Displaying items by tag: coral
Coral Found by NUIG Scientists on Ireland's Continental Shelf Effective Against Covid-19
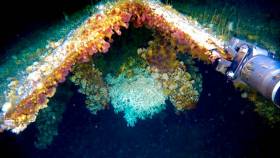
Marine Researchers at NUI Galway (NUIG) say an Atlantic coral that they discovered on Ireland’s Continental Shelf has a chemical compound which can act against the Covid-19 virus.
The cauliflower coral was found on the seabed about half a mile below the surface on the edge of Ireland’s Continental Shelf.
The coral contains a previously unknown chemical compound, and research into its make-up is being conducted in partnership with North America’s South Florida University.
The compound was isolated, and named "tuaimenal" – a blend of "tuaim" from the old Irish word for sounds of the sea, and “enal”, a chemistry term for a compound with an alkene aldehyde functional group.
The research showed that Tuaimenal A can block the major enzyme of the Covid-19 virus, known as Main Protease, which is responsible for the manufacture of virus particles inside the infected cell, according to NUIG.
 Dr Carolina De Marco Verissimo of NUIG’s Molecular Parasitology Laboratory conducted a study of the coral-derived Tuaimenal and how it interacts with the Covid-19 enzyme
Dr Carolina De Marco Verissimo of NUIG’s Molecular Parasitology Laboratory conducted a study of the coral-derived Tuaimenal and how it interacts with the Covid-19 enzyme
NUIG professor of zoology Louise Allcock said that while the scientists did not set out to find this specific species, they were “hunting for corals, especially soft corals, because of their potential in bio-discovery”.
Prof Allcock, who is director of NUIG’s Ryan Institute Centre for Ocean Research and Exploration, deploys the ROV Holland I submarine from Marine Institute research ship Celtic Explorer to hunt for deep-sea corals and sponges which may have novel chemical compounds with pharmaceutical potential.
"Nature never ceases to amaze - to think that a coral, which spends its life on the sea bed and is never exposed to viruses and diseases which affect humanity so profoundly, has the potential to influence treatments and therapies,”Prof Allcock says.
“Drug development is a lengthy process, but the first step is finding the magic compounds with bio-reactivity in the laboratory,” she says.
Dr Carolina De Marco Verissimo of NUIG’s Molecular Parasitology Laboratory conducted a study of the coral-derived Tuaimenal and how it interacts with the Covid-19 enzyme.
“Tuaimenal A represents what we term in science as a ‘lead compound’ – that is, a basic structure from which scientists can produce more potent and specific drugs that could be used for the treatment of Covid-19 and perhaps other viruses,” she has said.
Results of the recently published work can be found here
Health of Caribbean Coral Reefs Threatened by "Aggressive Alga"
Coral reefs are under pressure from hurricanes, pollution, bleaching and global warming, and scientists have now confirmed the extent of the threat from an aggressive alga.
The algae, known as peyssonnelid algal crusts (PAC), are colonising reefs in the Caribbean at such an aggressive rate that they are interfering with the reef’s natural ecosystem, according to new research.
Marine biologists from the University of Oxford, California State University Northridge and the Carnegie Institution for Science who have been studying the issue for four years describe the extent of the threat in the Scientific Reports.
The golden-brown, crust-like alga is rapidly overgrowing shallow reefs, and has been described as an “ecological winner” by Dr Bryan Wilson of the University of Oxford’s department of zoology.
“It aggressively occupies any vacant space on the reefs, rapidly overgrows and kills live corals, prevents free-swimming coral larvae from settling on the benthos and becoming adult colonies, and is unaffected by the regular destructive hurricanes that sweep through the area,”he says.
‘It is also seemingly resistant to grazing by fish, and as far as we know, is only fed upon by a single creature, the black spiny urchin (Diadema antillarum),”he said.
The spiny urchin was once abundant in the Caribbean, but was effectively wiped out in the 1980s by a mysterious disease, he says.
“Our research has initially looked into the microbiology of PAC and compared it with that of close relatives (the crustose coralline algae, or CCA) which are known to stimulate the recruitment of coral larvae to reefs,”Dr Wilson says.
A key finding was that the PAC alga manages to inhibit the growth of beneficial marine bacteria which otherwise produce chemical compounds that attract coral larvae to the seafloor.
This means that reefs colonised by the alga are unlikely to host corals again.
The alga is described as having a “dark brown and dirty orange veneer” which stands out among the white sands and light greens, pinks, yellows and other colours that make up the reef.
The scientists say it is unclear if PAC is made up of one algal species or several, and they don’t know what is causing its rapid spread – but describe it as an “alarming trend”
They say that the next stage of their research will be to unravel the alga's “complex physiological mechanisms for this ecological success”, through studying its genome. Ultimately, they say they “hope to find ways to mitigate against this new threat”.
New Study Finds Coral in Ireland's Deepest Submarine Canyon Survives Extreme Conditions
Irish cold-water corals can survive in extreme conditions within Ireland’s largest submarine canyon on the Porcupine Bank, a new study has found.
The coral even grows on precipices of high cliffs, and can withstand sea current speed of over 114 centimetres per second, according to the study published today in the science journal Nature.
This is the highest current speed ever recorded in a cold water habitat, according to University College Cork(UCC) scientist Dr Aaron Lim who led the research.
 An example of a 3D reconstruction of a cold-water coral habitat from -750 m water depth at the Porcupine Bank Canyon Photo: Aaron Lim
An example of a 3D reconstruction of a cold-water coral habitat from -750 m water depth at the Porcupine Bank Canyon Photo: Aaron Lim
Dr Lim’s team used the Holland 1 remotely operated vehicle (ROV) on the State research ship Celtic Explorer to explore how coral are living in the Porcupine Bank Canyon which is 3,500 metres deep.
 The Marine Institue's Holland 1 ROV being deployed from the RV Celtic Explorer as it 'holds' the deep sea monitoring system (attached to the front) before descending to the deep sea Photo: Aaron Lim
The Marine Institue's Holland 1 ROV being deployed from the RV Celtic Explorer as it 'holds' the deep sea monitoring system (attached to the front) before descending to the deep sea Photo: Aaron Lim
He was part of the 2018 expedition which explored and mapped the canyon some 320 km west of Kerry, finding it full of cold-water corals forming reefs and mounds which create a rim on the lip of the canyon.
This latest expedition found coral in a range of deep marine settings.
The scientists had to use deep marine monitoring stations and three-dimensional reconstructions as part of the work. .
“These cold-water corals are growing at the very edge of a near-vertical cliff face, in Ireland’s largest submarine canyon some 850 m below the surface in very intense conditions. They’re quite literally living on the edge,” Dr Lim said.
 UCC's deep sea monitoring system at the edge of the submarine canyon where it collects marine environmental data for months at a time
UCC's deep sea monitoring system at the edge of the submarine canyon where it collects marine environmental data for months at a time
As he explained, cold-water corals help to form deep-water reefs and mounds which can range from as little as ten metres to over 100 m high.
Some coral mounds have existed offshore Ireland for 2.6 million years, he said.
“Some of these habitats were predominantly alive, while others were mostly dead and so the aim of the study was to understand what is driving this?” Dr Lim said.
UCC marine geologist Luke O’Reilly described the canyon as “a strange-place; deep, dark and cold but full of life”.
“Together with the Marine Institute, we developed a monitoring system which could withstand these pressures and conditions for months at a time,” O’Reilly said.
Prof Andy Wheeler, head of UCC’s school of biological, earth and environmental sciences, noted that the coral can cope with the strong sea currents, but tend to feed when it slows down – such as when the tide turns.
The team have recently deployed monitoring stations in the canyon to gather information on survival over longer time scales.
The research was funded by Science Foundation Ireland and Horizon 2020, with co-funding by the Marine Institute and Geological Survey, Ireland. Shiptime was funded by the Marine Institute's National Shiptime Programme.
The study is published here
Marine scientists from University College Cork have discovered plastic at the bottom of a deep submarine canyon while investigating cold-water coral habitats.
UCC’s Marine Geology Research Group has been investigating cold-water coral habitats in the Porcupine Bank Canyon, some 320km due west of Dingle, on a research expedition led by UCC’s Dr Aaron Lim on board the Marine Institute’s RV Celtic Explorer.
The team had recovered eight novel monitoring stations, called ‘landers’, worth €450,000 and deployed between 700m and 2500m water depth by the Marine Institute’s Remotely Operated Vehicle (ROV) Holland 1 earlier this summer.
The monitoring stations record the speed, temperatures and direction of the currents around these habitats as well as trapping samples of the food, sediments and microplastic being deposited around the corals, to understand conditions and how the corals are coping with changing oceans.
The researchers found plastic in the bottom of one canyon at 2,125m water depth — as deep as ten Eiffel Towers stacked on top of one another.
The reach of human plastic waste is now confirmed as this deep, even 320km offshore.
“It’s always sad to see plastic rubbish in these otherwise pristine habitats. It’s quite incredible that our plastic waste can get this far out and so deep in the oceans,” said Professor Andy Wheeler of UCC, who has pioneered research on cold-water coral mounds offshore of Ireland over the past 20 years.
“I don’t think people think about this when that dump their rubbish. We’re also trying to see if microplastics are being fed to the corals from above. We’ve just got the samples; let’s hope we're wrong.”
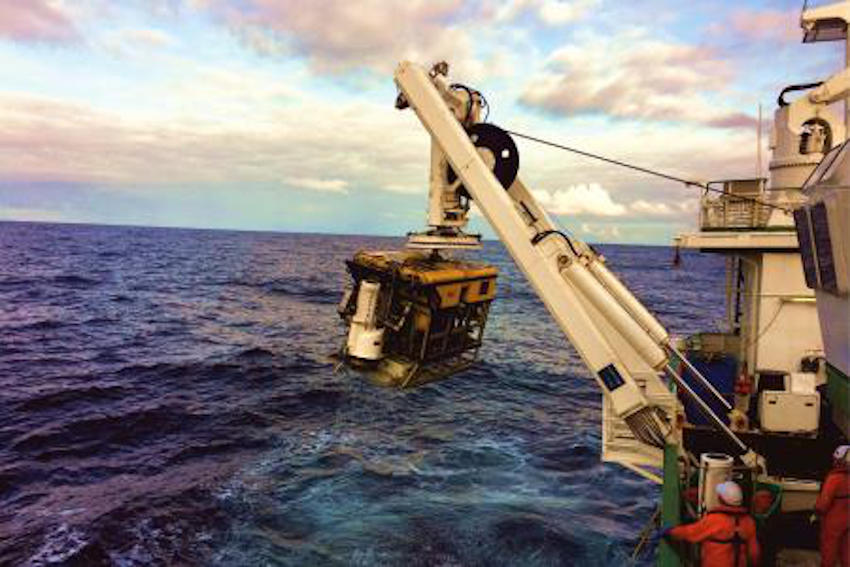 ROV Holland 1 recovering one of the monitoring stations | Photo: UCC
ROV Holland 1 recovering one of the monitoring stations | Photo: UCC
The Porcupine Bank Canyon is teeming with a whole range of cold-water coral habitats, just on Ireland’s doorstep, says Dr Lim.
“The environment is much more dynamic than we thought, with two of the monitoring stations knocked over by the currents; food supply for the coral is variable but the corals are doing okay.
“Some of these habitats have existed for millions of years and have grown so large they resemble hills made of coral, called coral mounds.
“This is the first time eight of these monitoring stations have been deployed and collected using the ROV Holland 1. It will provide scientists with an insight into the processes affecting these cold-water coral habitats, food sources and the impact of microplastics.”
Dr Lim said Ireland’s cold-water coral reefs are found in the cold, dark ocean at water depths of 600m to 1,000m along our continental margin.
“Not only is this expedition vital for understanding these habitats and our impact upon them, it also acts as a baseline to start monitoring how our deep-water habitats here are changing,” he added.
The team has a research agenda which will see them return to the canyon and other habitats alike for a number of years, to monitor the changes in the environment around these habitats. The monitoring stations will be brought back to UCC for detailed analyses.
This research survey is carried out with the support of the Marine Institute, funded under the Marine Research Programme 2014-2020 by the Government to support and promote the Atlantic Ocean Research Alliance, which facilitates common research and knowledge exchange for us to provide healthy, resilient oceans for our future generations.
The survey has also received funding from Science Foundation Ireland, Geological Survey Ireland and UCC.
Shipwrecks off the Irish coast are acting as artificial reefs for corals usually found much deeper in the Atlantic.
That’s according to NUI Galway ocean scientist Anthony Grehan, who told the Irish Examiner about his recent surprising find at the wreck of a cargo vessel 160 metres below the surface.
Using the new submersible robot Étáin from the University of Limerick, Grehan and a team on the RV Celtic Explorer found examples of the stony coral species lophelia pertusa, which usually found at depths of 500 metres or more.
And the new discovery suggests that such wrecks may provide the necessary stability for deep-water corals to thrive in shallower waters.
The Irish Examiner has much more on the story HERE.
Irish Deep Water Coral Reefs Changing Faster Than Previously Thought, Says New Research
#MarineScience - One of Ireland’s deep water coral reefs is changing at a rate of some 20% over four years, faster than previously thought.
That’s according to new research published by Dr Aaron Lim of the Marine Geology Research Group at University College Cork.
Images and samples were retrieved from the cold water reefs on two separate occasions using the Marine Institute’s ROV Holland 1 operated from the RV Celtic Explorer — representing “the first ever successful attempt at imaging an entire deep water reef” at 1km below the surface, explains Dr Lim.
“Over half the species of coral in the world are cold, deep-water species and many of them can be found in Irish waters between water depths of 600m and 1,000m,” he added.
One of the most prolific places on the planet for deepwater coral development is the Belgic Mound Province, at the Porcupine Bank on the Irish continental margin, where there are over fifty giant coral mounds and 300 smaller coral reefs.
In 2011 and 2015, the Holland 1 was used by marine scientists to capture images and footage of the entire surface of one of these reefs, “which has for the first time has provided us the insight into how the reefs grow at this scale,” Dr Lim said.
“Initial results showed that the reef was extremely variable and is coping with the contemporary environmental conditions,” said Prof Andy Wheeler, head of geology at UCC and who has been working in Ireland’s corals for 20 years.
“However, the issue is that it is so difficult to take images of the deep ocean that we can only get bits of information from these reefs during an expedition.”
Dr Lim added: “The importance of this technology and having access to the national research vessel has meant that we can get access to what was only a few decades ago inaccessible. We can now provide a detailed analyses of the reef, showing that it changed at a rate of 20% in four years.”
Unlike its tropical water counterparts, which suffer from mass coral bleaching events, the proportion of live coral on this reef did not change.
“The change was in fact an increase in the proportion of dead coral and coral rubble areas, which is not the result of live coral dying, but possibly due to the result of strong currents exposing dead coral buried beneath older parts of the reef,” Dr Lim said.
“Assuming the change continues at this rate, then in 20 years the reef will entirely change.”
Dr Lim and Prof Wheeler have commenced a sizeable research project to monitor a range of coral habitats on the Irish margin with the aim of understanding what is driving these habitats and what makes them change. This research has been funded by the Irish Research Council, the Marine Institute and UCC.
Aquatic Discoveries Among 2015 Irish Science Breakthroughs
#Innovation - Two very different aquatic breakthroughs have been listed among Silicon Republic's top 10 Irish innovations of 2015.
Afloat.ie has previously reported on University of Limerick graduate Cathal Redmond, who took home €7,000 as a runner-up in the James Dyson Awards for his revolutionary new diving apparatus.
Redmond will use the funds to develop his Express Dive concept, a lightweight device that allows divers to refill their air supply on the goal – for a fraction of the cost of standard SCUBA gear.
Also covered this past summer on Afloat.ie was the discovery of a new habitat for coral in Irish waters.
Prof Andy Wheeler led an international team of marine scientists on the coral survey in June that ventured into the Porcupine Bank Canyon some 300km off Dingle and found an unexpected variety of life.
He added that it is "not unfeasible that there is over 100 sqkm of coral habitat that was previously unaccounted for."
Silicon Republic has more on the story HERE.
Cold Water Corals Growing In Abundance Off Porcupine Bank
#MarineScience - An international team of scientists led by Prof Andy Wheeler of University College Cork have discovered a new habitat for coral in Irish waters – possibly doubling the amount of cold water corals previously thought to exist in the area – while on the Marine Institute's RV Celtic Explorer during the QuERCi survey.
While conducting research on Irish cold water coral reefs, Prof Wheeler investigated a submerged vertical cliff 800m below the sea surface and found it covered in coral.
"The seabed just falls away into a deep chasm. We couldn't wait to take a look down there, using the Holland I remotely-operated vehicle [or ROV] which is equipped with cameras and robotic sampling arms," he said.
Prof Wheeler and his team have been investigating Irish cold water coral reefs for over 15 years. In the deep, cold, dark Atlantic, these corals form reef habitats supporting a diverse and abundant ecosystem.
It was while mapping and inspecting some previously unconfirmed reefs on the edge of the Porcupine Bank Canyon, 300km offshore from Dingle, that the scientists decided to venture further into the canyon itself.
The ROV Holland I was manoeuvred from a 2,100m water depth in the middle of the canyon, up the canyon wall to the coral reefs clustered around the canyon top at 700m water depth. The bottom of the canyon was choked with organic-rich particles flushing down the canyon on the way to the abyssal plain.
"It was like flying the ROV through a snow blizzard," said Dr Chris McGonigle of Ulster University, "but we just pushed up the canyon and it got steeper and steeper and steeper until we faced this vertical cliff face several hundred metres high."
The cliff face, never seen by humans before, was covered in corals and other associated organisms.
"These near vertical habitats hardly feature on maps yet can be hundreds of metres high and extend for tens of kilometres. This is a massive habitat, barely explored, yet full of ocean life", said Dr Agostina Vertino of the University of Milan-Bicocca. "We found many species of coral, sponges, crabs and fish."
Prof Wheeler believes it is "not unfeasible that there is over 100sqkm of coral habitat that was previously unaccounted for."
The coral discovery site has already been designated a Special Area of Conservation due to coral reefs in the vicinity. Yet despite its protection, the international team lead by Prof Wheeler found snagged fishing gear and litter.
"It is a great shame, we are the first people to see this place yet despite of its remoteness there is still evidence of human impacts," he said.
The RV Celtic Explorer is Ireland's state-of-the-art research vessel and has been recently equipped with new seabed mapping sonars giving unprecedented views of the seabed. The ship is also the dive platform for the Holland I ROV.
"The quality of the data that this ship and ROV can now collect is phenomenal," said Dr McGonigle. "We were seeing details on the seabed that a few years ago we could only have dreamed of.
"This increase in data quality will allow us to develop a much greater understanding of the processes controlling the distribution of life in these unique environments."
Congratulating Prof Wheeler and the team on their discoveries, Mick Gillooly, director at the Marine Institute, said "we are delighted to see the recent upgrade of the Celtic Explorer and the ROV Holland's multibeam sonar suite producing such amazing results for this expedition.
"The high resolution images produced are fundamental in helping scientists with their research as well as helping us provide a better understanding our ocean."
Hopes for Evidence of Coral Reefs in Irish Sea
#MARINE WILDLIFE - Might there be evidence of coral reefs in the Irish Sea? Johnny Woodlock of the Irish Seal Sanctuary believes so.
Writing for Wildlife Extra, the Sea Fishery Advisory Group member recalls seeing a piece of coral that a former commercial trawler skipper said he had found in one of this nets more than 20 years ago while fishing off the Isle of Man.
Woodlock says he identified the sample as Lophelia pertusa, a coldwater coral that thrives in deeper water and one that was not previously linked to the Irish Sea, according to the records of the Marine Institute and the National Parks and Wildlife Service.
Then this past August, when Woodlock uncovered a similar piece of coral and identified it as the same species, he was able to find out the co-ordinates where both pieces had been netted and forwarded them to the Marine Institute.
Though the area of the Irish Sea in question "has been heavily trawled by larger boats pulling heavier nets for a number of years", Woodlock remains hopeful that the Marine Institute can find evidence of living coral in the depths.
Often mistaken for plant life, coral is actually a compact colony of very simple marine wildlife called polyps, encased in a skeleton of calcium carbonate which gives them their solid appearance.