Displaying items by tag: Hibernia Express
Emergency Fibre Optic Cable Repair off the South East Coast
The Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport has been advised that Global Marine Systems Ltd has been contracted to undertake an emergency repair to the Hibernia Express submarine fibre optic telecommunications cable in the Irish Sea on the outer limits of Irish Territorial Waters.
The CS “Wave Sentinel” (Callsign MZBC8) is scheduled to arrive on site in the evening 14th April 2016 to commence works.
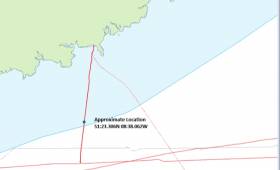
The estimated location is 51º23.306N 08º38.062W as shown on the map above and the duration of the cable repair will be approximately 5 days depending upon weather or other operational conditions. The vessel will be broadcasting/listening on VHF Channel 16 during the project.
#HiberniaExpress - The Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport advises that TE SubCom, on behalf of Hibernia Express, is carrying out a route clearance operation and a pre-lay grapnel run along the Hibernia Express cable route using the M/V Ile d’Aix (Callsign FICI) and M/V Atlantic Guardian (Callsign HO6566.
The operations, which follow earlier work on the same subsea cable route in March, commenced on 17 and 13 May 2015 respectively are expected to last until the end of June 2015, weather permitting.
The vessels will be towing grapnels astern at a distance depending on water depth, and as such, will be restricted in their ability to manoeuvre.
All vessels are requested to give these operation a wide berth. The project vessels will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
Details of co-ordinates for both vessels' work areas are included in Marine Notices Nos 18 and 19 of 2015, available to read or download HERE and HERE.
#HiberniaExpress – The Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport has been advised that TE SubCom, on behalf of Hibernia Express, is scheduled to carry out a Route Clearance Operation and a Pre Lay Grapnel Run along the Hibernia Express cable route off the South of Ireland and Bristol Channel. The department has issued a marine notice to all Shipowners, Fishing Vessel Owners, Agents, Shipmasters, Skippers, Fishermen, Yachtsmen and Seafarers.
TE SubCom is prime contractor to Hibernia Express to supply and install a trans-Atlantic subsea fiber optic telecommunications cable system designated the "Hibernia Express Cable System" between Halifax (Nova Scotia), Cork (Ireland) and Brean (United Kingdom). A schematic representation of the whole of the route of the cable is shown below, as well as the start and end points of the route position listings.
Position Listing for Hibernia Express from offshore Cork, Ireland to Brean UK:-
Start Point (WGS-84) 51˚ 15.0760" N 008˚ 39.2900" W
End Point 51˚ 17.1808" N 003˚ 00.8175" W
Position Listing for Hibernia Express from the Continental Shelf to offshore Cork, Ireland:-
Start Point (WGS-84) 51˚ 39.1700" N 015˚ 11.6480" W
End Point 51˚ 15.0760" N 008˚ 39.2900" W
Position Listing for Hibernia Express from Cork landing to offshore Cork, Ireland:-
Start Point (WGS-84) 51˚ 38.6875" N 008˚ 34.9908" W
End Point 51˚ 15.0760" N 008˚ 39.2900" W
Generally, at water depths less than 1,500 metres, the cable route will be cleared of debris and obstructions (including removal of out-of-service cables), the seabed will be cleared to receive the cable, and the cable will be laid and buried by plow within that trench. At water depths greater than 1,500 metres, the cable will generally be laid directly on the seabed.
A cable corridor which is cleared of all out-of service cables must be properly established. The width of the corridor will be between approximately 200 and 1000 metres, depending on water depth. This clearance will be by severance and lateral displacement of the out of service cables, with retrieval on board the ship of severed portions for ultimate disposal ashore.
In addition to clearance of out-of-service cables, grapnel drags will be performed over the corridors so established to clear away other sea-bed debris such as abandoned wires, hawsers or other gear. The grapnel drags will penetrate the seabed by 40-50 cm and materials recovered will similarly be retrieved on board ship for ultimate disposal ashore.
Although more than one ship in total will be required to perform the whole of the project, the vessel "MV Atlantic Guardian" (Callsign: V3AR3), will undertake these Route Clearance and Pre Lay Grapnel Runs along the cable route as depicted in the accompanying chart.
The operations will start in Brean, United Kingdom on 24th March 2015 and will head west from the Bristol Channel, into the Celtic Sea and south of Ireland onto the Continental Shelf. The route clearance operations will last for approximately 45 days, weather permitting. Overall, operations are due to complete in deep sea off the Continental Shelf in mid June 2015 weather permitting. "MV Atlantic Guardian" will be displaying the lights and shapes associated with the work.
The vessel will be towing grapnels astern at a distance depending on water depth and, as such, will be restricted in its ability to manoeuvre and all vessels are requested to give this operation a wide berth. The project vessel will be listening on VHF Channel 16 throughout the project.
All vessels, particularly those engaged in fishing, are requested to give the "MV Atlantic Guardian" and her towed equipment a wide berth and keep a sharp lookout in the relevant areas.
All mariners are reminded of their responsibilities under the International Collision Regulations and are reminded of Marine Notice No. 17 of 2007, which gives general advice in relation to the activities of vessels engaged in survey work for hydrographic, seismic, fishing research and underwater operations.
The International Regulations for Prevention of Collisions at Sea (COLREGS) are implemented in Irish law by the Merchant Shipping (Collision Regulations) (Ships and Water Craft on the Water) Order 2012 [S.I. No. 507 of 2012], and the Signals of Distress (Ships) Rules 2012 [S.I. No.170 of 2012]. See Marine Notice No. 06 of 2013. These Statutory Instruments may be purchased by mail order from Government Publications, Office of Public Works, 52 St. Stephen's Green, Dublin 2. Tel: (01) 6476834/1890-213434. They are also available online at: www.irishstatutebook.ie.
Irish Maritime Administration,
Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport,
Leeson Lane, Dublin 2, Ireland.
20/03/2015