Displaying items by tag: Shark
The European Commission is consulting the public about improving ways to protect and manage sharks and related marine ecosystems.
The consultation aims to gather the public's views to ensure an informed follow-up to the 2023 European citizens’ initiative ‘Stop Finning – Stop the Trade’ – which got over a million signatures.
“It is clear that how we treat sharks is an issue close to the hearts of many Europeans,” according to EU Commissioner for the Environment, Oceans and Fisheries Virginijus Sinkevicius, launching a Commission questionnaire available online until June 4. “While assessing environmental, social and economic impacts of measures that could improve shark protection, we also seek views of a wider public to make sure that the European Commission’s response to this initiative is the best possible one.”
This public consultation is addressed to civil society at large, NGOs, economic operators of the fisheries value chains, trade unions and consumer organisations, researchers, members of the academia, public authorities and international organisations, which will be used to feed into an ongoing impact assessment.
As part of the response to the Stop Finning – Stop the Trade, the Commission says it is considering potential measures to step-up shark protection and management, including:
- The possibility to only allow commercialisation of sharks with their fins attached – be it for consumption within the EU or for international trade (imports and exports)
- Bilateral agreements with the main international partners involved in shark fishing and consumption
- Sustainability certification schemes for shark products, and
- Promotion of a global trade ban on trade in loose shark fins
It said that it had already introduced enhanced enforcement of existing conservation and management measures and is increasing “international outreach to reduce shark fin consumption and end finning practices worldwide.”
TCD Marine Biologists Discover More Sharks May Have Warm-Blooded Traits
When the fearsome megalodon became extinct, it may have been because it didn’t have enough food.
Unlike most sharks, the star of the 2018 film, “The Meg”, had a large appetite due to its warm-blooded nature - like its descendant, the great white shark.
Most other shark species are cold-blooded fish, or so it has been thought until now.
However, newly published research led by Trinity College Dublin (TCD) scientists has discovered that the basking shark found in Irish waters and another “Meg” descendant, the smalltooth sand tiger, may also have warm-blooded traits.
The scientists have described it as both “surprising” and concerning, as this may reduce the ability of these species to cope with warming seas.
Their findings follow the results of tests conducted on live basking sharks off the west Cork coast, along with autopsies of the bodies of three small tooth sand tiger sharks washed up on Irish and British coasts earlier this year.
Dr Nicholas Payne of TCD’s School of Natural Sciences is senior author of the study, published this week in the journal, Biology Letters.
 Trinity College Dublin marine biologist Dr Haley Dolton tagging a basking shark off the west Cork coast. Results from temperature measurements of the basking shark show it also has warm-blooded traits. Photo: Dr Haley Dolton
Trinity College Dublin marine biologist Dr Haley Dolton tagging a basking shark off the west Cork coast. Results from temperature measurements of the basking shark show it also has warm-blooded traits. Photo: Dr Haley Dolton
As he explains, the three small tooth sand tiger sharks are a deep water species and a rare occurrence in these waters as they are not normally found north of the Bay of Biscay.
“We don’t know why they stranded, but the team in Britain did a lot of autopsy work,” he said.
During this research, it was found that the smalltooth sand tiger sharks had red muscles close to the vertebrae and a high percentage of compact myocardium in the ventricle heart – both being key signs of warm-blooded physiology.
Payne’s TCD colleague and lead author of the study, Dr Haley Dolton, found the same traits in basking sharks while conducting tagging on the large plankton-eating fish off the west Cork coast.
Known in Irish as “ainmhí sheoil” or “the beast with the sail” due to its dark fin, the basking shark is a protected species under the Wildlife Act.
She explains that body temperatures of basking sharks were measured in the tagging project, which took place with the West Cork Charters skipper David Edwards off Courtmacsherry, Co Cork.
Dr Payne describes the findings as very important, as it may mean that several other shark species also have “regional endothermy” or warm-bloodedness.
“This raises plenty of new questions as to why regional endothermy evolved, but it might also have important conservation implications,” he says.
“We know the seas are warming at alarming rates again now and the smalltooth tiger that washed up in Ireland was the first one seen in these waters. That implies its range has shifted, potentially due to warming waters, so a few alarm bells are ringing,”Dr Dolton adds.
The research team also included scientists from University of Pretoria, Zoological Society of London, University of Zurich, Swansea University, Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute and University College Dublin.
Dr Dolton’s work was funded by the Irish Research Council and Dr Payne was funded by Science Foundation Ireland.
Basking Shark Mystery Solved off West Coast
The West Coast of Ireland is the first place in the world where the annual reproductive behaviour of basking sharks has been seen.
“It is astonishing that this wonder of the natural world has remained hidden for so long,” according to Professor David Sims, Senior Research Fellow at the University of Southampton and lead author of a study carried out by biologists from the Marine Biological Association and the Irish Basking Shark Group.
It has revealed “the global importance of the West Coast of Ireland for the endangered species.”
Circling formations have been documented on a few occasions over the past 40 years in the North-West Atlantic off Canada and the USA. But although basking sharks are often seen filter-feeding plankton in the UK and Irish coastal waters during the summer, the circling formations were rarely seen. Until now, scientists could not explain the behaviour.
Using underwater cameras and aerial drones off County Clare from 2016 to 2021, scientists got video footage of 19 circling groups. Each comprised between 6 and 23 sharks swimming slowly at the surface, with others deeper down.
“This research has shown the importance of Irish waters,” says Dr Simon Berrow of the Atlantic Technological University, Galway and the Irish Basking Shark Group, who co-led the research: “How usually solitary basking sharks find a mate in the ocean’s expanse has been an enduring mystery. Our discovery of these basking shark grounds in our coastal waters makes it more urgent that this species gains protection in Irish waters from potential threats, such as collisions with marine traffic and the impact of offshore renewables.”
Legislation to protect basking sharks in Irish waters was drafted this year, although they are protected in many parts of the world. It remains to be signed into law.
‘Concern’ Over Shark Carcass Found in River Erne
Inland Fisheries Ireland has expressed concern over a shark carcass that was found in the River Erne in Co Cavan earlier this month, as BBC News reports.
The remains of what’s thought to be a small spurdog shark were found at Belturbet on Friday 17 September.
The State agency with responsibility for the protection and conservation of Ireland’s inland fisheries and sea angling resources believes the shark was caught at sea and later dumped in the river.
“The incident is a cause for concern for Inland Fisheries Ireland as the body advocates a ‘catch and release’ approach with shark species,” it said.
Flotilla on Liffey Highlights Need to Protect Basking Shark
A flotilla is steaming up the river Liffey today in the next stage of a marine wildlife campaign to secure legal protection for basking sharks in these waters.
Over 7,000 people have already voiced support for the Save Our Sharks campaign, which aims to deliver a letter personally to Minister of State Malcolm Noonan.
The letter highlights the need for legal protection of the world’s second-largest shark and fish – known as Liabhán chor gréine, or the “great fish of the sun” – within Irish territorial waters.
In May of this year, Social Democrat TD and former marine biologist Jennifer Whitmore proposed amending the Wildlife Act (1976) to include the basking shark.
This would provide legal protection to the shark in Irish territorial waters.
Scientists signed an open letter to Government last month, explaining that Irish coastal waters are “one of the few places globally” where basking sharks “regularly and predictably occur on the surface close to shore”.
“This surface swimming behaviour is the root of its deep cultural connections with western Irish coastal and island communities,” the scientists said.
The number of breeding individuals has been estimated at approximately 8,000-10,000 worldwide, the majority of which are in the northeast Atlantic.
The scientists believe section 23 of the Wildlife Act should be amended to protect the endangered species.
Celebrating Irish sharks of all shapes and sizes for Shark Awareness Day
Today, 14th July, the Marine Institute is recognising sharks of all shapes and sizes for Shark Awareness Day. Irish waters are home to 71 species of shark, skates and rays, 58 of which have been studied in detail and listed on the Ireland Red List of Cartilaginous fish. Irish sharks range from small Sleeper sharks, Dogfish and Catsharks, to larger species like Frilled, Mackerel and Cow sharks, all the way to the second largest shark in the world, the Basking shark.
Marine biologists have long wondered why some species like the white shark and bluefin tuna are warm-blooded when most fish are not.
Now newly published research led by a Trinity College Dublin (TCD) scientist has concluded that the ability to regulate body temperatures in this way gives these fish a competitive advantage as “elite” predators.
However, the study led by PhD candidate Lucy Harding in TCD’s school of natural sciences also confirms that this advantage doesn’t allow them to live in broader temperature ranges – meaning they are just as vulnerable to climate change.
The research, which is published today (Thurs July 1st) in the journal Functional Ecology (italics), found that white shark, bluefin tuna and other warm-water species can swim approximately 1.6 (one point six) times faster than their cold-blooded counterparts.
Only 35 species of fish are warm-blooded, but this is limited to parts of their bodies, Harding explained.
“Some can warm their brain, or their eyes or muscles or a combination of same – and the reasons for this will involve more research,” she said.
Up till now, it had remained unclear what advantages being warm-blooded provided to the particular fish, she said.
“Some scientists believed being warm-blooded allowed them to swim faster, as warmer muscles tend to be more powerful, while others believed it allowed them to live in a broader range of temperatures and therefore be more resilient to the effects of ocean warming as a result of climate change,” Harding added.
 Tiger shark: A tiger shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) swimming at the surface with a biologging package attached to dorsal fin. This package records temperature, swimming speed, depth, body movement and video footage. Photo: Diego Camejo (Beneath the Waves).
Tiger shark: A tiger shark (Galeocerdo cuvier) swimming at the surface with a biologging package attached to dorsal fin. This package records temperature, swimming speed, depth, body movement and video footage. Photo: Diego Camejo (Beneath the Waves).
The research team assessed these two possibilities by collecting data from wild sharks and bony fish, as well as using existing databases
Biologging devices attached to the fins of animals used in the research collected information such as water temperatures encountered by the fish in their habitats.
The data also recorded the speeds at which the fish swam for most of the day, and the depths of water most frequented.
“We noticed that these warm-blooded animals have the same characteristics – in that they tend to be shaped like a bullet, and have particular fin shapes and tail beats,” Harding said.
TCD assistant professor of zoology Nick Payne noted the faster swimming speeds of the warm-blooded fishes “likely gives them competitive advantages when it comes to things like predation and migration”.
“Additionally, and contrary to some previous studies and opinions, our work shows these animals do not live in broader temperature ranges, which implies that they may be equally at risk from the negative impacts of ocean warming,” he said.
“ Findings like these – while interesting on their own – are very important as they can aid future conservation efforts for these threatened animals,” Payne added.
The research was supported by Science Foundation Ireland.
Marine scientists have found that a critically endangered shark in southern African has been identified in waters over 2,000 km away from its usual habitat.
The scientists led by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) say that information and images dating back two years show that the endangered shorttail nurse shark (Pseudoginglymostoma brevicaudatum) is alive in waters off Mozambique
This represents a range extension of more than 2,000 kilometres (1,242 miles), from the coast of Tanzania, and 1,100 kilometres (683 miles) westward from Madagascar across the Mozambique Channel.
A paper published in the journal Marine Biodiversity says the discovery is based on underwater video surveys collected in 2019, recent photos of shore-based sport anglers’ catches, and the identification of a specimen collected in 1967.
The shorttail nurse shark - so name due to its small size – grows to approximately 75 centimetres (30 inches) and is found in coral reefs.
Coastal fisheries and habitat degradation are said to have influenced its decline in numbers, estimated at more than 80 per cent over the last 30 years.
The scientists state that one of the records of the shark - from Mozambique’s Ponta do Ouro Partial Marine Reserve - suggests that the species benefits from some degree of protection within a large coastal marine protected area (MPA).
However, the species range within Mozambique may span a large proportion of the country’s unprotected coral reef habitat, they note, with no specific regulations on its catch – apart from a listing on the Kenya threatened and protected species records.
The researchers recommend that the species should be considered for legal protection in Mozambique and throughout its limited range, and improved management measures should be initiated to reduce targeted and incidental catch.
WCS works on shark conservation around the world, and highlights how much of the global trade in both shark fins, and other products such as meat, is unregulated and is threatening many species with extinction.
This research was conducted in partnership with the Mozambique Instituto Nacional de Investigação Pesqueira, and the South African Institute for Aquatic Biodiversity.
Irish shark experts have called on newly elected MEPs to outlaw the growing shark fin fishery in European waters, following a fine imposed on a Spanish fishing vessel detained off the Irish coast.
The Sea Fisheries Protection Authority (SFPA) has confirmed that the fine of €2,500 and forfeiture of catch and gear worth €165,000 was imposed on the Spanish vessel Virxen da Blanca, following a guilty plea in Cork circuit court on May 23rd last.
The vessel had pleaded guilty to catches of Blue Shark with a small quantity of Mako Shark on board after it was detained by the Naval Service about 150 nautical miles south of Ireland last August.
A special sitting of Clonakilty district court last year also heard the vessel had 1,250kg of shark fins on board. The vessel was supposedly fishing for tuna.
Shark fins can fetch a high price in Asia, where they are used in shark fin soup. The fins are often removed while the shark is still alive and it can then no longer swim effectively and either suffocates or is eaten by other predators.
Sharks, rays and skates are the most threatened seafish in Europe, and several species of shark caught in Irish waters are on the “red list” of endangered species issued by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Dr Kevin Flannery, chair of the Irish Elasmobranch Group which is focused on protecting sharks, ray and skates, said that a loophole in the licensing of the tuna longline fishery was allowing a bycatch of shark off this coast.
The fine imposed on the Virxen da Blanca (italics) represented “just 50 cents” for each dead shark, given that the vessel had an estimated 5,000 on board, he said.
“We congratulate the Naval Service and SFPA and welcome the guilty plea, but we are calling on newly elected MEPs to close off this legal loophole and stop this barbaric practice,” he said.
“We know of nine non-Irish vessels working off this coast, targeting blue shark in particular, and using a loophole in the tuna longline fishery,” he said.
Minister for Agriculture, Fisheries and Food Michael Creed recently said he was in favour of a “considerably lower” permitted by-catch of certain shark species.
He was responding to a case made by the IEG for action on critically endangered species, such as angel shark.
SFPA chairwoman Dr Susan Steele said the SFPA was committed to preventing illegal shark fishing and said it had “zero tolerance “ for vessels “removing fins from sharks in our waters”.
“Luckily this infringement was detected, and we will continue to work with authorities across Europe to deter and detect any future illegal shark fishing violations,” Dr Steele said.
She paid tribute to the inter-agency cooperation between the Naval Service, Garda and SFPA which led to the Spanish vessel’s detention last year.
Asked to comment on reported new measures being introduced in relation to the protection of angel shark in Irish waters, the SFPA said that for security and operational reasons it could not go into details.
Short Tail Nurse Sharks Breed for First Time at Bray Sea Life Centre
It’s the Year of the Shark at Ireland’s Sea Life Centre where two Short Tail Nurse Sharks have bred for the first time. The eggs from the rare sharks, now facing a dramatic decline in the wild, can now be seen growing in their tank and the pups are expected to hatch towards the end of the year.
The female shark was born in Sea Life in 2006 from a wild caught egg and is one of the first of the species to breed in captivity. The male shark was also born in 2006, in Artis Zoo in Amsterdam and came to Sea Life on loan in 2013 as part of a European breeding programme. But they didn’t breed immediately, it took them four years to get together! This shark is only found in three locations in the wild, off the coasts of Tanzania and Kenya in East Africa and in the waters surrounding Madagascar.
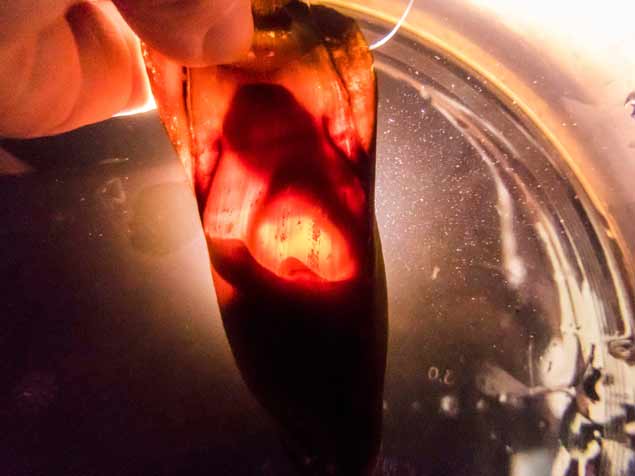 A shark embryo develops in one of the rare eggs from the Short Tail Nurse Shark at the National Sea Life Centre Bray
A shark embryo develops in one of the rare eggs from the Short Tail Nurse Shark at the National Sea Life Centre Bray
The Short Tail Nurse Shark has been placed on the ‘vulnerable’ list by the International Union for Conservation of Nature. Its decline has resulted from commercial overfishing for food and particularly for its fins, which are regarded as a delicacy in Asia and which sell for around £140 a kilo. The fish is also caught as a bycatch in the heavily fished inshore waters of East Africa. It also suffers from the destruction of its natural habitat, the coral reefs.
It is a fascinating animal to watch. An inshore bottom dwelling species, it has a unique feeding apparatus with a small mouth but an enlarged pharynx that allows it to create a vacuum and suck up its prey. It is a nocturnal feeder, preying on sea urchins, squid and octopus. It has a habit of regularly floating upside down and can live for up to 33 years in captivity, becoming mature when it is 56 cm long.
Pat O’Suilleabhain, Director of Sea Life Bray, says it is a great achievement to have these rare sharks breed successfully in Ireland and that Bray can be proud to be part of a European wide breeding programme. ‘We became a part of this very interesting programme when Artis Zoo in the Netherlands agreed to loan us the male shark. There is little known about their breeding habits so there is great excitement throughout Europe as we wait for the pups to hatch.’
The eggs and the parents are currently on display at Sea Life in Bray.
Sailing Coach Spots 'Shark' in Skerries Harbour, County Dublin (VIDEO)
Sailing instructor Kerri-Ann Boylan was out coaching kids in Optimist sailing dinghies at the weekend when she spotted a fin in the water in Skerries Harbour in North County Dublin.
'As I brought the kids into land and about to let them jump out of my boat we spotted a fin', she wrote on social media on October 10th.
'It's a very rare sight of a 'shark' being in that close to land and in the Irish Sea,' she added.

































































