Displaying items by tag: Port of Cherbourg
Brittany Ferries Gives Green Light to Port of Cherbourg-Bayonne, South-West France Rail-Freight Link
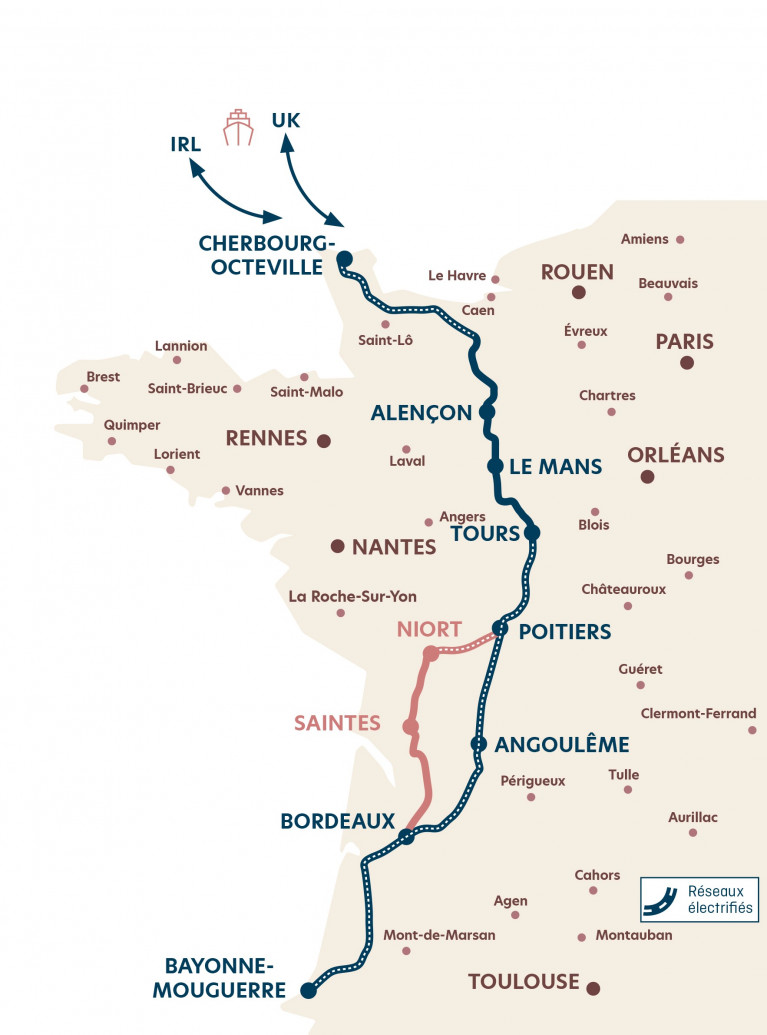
Brittany Ferries has given the go-ahead to a new rail-freight link connecting the Port of Cherbourg in Normandy and Bayonne in the Nouvelle Aquitaine region in south-western France.
The Breton based ferry company first announced the rail project back in February 2020, shortly before the COVID-19 health crisis hit, forcing a reduction in ferry services for nearly two years. But while the project—which Brittany Ferries deems strategic—was delayed, it was never cancelled.
During the pause, Brittany Ferries worked with French rail network operator SNCF Réseau and the Ministry for Ecological Transition to determine the routing for the new service, which will provide daily return journeys between Cherbourg and Mouguerre. Following a study into the modification of four railway tunnels on the Atlantic corridor route to allow the lowest available wagons to pass through, a framework agreement was signed, allowing the project to enter its concrete development phase.
With support from the French-state, Europe, and the regions of Normandie and Nouvelle Aquitaine, Brittany Ferries will open the ‘rail motorway’ linking the port of Cherbourg to the European Freight Centre at Mouguerre, near Bayonne, thereby connecting Spain to the UK and Ireland via the French railway network.
The launch of the new service, initially planned for 2022, is now expected by mid-2024.
Minimising transport’s environmental impact
To meet the needs of hauliers and logistics companies who wish to reduce harmful emissions and greenhouse gases, Brittany Ferries will diversify its freight offer, by offering a combined transport service for unaccompanied trailers along the French Atlantic Coast. The new link will form a natural extension of Brittany Ferries’ existing sea routes linking Cherbourg to Ireland and the UK, cutting the number of lorries transiting France by road by around 25,000 per year. Brittany Ferries will operate and sell the new service, effectively becoming a rail operator.
The next steps
Planning for rail movements using the French rail network is now underway.
The next phase will comprise the construction of two rail freight terminals in Cherbourg and Mouguerre, and the acquisition of wagons and specialised loading equipment for the Lohr Railway System which has been selected for the project.
Ports de Normandie, in its capacity as an investor, and the Port of Cherbourg in its capacity as a future operator, are also involved in planning for the next phase of the project. The first step is to organise a preliminary consultation with the residents of Cherbourg. The Normandy part of the project has received the support of Europe, the Normandy Regional Council, the Manche department, and the Communauté d’agglomération du Cotentin.
Brittany Ferries meanwhile will work closely with the Communauté d’agglomération du Pays Basque (CAPB) and the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region to carry out public consultation in Bayonne. The company has initiated discussions with the CAPB in order to acquire land for the Mouguerre rail freight terminal. In addition, a consortium comprising Mouguerre transport operators, the CAPB and Brittany Ferries has been formed to respond to a European Union call for proposals under the Connecting Europe Facility, which aims to develop new multimodal platforms.
Main characteristics of the ‘rail motorway’
- A rail service with sea connections linking Poole, Portsmouth and Rosslare (Europort) to Cherbourg, allowing seamless transport of unaccompanied trailers from Ireland and UK to the Iberian Peninsula and vice versa.
- A 970km rail journey replacing a 920km road journey
- A regular year-round service, with one daily return journey, six to seven days per week, operated by two trains:
- Each train is composed of 21 MODALOHR UIC wagons with double pockets, allowing 42 trailers to be transported. Trailers are rolled on and off using specialised horizontal handling equipment.
- Parts of the route are not currently electrified. Initially the trains will be hauled by diesel locomotives, but in the future these could be replaced by dual-mode locomotives, further reducing emissions.
- From 2024 trains will be routed via Saintes, then from 2026 via the Poitiers-Angoulême-Bordeaux mainline.
- High service reliability and punctuality will foster customer loyalty.
- Journeys have been timetabled to connect with ferry arrival and departure times, whilst also avoiding periods of peak road traffic in Cherbourg.
The southbound service will depart Cherbourg at 19:15, arriving in Bayonne/Mouguerre the following day at 11:00. The northbound service will depart Bayonne/Mouguerre at 19:26, arriving at Cherbourg the following day at 11:08.
The service will be available to customers of all Cherbourg ferry operators, as well as logistics companies based in the wider Cherbourg area.
Modalohr railway wagons for sustainable transport
Founded over 50 years ago, the Alsace-based LOHR group offers its customers transport systems that meet the needs of an increasingly environmentally-aware transport sector.
Modalohr wagons combined with fixed equipment at terminals allow rapid and secure loading and unloading of semitrailers. Since 2003 this French technology has allowed more than two million trucks to be shifted from European roads to railways, cutting carbon dioxide emissions by more than 2 million tonnes. Each time a semitrailer is transported over 1000km by rail instead of road, negative externalities such as accidents, noise, congestion and emissions are reduced by €800.
Overnight Sailing Marks End-of-Seasonal French Route
The former Scandinavian cruiserferry was built in 1987 to serve on Color Line's Oslo-Kiel route as their Kronprins Harald. In 2007 she was sold to start French sailings and at 31,914grt, she is the largest cruiseferry to operate under Irish Ferries continental routes. Passenger capacity is just shy of 1,500 and cars total 730 in addiition space for around 90 freight vehicles. For a virtual tour of the cruiseferry's on board facilities and exterior deck views click HERE.
Winter sailings will run to the end of the year with a final departure on 30th December outbound and returning from France on 2nd January 2012. Thereafter there will be a no sailings as the cruiseferry is to undergo annual dry-docking before resuming sailings. The first sailing from Ireland is 19th February and the corresponding return sailing from France is 21st February. To keep up-to-date with sailing schedules click HERE.