Displaying items by tag: pontoon
Firm With Irish HQ Installs Portside Pontoon for Servicing Scotland’s Largest Wind Farm
An Irish company has installed a new pontoon for the servicing of Scotland’s largest offshore wind farm, as Marine Industry News reports.
Inland and Coastal Marina Systems, which is headquartered in Banagher in Co Offaly, was contracted to provide for the 30m x 4.4m heavy-duty pontoon.
It will allow allow safe berthing and access for vessels transferring work crews to and from the Seagreen wind farm project, which is currently under construction in the North Sea some 27km off the county of Angus.
The pontoon is installed at Montrose Port’s South Quay and comes with specialised anti-slip decking and a 20m access gangway with a cantilevered shore frame platform.
Marine Industry News has more on the story HERE.
Inland & Coastal Marina Systems Provides Conwy Marina with Waiting Jetty Solution
County Offaly marina firm Inland and Coastal Marina Systems has successfully upgraded the ‘waiting’ jetty at Conwy Marina in North Wales. The new pontoon is now in constant use, providing users with a safe and secure place to wait for entrance into the marina.
Inland and Coastal installed a Continuous Concrete Pontoon (CCP), increasing berthing and load capacity for larger vessels. With greater wave reduction and stability properties, the system also requires less maintenance.
Due to varying water levels between the outer harbour and marina basin, access to the 500-berth marina is via a tidal sill.
“The large tidal range in the estuary here often causes the holding pontoon to ground at low water springs,” says Jon Roberts, Conwy Marina Manager. “Inland and Coastal’s continuous pontoon design works perfectly. The attention to detail also made the installation process extremely efficient. The work progressed during specific tidal gates without interfering with daily operations and I am delighted with the quality of the new structure.’’
Jon continues: “Our customers’ first impression of the marina comes from their experience on the waiting pontoon. The new pontoon, with its additional safety features and the reangled ramp to give less steep walk ashore access, make me confident that we are giving the best welcome possible.”
“Conwy is a stunning part of the coastline,” says Oliver Shortall, Inland and Coastal Managing Director. “We were delighted to provide a robust ‘waiting’ jetty. Our concrete pontoons have double the lifespan of wooden ones. The solid surfaces also offer much better grip properties - especially when wet.”
As well as continuously developing pontoon solutions for marina operators, yacht clubs and port authorities, Inland and Coastal is the official UK supplier of SeaBin, demonstrated at the recent Southampton International Boat Show.
Inland and Coastal will be exhibiting at METSTRADE on stand 05.514 in the Marina and Yard Pavilion.
Youghal Harbour Pontoon Now Open For Business
Youghal’s long-awaited harbour pontoon is now open for business in what’s expected to be a major boost for the East Cork town.
Mooring fees are €10 per day or €25 a week, applicable to all users — whether casual, commercial or sailing club members.
Preliminary rules for users have been posted on the pontoon, and the necessary key fobs are available from Youghal Town Hall.
There was some confusion last month over the status of the facility, which was installed in early May but without an official opening date, prompting concern among some boaters.
Meanwhile, Youghal’s first full-time harbour master is expected to take up their role next month, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
Youghal’s New Pontoon Now Under Assembly
#Youghal - The components for Youghal’s new marina pontoon have arrived, and the amenity is currently being installed in the East Cork town.
Preparation for the new embarkation pontoon began last November with pile driving works in the harbour, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.
The pontoon marks the fruition of longstanding community efforts to build a marina for the town — and is hoped to “bring a welcome boost to our capability as a destination for marine tourism”, according to the Build a Marina in Youghal page on Facebook.
Embarkation Pontoon for Youghal in County Cork is Underway
An 'Embarkation Pontoon' at Youghal Co. Cork is underway allowing boating visitors to get on and off their boats without having to resort to dinghies.
According to the local 'Build a Marina in Youghal' Facebook page, pile driving will be undertaken next week, followed by the testing of the piles.
The pontoon is being manufactured off site. The installation of the pontoon and gangway will take approx three days and is scheduled to happen the 1st week in December. The pontoon will not be left in the water over the winter months.
Last year visitor moorings were installed in Youghal to facilitate visiting boaters.
Afloat.ie readers will be aware of the community efforts to build a marina in the town to 'achieve a positive maritime impact for the town and it's prosperity'.
Marina Pontoon Works Underway at Cape Clear Island
Marina pontoon installation work is well underway at Cape Clear Island's North Harbour where pontoons to the value of €200,000 have been procured for the West Cork island harbour.
Under the 2017 fishery harbour and coastal infrastructure capital programme, Junior Minister Andrew Doyle told the Dail Harbour's debate in June he had allocated €720,000 for maintenance and development works at the Island's North Harbour.
'The 2017 programme provides €200,000 for pontoons at Cape Clear and €250,000 for the design, preparation of contract documents and planning for additional repair work to Duffy's Pier' he said.
Read more on the works in our June report here.
Lower Aghada Pontoon Reinstalled for Boating Season
The Lower Aghada pontoon has been reinstalled for the coming boating season in Cork Harbour.
Local community efforts in Aghada in 2011 led to an upgrade in the underused and deteriorating pier. It is now a popular Cork Harbour destination for boaters.
These efforts led to the Port of Cork and Cork County Council co-operating with the community in a €350,000 upgrade of their pier which has seen it developed with seasonal pontoon installation as a new destination for visiting boats in the lower harbour. More on this from Afloat.ie in 2011 here.
 Lower Aghada is on the eastern shore of Cork Harbour Image: Google Maps
Lower Aghada is on the eastern shore of Cork Harbour Image: Google Maps
Green Light for Youghal Pontoon As Funding Approved
Cork East Fine Gael TD and Minister of State at the Department of Justice, David Stanton has welcomed the funding announcement of €112,500 for the development of a pontoon and gangway in Youghal.
News of the proposal broke on Afloat.ie last March here.
“The announcement is great news for Youghal and will allow for the supply and installation of a pontoon and gangway in Youghal Harbour. Cork County Council has done a huge amount of work to get this project underway and has already secured the necessary planning permission and foreshore licence to allow the development to proceed”, said Minister Stanton.
“Last year eight visitor buoys were put in place in Youghal harbour and these have been very successful in attracting marine leisure tourism to the town. I am confident that the pontoon will build on the success of these buoys and greatly enhance Youghal’s marine tourism offering and lead to an increase in visitors to this historic town.
“This funding is another substantial investment in Youghal’s tourism product. In addition to the development of Youghal’s heritage trail which includes the Raleigh Quarter, the medieval town walls, St Mary’s Collegiate Church and gardens next door, Youghal Clock Gate was opened to the public at the end of last year and is proving very popular. The refurbished boardwalk is also widely used by locals and visitors alike.
“Youghal wastewater treatment plant is also due to be completed by the end of this year and this project along with the other wastewater infrastructure works will allow for further development in the town into the future.
“I am very pleased that Youghal pontoon project has been awarded funding under the Local Authority Harbour programme. This scheme provides for 75% funding by the Department of Marine with the balance being supplied by Cork County Council. I would hope that, if this project is as successful as expected in attracting visitors to the town, this project would lead to further investment in marine leisure facilities in Youghal in the not too distant future.
A completely new 60-metre Visitors Pontoon is being installed in Dunmore East in a location immediately northwest of the old Lighthouse and the steel tank pontoon which was placed there as a temporary measure for visitors two years ago writes W M Nixon.
The new pontoon – designated totally for visitor use – is of the same high standard as the new small fishing craft pontoon recently completed in Howth. Features of the Howth pontoon – such as dedicated disabled access – will be replicated in Dunmore East, where the popular Harbour Master Harry McLoughlin is confident that the new facility will be opened as scheduled on July 1st, for although work started as recently as May 9th, the final pile is due to be driven today (May 30th).
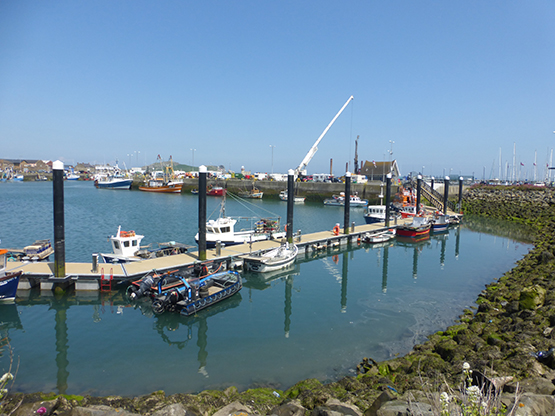
The new small fishing craft pontoon in Howth, which shows the standard of the facility being installed at Dunmore East. The Howth Lifeboat is temporarily berthed at the new pontoon until a purpose-built Lifeboat Berth is completed at the Lifeboat House itself – the crane beyond is working on this project. Photo: W M Nixon
Contractors at Dunmore East are L & M Keating of Kilmihil, Co Clare, who have carved out a special niche in Ireland as the “can do” engineers to go to when quality harbour and waterfront works are required. One of their most recent contracts was the award-winning extension of the challenging little ferry port at Doolin in County Clare, which is hugely busy with tour-boats cruising the nearby Cliffs of Moher or making the shortest sea crossing to the nearby Aran Islands, while the firm are also investors themselves in the shoreside infrastrucuture, as they own and operate Kilrush Marina & Boatyard.
As for future developments in Dunmore East (where a massive dredging operation was recently completed), the word on the grapevine is that a consultative programme has been officially started to explore ways and means of installing an additional breakwater which could lead to the provision of a proper marina.
A busy day in late April at the newly-extended ferry port at Doolin in County Clare. Contractors L & M Keating Ltd received an award for the complete project, which included extensive shoreside works. At high water - as seen here - the old pier (foreground) can be used for additional berthing, but at low water the only ferry access is via the new outer pier. Photo: W M Nixon
Mooring & Pontoon Development in Youghal Harbour
Floating pontoons and visitors swing moorings at Nealon's Quay and Youghal have been proposed by Cork County Council. The plans of the long overdue development are available for inspection at County Hall in Cork over the next six weeks.
Installation includes 'steel piles, access gangway, visitor swing moorings and associated indfrastructure' according to the notice that is posted below.
The notice follows a story on January 13th on Afloat.ie that pointed to pontoon development on the south coast town. A local pressure group, however, indicated that talk of a 'much needed' town marina was premature.









































































