Displaying items by tag: white diesel
RYA Northern Ireland Seek Further Clarity on Red Diesel Withdrawal from Recreational Boaters
The Royal Yachting Association of Northern Ireland (RYA Northern Ireland), together with British Marine and the Cruising Association, met yesterday with representatives from HM Revenue and Customs and HM Treasury to discuss the difficulties for private pleasure craft in Northern Ireland resulting from the decision to withdraw the use of red diesel.
Recreational boaters and the marine industry urgently need clarity surrounding the Government's plans for implementation and how it intends to address the practical difficulties before June.
As Afloat reported earlier, the Cruising Association has said no white diesel supply exists in Northern Ireland leaving boaters without options later this summer
The discussions took place against the background of the Protocol on Ireland/Northern Ireland and in particular Article 8 concerning Union VAT and excise law that applies to Northern Ireland.
To achieve consistency with the 2018 judgment by the Court of Justice of the European Union and to ensure that the UK meets its international obligations under the Protocol, private pleasure craft users in Northern Ireland will no longer be able to use red diesel for propelling their craft.
It is proposed that this change will take effect by June this year. The RYA has stressed the difficulties presented by this short timescale and requested a longer period to address the white diesel supply issues that the decision presents. Once implemented, private pleasure craft users in Northern Ireland will have to use white diesel for propulsion instead of red diesel.
Private pleasure craft users in Northern Ireland with only one fuel tank on board for propulsion and non-propulsion will not have to pay a higher rate of duty on their non-propulsion use of diesel than they would otherwise have to pay. The Government are intending to introduce a new relief scheme in Northern Ireland which will become effective from the date that users become obliged to use white diesel.
The RYA is concerned that the volume of sales of diesel to private pleasure craft is not great enough for suppliers to justify the expense of providing a second pump at the waterside, which is going to cause significant supply problems.
HMRC have confirmed that once the change does take effect, it would be illegal to buy red diesel for private pleasure craft propulsion in Northern Ireland, but fuel already present in tanks could be used without penalty. Private pleasure craft from Northern Ireland that fill up in Great Britain (GB) in future could do so under the Istanbul Convention which will allow red diesel legitimately purchased in GB to be taken back to Northern Ireland in the main fuel tanks of a boat.
The RYA recommends that recreational boaters with marked 'red' diesel purchased in GB:
- Keep receipts for diesel purchased in GB, to prove that it was bought in the GB, and request that your retailer marks them "duty paid."
- Log the date of refuelling and engine hours to reinforce these records; and
- Do not carry marked diesel anywhere other than in their craft's main fuel storage tanks.
Chief Operating Officer of RYA Northern Ireland, Richard Honeyford, commented: "RYA Northern Ireland welcomes that there will be a new duty relief scheme in place to help avoid disproportionately penalising Northern Ireland boaters and details of this scheme are to follow.
"We also welcome a number of clarifications from HMRC and look forward to continuing to work closely with RYA, HM Treasury and HMRC to ensure that boaters in Northern Ireland are clear on all guidance. RYA Northern Ireland will continue to update its members as and when further information is available."
Howard Pridding, RYA Director of External Affairs, commented: "The meeting with Government was productive and both sides now have a clear idea of the issues ahead. We will continue to work with our colleagues in RYA Northern Ireland to talk to Government about the practical difficulties that these issues present and work constructively with HM Treasury and HMRC officials to develop guidance that will inform boaters about the new fuel situation in Northern Ireland."
Where's the White Diesel? No Options for Leisure Boaters in Northern Ireland Says Cruising Association
From 30 June non-commercial vessels wishing to refuel in Northern Ireland must do so with white diesel. What’s the snag? There are no marine white diesel pumps in Northern Ireland, and demand is insufficient for commercial operators to make provision say the Cruising Association, the body representing cruising sailors and motor cruisers, with over 6,300 members around the world.
At a meeting this week with HMRC, and involving the Cruising Association (CA), the RYA and British Marine, it became clear that there will be only three alternatives to the illegal purchase of red diesel in Northern Ireland after June.
Firstly, sail a minimum of 90 miles to Scotland or the Isle of Man to lawfully purchase red diesel, which can be reimported to Northern Ireland, upon documentary proof, under the Istanbul Convention. Or, secondly, sail a minimum of 75 miles, to the nearest white diesel Marine pump, which is in Dublin. Plus the return journey of course. Thirdly, the purchase of white diesel from filling stations in jerry cans where the marine rebate will not be available, and where the number of cans/journeys required for most boats would be considerable. In addition, there is the environmental hazards and regulations associated with refuelling by this method.
Given the short time for the proposal to be enacted the CA, with the RYA, urged HMRC to rapidly issue clear guidance to owners and fuel suppliers facing this unprecedented situation.
Julian Dussek, President of the Cruising Association said, "Although these options may be viable, they are completely unreasonable. I cannot imagine another situation in which legislation would be passed knowing that compliance was well-nigh impossible."
He urged the Treasury to work with the Northern Ireland Assembly to produce financial incentives for the fuel industry to create a viable marine supply of white diesel in the province.
Update On White Diesel Supply At Irish Marinas For June 2020
Rossaveal joins the list of coastal marinas where white diesel is available for cruising vessels to refuel around Ireland.
The news comes in the latest update from Norman Kean of ICC Publications, who has done sterling work keeping up to date on the changes since the law banning green diesel for leisure boating came into force.
A local filling station will now bring a towable bowser to the south Connemara harbour for boats that need it, while in West Cork, boats visiting Baltimore — where white diesel is presently in cans — can avail of hose supply from July.
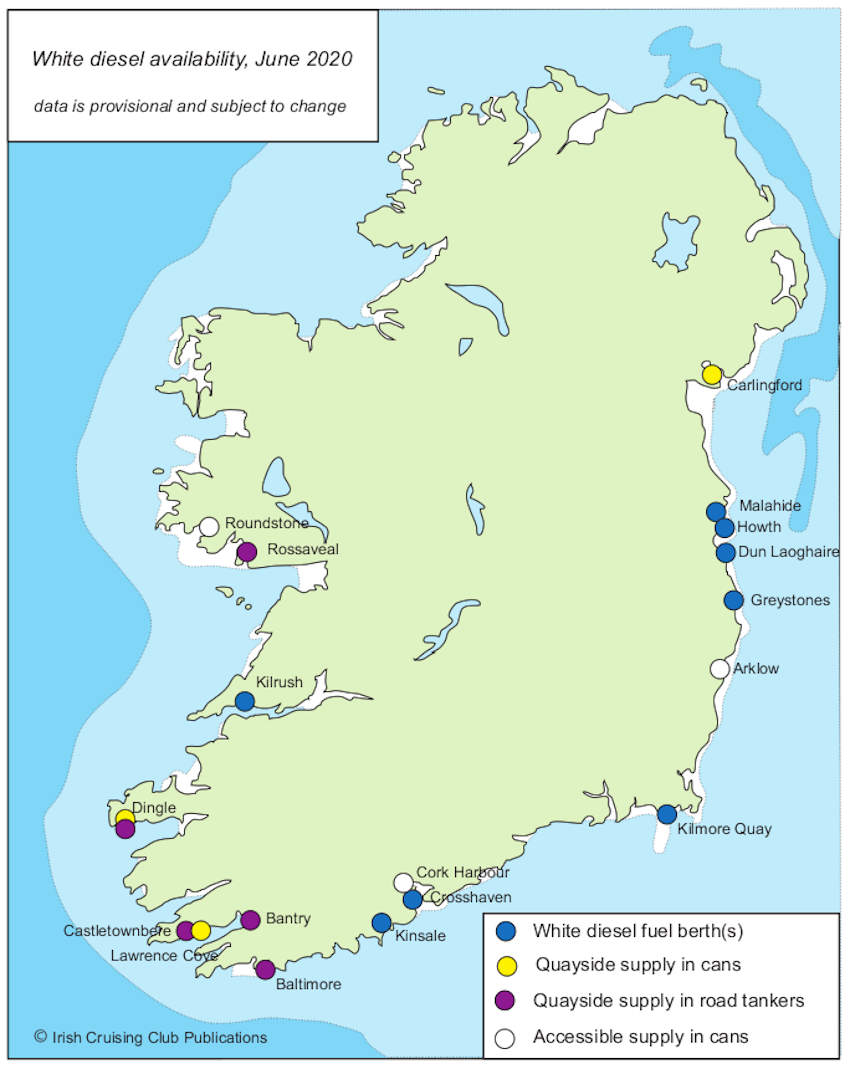
Before the coronavirus emergency closed down the country’s marinas and harbours for three months, Carlingford Marina had been the most recent to make moves to install a white diesel tank for pump supply.
However, for now pump supply remains concentrated to the East and South Coasts, at seven marinas between Malahide and Kinsale.
Kilrush is the only marina with white diesel fuel berths on the West Coast, though quayside supply is available at a number of points between Galway Bay and West Cork.
Following the most recent update on white diesel supply for leisure vessels around the Irish coast, Carlingford Marina informs Afloat.ie that it will shortly install a second diesel tank for white diesel.
While the marina on the Cooley Peninsula in Co Louth previously conformed it would keep a stock of white diesel in cans, it is now making moves to have both MGO green and DERV white diesel available at the pump to all marina users.
The marine also confirms it keeps a stock of 2,500 litres of both fuel types, but can order in extra with 48 hours’ notice.
Latest Update On White Diesel Supply & Fuel Tax For Leisure Vessels
White diesel supply is improving around the Irish coast, with marinas at Kilmore Quay and Kilrush the latest to switch their pumps, writes Gail McAllister.
In particular, this provides a welcome source of fuel midway between Dun Laoghaire and Cork, at a strategically placed harbour which is a key landfall port.
Lawrence Cove Marina has recently announced that it will provide white diesel in cans in 2020. White diesel will also be available in cans at Dingle and Carlingford.
Howth and Dun Laoghaire marinas, at least two at Crosshaven, and at least one in Kinsale will have white diesel available from their pumps.
Oil suppliers at Castletownbere, Bantry and Dingle will have white diesel available by tanker on the same basis as they used to supply green — in modest quantities and at relatively short notice.
Leisure boaters who still have green diesel in their tanks from last year have been given some reprieve by the Revenue Commissioners “on an operational basis”, though it is expected that “such residue will be used up very quickly”.
This may raise concerns over Revenue’s understanding of how leisure craft are used and refuelled as opposed to road vehicles.
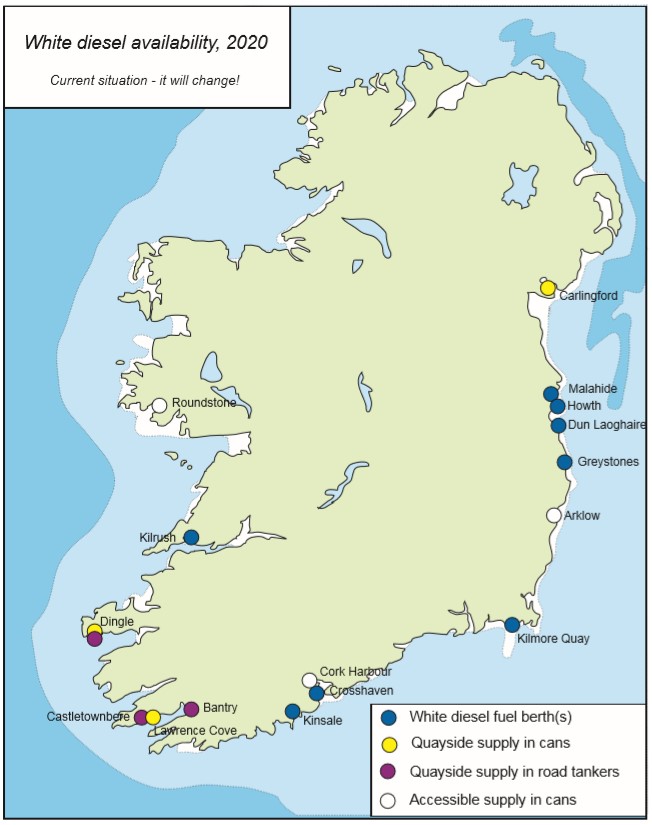 Map of white diesel fuelling locations as of February 2020 by Norman Kean
Map of white diesel fuelling locations as of February 2020 by Norman Kean
Tax matters
In order to protect against any possible future prosecution for misuse of green diesel, leisure sailors are advised to pay the additional excise duty on green diesel purchases made in 2019 before the deadline of Sunday 1 March.
This can be done by completing form PPN1, available on revenue.ie (search on the site for ‘form PPN1’ or ‘private pleasure navigation’), giving details of the fuel source and quantity (receipts from suppliers not required). The current rate of tax is 47.9c per litre.
The easiest way to pay the tax and get a receipt is to use the Revenue Online Service (ROS). Find a page with ‘Marked Gas Oil tax’, pay by bank transfer, take a screenshot or save a PDF of the payment page, print it and keep a copy aboard the boat.
Be sure to measure your current tank contents, and keep a log of your engine hours, diesel consumption and purchases. And of course buy only white diesel; quayside suppliers and tankers will, in any case, refuse to put green diesel in the tank of a leisure vessel.
In the event that your tank is dipped by Customs and you are accused of using green diesel when in fact what you have is a mixture, insist on a quantitative measurement of the mix. They can do this easily by measuring the concentration of a marker called Accutrace, which is added to green diesel along with the dye.
If you have diesel in your tank from another jurisdiction, such as red from the UK, it is considered very unlikely that Customs will be concerned. Tax-paid diesel from Spain (Gasoleo A) is faintly green in colour, but apart from that, nobody else in Europe uses a green dye.
Thanks goes to Irish Sailing’s Cruising and Representation Policy Group representative, Norman Kean of ICC Publications, for his diligent research into this subject.
If green diesel is found by the Revenue Commissioners in the fuel tank of a private pleasure craft during the early part of 2020, the owner of the craft may be liable for prosecution unless he or she can demonstrate clearly that the diesel is a residue from 2019, and that the boat has not been used in 2020 up to that point where the residue of MGO was detected.
It follows a situation in the marketplace this Spring where some resellers are reported to be continuing to sell green diesel to pleasure craft despite a ban in force since January 1.
As Afloat reported previously, In October 2019, the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport informed the public of the Department of Finance's intention to change the law regarding the use of Marked Gas Oil for Private Pleasure Navigation from 1 January 2020.
Fuel used for private pleasure navigation has, since 2008, been liable to Mineral Oil Tax (MOT) at the standard rate for diesel used as a propellant (‘white diesel’). The reduced rate of MOT charged for green diesel (Marked Gas Oil/MGO) has not applied to fuel used for private pleasure navigation since a derogation under the Energy Tax Directive, allowing Ireland apply a reduced tax rate for fuel used for such purposes, came to an end in 2008.
When the derogation came to an end, arrangements were provided for in national legislation to permit owners of private pleasure craft to use MGO on condition that they made an annual declaration of usage to Revenue and submitted a balancing payment representing the difference between the MOT they would have paid had they have purchased the same quantity of white diesel and the MOT they actually paid when purchasing MGO. On 17 October 2018, these arrangements were found by the European Court of Justice to be in breach of the Fiscal Marking and Energy Tax Directives.
Ireland accepted the CJEU ruling and informed the Commission that the necessary legislative changes would be brought forward in the Finance Bill 2019. In October 2018 the Department of Finance informed the relevant State authorities of the ruling, its import and the timeline for its implementation so that they could consider what issues, if any, needed addressing from their perspective.
In December 2018, Waterways Ireland published Marine Notice 132 of 2018 informing owners of private pleasure craft of the import of the CJEU ruling and the implementation timeline set out by the Department.
In November 2019 the Department of Transport, Tourism and Sport published a further notice, Marine Notice 52 of 2019, informing the public of upcoming changes to the law regarding the use of Marked Gas Oil for private pleasure navigation from 1st January 2020.
Section 41 of the Finance Act 2019 came into legal effect from 1 January 2020. The net result of the legal changes made is that the special arrangements, permitting the use of MGO for private pleasure navigation on condition of submitting an annual return and payment of MOT due, came to an end.
The use of MGO is no longer permitted for private pleasure navigation and unmarked, duty paid diesel must be used for such purposes. In addition, the supply of MGO for use in private pleasure navigation is no longer permitted. Revenue’s website has been updated accordingly and more detailed information will be published over the coming weeks. It should be noted that the legislative changes do not impact on the operation of the relief from MOT for fuel used for commercial sea navigation, including commercial fishing.
Owners of private pleasure craft who purchased MGO for private pleasure navigation in 2019 are required to submit a return and pay any MOT due by 1 March 2020. In relation to MGO residue remaining in the fuel tanks of private pleasure craft, Revenue will, on an operational basis, allow owners to use MGO that was in a craft’s fuel tank before the end of 2019. It is anticipated that such residue will be used up very quickly.
Revenue says they will enforce the new arrangements on a risk basis. Private pleasure craft owners must ensure that they only purchase white diesel for private pleasure navigation from 1 January 2020 onwards. If MGO is found by Revenue in the fuel tank of a private pleasure craft during the early part of 2020, the owner of the craft may be liable for prosecution unless he or she can demonstrate clearly that the diesel is a residue from 2019, and that the boat has not been used in 2020 up to that point where the residue of MGO was detected.
British Boat Users Sailing Abroad Risk Fines Over Red Diesel
#NEWS UPDATE - British boat users are risking big fines if they sail their craft outside UK waters due to new laws on the use of red diesel, the Daily Telegraph reports.
New laws coming into force on 1 April "will require anyone moving into international waters to sign a declaration that their boat is not being powered by red diesel".
Red-dyed diesel is used by farmers and commercial fishermen throughout the UK at a lower rate of duty. It is also widely used by recreational boaters and yacht owners, as is green diesel by Irish pleasure boaters, though such users have been required to pay the full rate of tax for a number of years now.
However, the European Union is now clamping down on the use of dyed diesel.
The decision by Brussels is causing consternation among the yachting community, which argues that unmarked or 'white' diesel is not widely available in harbours and marinas.
And concerns remain over the presence of biofuels in white diesel which, as previously reported on Afloat.ie, can be harmful to marine engines.
The Daily Telegraph has more on the story HERE.

































































