Displaying items by tag: Mapping
New Project Uses Seabed Mapping To Study Behaviour Of Fish
#MarineScience - Ciaran O’Donnell, a specialist in fisheries acoustic research with Fisheries Ecosystem Advisory services at the Marine Institute, has just begun a PhD research project that will link fisheries and seabed mapping acoustic technologies.
By using both technologies, he aims to learn more about how fish behave during acoustic surveys and therefore increase the precision of fish stock assessments.
O’Donnell’s research will focus on pelagic species – fish that swim in the water column – to see if there is avoidance behaviour during acoustic surveys and also to look at schooling behaviour and preferred habitat.
He’ll use the state-of-the-art multibeam echosounder system that has just been installed on the RV Celtic Explorer to look beyond the data normally captured during acoustic fisheries surveys to see if some or any of the fish being targeted by the survey are moving away from the research vessel as it passes overhead them.
“I’m really looking forward to the sea trials of the new multibeam next week (16-24 February) when we’ll get a chance to use the most advanced seabed mapping technology alongside acoustic fisheries technology. We should be able to see a much broader picture than before," said O'Donnell, a chief scientist on annual surveys for blue whiting, Celtic Sea herring and boarfish.
“Acoustic surveys are very targeted and focussed and this will allow us to capture new information about what the fish are doing beyond the target of the downward-looking fisheries echosounder. It will be like getting enhanced peripheral vision of the sea around the ship.
“We’ll be able to see if fish are moving away from the research vessel and out of the survey path and therefore will potentially enhance the precision of our current survey methods.”
The project will bring together technology and data from fisheries and seabed mapping and O’Donnell will work closely with the INFOMAR team and the advanced mapping services at the Marine Institute.
The research project, originally designed by the INFOMAR team, brings together a number of experienced researchers including Dr Chris McGonigle and Dr Rory Quinn of the University of Ulster, Dr Fabio Sacchetti of INFOMAR and the Marine Institute, and Dr David Reid of the Marine Institute and UCC.
Discovering our (Underwater) Past

Map of the Aran Sound in Galway Bay
Speakers at this annual seminar of the INFOMAR (INtegrated Mapping FOr the Sustainable development of Ireland's MARine Resource) programme will discuss the discovery of new and historic underwater wreck sites, the application of seabed mapping in the selection of sites for generating wave energy, the protection of fish spawning grounds, and the planning of fish farm sites.
The INFOMAR programme is a jointly managed programme between the Marine Institute and the Geological Survey of Ireland (GSI) and is funded by the Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources (DCNER).
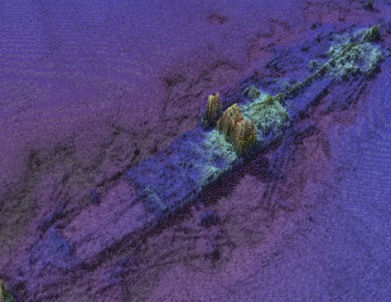
Wreck of the SS. Manchester Merchant
The event will also feature the latest results from a range of EC funded marine mapping initiatives and stunning underwater footage from the recent Irish mission to the volcanic vents of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge over 3,000 metres below the surface of the sea.
Opening the seminar Dr. Peter Heffernan, CEO of the Marine Institute said, "Ireland is leading the way for Europe in marine mapping and in laying the foundations for the sustainable management of our ocean space. Surveying the gateways to our ports, mapping our fish spawning grounds, finding routes for marine telecommunications cables and selecting the best sites for ocean energy generation all rely on accurate seabed mapping capability, which Ireland now possesses."
In addition to its large scale marine mapping remit, INFOMAR's Value Added Programme is co-ordinating an integrated multidisciplinary approach to the handling, processing and application of its ever-expanding marine data set.

Deepwater photograph from the mid-Atlantic Ridge
As a result of its latest call for research proposals, INFOMAR received 32 submissions for studies on such subjects as the appraisal of seabed data for tidal energy generation, the integration of satellite and marine data for coastal mapping and the use of new graphic animation techniques to integrate environmental information into seabed mapping displays.
"INFOMAR is a key mechanism to unlock the economic potential of our ocean territory," said Koen Verbruggen of the GSI. "By linking industry and academia to the realisation of our government's objectives and requirements around sustainable ocean development we will strengthen Ireland's position on this new frontier and expand our capability to deliver services and solutions to all marine sectors – in Ireland, in Europe and across the world."

Wreck of the sunken Guinness ship W.M. Barkley off Dublin Bay
As well as looking to the future, Ireland's maritime past will be explored in a presentation by the Underwater Archaeology Unit of the Department of Arts, Heritage and the Gaeltacht on the discovery of a probably late 16th century wreck off Rutland Island, Co. Donegal. The wreck, which may have been an armed merchant ship, a pirate or naval vessel potentially associated with the local Gaelic lordships or the Spanish Armada of 1588, is an extremely important find that could add greatly to our understanding of Ireland's maritime heritage.
Software Instrumental to Rescue of Rambler 100 Crew
Search and rescue mapping software developed in Rhode Island was "instrumental" in efforts to retrieve crewmembers from the stricken Rambler 100 off Fastnet last week.
The SARMAP software, developed by ASA (Applied Science Associates, Inc) provides rapid predictions of the movement of drifting objects and missing persons at sea.
For search and rescue units it can provide search patterns and calculate the probability of containment, probability of detection, and probability of success.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the Rambler 100 capsized off the Cork coast while competing in last weekend's Rolex Fastnet Race.
The Rambler 100’s personal locator beacon activated when the yacht overturned, which alerted rescuers to the location of the 16 stranded crewmembers still with the vessel, but recovering the five lost at sea required a more advanced approach.
The Irish Coast Guard used SARMAP’s sophisticated tracking capabilities to predict the movement of the drifting survivors and calculate a precise search area.
ASA president Eoin Howlett commented: “We have successfully worked with the Irish Coast Guard for many years; they are an innovative agency and have a history of implementing the latest in ocean technologies.
"We are very pleased that our software, combined with their rapid decision-making, resulted in such a positive outcome.”
































































