Displaying items by tag: marine wildlife
A group of Ireland’s environmental NGOs are teaming up this spring for a rather unique education project lead by the Irish Whale and Dolphin Group. The exciting Floating Classroom initiative is combining ocean exploration with an educational schools programme which aims to raise awareness of Ireland’s marine biodiversity. Taking to the seas in the IWDG’s research vessel Celtic Mist, the team of marine biologists and ocean literacy experts will be making their way down Ireland’s south-east coast from Arklow to Cork, calling into coastal communities providing engaging workshops to schools along the way.
After an extensive refit during the winter in Grand Canal Docks, Dublin, the 56-foot ketch yacht will also be open to the public when docked at local marinas and harbours, giving the public an opportunity to see the workings of a dedicated whale and dolphin research vessel and how researchers live and work at sea.
Apart from raising awareness for Ireland’s rich marine wildlife, the team will be emphasising the importance of taking care of our seas and oceans. With challenges such as plastics pollution, climate change and biodiversity loss now frequently in the news, there is a pressing need for communities to work together to tackle environmental issues.
While pupils will be introduced to the wealth of marine and coastal wildlife on their doorstep, each school will be asked to come up with three ways in which they feel they can make a difference for their local blue environment.
The team of biologists will also be proposing ways in which the public can get involved, including citizen science projects that encourage people to report their sightings of whales, dolphins, seabirds and even shark eggs! Schools will be encouraged to get involved in other community-based initiatives too, such as beach cleans being run by organisations in their area.
Environmental NGOs involved in the Floating Classroom include the Irish Whale and Dolphin Group, Marine Dimensions, the Irish Wildlife Trust and the Irish Ocean Literacy Network. Funding for the Floating Classroom has been kindly received by the Irish Environmental Network through their Capacity Building Grant.
Sailors Asked To Help Spot Migrating Puffins
I remember when I first saw the Puffin seabirds.
It was my first time sailing along the Kerry coastline and it was off Portmagee, on the appropriately named Puffin Island.
We had closed the small Island south of Valentia which is a wild bird conservancy for a look and it was, for me, a magical moment that I always remember.
Crowded along the cliff face, some in the water, I saw Puffins about which I’d heard so much, up close for the first time. My immediate image association was with clowns I had seen as a youngster at circus performances. The facial expressions, seen close-up through binoculars, their colour from blue to yellow and red striped beaks, the webbed orange-red feet, the waddling gait, and the way they bobbed around on the water.
"As sailors, we should be interested in the welfare of seabirds which can tell us so much about the marine environment"
I’ve seen them since, from a distance around the Skelligs, Horn Head in Donegal, on the Cliffs of Moher and the Great Saltee and why I’m telling you about them is because their hormones are driving them back to Ireland. As their European population has suffered a decline, the shores of our island nation are an important location for them to breed. I’ve been told by BirdWatch Ireland, the national voluntary organisation which protects Ireland's birds and habitats, that this is part of a huge seabird migration underway to Ireland that is hidden from the eyes and ears of most, but sailors may see it and can help. A special website has been set up for the purpose here.
As sailors, we should be interested in the welfare of seabirds which can tell us so much about the marine environment.
For me, the mention of Puffins, so synonymous with the sea, brought back memories of earlier sailing days. There are many other species on the way to our shores. You can hear more about all of this on my Podcast with Niall Hatch of BirdWatch.
• Listen to the Podcast below
#dublinbay - As part of the Bullock Harbour Bicentenary lecture series to mark and celebrate the construction of the small scenic south Dublin Bay harbour in Dalkey, a panel discussion will focus on the Bay itself.
The Bullock Harbour Preservation Association (BHPA) in conjunction with the Dublin Port Company have been organising the series which began in November last year.
Likewise of previous lectures this penulitmate event will be held in the Dalkey Castle & Heritage Centre on Tuesday, 9 April at 8pm. All are welcome to the Panel Discussion which is free and there is no need to book in advance.
The panel discussion will focus on the environment of the bay, present and future, covering biodiversity and the conservation of the marine and bird life.
Speakers include:
Ann Murray, DLRCC Biodiversity Officer and Dublin Bay Biosphere Partnership
Richard Nairn, Ecologist and author of 'Dublin Bay: Nature and History'
Hannah Keogh, Irish Whale & Dolphin Group
Professor John Brannigan, UCD, on Cultural Aspects of Coastal Environments
For further information in general about the harbour visit the BHPA website here.
Alarmed: Birdwatch Ireland at Port Planning Shortcuts
#irishports - Independent.ie writes Birdwatch Ireland is "alarmed" at emergency orders that could be utilised by the Government to override planning procedures for a no-deal Brexit scenario at Dublin and Rosslare ports.
The group is concerned for the safety of birds who make their habitats within Ireland, including a colony of terns in a special protection zone at Dublin Bay.
The Government is set to rely on emergency planning orders in the wake of any no-deal Brexit on March 29.
Oonagh Duggan, assistant head of policy and advocacy at Birdwatch Ireland, said: "We are living in an ecological emergency, with 68pc of regularly occurring birds in Ireland on the red and amber lists of the Birds of Conservation Concern in Ireland. Any shortcuts on environmental assessment could have devastating consequences on wildlife."
#coastalnotes - As part of the RDS Library Speaker Series will be a presentation ‘Snapshots and Science - The Shallow Seas of Ireland’ which is to be held next Wednesday March 13 between 18:30-20:00.
The presentation by leading underwater photographer Paul Kay will feature an exploration of Ireland’s rich underwater world, one which is hidden from most of us and one which is still being explored.
It will showcase some extraordinarily beautiful species and locations and will also illustrate just how little we know and understand about the seas and how we utilise them. In an information rich era it will no doubt surprise many to see what lies below the waves.
The event held in the RDS, Ballsbridge, Dublin 4, is free of charge and open to all, but online booking is required. To book click here.
Short Tail Nurse Sharks Breed for First Time at Bray Sea Life Centre
It’s the Year of the Shark at Ireland’s Sea Life Centre where two Short Tail Nurse Sharks have bred for the first time. The eggs from the rare sharks, now facing a dramatic decline in the wild, can now be seen growing in their tank and the pups are expected to hatch towards the end of the year.
The female shark was born in Sea Life in 2006 from a wild caught egg and is one of the first of the species to breed in captivity. The male shark was also born in 2006, in Artis Zoo in Amsterdam and came to Sea Life on loan in 2013 as part of a European breeding programme. But they didn’t breed immediately, it took them four years to get together! This shark is only found in three locations in the wild, off the coasts of Tanzania and Kenya in East Africa and in the waters surrounding Madagascar.
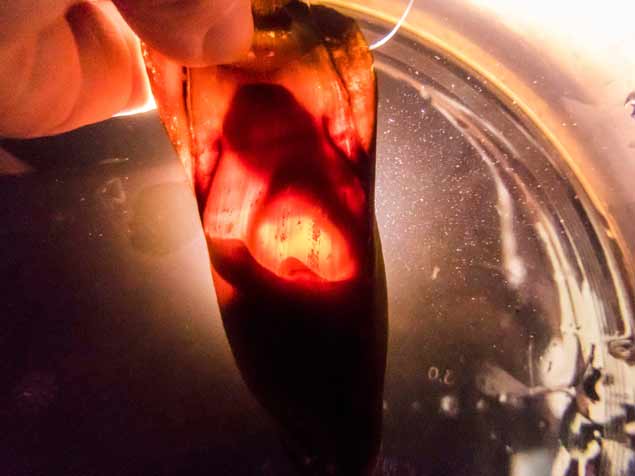 A shark embryo develops in one of the rare eggs from the Short Tail Nurse Shark at the National Sea Life Centre Bray
A shark embryo develops in one of the rare eggs from the Short Tail Nurse Shark at the National Sea Life Centre Bray
The Short Tail Nurse Shark has been placed on the ‘vulnerable’ list by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. Its decline has resulted from commercial overfishing for food and particularly for its fins, which are regarded as a delicacy in Asia and which sell for around £140 a kilo. The fish is also caught as a bycatch in the heavily fished inshore waters of East Africa. It also suffers from the destruction of its natural habitat, the coral reefs.
It is a fascinating animal to watch. An inshore bottom dwelling species, it has a unique feeding apparatus with a small mouth but an enlarged pharynx that allows it to create a vacuum and suck up its prey. It is a nocturnal feeder, preying on sea urchins, squid and octopus. It has a habit of regularly floating upside down and can live for up to 33 years in captivity, becoming mature when it is 56 cm long.
Pat O’Suilleabhain, Director of Sea Life Bray, says it is a great achievement to have these rare sharks breed successfully in Ireland and that Bray can be proud to be part of a European wide breeding programme. ‘We became a part of this very interesting programme when Artis Zoo in the Netherlands agreed to loan us the male shark. There is little known about their breeding habits so there is great excitement throughout Europe as we wait for the pups to hatch.’
The eggs and the parents are currently on display at Sea Life in Bray.
Bray Aquarium Welcomes New Baby Stingray
#MarineWildlife - Bray’s National Sea Life aquarium has announced the birth of Ireland’s first tropical stingray, as TheJournal.ie reports.
The junior Atlantic cownose ray was born a month ago but staff at the North Co Wicklow marine wildlife centre wanted to ensure it was healthy before making the announcement.
About 30cm long, the ray is one of a ‘near threatened’ species that only reproduces once a year. It has also yet to be named, as its sex won’t be determined for a while yet, but is presumed to be female.
And she’s already making friends with the aquarium’s visitors, with National Sea Life managing director Pat Ó Súilleabháin saying: “She comes right up to the edge of the tank to say hello.”
In other marine wildlife news, the carcass of a porpoise was found on a river bank in Newry last weekend, according to the Belfast Telegraph.
Animal rescuers responding to public concerns said the harbour porpoise had likely been dead for some time but was no cause for alarm for the health of a known group of porpoise in nearby Carlingford Lough.
Harbour porpoise, like their dolphin cousins, are sometimes found swimming upriver in estuaries or coastal areas – and it’s not unheard of to see them hundreds of miles inland from the sea.
First Humpback Whale Of New 2017 Season Sighted Off West Cork
#MarineWildlife - The first humpback whale sighting for the new season in Irish waters was made last week off the Beara Peninsula.
The Irish Whale and Dolphin Group’s (IWDG) Patrick Lyne was in prime position to witness the unmistakable tail fluke some 5km offshore from Beara in West Cork on the afternoon of Wednesday 5 April.
While not the first humpback sighted this calendar year — that honour goes to a giant spotted off Wexford in early January — it’s still considered the first of the 2017/18 ‘large whale season’.
The sighting also continues a trend of earlier arrivals for Ireland’s regular humpback visitors over recent years, with 2016’s first recorded only four days later and spotted just 4km away.
Last Wednesday was a bumper day for marine wildlife sightings off Co Kerry, too, where Nick Massett spotted at least a dozen minke whales between Ventry, Slea Head and the Blaskets.
Many of these locations feature in Colin Stafford-Johnson’s new BBC TV series Wild Ireland, as BBC News reports. The two episodes are currently streaming via the BBC iPlayer, where available.
In other cetacean news, researchers believe that whale strandings may in part be caused by exhaustion when cetaceans flee human-made noise in the ocean.
According to the Irish Independent, a study by marine scientists at UC Santa Cruz found that beaked whales startled by low-frequency sonar raise their energy consumption by almost a third, increasing demands on their limited oxygen supply while below the surface.
The news will be fuel to those who suspect human activity at sea plays a major role in increased cetacean stranding rates.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, 2017 became the worst year on record for whale and dolphin strandings by mid February.
Marine Wildlife Wows Viewers In New TG4 Documentary
#OnTV - A documentary on the wildlife of Ireland’s West Coast that’s wowed TV viewers during Seachtain na Gaeilge is now available to watch online.
As Independent.ie reports, the two-part Éire Fhiáin has been compared to Blue Planet for its incredible footage — from the Skelligs and Blasket Islands in the first episode to the rugged charms of Connemara and Mayo this past week, among other breathtaking locations.
Director and presenter Eoin Warner and his team used some of the latest filmmaking technology, including night-vision lenses and slow-motion cameras, to capture Ireland’s marine wildlife – and their land-lubber friends – like they’ve never been seen before.
And the results saw the hashtag #EireFhiain take off on social media last week — though if you missed the Irish-language series first time out, you still have time to catch up by streaming it via the TG4 Player.
Sperm Whale Carcass Washes Up On Wexford Beach
#MarineWildlife - The carcass of an 11-tonne sperm whale has washed up at Carnsore Point in Co Wexford, as the Gorey Guardian reports.
The 8.5m whale — discovered by local man Davie Rea on the rocky shore at the end of last week — was identified as an adult female by the Irish Whale and Dolphin Group (IWDG).
Kevin MacCormick of the IWDG added that the giant marine mammal appeared to be emaciated “so most likely it was not in good health”.
It’s been five years since the last sperm whale stranding on the Wexford coast, as the species is more often found in western waters.
The Gorey Guardian has more on the story HERE.






































































