Displaying items by tag: Guidance Notes
Dublin Port Company
Dublin Port Company
Dublin Port, the largest port in Ireland, is situated in the heart of Ireland's vibrant capital city. Dublin Port Company's mission is to facilitate the flow of goods, passengers and information through the port.
Dublin Port, as an organisation, has a long and remarkable history, dating back 300 years from 1707 to 2007. There have been many famous moments and famous visitors in that time Captain William Bligh's (of 'Mutiny on the Bounty' fame) involvement in the Port in 1800 has left a lasting legacy.
Bligh conducted a study of the tidal flows in Dublin Bay, which led to the construction of the Great South Wall. This construction has resulted in the formation of the present Bull Island, which did not exist in 1800.
Another famous person, involved in the development of the Port was the famous Port engineer Bindon Blood Stoney. He designed the diving bell now located on Sir John Rogerson's Quay, which was used in the construction of the North Wall Extension. (Pictured: sugar storage at Custom House Docks).

Dublin Bay Guidance Notes for Leisure Craft
For all recreational craft using Dublin Port and Bay, compiled by Dublin Port Company in consultation with local yacht and boat clubs
Facts to bear in mind:
1. As both the number of large commercial ships and recreational craft using Dublin Port is increasing it is essential that close quarter situations do not arise.
2. Commercial vessels using Dublin Port or Dun Laoghaire Port normally have a qualified pilot or certified master with proven local knowledge on board. They 'listen out' on VHF channel 12 when in Dublin Port’s jurisdiction.
3. Commercial vessels will follow the routes designated in the attached illustration. All recreational craft when obliged to navigate within such areas should do so with extreme caution following the Int. Collisions Regulations.
4. Large conventional commercial craft travel at a manoeuvering speeds of between 8 to 15 knots whilst within the ports jurisdiction. The lower limit varies from ship to ship and is 'as safe navigation permits'.
5. Ships will be traveling faster than you may estimate, even in congested waters.
6. Ships that are light or partially loaded, particularly in windy conditions, will require a higher minimum speed to remain under full control.
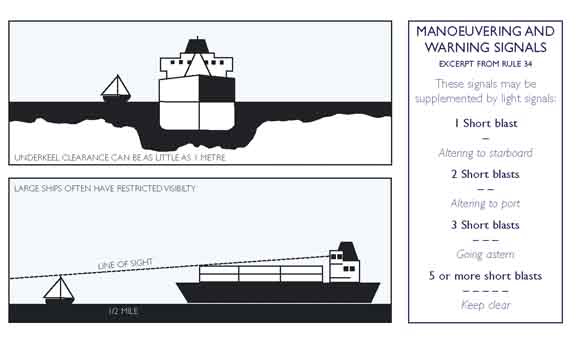
7. A large ship visible on the horizon may take no more than 10 minutes to reach you under clear conditions, under hazy conditions this time could be much less. At 10 knots a ship will travel a nautical mile in 6 minutes, at 15 knots it takes only 4 minutes to travel one nautical mile.
8. A large deep draught ship cannot easily avoid small craft in a narrow channel. It is up to leisure craft to keep clear (see Rule 9 Int. Collision Regs excerpt at end of this page).
9. A ship slowing down does not steer very well. It requires the action of its propeller to respond. When the propellor is going 'astern' the ship’s steering will be adversely affected.
10. As well as large cargo ships, a variety of working craft also use the port, tugs, pilot cutters, dredgers, fast ferries, barges under tow etc. In particular a towing line may be partly submerged and therefore potentially dangerous to other craft passing too close.
What should you do?
1. Avoid sailing in the buoyed channel area, avoid sailing within 0.5 nautical mile of the Dublin Bay buoy and in the separation schemes, (see illustration). This is especially critical in periods of reduced visibility. When obliged to cross the fairway, cross at right angles to the traffic flow. Also obey rule 9 of the Collision Regulations by either keeping to the starboard side of the channel or if the water depth allows outside the buoyed channel.
2. Keep a good lookout. Be aware of all ship movements, especially astern of you.
3. Do not underestimate the speed of ships. Allow plenty of time to take effective evasive action in the vicinity of large ships.
4. Be visible. At night make sure your navigation lights can be clearly seen. If you see the navigation lights of a vessel approaching and you think that he has not seen you, get out of the way. Also use a torch or search-light to illuminate the sails (if appropriate). Remember (as indicated in the attached illustration), from the bridge of a loaded container ship or large tanker the captain/pilot may lose sight of you a half a nautical mile ahead, although you can see that ship clearly from your vessel at all times.
5. Keep watch at night. You may have difficulty seeing a large ship approach, even on a clear night. In reduced visibility you may have little warning of its approach. If you see a black shadow against shore lights or as a growing shadow, at that point a close quarter situation is already imminent. Remember you cannot be easily seen at night (particularly in a background of lights) and judging distances at night can prove difficult.
6. Watch the ships navigation lights. If you see both ships sidelights you are dead ahead, follow the Int. Collision Regs. and any alteration of course should be early, substantial and be visible to the approaching ship. Be aware that ships alter course at the Dublin Bay buoy and No.3/No.4 buoys. Be aware of your position and the position of other vessels around you at all times.
7. Know the whistle signals (see illustration). Five or more short and rapid blasts on the ships whistle indicates the ship is in doubt about your action or the lack thereof. Check immediately if this signal was meant for you, if so take immediate and appropriate action. Three short blasts means 'my engines are going astern' one short blast means 'I am altering my course to starboard'. Two short blasts "I am altering my course to port".
8. Keep your VHF tuned to channel 12 the port working frequency, and have the volume high enough to hear above the noise of the engine. Listen for traffic information from Dublin Port V.T.S. Only if you are the controlling vessel in a flotilla of other vessels, and you observe a hazardous situation developing, or in the event of an emergency developing within the ports jurisdiction, you should transmit on VHF channel 12.
Remember CH 12 is Dublin Port’s primary working channel and used to manage port traffic. No private or unneccessary communications to take place on this channel.
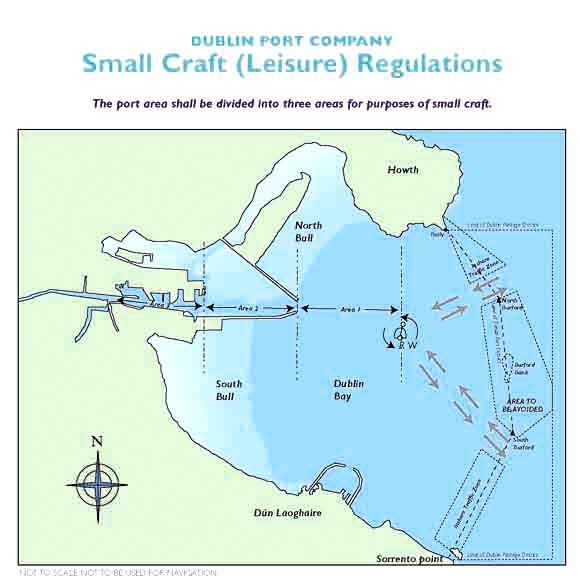
Area 1 - from Dublin Bay Buoy to Poolbeg Lighthouse
Small craft shall not navigate inside the fairway and should remain outside the line of buoys. If it is necessary to cross the fairway, crossing should be at right angles.
Area 2 - Poolbeg Lighthouse to No. 14 Buoy
Small craft shall comply with the International Regulations for Prevention of Collisions at Sea and shall keep as near to the outer limit of the channel which lies on her starboard side as is safe and practicable. Rule 9 does not apply outside the channel and craft may pass outside the buoys when and where it is safe to do so. If it is necessary to cross the channel, e.g. to enter area 3, crossing should be at right angles, at a position abeam of the ESB Jetty (Berth 48).
Area 3 - No. 14 Buoy to the west
All small craft should pass along the south side of the channel, remaining as far as is practicable to that side.
General
All craft shall operate under power when within areas 2 and 3, but may additionally raise their sails outside the channel but not in the channel.
1. No sailing in the channel, craft should only cross at right angles when it is safe to do so.
2. Maintain a listening watch on channel VHF 12 and avoid unnecessary communication.
Keep a sharp lookout and keep clear of all shipping.
Attention of all skippers is drawn to the annual Notice to Mariners No. 7 concerning small craft.
Capt. David T. Dignam, Harbour Master. 31st March 2006
Collision Avoiding Check List
Avoid the busy shipping channels and routes. Cross them at right angles and as quickly as possible after checking that it is safe to do so. Recreational users of the port area are particularly requested to be familiar with the Int. Collision Regulations (particularly Rule 9), Dublin Port Bye Laws, Small Craft (Leisure) Regulations (see chartlet) and Local Notices to Mariners (particularly No.7). Information is also available on the Dublin Port web site, www. dublinport.ie
Remember:
• Keep a good lookout, particularly at night
• Do not under-estimate the speed of ships
• Be visible
• Watch the lights of other vessels
• Know the whistle signals
• Keep your VHF tuned to channel 12
• Obey any instructions given by Dublin Port VTS. They are also interested in your safety.
International Regulations for the Prevention of Collisions at Sea
Rule 9 - Narrow Channels (Excerpt)
(a) A vessel proceeding along the course of a narrow channel or fairway shall keep as near to the outer limit of the channel or fairway, which lies on her starboard side as, is safe and practicable
(b) A vessel of less than 20 metres in length or a sailing vessel shall not impede the passage of a vessel which can safely navigate only within a narrow channel or fairway.
(c) A vessel engaged in fishing shall not impede the passage of any other vessel navigating within a narrow channel or fairway.
(d) A vessel shall not cross a narrow channel or fairway if such crossing impedes the passage of a vessel which can safely navigate only within such channel or fairway. The latter vessel may use the sound signal prescribed in Rule 34(d) or in doubt as to the intention of the crossing vessel.
Rule 10 – Traffic Separation Schemes (Excerpt)
(i) A vessel of less than 20 metres in length or a sailing vessel shall not impede the safe passage of a power-driven vessel following a traffic lane.
Dublin Port Company Port Centre, Alexandra Road, Dublin 1
Tel: 353 1 887 6000, Email: [email protected], fax 353 1 855 7400





























































