Displaying items by tag: Microplastic
New Data Reveals Higher Concentrations Of Ocean Microplastic Found Nearer Major Cities
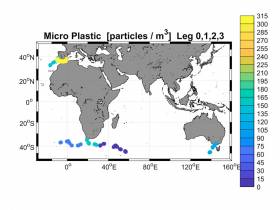
#Microplastic - Using data collected by Volvo Ocean Race team Turn the Tide on Plastic, marine scientists have identified 75 particles of microplastic per cubic metre in waters near Hong Kong and 87 per cubic metre along the coast near Melbourne.
Lower concentrations of 39 microplastic particles per cubic meter were found up the east coast of Australia, and values of 48 particles per cubic meter were found in South East Asian waters.
The highest levels of microplastic so far have been found in European waters where the Mediterranean Sea and Atlantic Ocean meet. A peak of 307 particles of microplastic per cubic metre was discovered there.
The tiny particles of plastic, which break down from larger pieces such as single-use plastic bottles, were collected using a state-of-the-art instrument by Turn the Tide on Plastic during the round the world race.
Dr Sören Gutekunst, of the GEOMAR Institute for Ocean Research Kiel funded by the Cluster of Excellence Future Ocean, analysed the preliminary microplastic data at their laboratory in Kiel, Germany.
“We are finding that the concentrations of microplastics increase when the samples are taken closer to higher density populations such as Hong Kong, and in areas where ocean surface currents tend to converge and concentrate marine debris, such as in the Great Australian Bight,” Dr Gutekunst said.
“The potential to model the data in combination with ocean current information will provide an exceptional insight into where plastic pollution is originating and accumulating.
“Regardless of where the data is taken, from remote parts of the ocean, such as the Antarctic, to areas close to major urban conurbations, we are consistently finding levels of microplastics which clearly illustrates how pervasive they have become.”
Microplastics are often invisible to the naked eye and can take thousands of years to degrade. By collecting information on their levels, the mission is helping scientists gain insight into the scale of plastic pollution and its impact upon marine life.
As part of the Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme, during four of the Volvo Ocean Race legs a total of 28 drifter buoys from the NOAA drifter program are being deployed by the vessels, at crucial oceanic regions to measure sea surface temperature and ocean current velocities. This will also help scientists understand how ocean currents could influence the movement of microplastic particles.
Team AkzoNobel are now the second team to have signed up to the Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme, helping capture valuable data from the remotest parts of our seas.
Both AkzoNobel and Turn the Tide on Plastic will be collecting data during the current 7,600-nautical-mile leg from Auckland to Itajaí in Brazil, a race that passes by some of the remotest stretches of ocean on the planet.
In January, it was reported that microplastic particles have been found even in waters close to Antarctica as revealed by data collected on the race’s third leg.
Now with two sets of data to compare, the findings are expected to be more robust and deliver a wider range of data, as the boats may follow different routes and therefore collect information from different parts of the oceans the race travels through.
This oceanographic data will provide important direct measurements to increase knowledge and future insights into ocean health and climate predictions.
“We know very little about exactly how much microplastic is contaminating our oceans so each new data sample is providing valuable information to further our scientific knowledge,” said Anne-Cecile Turner, sustainability programme leader for the Volvo Ocean Race.
“The Volvo Ocean Race provides an exceptional opportunity to directly sample remote areas and to shed light on the global scale and geographical distribution of microplastics pollution in the ocean.
“Having a second boat collecting information on the health of our oceans will only further enhance the quality of our Science Programme.”
Dr Paulo Mirpuri, president of Volvo Ocean Race principal sustainability partner The Mirpuri Foundation said: “We were not expecting microplastic to be found in the most remote areas of our seas like the Southern Ocean. This came as a complete surprise to us, the dream that we would still have pristine and plastic free seas somewhere in this planet is gone and means the problem is a lot bigger than our initial assumptions. We all need to take action right now and hope it is not too late.”
The Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme is funded by Volvo Cars, which is donating €100 from the first 3,000 sales of the new Volvo V90 Cross Country Volvo Ocean Race edition to support the initiative.
“Volvo Cars is delighted to be supporting this innovative programme, whose approach to environmental care is a strong fit for us - not least as we head towards an electric future,” said Stuart Templar, director of sustainability at Volvo Cars.
“We are keen to get an even clearer picture of the scale of the problem as the boats now head into leg seven and the most remote waters of the world. This sets an invaluable benchmark for future research and action.”
#MarineScience - Microplastic particles have been found in the oceans close to Antarctica, data collected during the Volvo Ocean Race has revealed.
Scientists with the Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme, funded by Volvo Cars, analysed water samples gathered at points during Leg 2 of the yacht race between Lisbon and Cape Town and Leg 3 from Cape Town to Melbourne.
The results, announced at the Volvo Ocean Race Hong Kong Ocean Summit, found microplastics in the Southern Ocean close to the Antarctic Ice Exclusion Zone.
Compared to other oceans, the number of microplastic particles was small, but four microplastic particles per cubic metre were still found.
Over one million microplastic particles per square kilometre of ocean were found in the Southern Atlantic Ocean, west of Cape Town. And on the third leg of the race, one and a half million microplastic particles per square kilometre of ocean were discovered east of South Africa.
In Australian waters, close to Melbourne, one million microplastic particles per square kilometre of ocean were found.
The tiny particles of plastic, which break down from larger pieces such as single-use plastic bottles, were collected by race team Turn the Tide on Plastic, which features Ireland’s own Annalise Murphy in its crew rotation.
“This new information confirms the results we had previously collected from European waters and shows that there are consistently high levels of microplastic in the ocean and we are also seeing low levels of microplastics in waters close to the Antarctic,” said Sören Gutekunst, who works at GEOMAR, an ocean research institute in Kiel, Germany.
“The Turn the Tide on Plastic race team is collecting extremely valuable scientific data that will help us gain a clearer picture of the amount of microplastics in our oceans.”
Microplastic has the potential to enter the food chain, in species such as tuna and mackerel, and can cause harm to humans, too. It consists of small particles of plastic, often invisible to the naked eye and less than 5mm.
At the Hong Kong Ocean Summit, Daisy Lo, assistant director of environmental protection with the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region (HKSAR) government, pledged to explore ways to reduce plastic at source, revealed plans for a $HK20 million fund for upgrading plastic recycling facilities and talked of efforts to clean up the marine environment.
Anne-Cecile Turner, sustainability programme leader for the Volvo Ocean Race, said: “We know very little about exactly how much microplastic is contaminating our oceans so this data provides information for the scientific community and the wider public.
“Volvo Ocean Race Ocean Summits offer a platform to showcase innovative solutions to the global crisis of plastic polluting our oceans.”
The news comes as Volvo Ocean Race boat Team AkzoNobel has been announced as the second team to use the on-board data gathering equipment to measure water quality and composition, as well as microplastics in some of the world’s remotest oceans.
The scientific research was collected using a state-of-the-art instrument designed especially for the Volvo Ocean 65 racing yacht.
Volvo Cars is funding the Volvo Ocean Race Science Programme by donating €100 from the first 3,000 sales of the new V90 Cross Country Volvo Ocean Race edition vehicle.
Consisting of three key pillars – meteorological data collection, scientific drifter buoy deployment, and on board analysis of key metrics for ocean health including salinity, temperature, dissolved CO2 and Chlorophyll a – this marine science programme aims to create a snapshot of the health of the oceans to help scientists worldwide.
Last week, the Marine Institute in Galway declared its support for Ireland’s commitment to legislation prohibiting the sale of certain products containing microbeads, as previously reported on Afloat.ie.