Displaying items by tag: Docklands
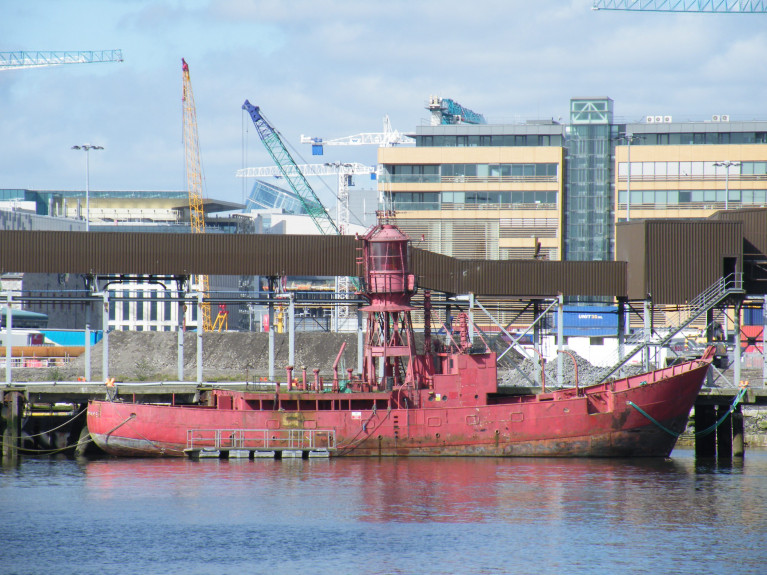
Dublin 'Docklands' Developer Harry Crosbie Seeks Return of former Lightship ‘Kittiwake’
The Dublin 'docklands' developer, Harry Crosbie is launching a campaign for the return of the 134ft (floating) landmark, Kittiwake.
The former lightship which he (had berthed) alongside the Liffey and (opposite) of The Point Depot, now the O2, then one of his many docklands business ventures.
But the distinctive red ship, which was sold to him by its owners, the Commissioners of Irish Lights (CIL), for a reputed €60,000, is now in the possession of Dublin Port, which has docked it away from public view in Alexandra Basin within the port complex.
For more on this development of the former lightship, Independent.ie reports here.
As Afloat previously reported, it is almost a decade since Crosbie's plans to relocate the former lightship Kittiwake on the North Quay Wall, in front of the O2 Theatre, were refused permission.
The 1959 built lightship was converted in the 1980's by Irish Lights into an Automated Light-Float (ALF) and last served on station at South Rock off the Co. Down coast until 2005.
ALF Kittiwake was the second last lightship to operate in waters around Ireland.
Reclaim Land From Sea At Clontarf To Tackle Housing Crisis, Suggests Docklands Developer
Clontarf residents will likely be wide-eyed at a recent “radical” proposal by Docklands developer Harry Crosbie to reclaim land from the sea off the North Dublin suburb.
According to The Irish Times, the property mogul suggests using Dutch engineering knowhow to reclaim some 250 acres between the existing Docklands and Clontarf Road, which currently lie within the River Tokla Estuary Special Protection Area, that could be repurposed for homes for 65,000 people and help tackle the housing crisis.
Crosbie — whose former warehouse on Tolka Quay Road was recently licensed by the State for post-Brexit freight checks — admitted to Marian Finucane on RTÉ Radio 1 on Saturday (17 August) that his plan was “radical” but that the people of Clontarf would come to see it make the area “a nicer place to live in over a period of 10 years”.
He also shot down similar recent proposals by Royal Institute of the Architects of Ireland president David Browne to reclaim land off Sandymount Strand, on the opposite side of Dublin Bay, as “a bridge too far”.
The Irish Times has more on the story HERE.
On RTE One Tonight: New Documentary 'Starboard Home'
A new documentary 'Starboard Home' (on RTE One tonight at 10.15pm) which formed part of the 1916 Easter Rising centenary commemorations held in Dublin, involved musicians commissioned to produce works inspired by the capital, its port and the Liffey.
In a rare musicial opportunity, Dublin Port and the National Concert Hall invited Irish musicians to respond to the theme resulting to an acclaimed modern song cycle that rekindles the formative bond between the city and Dublin Bay through music, song and the spoken word.
Among musicians lined up for the unique commemorative event were James Vincent McMarrow and Gemma Hayes.
In conjunction with tonight's broadcast, Moira Sweeney’s film ‘Keepers of the Port’ will be airing on RTÉ’s Culture website.
So keep a look-out! for the Starboard Home documentary which is one not to be missed!
Ringsend Remembers First Irishman To Die In Great War
#DublinPort - A plaque commemorating the first Irishman to die in the First World War has been unveiled in his home neighbourhood of Ringsend in Dublin's south Docklands, where many of his descendants still live.
As The Irish Times reports, Joseph Pierce Murphy died among 151 sailors who perished when the Royal Navy cruiser HMS Amphion was sunk by a mine in the North Sea on the morning of 6 August 1914.
Seven sailors from Cork were also killed that morning, and three of them were remembered at a Mass at the Naval Service base on Haulbowline in Cork Harbour last weekend.
The plaque unveiling on Wedneday 6 August behind St Patrick's Church on Thorncastle Street – just around the corner from Muphy's home at 2 Thorncastle Place – was presided over by Lord Mayor of Dublin Christy Burke and British Ambassador to Ireland Dominick Chilcott.
Also in attendance was Dublin Port Company chief Eamonn O’Reilly, who said: “It is appropriate and important that his family and the local community can pay tribute to the life of this young Navy sailor in his hometown of Ringsend, and I would encourage people to see the plaque in his honour.”
The Irish Times has much more on the story HERE.
#Docklands - Local business interests and marine authorities are mooting ambitious new plan to construct a dozen pontoons along the River Liffey in Dublin's Docklands in 2014.
The Sunday Times last weekend reported that the €4 million scheme, put forward by the Docklands Business Forum, has the backing of the Dublin Port Company and Waterways Ireland as well as Dublin City Council.
It forms part of the port's 30-year 'masterplan' and is intended to revive the Royal and Grand Canals that feed into the Liffey on the north and south sides respectively, and encourage visiting yachts to moor closer to the city centre.
"The Docklands has a huge resource for boats which we just need to improve," said the forum's chief executive Alan Robinson.
Among those suggested improvements is the refurbishing of Camden Lock on the Grand Canal Basin - but first in line are the pontoons, which were a temporary feature of the capital during last year's Tall Ships Festival.
The intention is to make these pontoons a permanent fixture between the East Link Bridge and the Samuel Beckett Bridge, to "generate a new type of activity in the city" in an area that recently hosted its first annual Riverfest, not to mention the once-in-a-lifetime FlightFest.
Marine Notice: Works on Quay Wall at North Wall Quay
#MARINE NOTICE - The latest Marine Notice (No 61 of 2012) from the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport (DTTAS) advises that J Murphy & Sons, on behalf of Dublin City Council, will construct a 600mm emergency overflow pipe from Spencer Dock Pump Station through the Liffey quay wall at North Wall Quay/New Wapping Street Junction, Dublin 1.
The work will commence on or around 23 November 2012 and will last approximately two weeks, weather permitting. The location of the works relating to maritime positions is:
Latitude 53° 20’ 49.431 N / Longitude 006° 14’ 08.171 W
The works area will be marked by red buoys. These buoys will be an appropriate distance from the works area and will clearly identify the scaffold when submerged due to high tide. The cantilever beams will project 1.5 metres out from the quay wall.
The only vessel used during the works will be a rescue boat which will be moored at the works location for its duration.
Dublin Hosts Ocean Energy Conference
#POWER FROM THE SEA - The fourth International Conference on Ocean Energy (ICOE) begins tomorrow Wednesday 17 October at the Convention Centre in Dublin's Docklands.
Over 750 international experts and world-leading companies in ocean energy will gather in Ireland’s capital city for the three-day conference, hosted by the Sustainable Energy Authority of Ireland (SEAI) in association with the European Ocean Energy Association.
Global industry and academic experts in marine renewable energy will present over a hundred papers on themes important to growing this new marine sector.
The conference also provides an opportunity for a trade exhibition where many of the top industrial players will demonstrate the latest technologies in harnessing renewable energy from the sea.
The International Conference on Ocean Energy is the global marine energy event focused on the industrial development of renewable marine energy. Held every two years, the goal of the conference and exhibition is to share recent experiences from research and demonstration efforts.
It aims to accelerate development by stimulating collaboration networks between companies and research and development centres. It also specifically targets engagement of the experience of operators in related marine and power industry sectors.
For more details see the information flyer available to read or download HERE.
Step Aboard the Tall Ships in Dublin This Weekend
#TALL SHIPS - Organisers of the Tall Ships Races Festival - which kicks off today in Dublin's Docklands - have announced visiting hours for members of the public to step on board some of the 43 vessels docked on the city's quays between now and Sunday.
A total of nine tall ships will have free access to the public at different times over the weekend, available on a first come first served basis.
On the south quays, the Amerigo Vespucci will be open today from 3pm to 7pm, tomorrow from 10.30am to 1pm and 3pm to 6pm, and Saturday from 10.30am to 1pm and 3pm to 7pm.
The Mexican tall ship Cuauhtemoc - the last of the fleet to arrive this morning - will be open till 7pm today, and from 10am till 11pm tomorrow and Saturday.
The Danmark has open hours today from 3.30pm to 5pm, from 1.30pm to 5pm tomorrow and on Saturday from 1pm to 4pm.
The Guayus stays open to the public today till 9pm this evening, and will be open again tomorrow and Saturday from 10am till 9pm, and on Sunday before the Parade of Sail from 10.30am to 1pm.
The Lord Nelson will be open on Saturday from 10am to 1pm and 2pm to 5pm, while the Pelican of London is open tomorrow and Saturday from 10am to 1pm and 3pm to 6pm, and on Sunday morning from 10.30am till 1pm.
Completing the south quays moorings, the Stavros S Niarchos will be open tomorrow from noon till 5pm and on Saturday from noon till 6pm.
On the north quays, the Fryderyk Chopin is open till 1pm today and again from 3pm to 6pm. It reopens tomorrow and Saturday from 10am till 1pm, and on Sunday from 10.30am to 1pm.
And the STS flagship Pogoria will welcome the public tomorrow from 10am to 6pm and again on Saturday from 10am till 2pm.
Meanwhile, don't forget that another great way to see the tall ships at their moorings is from the water on board the Allianz All-Aboard Liffey Cruise, with seats available from just €1!
Teen Rescued from Docklands During Tall Ships Festival Prep
#TALL SHIPS - A 15-year-old boy was rescued from the water at Dublin's Grand Canal Dock yesterday after getting into difficulty while swimming.
According to RTÉ News, the teenager from Blanchardstown was swimming with a number of friends at Hanover Quay amid preparations for the Tall Ships Races Festival when he went missing around lunchtime yesterday.
Fire officers reportedly retrieved the boy from the water and gave him CPR on the quayside before he was transferred to St Vincent's Hospital in Merrion.
The Irish Times reports that the teen was in the area to volunteer with the Kings of Concrete urban sports display group as part of the Tall Ships Races events.
Organisers later confirmed that the boy was not preparing for his volunteer work at the time of the incident, which underlines the importance of water safety for all volunteers and visitors at the Docklands festival starting tomorrow.
Safety is also paramount aboard the tall ships fleet as they make their way to the capital, with damage inflicted on nearly all the more than 40 vessels in stormy conditions in the Bay of Biscay, according to the Irish Independent.
Ecuadorian naval ship the Guayas suffered eight ripped sails in the storm, but the worst damage was sustained by the Polish schooner Captain Borchardt, which arrived in Dublin with a broken mast.
However, master of the skip Janus Zbierajewski jokingly described the experience as "absolutely perfect weather".
The bad weather was enough to force at least once ship to abandon the final race leg, with Sail Training Association flagship STS Pogoria arriving in Dublin Port some days ahead of schedule.
Waterways Ireland wishes to advise masters and owners that as part of the Docklands Summer Festival, yacht racing will take place in the Grand Canal Basin from 09.00 hrs until 16.00hrs on Sun 26th June.
On Sat 25th, there will be a practice session from 13.00hrs until 19.00hrs.
In addition 'Come and Try It' activities including canoeing and paddle-boarding for novices will take place in the inner basin beside the Waterways Ireland Visitors Centre, from 10.00hrs until 18.00 on both days.
There will be restricted movement of vessels in the Grand Canal Basin during the events, lock operations will be suspended once the events have commenced.
Commercial operators in the Dock are requested to adhere to these restrictions and the planned routes and schedules for the duration of the event.
Boat owners presently in the Grand Canal Basin should comply with all reasonable instructions and guidance from event marshals.