Displaying items by tag: Bremore Port
Marine Leisure Facilities Will Be Included in Bremore Port
Marine leisure facilities will be included, including the possibility of a new marina on the north-east coast, because there is room for one in the Bremore Port development at Drogheda.
Dr. Joe Hiney, a director at Bremore Port and an international port consultant, says this is an exciting prospect for sailing and boating users and the general public.
The intention is to create a facility providing facilities in an area of the coastline which can be opened up to this marine sector.
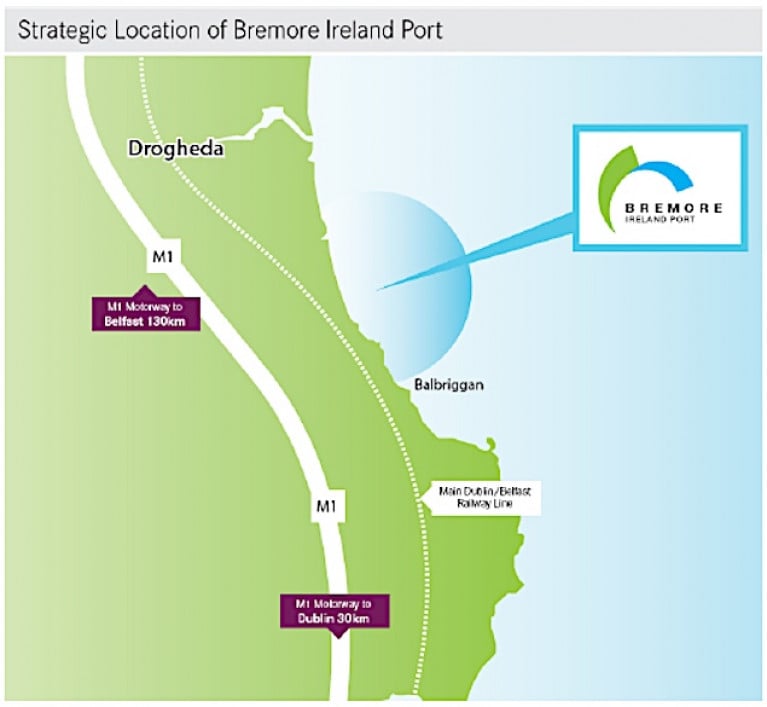
 The location of Bremore Port development on the Drogheda coast
The location of Bremore Port development on the Drogheda coast
On the December edition of the Maritime Ireland Podcast, he outlined what is being considered.
Podcast below
Bremore Plans to be Ireland's Leading Deepwater Energy Port
Bremore Ireland Port has unveiled its vision for what it says “will become the first new deepwater port development since the foundation of the Irish State.”
The ‘Vision for Bremore Ireland Port’ developed by Henning Larsen,’ a leading global architecture firm, proposes “a world-class deep-water multi-modal energy port that will transform Ireland's energy landscape and aims to create a new Innovation District in Co. Meath.”
“Bremore Ireland Port's location on the Dublin-Belfast economic corridor, deepwater, and existing intermodal connections on the M1 and Dublin-Belfast rail line play a pivotal role in establishing it as a centre of growth both nationally and locally,” Paul Fleming, Drogheda Port Company, said at the launch of the plan.”The Innovation District will be a space where urban development and cutting-edge technology converge and is designed to foster economic growth, facilitate research and development, develop a new university hub, and provide new residential areas with essential community services.”
Bremore Ireland Port’s strategic focus initially is on the offshore wind sector, with the port to be equipped with purpose-built infrastructure, including specialised quays for wind turbine assembly and facilities for bulk, break-bulk and ferries. Bremore Ireland Port will also support Ireland’s National Hydrogen Strategy objectives as it will be equipped to convert offshore wind energy to green hydrogen energy.
The Bremore Ireland Port project, reinitiated in 2019, is to present a detailed planning application by 2026/2027, following public consultation, to get the views of the local community and stakeholders.
Initial berths are projected to be functional between 2028-2030, following planning decisions. The project's phasing is comprehensive, spanning a number of years, and the foremost phase emphasises offshore wind and bulk/break-bulk cargo. Economic and commercial forecasts by Black Quay Maritime Consulting and EY suggest market potential exists for Bremore Ireland Port to become one of Ireland’s largest ports. The forecasts also have shown that Bremore Ireland Port has the potential to generate significant commercial revenues and economic benefits for the local region and nationally.
Minister Darragh O’Brien, Minister for Housing, Local Government and Heritage, has welcomed the plan. “The Government recognised the significance of Bremore Ireland Port in the port policy statement issued in December 2021 as one of several ports that are needed to deliver Ireland’s renewable energy objectives. I'm optimistic about Bremore Ireland Port’s potential impact on decarbonisation, energy security, job and housing creation and industrial opportunities, particularly along the Dublin-Belfast Economic Corridor of Louth, Meath and Fingal.”
Paul Fleming, CEO of Drogheda Port Company, says Bremore will “become Ireland’s leading deepwater energy port with world-class facilities capable of assembling offshore wind turbines, producing green hydrogen, and distributing eco-friendly fuels in the first development phase, including bulk, break-bulk and ferry facilities. We also aim to develop an Innovation District, which will bring together light manufacturing, urban production, R&D offices, community services, residential areas, and a dynamic university hub.”
The development of Bremore and its development in relation to Dublin Port has been a controversial topic for some years.
Plans for a deepwater port at Bremore in Co Louth are to be unveiled by Drogheda Port Company and a private developer next week.
Ronan Group Real Estate is participating in a joint venture at Bremore with Drogheda Port Company.
“Bremore Ireland Port aims to deliver new port capacity and advance the shift to a green energy economy to support Ireland’s climate action and hydrogen strategy objectives,” they state.
Architecture firm Henning Larsen will present the plan at an event in Dublin on October 11th, which will include a speech by Minister for Housing and Local Government Darragh O’Brien.
Drogheda Port Company chief executive Paul Fleming and Ronan Group Real Estate chief executive Rory Williams will also speak at the invitation-only event.
Project Planners Sought in Tender for Proposed Bremore Port
The Irish Independent reports that a proposed new port for the East Coast has taken another step closer to fruition with the launch of a tender for the team to plan the project.
As previously reported on Afloat.ie, Drogheda Port Company is the driving force behind the Bremore Port proposals at a site in Co Meath just north of Balbriggan in Co Dublin.
The new port is set to be one of the largest national infrastructure projects in recent years, and is being touted as driving “green innovation to support Ireland’s climate action targets”.
Open until noon next Friday 10 September, the tender “seeks to establish a single party framework agreement to provide civil and structural engineering consultancy services for the development of a new port on the north of Bremore Head”.
The Irish Independent has more on the story HERE.
New International Feasibility Studies Institute in Ireland Will Focus On The Growing Maritime Sector
A secretive organisation known as SFA (the Studying Feasibility Alliance) is working behind the scenes to encourage the establishment of a professional body for one of the fastest-growing business sectors in the marine and other spheres in Ireland, the lucrative world of Feasibility Studies.
It's surprising that, so far as is known, there is still no Feasibility Studies Institute in Ireland, north or south. For many decades - and particularly since the Troubles of 1969-1998 began to break out in the late 1960s - if it was felt that if an identifiable socio-economic or infrastructural problem was seen as contributing to the difficulties of the situation – both in the north and cross-border - a budget would be allocated to plan a solution, and a substantial part of that budget would be set aside for the completion of at least one Feasibility Study before going any further.
As it was realised how complex such studies could become, it sometimes became necessary to commission Feasibility Studies into how many different Feasibility Studies would be required in order to validate some major project. And in most cases, the authorities quietly hoped that in due course, the only industry to make a clearcut profit would be in architecture and construction to create appropriate archive storehouses, places where the numerous Feasibility Studies could gather dust in peace.
But despite the fact that many professional partnerships and university departments in several disciplines have made good money out of the public purse and international philanthropic funds in these ultimately intangible researches - with several individuals enjoying a glittering career in feasibility analysis – the sector has remained fragmented.
Thus it's difficult to escape the feeling that these established specialists prefer to do it in this piecemeal way, rather be in some way answerable to a central professional Feasibility Institute which could set standards, hand out internationally-recognised fellowships, and maybe even encourage the establishment of degree courses in Feasibility Studies.
But the Young Turks of the SFA think otherwise. They feel that there is a public perception that officially-commissioned Feasibility Studies are a bit of racket, and that the only way to respond is to go public, shine a spotlight on their activities, and define and clarify what they do in a way which will ultimately enable them to charge even more for their services.
The establishment or otherwise of a Feasibility Studies Institute is of special current interest to Ireland's maritime sector in its broadest sense, as two major infrastructural questions currently being analysed as matters of public interest are the general development and possible relocation of some and possibly all of the shipping functions of Dublin Port, and the other is the creation of a new Scotland to Northern Ireland link via a tunnel or a bridge, or something in between.
 Dublin and its port from seaward. Unlike Sydney, Dublin is not a large natural port, but rather it's a harbour created out of a deepened river in which the entire commercial port is now on "new" land created by infill. Thus the special character of the city is in part created by the need for residential and commercial areas to share space with shipping requirements.
Dublin and its port from seaward. Unlike Sydney, Dublin is not a large natural port, but rather it's a harbour created out of a deepened river in which the entire commercial port is now on "new" land created by infill. Thus the special character of the city is in part created by the need for residential and commercial areas to share space with shipping requirements.
"Dublin Port is a tricky one for us", says an SFA spokesman. "Its administration and organisation is run in an imaginative and energetic way in which dynamic cultural interactions with the public are being created and strengthened on several fronts. Thus although some high-profile, high-powered developers and economists are arguing that the port should be moved elsewhere like some other arguably comparable ports, Dubliners will often respond that they like having a real living port in the midst of their city, and that Dublin didn't get where it is today by simply copy-catting other major ports.
But then, if we promoters of Feasiblity Studies argue that there should at least be research into possible alternative sites for the heavy work of Dublin harbour, we find that the Dublin Port authorities have got there before us anyway, with their exemplary recently-published research papers, which included carefully analysed proposals for alternative news ports for Arklow in County Wicklow, or Bremor in the far north of Fingal.
Dublin Port score double for their proposals for Bremor, as we can compare it with a nearby plan which has been released for a private-developer-supported port further north. This plan proposes new harbour breakwaters in straight lines with marked corners. When the sea is in destructive mood, it just loves clearcut corners in major breakwaters – it will chew them away in jig time.
 The proposed new shipping port on the Meath coast as planned by a public-private partnership. In storm conditions, any breakwater with such clearcut corners would be especially subject to erosion
The proposed new shipping port on the Meath coast as planned by a public-private partnership. In storm conditions, any breakwater with such clearcut corners would be especially subject to erosion
 Dublin Port's longterm suggestion for an additional facility at Bremore takes full account of the Irish Sea's conditions in onshore gales.
Dublin Port's longterm suggestion for an additional facility at Bremore takes full account of the Irish Sea's conditions in onshore gales.
But the Dublin Port proposal is based on curving breakwaters which are much better at repelling and absorbing the waves. So clearly theirs is a serious proposal, whereas the other has the whiff of kite-flying about it.
Thus our problem with Dublin Port is that they seem to have a very productive in-house Feasibility Studies Institute already in being. So we have to look elsewhere for a flagship project with which to launch our new Institute in style, and the North Channel Link looks to be a God-given gift".
Certainly as any regular readers of Afloat.ie will be aware, suggestions for a Trans North Channel Link from Scotland to Ireland, whether by bridge or tunnel or a combination of both, or by some sort of tube – floating or otherwise - have been coming in thick and fast, ever since British premier Boris Johnson made it a central part of his transport infrastructure upgrade policy.
As it's unlikely that any private partnership capital will become available for such a project, which is at and beyond the extremes of engineering and economic viability, several rigorous Feasibility Studies will be required into many aspects of the project and its support connections.
 Fixed connections across the North Channel have to withstand the problems of storms, extremely powerful tides, exceptionally varied water depths, and the remoteness and lack of connectivity of terminals on the Scottish side, making it a very rewarding area for Feasibility Studies.
Fixed connections across the North Channel have to withstand the problems of storms, extremely powerful tides, exceptionally varied water depths, and the remoteness and lack of connectivity of terminals on the Scottish side, making it a very rewarding area for Feasibility Studies.
Thus the SFA feels the time was never more appropriate for the establishment of globally-recognised International Feasibility Studies Institute, and they suggest it should be located in a Dublin Docklands Office Complex in acknowledgement of the high standards already set in this area of research and study by Dublin Port.
An SFA spokeswoman explained to Afloat.ie that the only clear boundary in the area of Feasibility Studies is whether the basic funding is public or private.
"You'll probably have heard" said she, "the story of how one of the glamour high tech companies was setting up state-of-the-art "canteen" facilities for their decidedly pampered staff in their European HQ in Dublin. They retained a noted chef full-time to work on commissioning the new facility, and then seeing it through into smooth operation. When he asked what sort of budget he'd be operating within, they said there was no budget - just get it done, and we'll look after whatever it takes."
While there may be times when such flagship projects as the new Children's Hospital in Dublin, the new Airport in Berlin, and the new HS2 High Speed Rail Link in the south of England look as though they've been planned on the "whatever it takes" budgeting principle, we can be quite sure there were Feasibility Studies at different stages of each project, and one of the courses envisaged as being central to the new International Feasibilities Studies Institute is how you style your completed study.
"We may even have a course in "Know The Psychology of the Client" says the SFA. "If it's clear that it's something of a vanity project, we hope to provide what we in the trade call the Cosmetic Feasibility Study, which looks good and businesslike, but cleverly makes almost indiscernible important provisions and reasons for major cost-over-runs.
If, however, it's a rather boring project in which no-one personally has a special interest, we can offer our attractively priced Standard Comprehensive DG Feasibility Study, which looks good, and smothers the reader in graphs and computer-generated drawings, yet the experienced assessor will immediately know that DG is not "Director General", but on the contrary is "Dust Gatherer"."
The leading members of the SFA are particularly impressed by the proposal for a floating tunnel across the North Channel put forward by Heriot-Watt University of Edinburgh.
 The Floating Tunnel for the North Channel proposed by Heriot-Watt University of Edinburgh, which might offer the advantage of being towed away for use elsewhere in calmer waters if the North Channel proves to be too rough
The Floating Tunnel for the North Channel proposed by Heriot-Watt University of Edinburgh, which might offer the advantage of being towed away for use elsewhere in calmer waters if the North Channel proves to be too rough
"It's a simple and feasible yet massive idea, put forward with style. Showing a car driving through gives it an instant credibility with which modern society can identify. And we note that realistically they propose it starts at Portpatrick on the Scottish side, but instead of going the longer distance to Larne, we would suggest they bring the western end ashore on the much nearer and uninhabited Copeland Island close north of Donaghadee, with the island providing space for the tunnel's administrative centre. Finally, we would suggest that as an additional selling point, they can say that if it doesn't work because of the exceptional roughness of the seas of the North Channel, it can always be towed away and used somewhere else to cross a calmer waterway".
 It would never get built nowadays……the eccentric and much-loved Basilica de la Sagrada by Antoni Gaudi in Barcelona
It would never get built nowadays……the eccentric and much-loved Basilica de la Sagrada by Antoni Gaudi in Barcelona
The need for reasonably credible feasibility studies is growing more urgent all the time, with immediate public scrutiny of proposals through online publication, and aggressive discussion in social media. Thus the members of the SFA readily admit that two of the world's most famous and best-loved buildings, the Sydney Harbour Opera House and the Basilica de la Sagrada Familia in Barcelona, would today require extremely creative Feasibility Studies by masters of the art if they were ever going to get built at all.
"But we don't despair" say the SFA. "If we ever get the IFSI up and running, our motto will be: "We are the light at the beginning of your tunnel".
Update (April 1, noon): Thank you for reading our 2021 April Fool's yarn
Bremore: A New County Meath Port & Logistics Hub for Ireland's North East
Drogheda Port Company has announced it is to develop a new deepwater port, to be located on the Meath coast north of Bremore Head, that will support Ireland’s Climate Action and EU Green Deal targets and act as a national logistics hub.
The new port is set to be one of the largest national infrastructure projects in recent years, will drive green innovation to support Ireland’s climate action targets, and will create a critical logistics hub that will deliver much needed sustainable jobs in the north east, the Drogheda Port Company said.
Paul Fleming, Drogheda Port Company CEO, said: “This project is a reflection of today’s policy demands for infrastructure that meets national and EU goals to decarbonise transport, to produce alternative energy sources and to build in a sustainable manner. We will also develop the scope and design of the project to meet the demands of the regional economy and the needs of the local community.”
“Ireland’s relationship with our nearest neighbour is changing fundamentally and Brexit requires us to reimagine the east-west trading environment as well as our direct infrastructure links to our EU partners. This project will add significant capacity and opportunity to Ireland’s existing infrastructure and will shape our economic development and trade policies for decades to come.”
“This announcement allows the project partners to start a public consultation to develop a socially, economically and environmentally sustainable project. Discussions are underway with relevant government departments to progress the necessary consents in terms of public policy objectives. In accordance with the Public Spending Code, a Strategic Assessment Report will be submitted to the relevant departments to progress this engagement further in the near term.”
Drogheda Port Company also announced it has, after a public procurement process, completed a partnership agreement with Ronan Group Real Estate (RGRE) to develop the port and the wider port estate. The partnership provides for a mixed development project that will maximise the socio- economic potential of the area based on proximity to a deepwater port, the Dublin/Belfast rail line and the national motorway network. The partners have assembled a team to support the development through the government consenting, public consultation and planning processes.
The Bremore development will provide additional capacity to current port services located at Drogheda, which will continue to develop with the construction of the Northern Port Access Route and the publication of a Drogheda Port Masterplan in early 2021.
 Bremore Port - Phase one as released by Drogheda Port Company
Bremore Port - Phase one as released by Drogheda Port Company
Rory Williams, RGRE CEO, added: “This project will be one of Ireland’s biggest infrastructure investments in many years. As well as port and logistics operations, the development will make a significant contribution to regional social and economic infrastructure, delivering sustainable jobs to the region and providing a much needed shot in the arm for the Irish economy as it faces into the challenges of a post-pandemic and post Brexit world. The north east rarely features in national conversations on infrastructure and economic development, and so this will also bring much needed investment to a region that will benefit hugely.”
To be delivered in partnership with the private sector, the new Bremore Port will:
- Act as the landing site, assembly point and support centre for the turbines that will power the off-shore wind farms being developed in the Irish Sea;
- As part of being a major Irish hub for green innovation become a hub for the production and distribution of ‘green hydrogen’ – a ground-breaking zero-carbon energy source that has the potential to contribute significantly to Ireland’s climate action goals and power needs;
- Be one of the biggest infrastructure projects, portside and landside, undertaken in Ireland in recent years and funded primarily through private means;
- Drive regional social and economic infrastructural development by delivering sustainable jobs to the local economy, on the port estate and across the wider property development;
- Bring much-needed resilience to Ireland’s port infrastructure which will help to mitigate disruptions in international trade and logistics from events like Brexit;
- Offer competitive choice to shipping lines to develop and future proof their business sustainably in a central but uncongested location;
- Allow for the latest generation of technology in construction and operation as Ireland’s newest port;
- Become the logistics hub of the north-east region by offering extensive warehousing and logistics services right beside the M1 serving the entire island though the motorway and rail network.
Bremore Ireland Port Is Up For Sale
#Ports - Drogheda Port Company is selling its Bremore Ireland Port DAC and its interest in developing the proposed deepwater port near Balbriggan.
Bremore Ireland Port DAC is a wholly-owned subsidiary company established in 2006, and which has carried out feasibility works in relation to developing a multi-modal deepwater port at Bremore.
Plans for Bremore plans were put on hold a number of years ago due to lack of State support for the project.
However, Drogheda Port Company maintains that the development “can potentially provide a world class deepwater port with ancillary port centric logistics centres and business parks located away from the existing congested hub of Dublin City.”
The site, just north of Balbriggan in Co Dublin, is adjacent to the Dublin-Belfast rail line and minutes from the M1.
Drogheda Port Company is seeking offers for the sale of the company or other such proposal which may be of interest. A prospectus on Bremore Ireland Port outlining studies undertaken is available on request from [email protected].
Offers and/or proposals should be forwarded to Drogheda Port Company, Harbourville, Mornington Road, Drogheda, Co Meath on or before Friday 6 July.
Plans for Bremore Port Project in Deep Water
#BremorePort – It appears that plans for the proposed €350m development of the deep-water port at Bremore, near Balbriggan, Co. Dublin has been effectively shot down under the government's new ports policy blueprint.
The proposed port was to be developed to provide support for Drogheda and Dublin ports.
A government source confirmed that the new policy indicated that "there was no need for new capacity development and that any main developments should be done at Dublin, Cork or Shannon, so it's unlikely that Bremore will be progressed."
The news has been greeted as a blow to the local economy by Balbriggan Chamber of Commerce.For more on this story the NorthCountyLeader.ie has a report.
The need to ensure that Dublin Port and Dublin City are integrated and that the Port "turns its face" to the City, by removing physical barriers to integration and encouraging more people to visit the Port or view the activities taking place in the Port.
Widespread acceptance that Dublin Port is a key part of national strategic infrastructure and plays a key role in the life of the City and the greater Dublin area.
The importance of facilitating international trade in Ireland.
Unanimous agreement that everything possible should be done to encourage and facilitate the increased presence of Cruise Ships in Dublin Port.
General agreement that DPC faces significant challenges in operating and growing the Port in light of the location of the Port alongside sensitive environmental zones.
A common view that DPC should fully exhaust all viable alternatives to meet the operating requirements of the Port before engaging in additional reclamation works.
Widespread recognition that the creation of new port facilities at Bremore or elsewhere was not likely in the medium term given the financial challenges facing such a project in light of current national capacity, the scale of the engineering project involved and current funding.
The process sought views from a wide circle of stakeholders whose views on the operations and future of the port are important. Community briefings attracted over 100 people from Clontarf, East Wall and Ringsend. A conference was attended by 140 key stakeholders, while additional briefings were held with 12 organisations and groups.
Commenting, Mr. Eamonn O'Reilly said: "The objective of growing Dublin Port to allow it to handle 60m tonnes by 2040 is generally regarded as a reasonable basis for long term planning of the port. We are delighted with the response to our consultation process to date and we will make every effort to respond to all inputs we have received.
The Masterplan will help drive our national competitiveness by planning responsibly for an efficient and effective infrastructure to underpin the trading needs of our economy into the future. We are very conscious of the challenge of doing this, while integrating well with the city of Dublin and its citizens and expanding in a responsible and environmentally friendly manner."
Arising from the Consultation Process and the responses to the Issues Paper, there are a number of additional reports and studies that will be considered in the context of finalising the production of the Masterplan and a number of further meetings will be arranged with specific stakeholders.
Varadkar Supports Deepwater Port at Bremore
Drogheda Port Company successfully managed to navigate the global economic downturn with an improved and solid performance for 2010, delegates where informed during its annual report released yesterday, writes Jehan Ashmore.
Speaking about the performance of Drogheda Port Company, Leo Varadkar TD, Minister for Transport, Tourism and Sport said; "I congratulate the company on its solid trading performance in 2010 following a difficult year in 2009. Both imports and exports through the port returned to growth in 2010. The company has managed its costs well and remains profitable. I support the company's plans to develop the existing port and indeed to continue to progress its proposal for a new deepwater port at Bremore.
The Minister added "this country's return to economic prosperity will be export-led and Irish ports will play an important role in facilitating that trade. The overall structure of the State's ports will be reviewed later this year as part of the current Ports Policy Review and will take account of the recent recommendations of the McCarthy Group. Irrespective of the outcome, well managed and profitable ports such as Drogheda will continue to play an important role in serving the market and facilitating industry and jobs.
As part of the ongoing the Ports Policy Review a Consultation Document was issued in October 2010, which highlighted the important role of ports to facilitate the return to economic growth when it occurs. In addition new capacity will be required in the medium to long term and this needs to be planned for now.
The consultation also acknowledges the continuing trend towards larger ships requiring deep-water ports, the reduced availability of ships to serve smaller ports and the emergence of the concept of port-centric logistics as a key driver for future port development.
As for this year "a number of new port records were established in 2010" said Mr. Paul Fleming, Drogheda Port chief executive. "In March, the longest ever vessel to be accommodated in the port, the Rusich 1 at over 128m in length berthed at Tom Roes Point Terminal". The 4,970 tonnes vessel arrived from Vyborg, Russia with a cargo of fertiliser.
Mr Fleming also referred to the largest gas tanker ever to visit its facility at the Flogas LPG terminal when the 1,720 dwt tonnes Thresher docked last October. The Dutch flagged Thresher had arrived loaded with a cargo from the Whitegate Refinery, Cork Harbour and is operated by Chemgas which operate one of the most modern gas carrier fleets in the world.
In addition to last year's performance, first quarter figures for 2011 were revealed with trading volumes reporting an increase of 18% based from the same quarter for last year. The rise was primarily driven by export volumes of existing and new commodities.