Displaying items by tag: ferries
The Government has approved an emergency incentive to three ferry companies to keep five strategic maritime corridors between Ireland, Britain and Europe open during the COVID-19 pandemic writes Lorna Siggins
Minister for Transport Shane Ross says the government has approved an “emergency provision” of a maximum of 15 million euro towards the costs of maintaining passenger ferry services on the corridors.
The five routes - Dublin/Cherbourg and Rosslare/Fishguard, Pembroke, Cherbourg and Bilbao - have been designated as public service obligation (PSO), he said.
He said the financial measures are in compliance with the European Commission’s requirements under the emergency PSO arrangements, and the emergency procurement arrangements published in response to COVID-19.
The emergency measure will last up for a period of up to three months and apply to three companies, Irish Ferries, Stena Line and Brittany Ferries, serving these routes.
Stena Line confirmed earlier today that it is to “furlough” 600 staff and to make 150 redundant, as an “unavoidable response” to the COVID-19 crisis.
Mr Ross said the support package will be restricted to the five designated routes and will be targeted at compensating the gap between specified costs and revenues generated on the services - the details of which will be established in contracts with the ferry companies.
He said transport companies will continue to pay shipping companies for the services on these routes as usual.
“Measures to control the coronavirus pandemic have now practically stopped passenger traffic on combined passenger/roll-on roll-off ferries on the southern and Continental routes to and from Ireland,” Mr Ross said, explaining that the revenue was “necessary for the operations’ economic viability”.
Some 84% of Ireland’ s total trade volume is transported by sea, representing 62% of the value of all Irish trade. Some 50 per cent of the trade is on combined passenger/RORO services.
“The five routes in question are of strategic importance to Ireland because they ensure the robustness and resilience of Ireland’s lifeline supply chain which is critically important at this time for the movement of goods, including food and medical supplies, into and out of Ireland,” Mr Ross said.
He said that the routes also provide alternatives and “maintain contingency options” to the main route in and out of Dublin port during COVID-19.
He noted it was “critically important” the routes were working when economic activity “resumes in the coming months, and we prepare for Brexit”.
Ferry Passenger Numbers Up
Ferry passenger numbers travelling to and from Ireland increased by 4% during the first quarter of 2013 when compared to the corresponding period last year, while tourist car numbers increased by 1%, according to the latest figures from the Irish Maritime Development Office (IMDO).
This is the first quarterly increase since Q1 2011 for both tourist passengers and cars. Analysing these numbers on a country basis shows that for the Republic of Ireland, passenger numbers increased by 5% to 353,306 while car numbers increased by 1% to 99,277. For Northern Ireland, tourist numbers increased 4% to 260,144, while tourist car numbers increased by 2% to 80,029.
On the cross channel routes between the UK and the Island of Ireland, which accounts for 92% of total traffic, passenger numbers grew by 5%. Continental passenger traffic between Ireland and France fell by 15% during the first quarter. Quarter 1 tends to be the quietest quarter for the continental sector, which normally sees its busiest periods in Quarter 2 and Quarter 3.
While these headline figures represent positive news for the sector, the impact of Easter falling in Q1 instead of Q2 is likely to have had an impact on the passenger volumes. Initial data shows that passenger and tourist car numbers correspondingly declined in April due to the above factor, with overall numbers expected to be down for the first four months compared to same period last year.
GPS Backup Goes Live in World's Busiest Shipping Lane
#Shipping - The General Lighthouse Authorities of the UK and Ireland (GLA) have announced that ships in the Port of Dover, its approaches and part of the Dover Strait can now use eLoran radio navigation technology as a backup to satnav systems like GPS and Galileo.
The ground-based eLoran system provides alternative position and timing signals for improved navigational safety.
The Dover area, the world's busiest shipping lane, is the first in the world to achieve this initial operational capability (IOC) for shipping companies operating both passenger and cargo services.
This recent announcement represents the first of up to seven eLoran installations to be implemented along the East Coast of the United Kingdom.
The Thames Estuary and approaches up to Tilbury, the Humber Estuary and approaches, and the ports of Middlesbrough, Grangemouth and Aberdeen will all benefit from new installations, and the prototype service at Harwich and Felixstowe will be upgraded.
Although primarily intended as a maritime aid to navigation, eLoran could become a cost-effective backup for a wide range of applications that are becoming increasingly reliant on the position and timing information provided by satellite systems.
"Our primary concern at the GLA is for the safety of mariners," said Ian McNaught, chief executive of Trinity House, "But signals from eLoran transmitters could also provide essential backup to telecommunications, smart grid and high frequency trading systems vulnerable to jamming by natural or deliberate means.
"We encourage ship owners and mariners to assess eLoran in this region and provide feedback to the GLA on its performance."
P&O Ferries has installed an eLoran receiver on its new vessel Spirit of Britain. She will be based at Dover and is one of the largest passenger ships the busy Dover/Calais route has ever seen.
"Accurate real-time positional information is essential for the safe navigation of ships with modern electronic charts," said Captain Simon Richardson, head of safety management at P&O Ferries.
"Satellite navigation systems are vulnerable to degradation of signal strength and our ships have also experienced occasional loss of signal.
"We welcome the development of a robust alternative to provide redundancy in real-time positional information and we see eLoran as the most effective solution to countering the problem."
Commenting on the announcement, Britain's Shipping Minister Stephen Hammond said: "I congratulate the General Lighthouse Authorities on this initiative which seeks to improve navigational safety in what is the busiest shipping channel in the world, through the development and deployment of technology. I look forward to receiving reports of its effectiveness."
Marine Life Researchers Get Free Passage Across Irish Sea
#MARINE WILDLIFE - Seatruck Ferries is providing free passage this autumn for surveyors with a UK-based marine wildlife charity to discover how many dolphins and seabirds make their home in the Irish Sea.
MARINElife will be extending its marine conservation research on existing sailings operating between Liverpool and Dublin - and it is hoped its surveyors will spot a variety of cetaceans en route, including minke whales, common dolphin, Harbour Porpoise and Risso's dolphins.
Grey seals, basking sharks and a host of seabirds from the gannet to the Manx Shearwater, which winters off the coast of Brazil, may also be spotted.
The charity will be running monthly scientific surveys - the first started last week on 27th September – and its recorded sightings will be posted on the MARINElife website.
It's expected that the data collected will contribute to a better understanding of the distribution and abundance of dolphins, porpoises, seals and seabirds in the Irish Sea.
The research with Seatruck Ferries also contributes to a larger project operating on ferries around the UK coastline.
Kevin Gilland, Seatruck Ferries representative involved in the project, said: "We are delighted to expand our help to MARINElife so they can further develop the understanding of the wildlife in the area. We look forward to hearing more about the wildlife encountered on these routes."
Adrian Shephard, trustee for MARINElife, commented that "ferries, or ships of opportunity as we refer to them, are a very convenient way of carrying out off-shore surveys.
"They allow us to access the same areas of ocean and monitor for changes over time - vital information which forms the basis of conservation decisions."
MARINElife research director Dr Tom Brereton described the ferry routes across the Irish Sea as "particularly vital as the area is an important passage for whale, dolphins, sharks and even turtles."
Family Fun Day Cruise’s from Belfast
The 'cruise' onboard the ferry Stena Navigator (for virtual tour click HERE) is based on a return excursion on the North Channel route.
So what's included?...there's live music, disco / karaoke, face-painting, balloon modeling and party games for the children. For further family entertainment there's even a magician, Wii-games, free movies and free Wi-Fi.
In addition a 10% discount is available from the onboard shop, though exclusions apply.
Cruises are not catered for vehicles but apply to 'foot' passengers, for further details on terms and conditions, cruise itinerary and travel dates click HERE.
Seasonal Scenes Set for Fishguard
Fast-ferry Stena Lynx III departed Dun Laoghaire for Fishguard Harbour on a repositioning voyage today, writes Jehan Ashmore.
The 80m craft built in Hobart, Tasmania is due to dock at the Pembrokeshire port this afternoon in advance of seasonal sailings on Stena Line's Fishguard-Rosslare.The Stena 'Express' fast-ferry service is to resume in just over a fortnight's time. Sailings are scheduled to a daily single round trip between 1 July-4 September.
The 627 passenger / 120 car capacity fast-ferry will operate in tandem with the year-round operated conventional ferry-service served by the Stena Europe. Passage times are 120 minutes for the fast-ferry service while the Stena Europe takes 3 hours 30 minutes to sail across the St. Georges Channel.
In the same week that the fast-ferry takes up summer sailings from Fishguard, the small French flagged cruiseship Le Diament is to make the first of three calls in July and once in August.
The motoryacht-like vessel which can accommodate 226 passengers is the first cruise caller of the season and is run by the only French-owned cruise operator Compagnie De Iles Du Ponant.
Trade Levels Continue to Grow for Dublin Port
Dublin Port Company today published trade statistics for 2010 which showed an increase in the port's volumes of 6.1% in 2010.
Total throughput for the year was 28.1m tonnes which is less than 10% down from the port's best ever performance in 2007 at the height of the boom. Export traffic was particularly strong with 12.6% growth in the year.
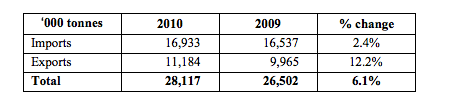
Growth was concentrated in the unitised modes but was partially offset by declines in bulk liquid and bulk solid cargoes due directly to the sluggish performance of the economy.
The volume of Ro-Ro freight units increased by 12.8% to 725,665 which is less than 1% down from the port's highest ever throughput. This performance confirms Dublin Port as the island's premier port for Ro-Ro. Growth in the year was driven in part by the new CLdN Ro-Ro services to Zeebrugge and Rotterdam.
Growth in Lo-Lo container volumes was 1.1% with an outturn of 554,259 TEU in 2010.
Dublin's position as the island's largest unitised port was reinforced by the commencement of rail freight services linking Dublin to Ballina. Demand for these services continues to grow and during 2011, we expect rail freight to remove up to 10,000 trucks from the road.
Further underpinning Dublin Port's popularity among RoRo shipping lines was the decision by Seatruck Ferries yesterday to announce a new freight- only service linking Dublin with Heysham which will commence Monday 14 Feb 2011.
Imports of fuel oil products (motor fuel and aviation spirit) dropped 6.5% in the year to 3.8m tonnes. Notwithstanding this decline, Dublin Port remains the country's most important port for oil imports, accounting for more than 50% of national demand.
In the bulk solid mode, there was a 7.9% decline to 1.5m tonnes in the year due to the continued decline in demand for construction materials. Trade cars imported through Dublin Port doubled to 47,249 in the year and there was also a strong performance in the ferry passenger business with numbers up 17.6% to 1.8m.
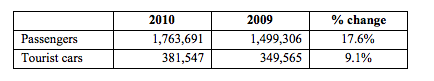
In addition to the ferry business, Dublin Port remained the country's largest port for cruise ship visits with 85 cruise ship calls bringing 130,000 tourists and crew to the city during the year.
Discussing Dublin Port Company's outlook for trade levels in 2011, Eamonn O'Reilly, Chief Executive of Dublin Port Company, said:
"2010 was an exceptional year for Dublin Port. Notwithstanding the poor performance of the economy, port volumes grew by 6.1% as importers and exporters sought to minimise the cost of moving goods to market. Passenger and tourism volumes were also very buoyant as the benefits and reliability of ferry travel became clear particularly during the ash-cloud crisis.
"For 2011, we are projecting continued growth, albeit at a reduced level compared to 2010."Dublin Port's success is due to its location at the centre of the largest concentration of population on the island and also to the exceptional connections to the national road and rail networks. Dublin is close to the main markets, and shipping services are available from a wide range of excellent ferry and container lines offering importers and exporters competitive and reliable routes to market. We are very conscious of the central role Dublin Port plays in facilitating merchandise trade, the value of which is in excess of 80% of Ireland's GDP, and we are committed to continuing to develop the port in line with the needs of the economy and funded from our own resources."
Dublin Port Company's Annual Report for 2010 will be published later in the year.
How Many Times Do I Have to Say the Sea is Vital to Ireland?
Ireland has the largest maritime area-to-land mass in the European Union, but derives only 1% of GDP from the maritime sector. At a time when the economy needs every benefit it can get this figure is startling, particularly when compared to countries with other extensive coastlines, such as Norway where the figure is 20%, Denmark where it is 11% and even the UK which has increased its figure to 5%.
Despite being an island nation with a strong dependency on the sea, the Irish maritime economy is still in its infancy, both in terms of investment and of recognition.
Once again the importance of the sea was shown in the pre-Christmas weather problems. When air transport again failed the public, the ferries continued to operate. When road transport needed salt for gritting to keep roads open, it was ships which brought the salt to Ireland.
How many times do I have to challenge the ignorance and stupidity of the State, of Government, towards the sea? How many times do I have to remind the public of how dependent we are on the sea as an island nation?
Though still considered a low priority by Government, the maritime sector is worth €3 billion to the nation and supports 440,000 direct and indirect jobs. According to the Marine Institute in the "SeaChange Programme," this could be increased by at least 50%.
In Cork the Coastal and Marine Resources Centre which is part of UCC's Environmental Research Institute and has been working out of the Naval Base on Haulbowline Island has changed its name and is planning to move to a new maritime research facility. It has become the "Coastal and Marine Research Centre".
For over ten years the CMRC has been promoting the use of integrated coastal zone management as a means of achieving sustainable development in the use of coastal and marine resources, including marine ecology, seabed mapping, coastal processes, remote sensing, geology and geomatics.
A new maritime research facility is planned at Ringaskiddy, adjacent to the National Maritime College, part of the announced intention to establish a Maritime and Energy Research Campus and Commercial Cluster. The Department of Communications, Energy and Natural Resources, Bord Gais and the UCC Glucksman Foundation contributed funding, together with €7.5m. from the Higher Education Authority. As part of the National Ocean Energy Strategy, it will "bring together on one site the people, their ideas and the infrastructure to support the development of ocean energy," according to MERC Chairman, Peter Coyle. "Our aim is to produce innovative technical solutions to support the development of the Irish maritime sector."
This will include ocean energy opportunities, such as wave power where Irish companies have been leading the way. Shipping, logistics and maritime transport, marine recreation, maritime security research and maritime space applications are amongst other aspects of research work to be undertaken in Ringaskiddy.
Valerie Cummins, who led the Coastal Marine Resources Centre over past years has been appointed Director of MERC and is being replaced as Director at the newly re-named Coastal and Marine Research Centre by Jeremy Gault.
This article is reprinted by permission of the EVENING ECHO newspaper, Cork, where Tom MacSweeney writes maritime columns twice weekly. Evening Echo website: www.eecho.ie
Multi-role Rosslare Europort
The port of Rosslare Europort is synonymous with ferries plying the southern Irish Sea on routes to Wales and continental services to France, writes Jehan Ashmore. Apart from ferries the port also caters for a small fishing fleet and in more recent years has been a destination point for the importation of wind-turbine componants in addition to French-built trade vehicles.
Other types of commercial shipping activity are catered for with the recent call of the Ballyheally, a Panamanian flagged, but Irish owned general dry-cargo short-sea trading vessel. Ballyhealy was awaiting orders while moored at her 'homeport' of Rosslare. Several days later, Ballyheally departed the south-east port to load scrap-metal at New Ross on 13 August. The ship was bound for Liverpool and arrived in the Mersey to berth in Canada Dock on 15 August.
Ballyheally is owned by the O'Flaherty Brothers, who operate a diverse range of shipping interests. This consists of a large fishing trawler fleet and processing plant based in nearby Kilmore Quay. In addition to operating Celtic Link Ferries Rosslare-Cherbourg route conveying passengers, freight vehicles and uniquely conveying livestock.
After the closure by P&O Irish Sea of the Rosslare-Cherbourg route, the O'Flaherty Brothers purchased the route and ship from the large ferry shipping company in 2005 so to ensure fish exports from Kilmore Quay were retained on the direct transport links to the continent to include markets in Germany, Italy, France and Spain. The 17-hour route is served by the chartered Norman Voyager,a ro-pax designed vessel.
The term Ro-Pax refers to the ferry industry terminology for a vessel designed pre-dominantly to cater for large volumes of freight vehicles across most of the vessels decks. In addition to incorporating a small passenger capacity though with less facilities than those available on conventional ferries. Ro-Pax vessels tend to have a higher speed than standard ferries, suiting the demands of freight customers and condusive to daily deliveries of supermarket perishable products.






































































