Displaying items by tag: PSE Kinsale Energy Limited
Marine Notice: Inshore Pipeline Survey at Kinsale Gas Field
PSE Kinsale Energy Limited is undertaking an inshore pipeline survey along the route of a decommissioned pipeline from the Kinsale Gas Field.
Works will focus on the pipeline in the Celtic Sea close to Inch Beach in Co Cork.
The estimated duration of the survey is up to two days within a window from Friday 7 to Sunday 30 April, subject to weather and operational constraints.
Survey works will be conducted by the survey vessel Barnacle (callsign EIA2122) which will operate during daytime only and will display appropriate lights and signals.
Within the defined work areas, the vessel will be undertaking an acoustic survey using a multi-beam echo-sounder and a towed side-scan sonar.
All other vessels, particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to leave a wide berth during the operations and to keep a sharp lookout in the relevant areas. The work vessel can be contacted on VHF Channel 13.
A map of the survey area, relevant coordinates and contact details are included in Marine Notice No 19 of 2023, attached below.
Continuing its Kinsale area decomissioning project, PSE Kinsale Energy Limited advises that its Kinsale Head platform removal campaign will commence later this month and is expected to run through to September.
Works will be conducted by the semi-submersible, self-propelled crane unit Thialf (callsign 3EAA4) assisted by a number of cargo barges towed by the MV Kolga (callsign PCTR) and MW Bylgia (callsign PBMQ). The Merel G (callsign HO6511) will be used for crew transfer between the vessels and shore.
Backloading of removed compoents onto the cargo barges is planned for the offshore location but may be performed inshore depending on environmental conditions.
All work vessels may be contacted on VHF Channel 16 throughout the operation. All other vessels, particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to give the vessels a wide berth and to keep a sharp lookout in the relevant areas.
Details of relevant coordinates and contact information can be found in Marine Notice No 24 of 2022, attached below.
PSE Kinsale Energy advises that it is engaging in works to decommission subsea wells at the Southwest Kinsale, Seven Heads and Ballycotton gasfields from this week for the next eight months.
Weather depending, advance works were set to begin between today, Monday 22 and Wednesday 24 March ahead of the arrival of the work vessel Stena Spey next month.
Stena Spey (callsign GCWP) is a Mobile Offshore Drilling Unit (MODU) which will be first deployed to the Southwest Kinsale Gasfield for a period of some 90 days, where it will be positioned using eight pre-laid anchors, before moving on to the Seven Heads field.
Anchor handling vessels MV Maersk Maker (callsign OZGO2) and MV Maersk Marine (callsign OWGQ2) will accompany the Stena Spey throughout the well abandonment campaign.
Other work vessels of note are the ad-hoc anchor handling vessel MV Maersk Lancer (callsign OUHX2) and standby vessel MV VOS Pathfinder (callsign 2ALO7). All will listen on VHF Channel 16 throughout the operation.
Further details on the campaign, including the locations of rigs and anchor positions, are included in Marine Notice No 12 of 2021, a PDF of which can be downloaded below.
Mariners Beware Of Seabed Obstruction Off South Coast
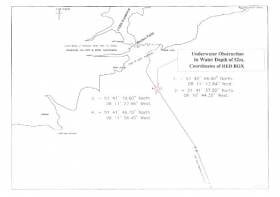
#MarineWarning - PSE Kinsale Energy Ltd advises that, that following a recent survey of the Kinsale Head Gas Field pipeline, it has identified a possible seabed obstruction off the South Coast of Ireland.
The nature of the obstruction, south-east of Roches Point on the approach to Cork Harbour, may present a hazard to ground fishing equipment, so any fishing vessels operating within the area are advised to proceed with caution.
Details of co-ordinates of the affected area are included in Marine Notice No 26 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
Sailors Beware Of ROV Visual Survey Off South West Coast
#MarineNotice - Sailors and other mariners off the South West Coast should keep on the lookout for a visual survey by remote operated vehicle currently being undertaken by PSE Kindle Energy Ltd.
The survey, which was set to commence on Tuesday 9 May, will run for the next three weeks in the environs of the Kinsale Head Gas Field, subject to weather conditions, and is being carried out from the Skandi Olympia (Callsign C6XY8).
The vessel will have an ROV deployed close to the seabed and its travel rate (survey rate) is approximately 0.4 knots over the ground on a weather-dependent heading.
Regular safety messages will be broadcast on VHF Channel 16. All vessels, and particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to give the Skandi Olympia a wide berth and keep a sharp lookout in the revenant areas, as detailed in Marine Notice No 19 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
In case of any doubt, call the vessel on VHF and a safe course to follow will be given.
Marine Notice on Pipeline Survey in Celtic Sea
#NEWS UPDATE - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises on a pipeline survey in the Celtic Sea next month.
PSE Kinsale Energy Limited will be commencing the survey of the 24" Gas Export Pipeline on 6 March 2012 using the Marine Institute vessel RV Celtic Voyager (call sign EIQN). The survey is expected to last 1 to 2 days, depending on weather conditions.
The survey will take place along the existing pipeline route in the Celtic Sea, between the shoreline at Inch Beach in Co Cork and gas platform 'Alpha'.
The RV Celtic Voyager will display appropriate lights and signals, and will be towing side scan sonar with cables of up to 200m long. A Radio Navigation Warning will be issued via the Irish Coast Guard (schedule Bravo, four times a day) prior to the vessel's arrival at the survey area. The vessel will also keep a listening watch on VHF Channel 16.
All vessels, particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to give the RV Celtic Voyager and her towed equipment a wide berth and keep a sharp lookout in the relevant areas.
Further details for seafarers, including relevant co-ordinates, are included in Marine Notice No 7 of 2012, a PDF of which is available to read and download HERE.