Displaying items by tag: monkfish
Marine Notice: Annual Monkfish & Megrim Survey
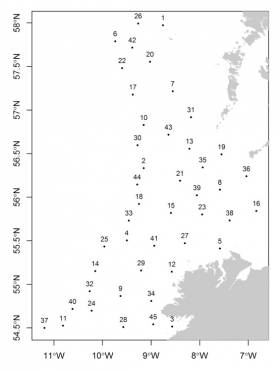
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises that the Marine Institute is carrying out its annual Irish anglerfish and megrim survey (IAMS 2017) in fulfilment of Ireland’s Common Fisheries Policy obligations from this Tuesday 14 February to Friday 17 March.
The IAMS is a demersal trawl and beam trawl survey consisting of around 85 otter trawls (60 minutes) and 25 beam trawls (30 minutes) in International Council for Exploration of the Sea (ICES) area 7b, 7c, 7g, 7h, 7j and 7k off the West, South West and South Coasts.
Fishing in 2017 will take place within a three-nautical-mile radius of the positions indicated in Marine Notice No 5 of 2017, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), which will display all appropriate lights and signals during the survey and will also be listening on VHF Channel 16.
The vessel will be towing a Jackson demersal trawl or two 4m beam trawls during operations. The Marine Institute requests that commercial fishing and other marine operators to keep a 3nm area around the tow points clear of any gear or apparatus during the survey period outlined above.
While there is no statutory provision for the loss of gear at sea, the Marine Institute will make every effort to avoid gear adequately marked according to legislation that may be encountered in the notified areas.
In the event that an operator has static gear or other obstructions within 3nm of the points listed, it is the responsibility of the owner to notify the survey managers or vessel directly.
This should be communicated by identifying specifically which ‘station’ is of concern using the appendix and contact details provided in the Marine Notice. It is not required to provide positional details of commercial operations beyond 4nm of the survey points provided.
Specifics of any fishing gear or other obstructions that are known and cannot be kept clear of these survey haul locations can be notified using the contact details provided.
Marine Notice: Demersal Monkfish & Megrim Survey Off North Coast
#MarineNotice - The latest Marine Notice from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises that the Marine Institute is carrying out a monkfish and megrim trawl survey off the north of Ireland between Friday 26 February and Sunday 6 March 2016.
The survey consists of a maximum of 45 fishing stations of one-hour duration each in ICES (International Council for Exploration of the Sea) area VIa.
Bottom trawling will take place within a 3nm radius of the locations detailed in Marine Notice No 7 of 2016, a PDF of which is available to read or download HERE.
The survey will be conducted by the RV Celtic Explorer (Callsign EIGB), which will display all appropriate lights and signal during the survey and will also be listening on VHF Channel 16. The vessel will be towing a commercial monkfish demersal trawl during fishing operations.
The Marine Institute requests commercial fishermen to keep a 3 nm area around the tow points clear of all commercial gear during the period.
While there is no statutory provision for the loss of fishing gear, the Marine Institute will make every effort to avoid gear adequately marked according to legislation that may have drifted into the notified areas.
In the event that a fisherman has static gear or other obstructions within 3mn of the points listed, it is the responsibility of the owner to notify the survey managers or vessel directly using the contact information provided.
Skipper Seeks Costs Over Fishing Offence Aquittals
#Fishing - After two lengthy trials – and two acquittals – a trawler skipper from the Aran Islands accused of breaching fishing regulations is seeking costs against the State, as The Irish Times reports.
Inis Mór fisherman John Conneely was twice taken to Galway Circuit Criminal Court this year over two separate alleged incidences of incorrect log entries for his monkfish catch on dates in 2006.
In the first trial in January, the jury found Conneely not guilty of one breach of EU fishing regulations relating to the strictly quota-managed species – a victim of the widely criticised discards policy.
The second trial last week, over similar alleged offences, saw Judge Rory McCabe direct the jury to find Conneely not guilty of a charge relating to keeping more monkfish on board than allowed by quota.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Giant Monkfish Among West Coast Fishermen's Strange Catches
#Fishing - Irish fishermen have reported some unusual catches in recent days, according to The Irish Times.
Galway trawler Martins Marie brought home a massive lobster weighting almost 3kg with a carapace of more than 15cm.
But Rossaveal vessel Virtuous did one better on their trip to the Porcupine Bank by landing a giant monkfish that weighed in at 40kg even after gutting.
The Irish Times has more on this story HERE.
Fisherman Defends Giveaway of Over-Quota Monkfish
#FISHING - A Wexford fisherman has defended the free giving away of monkfish to the public yesterday morning after exceeding an EU quota.
RTÉ News reports that Seamus O'Flaherty, owner of the trawler Saltees Quest, handed out the fish to hundreds of passers-by at Kilmore Quay rather than have the surplus catch thrown back into the water.
The vessel's skipper Jimmy Byrne defended the move as a protest against an EU rule that requires over-quota fish to be discarded at sea.
According to The Irish Times, officers with the Sea Fisheries Protection Authority, who observed the monkfish giveaway yesterday, have prepared a file for submission to the Director of Public Prosecution.
The authority said it found a large quantity of monkfish retained on the vessel which had been logged as having been discarded - and emphasised that catches landed that are not declared as discards are still counted against the national quota.
Byrne, meanwhile, described the practice of discards of dead fish as "crazy" especially when many people in Ireland are "going hungry".
He commented: “I have a certain quota of fish to catch and the monkfish end up getting caught. There’s more monkfish in Ireland than ever before. I can’t tell the monkfish not to go into the net."
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
Cumbrians Urged to Try New Fish to Save Irish Sea Stocks
#FISHING - Seafood lovers of Cumbria in north-west England have been urged to broaden their tastes to save depleted stocks of their favourite fish in the Irish Sea.
According to the News & Star, some 80% of Britons "insist upon eating just five types of fish – cod, tuna, salmon, prawn and haddock."
But the Cumbria Wildlife Trust says that with coastal waters facing the serious threat of overfishing, a rethink is needed among both consumers and suppliers alike.
“The Irish Sea has a wide range of edible fish species but you wouldn’t know it judging by the fish counters in supermarkets across the county," says Lindsay Sullivan of the trust's Wild Oceans project, an 18-month scheme that hopes to "turn the tide for seafood".
A big part of this is encouraging consumers to skip the usual white fish and try different species such as flounder, monkfish and red mulllet, creating demand for cheaper and more sustainable fishing.
The News & Star has more on the story HERE.