Displaying items by tag: Royal Canal
Waterways Ireland advises boaters on the Royal Canal that there will be restrictions to navigation in the Castleknock area west of Lock 12 from next Monday 18 May until Friday 29 May.
This is for previously notified site investigation works on the waterway that were delayed due to Covid-19 restrictions.
A pontoon is being used as part of works west of Lock 12 towards Coolmine, and while it is in place other craft will be unable to pass.
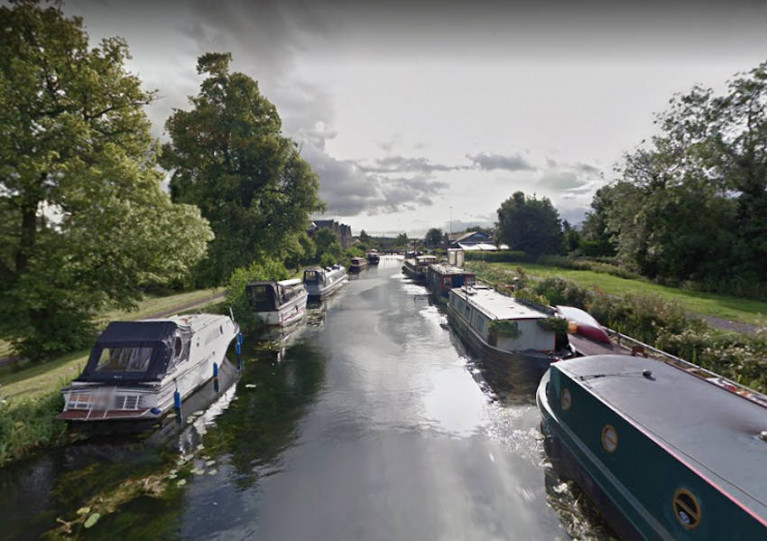
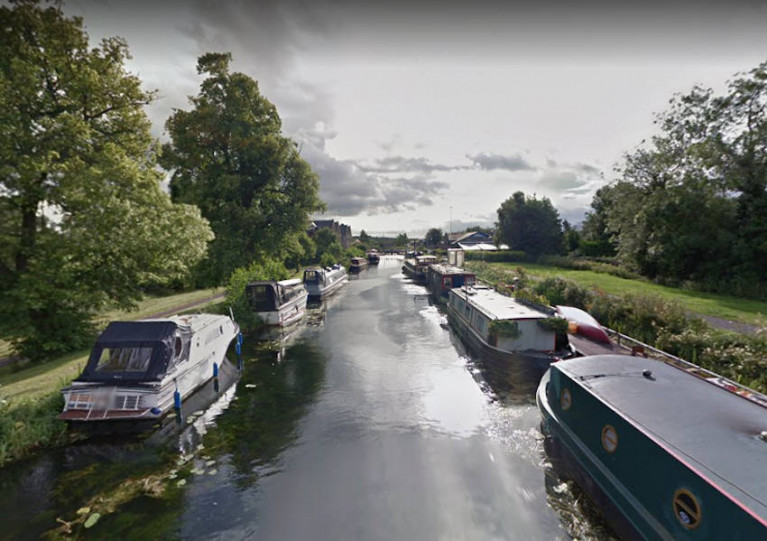
For those of you missing Ireland’s inland waterways, you can now view the stunning Royal Canal, Grand Canal Barrow Line and Barrow Navigation along with the Shannon through Google Maps and Google Earth.
Waterways Ireland, in partnership with the Google Trekker Loan Programme, has continued to capture Ireland’s inland waterways and make them accessible online.
Last year, street view imagery was captured along the Royal Canal, Grand Canal Barrow Line and Barrow Navigation to compliment the stunning Shannon imagery captured in 2018.
So now you can follow some of Ireland’s most beautiful and popular waterways destinations from the comfort of your own home — and hopefully plan a visit when conditions allow.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, winter mooring has been extended until Sunday 31 May to ease the pressure on the inland boating community amid the current coronavirus restrictions.
And while the outdoor exercise distance has been extended to 5k from home, the advice for those using canal towpaths to maintain social distancing remains in place.
Waterways Ireland Suspends All Passage In & Out Of Dublin On Royal & Grand Canals Until Further Notice
Waterways Ireland has issued notice to masters and owners of vessels that boat passage into or out of Dublin on the Grand Canal and Royal Canal will be postponed until further notice.
This postponement also applies to bookings for Newcomen Bridge passage on the Royal Canal.
The cross-border body for Ireland’s inland waterways adds that navigations elsewhere are generally remaining open for boats.
Albert Lock and the Jamestown Canal on the Shannon Navigation recently reopened after lock gate replacement works and the easing of flooding issues.
Details On Canal Passage In & Out Of Dublin For 2020
Waterways Ireland reminds masters and owners of boat passage arrangements in or out of Dublin on the Royal and Grand Canals ahead of the start of the 2020 boating season in mid-March.
Movements in or out of the city via the waterways will be organised by prior arrangement, to take place as a single movement in one day.
Boaters will only be facilitated if their passage is considered to be safe by Waterways Ireland and they have the valid permit(s) for mooring and passage.
In order to plan the necessary lock assistance for movements east of Lock 12 on either canal, masters are required to contact the Waterways Ireland Eastern Regional Office (weekdays 9.30am to 4.30pm) on 01 868 0148 or email [email protected] prior to making passage.
At time of making contact, the following details should be provided:
- Length, beam, water & air drafts of your craft (provide approximates if don't have exact dimensions)
- Phone/email contact details
- Permit number and expiry date of current canal permit
On the Grand Canal, a minimum of two days’ notice prior to planned passage must be given and, with the exception of pre-arranged events, a maximum of two boats per day will be taken through the locks, travelling either east or west. In certain circumstances, eg for slower or larger barges, the limit will be one boat per day.
Due to periodic anti-social activity along some of canal route into Dublin, boat passage will also not be possible in certain weather conditions and at weekends over the late spring and summer period. This can be planned for at time of making contact, and suitable arrangements for passage made.
On the Royal Canal, two weeks’ notice of bridge passage (Newcomen Lifting Bridge) is required for the pre-set lift date, and lock assistance will then also be arranged. A minimum of two boats is required for a bridge lift to go ahead. A maximum number of boats passing will be implemented, 16 for weekend lifts and eight for weekday lifts. Priority will be given on a first come, first served basis.
The pre-set lift dates and times are set out below:
- Thursday 16 April, 11am–1pm
- Sunday 3 May, 9am–1pm
- Saturday 30 May, 9am–1pm
- Thursday 11 June, 11am–1pm
- Friday 26 June, 11am–1pm
- Tuesday 28 July, 11am–1pm
- Tuesday 25 August, 11am–1pm
- Thursday 24 September, 11am–1pm
Masters and owners are also reminded to ensure that they have the following before making the passage through the city locks on both canals. Waterways Ireland reserves the right to postpone passage to another day if all of these are not in place:
- Adequate fuel on board
- Competent and adequate crew to operate the boat and locks (minimum crew of 3)
- A lock key on board their boat
- Mooring lines of adequate length to handle vessel through a lock (approx 15m length)
- No known mechanical problems with their boat
Passages can only be arranged in the boating season from mid-March to end of October. Also note that aquatic weed is generally more prevalent as the season progresses beyond Spring and may hamper passage.
Boaters will be facilitated as far as practicable although Waterways Ireland cannot guarantee that passage will be possible on every planned date. Early contact will greatly assist planning and facilitate the making of the necessary arrangements.
Waterways Ireland Warns Of Reported Leptospirosis On Royal Canal
Waterways Ireland have been notified by the HSE of a number of cases of Leptospirosis reported recently following exposure to the water on the Royal Canal in North Dublin.
Individuals are instructed not to engage in swimming, diving or immersive activity such as deliberate capsizing in the waterway pending further advisory.
Any facilities/activity providers are also requested to ensure, to the best of their ability, that clients do not engage in the same activities.
The HSE further advises all individuals partaking in watersport (and in turn for activity providers to advise their clients) of the risk, which is small but real, of acquiring Leptospirosis from water-based activities.
Persons with symptoms (a flu-like illness) within a three-week period after engaging in a water-based activity should seek medical attention immediately, mentioning any watercourse exposure.
Further information on Leptospirosis is available from the HSE website. Other enquiries can be directed to [email protected] or by contacting the Waterways Ireland Communications Office on 071-9650787.
What is Leptospirosis?
Leptospirosis is a bacterial infection frequently found both in domestic and wild animals, which can spread to humans. Leptospirosis in Ireland is usually picked up from rats. The infection is spread through contact with rats, or rat urine generally.
Leptospirosis is a recreational hazard for those who participate in outdoor sports in contaminated areas and has been associated with water sports.
Occupations at risk would include veterinary surgeons, farmers, meat inspectors, butchers, abattoir and sewer workers.
High-risk water includes stagnant, dirty-looking or obviously polluted fresh water found in ditches, drains, ponds, lakes or rivers. Sea water poses less risk.
What precautions should I take?
- Do not go swimming or boating in water which is known to be or obviously polluted.
- Cover any cuts or abrasions with a waterproof dressing while swimming or canoeing.
- Shower thoroughly as soon as possible following water activities.
- Make sure the sporting clothing you wear minimises your contact with water.
- Wash your hands after water activity, handling any animal or contaminated clothing and always before eating, drinking or smoking.
- Clean any cuts acquired during swimming, fishing or other near-water activities. Apply first aid as soon as possible.
Rinsing dogs who have been swimming in high risk water reduces the risk of infection. - High-risk workers should always wear their personal protective equipment and clothing at all times when in high risk situations.
- If you get a flu-like illness within a three-week period after engaging in any of these activities you should visit your doctor immediately, and tell her or him of your concerns and possible exposure to dirty or stagnant water.
€1m Funding Package Announced For Royal Canal Greenway's Second Phase
Minister Kevin ‘Boxer’ Moran TD announced midweek a significant package of funding totalling €1m for Phase 2 of the Royal Canal Greenway.
When launched in early 2020, it will be the longest greenway in Ireland, totalling 130km in length along the inland waterway connecting Maynooth in Co Kildare with Clondara in Co Longford.
The funding will be provided from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport Budget 2020 allocation for greenways.
The Royal Canal Greenway is a dedicated off-road cycling and walking route which is currently being developed by Waterways Ireland and the local authorities of Kildare, Meath, Westmeath and Longford using the existing towpath along the Royal Canal.
The funding will be used to complete the basic infrastructure to ensure the delivery of a greenway that is "fully functional, animated and activated to reach international trail standards".
Minister Moran said: “I warmly welcome this funding from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport which will be used to complete and enhance this wonderful amenity for the midlands.
"This co-operation between department, local authorities, Waterways Ireland and all of the groups connected with the greenway exemplifies what can be achieved and I look forward to good progress being made in realising this significant goal.
"Once completed, this greenway will connect Dublin to Longford, adding substantially to the existing network of greenways throughout the country. I have no doubt that visitors from home and abroad will enjoy this top-class experience and that it will motivate those interested in cycling and walking in this beautiful countryside to come and visit and see it first-hand.”
For more about the status of the Royal Canal Greenway developments see waterwaysireland.org/royalcanalstatus
Inland Fisheries Ireland (IFI) says it has confirmed a significant fish kill on the Royal Canal in Kilcock, Co Kildare earlier this week.
A report was received on Monday 1 July from Waterways Ireland of the fish kill, which has claimed some 300 fish of various species including roach, rudd, bream and pike.
The investigation, which commenced immediately and remains ongoing, has identified agricultural discharge to a River Ryewater feeder that enters the canal at Kilcock.
IFI says work is now ongoing to ensure that there is no further polluting discharge to the system from this location.
It has also has issued a fresh appeal to farmers to remain vigilant in avoiding water pollution during the summer months when harvesting silage and spreading slurry.
Silage effluent is a significant pollutant and if allowed to enter a waterway can potentially lead to fish death and habitat degradation.
IFI has a confidential hotline number at 1890 34 74 24 or 1890 FISH 24 for the public to report incidents of water pollution, fish kills and illegal fishing. For more visit fisheriesireland.ie.
Waterways Ireland has issued Marine Notices related to a number of events taking place on Ireland’s inland waterways this weekend.
On the Royal Canal, a Junior Canoe Polo Competition will take place at Kilcock Harbour from 10am to 6pm tomorrow, Saturday 22 June.
Passage will be possible between 1pm and 2pm. Masters of other craft are requested to proceed at slow speed and with minimum wash and note any directions issued by the stewards.
On the Shannon-Erne Waterway, masters and owners of vessels are advised that they may experience short-term delays between Lock 1 at Corraquill and Ballyconnell Marina between 1pm and 6.30pm tomorrow due to the waterway’s 25th anniversary event.
Masters are requested to proceed at slow speed and heed any instructions issued by the event marshals.
Elsewhere on the River Shannon, the swimming element of a triathlon event will take place in Tarmonbarry on Sunday 23 June between 9.30am and noon.
Tarmonbarry lock will be closed to traffic during this time, and the N5 Shannon lifting bridge will also be closed, requiring large airdraft vessels to berth north of the bridge for the period.
A children’s swimming event will take place at 6pm on Saturday in Tarmonbarry, but this will not affect vessels in the navigation.
Masters are requested to proceed at slow speed and with minimum wash when approaching this section of the river and heed any instructions issued by the event marshals.
Meanwhile, on Upper Lough Erne, masters and owners of vessels are advised that dredging works are due to commence at Kilmore Quay on Monday 1 July and last for approximately nine weeks.
The map below shows the area to be dredged and the route the vessels will be taking in order to bottom-dump the material.
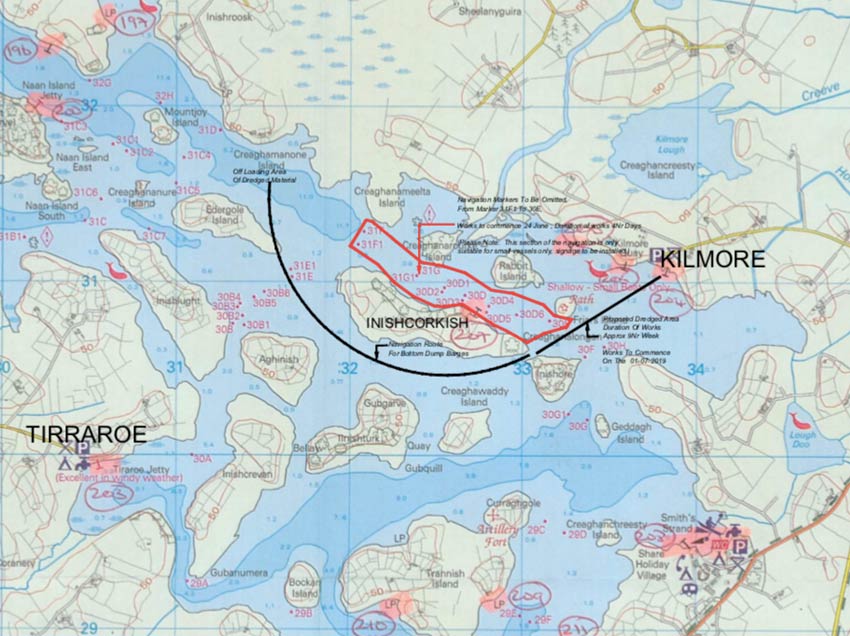
Masters of vessel are requested to proceed with additional caution in the vicinity of the dredging operations and dredging vessels.
Waterways Ireland thanks its customers for their co-operation in this and all other matters.
Tributes Paid On Death Of Royal Canal Campaigner Ian Bath
Shannonside FM reports that veteran inland waterways campaigner Dr Ian Bath has died aged 90.
Beginning in the 1970s, Dr Bath led the charge to revive the Royal Canal between Dublin and the River Shannon as a tourism amenity.
Through the efforts of Dr Bath and other volunteers in the Royal Canal Amenity Group, 74km of the waterway between Blanchardstown and Mullingar were reopened to navigation by 1990.
And another 20 years on, in October 2010, some months after Dr Bath’s history of the canal with Ruth Delany was published, the full length of the canal from the Shannon to the Liffey was officially reopened — an achievement for which Dr Bath was recognised with Afloat’s Sailor of the Month award for December 2010.
Shannonside FM has more on the story HERE.
Appeal For Sightings Of Invasive Coypu On Royal Canal In Dublin
Waterways Ireland advises all users of sightings on the Royal Canal at Ashtown of a large invasive rodent species that is highly damaging to river, lake and canal banks.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, the coypu — also known as the nutria in the United States — is regarded as a destructive invasive species and pest, posing a threat to agriculture, the stability of river banks and even coastal defences.
The coypu is an EU-regulated species of concern with trade, transport and reproduction restrictions in place (No.1143/2014).
The large river rats can also carry a number of serious diseases communicable to humans and domestic animals.
Waterways Ireland says coypu eradication programmes can cost up to several millions of euro and are not always successful.
Most recently there were sightings of the rodents in Cork city two years ago, after a number were trapped by the National Parks and Wildlife Service (NPWS) in a tributary of the River Lee.
But their presence across the country in the capital raises concerns about their further spread throughout Ireland’s inland waterways.
Waterways Ireland has provided a checklist for how to spot a coypu, which are often confused with common otters:
- Large semi-aquatic rodent up to 1 meter in head to tail length. Features same in juveniles.
- It can weigh 5-9kg.
- It has webbed hind feet.
- Dark fur often with lighter ends and has a white muzzle.
- Has long cylindrical tail (not fur tail like otter) and small slightly protruding ears.
- Distinctive features are large bright orange-yellow incisor (front) teeth usually visible.
- Coypu are generally found near permanent water.
Do not attempt to engage, trap or harm these animals.
Waterways Ireland appeals for the public keep a lookout along the waterways and especially along the Royal Canal at Ashtown, and report sightings (with photos is possible) to any of the following:
- Waterways Ireland Environment Section 061-922141
- NPWS at [email protected] or your local NPWS ranger with details of location/date and a photo if available
- [email protected]
- records.biodiversityireland.ie
For more information visit species.biodiversityireland.ie.






































































