Displaying items by tag: Lambay Island
Lamb Rescued After Cliff Fall on Lambay Island
Howth’s Irish Coast Guard unit were tasked to an unusual incident yesterday (Sunday 29 August) after a seven-month-old lamb fell off a cliff on Lambay Island.
Nicknamed ‘Lucky Louis’, the young sheep had fallen 10 metres down a cliff on the east side of the island — east of Portrane in north Co Dublin — and was trapped among the rocks at the cliff base.
Despite his ordeal, the lamb was hesitant when coastguard crew arrived and tried to hide in a nearby cave.
But he was swiftly rounded up and brought back to staff on the island with some small cuts but otherwise in good spirits.
“All’s wool that end’s wool,” the coastguard unit said.
Dead Wallaby Washes Up On North Dublin Beach
The Irish Mirror reports on the discovery of a dead wallaby on Malahide Strand in north Co Dublin earlier this week.
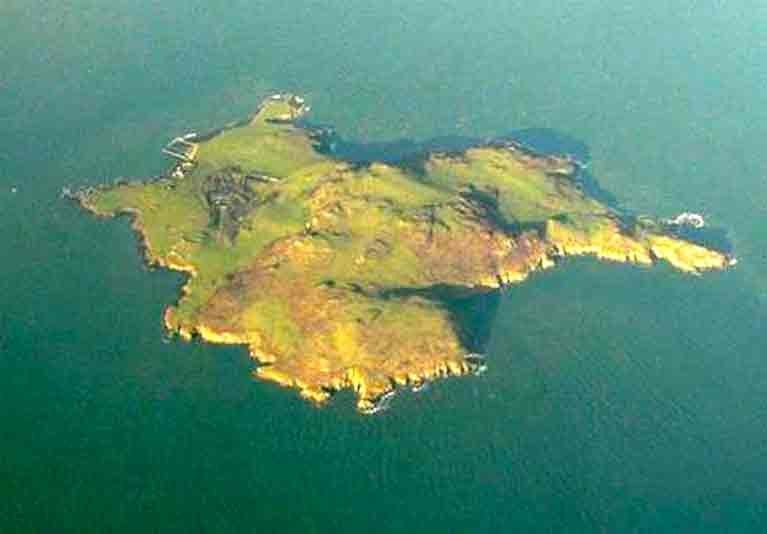
It’s believed the animal died after falling off a cliff on Lambay Island, which has had a colony of the marsupials since the 1950s.
And it’s not the only unexpected wildlife sighting in recent days.
Yesterday (Thursday 14 May) the carcass of a smooth hound shark was found just south of Malahide, in Portmarnock, which was also recently visited by a wayward octopus.
So my friend Cathy rescued an Octopus on Portmarnock Beach this morning with another gentleman. Social distancing was observed and this beautiful creature saved. It makes me more determined to protect these waters. pic.twitter.com/blM4UfPa03
— Sabrina Joyce-kemper (@kemper_sabrina) April 1, 2020
And a fisherman in Kerry was surprised to find in his nets a giant box crab, a deep-ocean species with spider-like legs that normally resides miles below the surface in the Porcupine Trough.
Fingal Rowing Club Hosts Lambay Challenge This April
#Rowing - Fingal Rowing Club will host the Inaugural Lambay Rowing Challenge on Sunday 15 April.
The 19km fundraising race from Rush Sailing Club to Lambay Island and back is open to all open water rowing vessels including but not limited to traditional wooden working boats, currachs, skiffs and Celtic longboats.
Funds raised on the day will go towards Fingal Rowing Club’s new skiff boat build.
The newly formed club says the event will be a great way to shake off those off-season cobwebs in preparation for the East Coast rowing season and longer distance races.
The challenge promises a day of fun but its not for the faint of heart and will test the crews involved, so only experienced coastal rowers need apply.
Find out more on the Facebook page for the Inaugural Lambay Challenge HERE.
Medical Emergency On Lambay Island Prompts Skerries Lifeboat Launch
#RNLI - Skerries RNLI launched yesterday evening (Sunday 22 October) after receiving reports of a medical emergency on Lambay Island.
Shortly after 8.30pm, the alarm was raised by a member of the crew when they received a call from Lambay Island, indicating that a person was unwell and requiring immediate medical assistance.
Skerries RNLI volunteers launched their Atlantic 85 inshore lifeboat Louis Simson with David Knight at the helm and crewed by Steven Johnston, JP Tanner and Jack Keane.
The lifeboat proceeded to the island where they went ashore and began to administer first aid to the casualty — as well as prep a landing area for the Dublin-based Irish Coast Guard helicopter Rescue 116, who transferred the casualty to a waiting ambulance on the mainland for treatment at Beaumont Hospital.
“There were multiple rescue agencies involved in this rescue and it’s great to see everyone working so well together,” said Skerries RNLI lifeboat press officer Gerry Canning. “Our thoughts are with the casualty tonight and we wish them a speedy recovery.”
In other rescue news, PSNI officers have been praised for their “swift action” in saving a man whose car entered Lough Neagh in the early hours of yesterday morning.
As the Belfast Telegraph reports, four officers entered the water to free the man, who was unresponsive, from the partial submerged Volkswagen. He was later transferred to hospital with suspected hypothermia.
#LambayIsland - Conor Lenihan has been revealed as a founding member of a new exclusive club "for the bold and inquisitive" based on Lambay Island, as the Sunday Independent reports.
The Lambay Club, started by members of the family that has owned the island off North Co Dublin for over a century, says it's aimed at protecting Lambay – known for its population of wild wallabies – "with a carefully shaped community of like-minded individuals" who will gather to "imagine, discuss and create".
It's understood that former junior minister Lenihan's role will be to help "shape the club and select the first founder members ... with a strong focus on diversity of age, gender and expertise."
The Sunday Independent has more on the story HERE.
Dublin Butcher's Contract For Lambay Island Beef, Lamb - And Wallaby?
#IslandNews - Lambay Island is already known for supplying beef to some of Dublin's most exclusive restaurants – but did you know it also has wallaby?
It's not just an urban myth: the lush green island off North Co Dublin, just 20km from the heart of the city, hosts a hardly mob of the marsupials among its wild grazing cattle, sheep and game.
And the lean meat from these Aussie interlopers could soon end up on plates across the capital, thanks to Dublin-based butchers M&K Meats' new 10-year exclusive deal with the island's guardians, as Business & Leadership reports.
Of course that novelty factor shouldn't distract from the quality of the succulent beef and lamb for which the island is best known.
Business & Leadership has more on the story HERE.
#hyc – Simplify the courses, make the starts more accessible, and sign up interesting boats, ideally with historical interest - those are some of W M Nixon's suggestions for stimulating sailing.
They're going back to their sailing roots in Howth. The historic Lambay Race in a fortnight's time will re-introduce the traditional direct course round the island for both the venerable Howth Seventeens, and a special class for Classics and Old Gaffers.
The annual race round Lambay has been a part of the local sailing calendar for at least 110 years. With the first known Howth regatta being staged in 1857, doubtless the island was used as a very clearcut race mark several times during the 19th Century. But it wasn't until 1899 that a Lambay trophy was finally put up by a member of the relatively new Howth Sailing Club (founded 1895), and it is 1904 before we find any reference to such a race being held.
Howth SC was a tiny club, and the earliest records of its sailing results are very sketchy. To keep the tally, they often ended up relying on inscribed trophies and the occasional newspaper reports. But trophies went missing, and with the big clubs on Dublin Bay and Cork Harbour getting any media attention going, Howth scarcely registered on the newspaper radar at all. Then with six members – or more than 10% of the active membership – killed during the Great War of 1914-18, there were other things to think of, and it isn't until the 1920s that we have anything like a clear idea of what was going on with the Lambay Race.
The way it was reported suggests that it had been a well-recognised event since the early 1900s, and the course was firmly established. Start off the pierhead (time to be taken from Findlater's clock), through the Sound leaving Ireland's Eye to starboard, then round Lambay leaving it to port, and back to the finish through the Sound, this time with Ireland's Eye to port. It's only about 16 miles in all, but it can be a course with a bit of everything.
And it was so beautifully simple - even the business of hitting the main mark of the course didn't merit disqualification as you were aground, and had more than enough problems to be going along with, without being chucked out of the race as well.
It was a format which worked well until the 1970s, when fancy notions of always having windward starts from a committee boat, with all sorts of other course permutations round laid marks, were added to the ancient mix. This new approach worked well enough for a while, as sailing numbers were increasing in any case. But the new devotion to serious racing began to stray from the old Lambay ideal of celebrating a coastline by racing round its main island.
Thus at a time when the straightforward Round Gotland Race in Sweden was building its steady rise to becoming the Baltic's most populous sailing event, and the equally straightforward Round the Island race round the Isle of Wight in the south of England was doing the same in the Solent, the much longer established Lambay Race in Ireland was straying further and further from the attractive simplicity of its original concept. Gung-ho Race Officers, obsessed with the ideal of the Olympic-style course, began setting ever-more artificial courses in which Lambay was so much reduced to being merely another mark of the course that, on one eminently forgettable occasion, the fleet didn't actually round the island at all.
My own disenchantment with the new regime came on a day of light westerly winds, when a Race Officer obsessed with fitting in a long windward leg set a Lambay Race course which also took in the Kish Lighthouse eight miles offshore. As it happened, our crew included two guys who had to be in Athlone that night by 9.30pm in order to play a weekly gig with a showband. In those pre-motorway days, just getting to Athlone was a night's work in itself. So when the breeze faded, we'd to pull out so they could get to work on time.
What could be simpler? A basic course using Lambay as the turning mark removes cockpit confusion
As it happens, the breeze filled in just enough for those still racing to complete the course minutes ahead of the absurdly late time limit of 8.0pm. With the calm in the middle, and then the better wind filling in later, the handicap placings were simply the reverse order of boat size. The smallest boat won, and as we were the second smallest boat racing, had we been able to stick at it we might have been at least second. Yet the disgruntlement wasn't directed at the demands of showband gigging in Athlone. On the contrary, the annoyance was with race officers who think that even the most traditionally fun-filled racing celebration of a beloved island and its nearby area of Irish coast should be made such a deadly serious business.
Just now and again, we need to lighten up in our sailing. By all means be vigilant in safety and in respecting the rules of the road in seafaring. But for heaven's sake just once in a while, let's race a simple course along attractive bits of coastline as much for the fun of being among other boats and sailing the sea, and the beauty of the coastline, as for the competitive sport involved.

The folk who have made it happen. Harriett Lynch on Echo's helm (left), with her father Bryan second from right. Our photo shows them last year as they were about to demonstrate to the Old Gaffers how to do it, by sailing their engine-less little boat round the Kish despite forecast of calms. This year, to celebrate Echo's Centenary, they and the rest of the Howth 17s will sail a traditional course round Lambay. Photo: Dave Owens
For this year's Lambay Race on Saturday June 7th, there's a glimmer of fresh hope. Bryan Lynch is a stalwart of the Howth 17 class. He has been involved with these attractive little boats since at least 1965, when he and his brother Mark bought Pauline, No 2. Then they were out of ownership for a little while, but soon back in together again with Echo (No 8) in 1969, and then in 1974 Bryan became Echo's sole owner as Mark had bought Eileen (No 16).
They were adventurous times for the Seventeens, as the Lynch brothers, in addition to the regular summer programme at Howth which provides the class with 60 races every year, also cruised with two of the boats to Ardglass and the Isle of Man. So although Mark has now moved on to a "plastic gaffer", the 22ft Cornish Crabber Alice, Bryan continues in the Howth 17s although these days the owner-skipper of Echo is his daughter Harriet.
Last year when the Old Gaffers were celebrating their Golden Jubilee in Dublin Bay, the Seventeens showed their mettle with the main fleet racing round The Baily to the celebrations at Poolbeg and in the Liffey, but the Lynches with Echo, together with Ian Malcolm in another Seventeen, Aura of 1898 vintage, elected to have a match race round the Kish even though the inaugural DBOGA race for the Leinster Plate, which might have raced to the Kish, was shortened to the North Burford as lighter winds were forecast.
But the two little Seventeens found enough breeze to get there and back. Ian Malcolm had brought along an outboard just in case, but Echo and her gallant crew were entirely wind-reliant, and it was the successful beginning of a buildup to this year's big celebration, which is Echo's Centenary.
She was built in Dublin by Hollwey of Ringsend in 1914, and to mark the special year, Bryan Lynch requested that for the 2014 Lambay Race, the Seventeens be sent on the traditional course which Echo will have sailed in her maiden season in 1914.
He found he was pushing on an open door. Not only have the grand fromages in Howth Yacht Club willingly agreed, but now they've leapt at the idea of having a start for classics and traditional boats over the old Lambay course as well, also starting off Howth's East Pier. The start gun for the Seventeens will be at 1130am on Saturday June 7th, and the Classic & Gaffers at 1135am, or maybe with all those bowsprits milling about, they might allow a full ten minute gap. Whatever. But who knows, there might even be enough interest for other cruisers who want more of the simple old course, to be given a gun five or ten minutes after that again.
This all means there's been a revival of interest in the Lambay Race of 1921. Thanks to an article in the annual Journal of the Humber Yawl Club for 1922, that's the earliest detailed record we have of the cruisers' section in any Lambay Race. The winner was John B Kearney's 36ft gaff yawl Ainmara, which he'd designed and built himself, while second was Pat Walsh's sweet little 25ft gaff yawl Sheila, an Albert Strange design built in Peel in the Isle of Man in 1905.
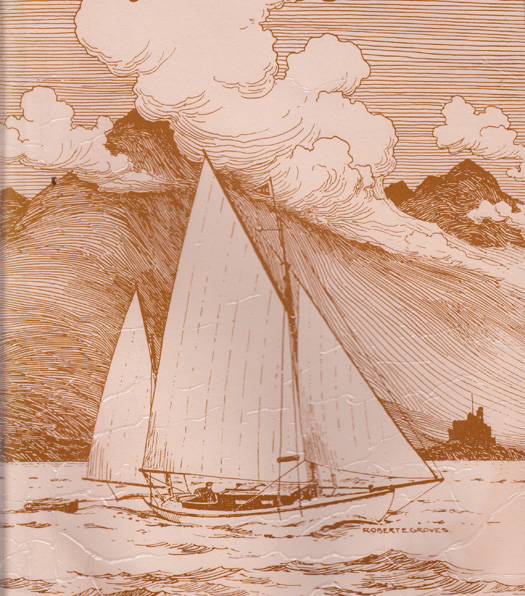

The 25ft Albert Strange-designed gaff yawl Sheila on the West Coast of Scotland in 1909 as sketched by her first owner, marine artist Robert E Groves. Sheila placed second in the Cruiser Class in the Lambay Race of 1921.
Remarkably, both boats still survive, but it is only Sheila which is still in original form. These days she's based on the River Deben in Suffolk on England's East Coast, and as it happens she has just been advertised for sale in prime condition through woodenships.co.uk at £22,000. So if you get your skates on (having won the Lotto), you just have the time to get her to Howth to race again against Ainmara on June 7th.

Sheila as she is today in Suffolk, in classic order and for sale at £22,000
Ainmara's hull today is unchanged, but though she was originally noted as a good heavy weather boat with a compact gaff yawl rig and a mainmast only 37ft 6ins long, in the 1930s she was given a massively heavy Bermudan mast. So when owner Dickie Gomes of Strangford Lough was fitting her with an alloy spar which he built himself with the help of specialist friends in the late 1960s, he moved the mast 18ins aft, as John Kearney had originally suggested when he heard – with misgivings – that the change to Bermudan was being made.
Ainmara was in Dublin Bay last year for the inaugural Leinster Plate, so she hopes to be back this year to defend it on May 31st, and then all being well she'll stay on for a week to race again round Lambay on the traditional course on June 7th. To get an idea of how she looked in 1921, this photo of her in 1967 under her first forward-located Bermudan mast is helpful if you can imagine the top third of the Bermudan mainsail removed, and visualise a gaff sail instead, set on a keel-stepped mast whose overall length was only 18 inches longer than the boat's hull LOA of 36ft.
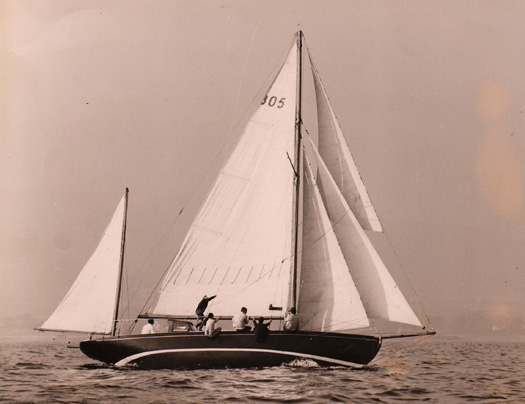

Ainmara in 1967, with the Bermudan mainmast still in the forward position. Try imagining her as gaff rigged, with the mainmast only a little bit longer than the hull. Photo: Denis Pogson
The photo also shows just how very right John B Kearney got his hull lines first time out. Ainmara is one very sweet shape. As Kearney had a fulltime and very demanding job in the engineers department in Dublin Port, his relatively few designs are of special interest, and there's always been particular interest in a design attributed to him from 1924, the 27ft straight-stem yawl Dolphin.
As even a brief study of Kearney designs reveal, he created a distinctive and yacht-like style. The 34ft yawl Sonia, which he designed for, and built with, Bill Blood Smyth in 1929 is essence of Kearney, as we can see from this photo when she was in the ownership of Pierce and Denis Purcell of Dun Laoghaire in the 1940s and '50s.
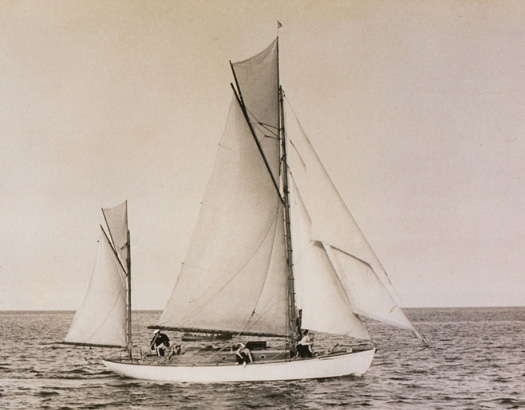

The 34ft 1929 Kearney yawl Sonia (now based in Vancouver) in the ownership of Pierce & Denis Purcell of Dun Laoghaire in the 1940s and '50s, bearing off to oblige the photographer, and showing a remarkably labour-intensive rig with a jib topsail, a topsail on the mizzen, and a topsail on the main. There'd be a mizzen staysail as well, in addition to a spinnaker....... Photo courtesy Pierce Purcell Jnr.
Yet the few written records and folk memories confidently assert that Dolphin is a Kearney design. I can remember her so well from many years around Strangford and Belfast Lough in the ownership of the great Davy Steadman, who once cruised her right round the southern half of Ireland, and then returned as planned through the Shannon and the Grand Canal, no problem as she was shoal daft and had her mainmast in a tabernacle.
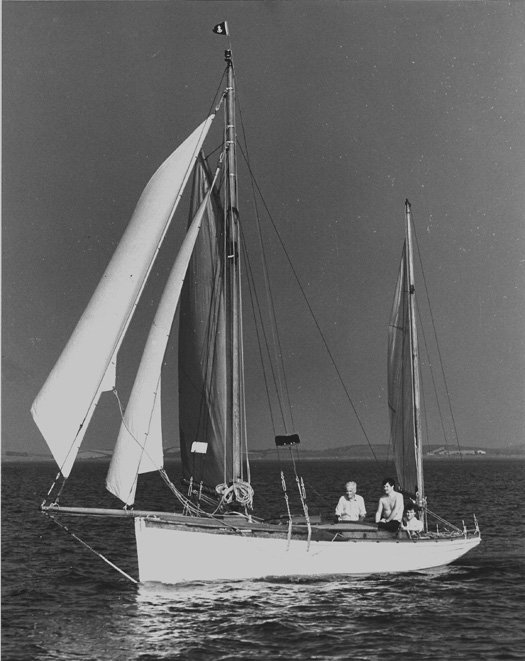

Dolphin on Strangford Lough during Davy Steadman's long and happy ownership. Photo: Ann Clementson
The answer to Dolphin's origins came in a real lightbulb moment at the final winter meeting of the DBOGA in Poolbeg Y&BC in March. You never know what's going to come up at these Gaffer gatherings. For instance, I now know in considerable and entertaining detail just why the Castletownbere lifeboat is called the RNLB Annette Hutton, thanks to DBOGA President Tim Magennis having to give us a brilliant impromptu talk when a scheduled speaker failed to show.
At the concluding meeting this Spring, the magic moment came at the end when Cormac Louth suddenly stood up and made an impassioned plea for any memorabilia of any kind at all relating to the fact that between 1818 and the outbreak of the Great War in 1914, there were very strong links between the old fishing community of Ringsend and the great fishing port of Brixham on the south coast of Devon. They were links so strong that today there are many people in Ringsend with Devon surnames, yet there is now virtually no contact between Dublin's most ancient maritime community and the "home port" in southwest England.
It's the sort of nugget of information you squirrel away to examine in detail later. But the lightbulb moment was the sudden realisation that, thanks to the Brixham link, Dolphin might indeed be a John B Kearney design. It's perfectly possible that in 1924 someone asked him to create the plans for a little clinker built cruising yacht whose lines would faithfully reflect the shape of the classic Brixham trawlers, which they'd known in Ringsend for nearly a hundred years.

A unique mix of Kearney designs in Donaghadee in 1966. On the left is Perry Greer's 1963-built 54ft Helen of Howth, John Kearney's last and largest design. At mid-harbour is the 36ft Ainmara (1912), his first yacht. And on the right is the 27ft Dolphin (1924), which seems to have been inspired by the classic form of the Brixham trawler. Photo: W M Nixon
Once the Napoleonic Wars ended in 1815, the men of Brixham could start expanding their fishing ambitions, and their increasingly superior boats out-performed most other ports, with the Brixham influence spreading as far east as Ramsgate in Kent, and as far west as Ringsend in Dublin.
With the technological developments accelerated by the World War I, sailing fishing boats were being rapidly replaced by steam and then diesel, but by this time the Brixham vessels had reached an exceptional standard. As big class yachting slowly revived after the war, the regatta circuit made its annual visit to Torquay just across the bay from Brixham. When the skippers of the giant cutters said they couldn't race in the strong winds prevailing as their rigs would become dangerous, the Brixham trawlers contemptuously went forth in full array to show their class, and the Brixham Trawler Regatta came into being.
But with the disruption of the Great War followed by the War of Independence, Ireland's links to Brixham had faded, yet for many in Ringsend, the Brixham trawler remained the ideal, for they were handsome yet able boats. And this gave me another magic moment on a recent Saturday evening in Bridie Keating's pub at Derrynane in far southwest Kerry.
There on the wall, amidst photos of local sailors including Damian Foxall, is an ancient colour photo of the Brixham Trawler Provident. For many years, she was owned by the co-operative known as the Island Cruising Club of Salcombe in Devon, and for most of its members, an annual cruise fetching up in the sublime anchorage of Derrynane, with a spot of conviviality ashore in Bridie's, was what life was all about.
Provident was built in 1924, and so too was Dolphin, and their hull resemblance is startling. Yet it's doubtful if the two boats have ever been together, and it's now unlikely if they ever will be. The last I saw of Dolphin was two years ago in a corner of a little old boatyard near Monkstown on Cork Harbour. Back in 2012, she could maybe have been saved, though only with enormous expense and effort. But it's unlikely that could be done now, yet if she still exists at all, it might be worthwhile to take off her lines.

A sad sight. Dolphin in 2012. Photo: W M Nixon

Although clinker construction poses special preservation problems, much of Dolphin's timber seemed in surprisingly good order despite years of exposure and neglect. Photo: W M Nixon
However, the news on the 70ft Provident is good. She's in fine shape after a recent major refit for owners Trinity Sailing Trust, and is based back home in Brixham, the very essence of what a first class Brixham sailing trawler was and is all about.
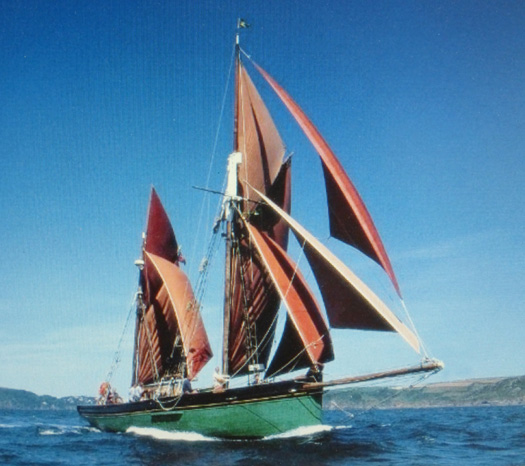

Provident in all her glory. Owners Trinity Sailing Trust have recently given this historic Brixham-based vessel a complete refit.
Lambay to Rush Swim For a Good Cause
Darragh Coffey will be among a group of hardy souls who are set to swim unaided from Lambay Island to Rush Harbour - all for a good cause.
The group will be covering the 4.5km of open sea in aid of kidney research at Beaumont Hospital.
Darragh and his colleages have already received a number of donations via bank transfer and the old reliable sponsorship card.
Anyone else interested in making a contribution can contact Darragh at [email protected] for details.
Lecture: Dublin’s Own Titanic-The 'Tayleur'
The venue and is the Dún Laoghaire College of Further Education on Cumberland Street where a lecture series programme is run by the Genealogical Society of Ireland (GSI). For further information on other forthcoming GSI lectures: www.familyhistory.ie/




































































