Displaying items by tag: Racing Rules
World Sailing Rules App Gets 2021-24 Update
Ahead of the 2021-2024 Racing Rules of Sailing which come into effect on 1 January, the RYA has released an update to the World Sailing Rules App — giving sailors access to a ‘one-stop shop’ for the 2021-2024 rules and associated documents.
Launched in 2016, the multilingual app was developed by the RYA in partnership with World Sailing and has proven popular with racing sailors and officials worldwide, ensuring they have all the relevant rules information at their fingertips.
Steen Ingerslev, RYA publications manager said: “We are delighted to be working with World Sailing once again. We’ve made huge advances with RYA eBooks and digital resources in recent years ensuring popular app features like the ‘Integrated eBook’ are more accessible than ever before.”
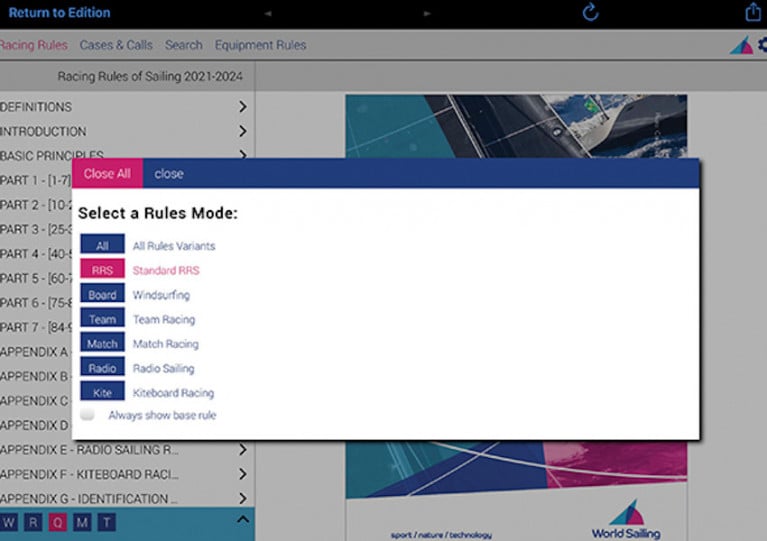
The ‘Integrated eBook’ links all the rules documents together, enabling the user to navigate seamlessly between the rules and cases, highlighting a number of cases for each rule in both overview and full case detail formats.
A rules mode in the settings allows the user to select Windsurfing, Team, Match, Radio or Kiteboard Racing amendments for their convenience. They can also select a country, enabling any translated rules and showing the local prescriptions from any participating National Authority.
The World Sailing Rules App can be downloaded for free through the Apple App Store and Google Play. If you’ve already downloaded the 2017-2020 version, it will be automatically updated. The ‘Integrated eBook’ will be available shortly as an in-app purchase.
Racing Rules of Sailing 2021-2024 RYA Edition is Out Now
Make sure you're ready for the 2021-2024 changes to the Racing Rules of Sailing with the RYA rules books. The new editions are now available from the RYA shop - www.rya.org.uk/shop.
Updated every four years by World Sailing, the Racing Rules of Sailing are compulsory for racing sailors around the globe.
As the Member National Authority for the UK, the RYA Racing Rules of Sailing 2021-2024 (order code YR1, RRP £10.99) not only features the World Sailing rules in full, but is also the only publication to contain the RYA Racing Charter, Racing Rules Guidance and the RYA National Prescriptions - essential for racing in the UK and Northern Ireland.
The compact, ring-bound and waterproof book is perfect for taking afloat. It covers not only the fundamentals of the race itself, including racing conduct and what is fair and unfair, but also details things like protests, hearings and appeals. You'll find everything competitors, judges and umpires need to know. Available here
2017-2020 ISAF Racing Rule Book Changes
ISAF Racing Rules committee member Bill O'Hara from Balyholme Yacht Club reviews the changes in the latest edition of the racing rules book signed off at the ISAF conference in China this week.
The racing rules committee have finished their work this year for the 2017-2020 rule book. Publishing and translation deadlines means it's impossible to take any submissions next year into account. Most of the changes are pretty dry and simply technical changes to sort out small problems found in the applications of the rules. In the next rule book there is a big change in that for the first time we have the introduction of the term ' support person' .
Support person – Any person who
(a) provides, or may provide, physical or advisory support to a competitor,
including any coach, trainer, manager, team staff, medic, paramedic or any
other person working with, treating or assisting a competitor in or preparing
for the competition, or
(b) is the parent or guardian of a competitor.
(proposed wording may be amended)
For years at both major and minor events we have incidents with people connected to a competitor . From 2017 onwards they will be under the jurisdiction off and subject to action under the racing rules. The final wording still has to be finalised but it will give the possibility that for example a parent who has been warned about their bad behaviour at an optimist event may if there is a further incident be protested and points deducted from the competitor they support.
There has also been some tidying up of the rules involving RRS 69 Gross Misconduct hearings. This is in direct response by recommendations from CAS ( Court of Arbitration for Sport) when dealing with the high profile America's Cup case that resulted in one sailor receiving a 5 year ban reduced to 18 months by CAS.
When possible the jury when dealing with a 69 issue will appoint one of their members to investigate and in essence act in the role of a prosecutor. The big difference is that he won't take part in the decision which he could have done in the past.
Bill O'Hara has been on the Racing Rules committee since 2004. Bill is a member of ISAF's working parties for RRS 42, Medal races and also for considering applications from events who want to try experimental rules. An Olympian in the Finn dinghy from 1984, Bill is an International Judge, Race Officer and Umpire.