years-old, with the entirely new Andy Dovell-designed hull before it was fitted under the deck and rig of his previous hundred footer Ragamuffin.
So if next time you're on Sydney Harbour and a peculiar-looking hundred foot motorboat comes tootling past with a slightly lost air to her, you'll know why. She could swear that once upon a time she had a deep keel and a great big mast. But she's out and motoring about because there's no way Australians will let a redundant hundred foot hull go to waste. Meanwhile, the new raceboat hull has barely had time for testing, but we're assured all will be well, and the something old, something new Ragamuffin 100 will be there on the line raring to go against Wild Oats, Comanche, Perpetual Loyal and Rio 100 in the battle for line honours.
But as old Hobart hands will tell you, the real race is almost something else altogether. You'll have noticed that in mentioning the Solas Big Boat Challenge, we only talked of line honours. But it has an equally important IRC element as well, and two weeks ago the winner was Matt Allen's Carkeek 60 Ichi Ban, with Gordon Maguire the main man.

She may seem a plump girl by comparison with some other boats, but Matt Allen's Carkeek 60 Ichi Ban has been winning races, including the Solas Big Boat Challenge 2014. For the Rolex Sydney-Hobart 2014, skipper Gordon Maguire will be joined by ace Irish-born navigator Adrienne Cahalan.
And Ichi Ban's challenge in the Hobart race is even more Irish, as the Allen-Maguire team have linked up with Offaly-born Adrienne Cahalan to be navigator. One of Australia's top women sailors in almost any role, her navigational skills are legendary, and in the 2013 race she was navigating the 55ft Wedgetail to such good effect approaching the Tasmanian coast that they held the IRC lead, only for it all to come tumbling about their ears with a dismasting, which is hardly the navigator's fault.
So this time to Hobart, Ichi Ban really does have the dream team aboard. And though we still wonder if she's not just a little too plump in her waterlines forward to have that real cutting edge, the boat's results over the past year suggest that she has what it takes, and if the cards fall her way at all, she'll be clear to win.
Looking again at the top ten IRC boats in 2013, it's significant that apart from the freak presence of the hefty Swan 82 Nikata at 7th overall, only Ichi Ban at 8th overall was over 50ft long. The rest of the top ten were all 50ft or under, and the outstanding design was the evergreen Cookson 50, represented by both the overall winner Victoire (Darryl Hodgkinson), and the ninth placed Pretty Fly III (Colin Woods).
We in Ireland know well of the New Zealand-built Farr Cookson 50's brilliance through Chieftain (Ger O'Rourke), which later became Adrian Lee's Lee Overlay Partners, thus putting the Fastnet overall win of 2007 and the Caribbean 600 overall win of 2009 on the Cookson 50 winner-board before Victoire added the Sydney-Hobart win in 2013. It's some going for a design which first saw the light of day more than ten years ago.

Privateer is one of the evergreen Cookson 50s, which have been consistently successful in the world's top offshore races for a decade
But as 2013's results show, doing well in the Sydney-Hobart has a huge element of horses for courses to it, and in 2010 the very new First 40 from Beneteau made a prodigious debut by taking first and second overall. They're still a very competitive boat, so not surprisingly there's five of them shaping up for the race to Hobart, and this is where the most direct Irish involvement comes, as Barry Hurley and his team have linked up with co-owner Mathew Vadas to put the beef in the crew of the First 40 Breakthrough. [Click to read Barry Hurley's preparations for this third successive Sydney–Hobart Race – Ed]
The same linkup saw Breakthrough take eighth in Class and 29th Overall in the 2013 race, but this time round Barry Hurley ships on board with the added experience of second overall and first in class in October's Middle Sea Race. With him to show that the boat is indeed sailing under the Dublin Bay Sailing Club colours are Catherine Halpin and Kenny and Alexander Rumball. And the word on the waterfront is that a shore support team not entirely unconnected with the Irish National Sailing School will be an enthusiastic presence in Sydney on December 26th. We look forward to hearing from them. Meanwhile, Happy Christmas everyone.
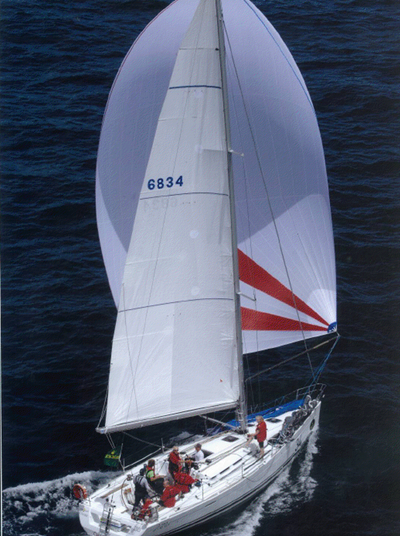

The First 40 Breakthrough will be racing under Dublin Bay Sailing Club colours in the Rolex Sydney-Hobart race 2014, starting December 26th
NI Fields First Full Team at Commonwealth Fly Fishing Championships
#ANGLING - Two Newtownabbey anglers are part of a six-man Northern Ireland team competing at the 2012 Commonwealth Fly Fishing Championships, which started yesterday in Tasmania.
The Newtonabbey Times reports that Kenny Ferguson and team captain Alan R McDade set out for the Australian island last Wednesday for the competition that runs till 19 February.
They join Campbell Baird and Harvey Hutchinson from Carrickfergus, Banbridge angler Neil Cardwell and Harry McAteer Jr from Belfast for the week-long contest.
The six - who qualified from contests held throughout Ireland organised by the Trout Anglers Federation of Ireland - also comprise the first full team that Northern Ireland has entered in the competition.
Stena Line to Resume ‘Express’ Service
In addition to the 'Express' service the St. Georges Channel route is served by the year-round operated conventional ferry, Stena Europe (1981/24,828 grt). The 1,386 passenger / 564-vehicle ferry recently underwent a £2m refurbishment and takes a more leisurely passage time of 3 hours 30 minutes.
For information on both fast-ferry and conventional ferry sailing schedules click HERE.
Seasonal Scenes Set for Fishguard
Fast-ferry Stena Lynx III departed Dun Laoghaire for Fishguard Harbour on a repositioning voyage today, writes Jehan Ashmore.
The 80m craft built in Hobart, Tasmania is due to dock at the Pembrokeshire port this afternoon in advance of seasonal sailings on Stena Line's Fishguard-Rosslare.The Stena 'Express' fast-ferry service is to resume in just over a fortnight's time. Sailings are scheduled to a daily single round trip between 1 July-4 September.
The 627 passenger / 120 car capacity fast-ferry will operate in tandem with the year-round operated conventional ferry-service served by the Stena Europe. Passage times are 120 minutes for the fast-ferry service while the Stena Europe takes 3 hours 30 minutes to sail across the St. Georges Channel.
In the same week that the fast-ferry takes up summer sailings from Fishguard, the small French flagged cruiseship Le Diament is to make the first of three calls in July and once in August.
The motoryacht-like vessel which can accommodate 226 passengers is the first cruise caller of the season and is run by the only French-owned cruise operator Compagnie De Iles Du Ponant.
Former US Navy Fast-Craft Re-opens Seasonal Dublin Route
Manannan's chequered career included a five year charter initially to the United States Navy but transferred to the United States Army Forces between 2001-2006. The 5,029grt craft (see photo) was used for various trials and demonstrations and in which saw service in the Persian Gulf in support of 'Operation Iraqi Freedom' and in 2003 'Operation Enduring Freedom' in the Horn of Africa.
An engine plant of 4 x Caterpillars diesel generates a speed of over 40 knots / 46 mph which provided logistical solutions by the High-Speed Vessel (HSV) to transport troops and supplies covering long distances in support of the Combined Joint Task Force.
Other tasks required by the force included the roles of operating as a mobile command centre which entailed working closely inshore and operating as a helicopter carrier. Helicopters landed at the craft's stern positioned helicopter landing deck.
The military role of the craft is in stark contrast compared to when the 96m ferry was launched in 1998 for civilian purposes as the Incat 050, the number representing the number of pioneering wave-piercing craft built by InCat in Hobart, Tasmania.
Asides her military days the 800-passenger / 200 vehicle fast-ferry has served the Hobart-Melbourne route, between New Zealand's north and south island and in European waters in the Mediterrean and to the Canary Islands.
Manannan (see photo) entered service last May after the Isle of Man Steam Packet Company (IOMSPco) purchased the vessel which was laid-up in Hobart. She made the long delivery to the northern hemisphere and was re-converted for ferry usesage during a refit in Portsmouth.
The 181 year-old company is the only sea-based passenger operator to the island on services linking Dublin, Belfast, Heysham, Liverpool and (Birkenhead) in the winter months.
There are rival companies such as the Ramsey Steamship Company but they are freight-only operators mostly running to Belfast and Liverpool using short-sea coastal traders and to other small Irish Sea ports.
An annual round island cruise is held and like last year the Manannan will be serving the cruise on Sunday 1 May departing Douglas at 11am for a journey of around 2 hours. The route closely circumnavigates the spectacular Manx coastline. For information on the island cruise and fares click here.


































































